mirror of
https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks.git
synced 2025-12-20 01:27:06 -05:00
Compare commits
78 Commits
sdk-codete
...
parasharsh
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
91aa7e04b0 | ||
|
|
2c3d3f446d | ||
|
|
44c8a632bb | ||
|
|
01d391f5c2 | ||
|
|
d4281967a2 | ||
|
|
b0ff1e1a5d | ||
|
|
df025e6a17 | ||
|
|
613db3158d | ||
|
|
c3a8c36297 | ||
|
|
e7ce245674 | ||
|
|
ef5844fffd | ||
|
|
e039b98ee6 | ||
|
|
05713689e0 | ||
|
|
7bb906b53c | ||
|
|
5726fe3ddb | ||
|
|
d10b1fa796 | ||
|
|
d7127de03c | ||
|
|
50787f4ccc | ||
|
|
06728004b6 | ||
|
|
f5bcc55fe3 | ||
|
|
f23fb58200 | ||
|
|
dbce7b8db2 | ||
|
|
303090adf6 | ||
|
|
b091d1f5f1 | ||
|
|
803d69c539 | ||
|
|
37848e9686 | ||
|
|
7d9227441e | ||
|
|
21c454b0f2 | ||
|
|
c7b0960ae4 | ||
|
|
14e11fefd6 | ||
|
|
4deaeb04cf | ||
|
|
ee78323df2 | ||
|
|
89c2622938 | ||
|
|
96b352e3be | ||
|
|
5280201f93 | ||
|
|
3825fd2c10 | ||
|
|
b936dd3505 | ||
|
|
7339c95ea0 | ||
|
|
32102e2aac | ||
|
|
a043769197 | ||
|
|
a0f3727cf4 | ||
|
|
0e8b42f8c7 | ||
|
|
2daafdbca1 | ||
|
|
fec2e97310 | ||
|
|
1a79e53935 | ||
|
|
900cc7a76b | ||
|
|
3148e52258 | ||
|
|
dda402db83 | ||
|
|
603f4a6434 | ||
|
|
114449dd9b | ||
|
|
de20b6c40e | ||
|
|
886ece1089 | ||
|
|
0dfe00d05a | ||
|
|
7a6fb8067f | ||
|
|
bb439ab2fd | ||
|
|
ea3abdde4f | ||
|
|
2e4eb8785c | ||
|
|
bfccb07dae | ||
|
|
94cd37e9fb | ||
|
|
cdeb4dddab | ||
|
|
e12637098a | ||
|
|
d5f8811f4f | ||
|
|
92d36a2db4 | ||
|
|
c5c76e8187 | ||
|
|
833d1d0f4e | ||
|
|
dd0c0264a2 | ||
|
|
52368bad81 | ||
|
|
604f6c18be | ||
|
|
829bc297f2 | ||
|
|
9e5101ea8c | ||
|
|
37e96f2ad6 | ||
|
|
d0c9bb330a | ||
|
|
b4c7932640 | ||
|
|
8fed628390 | ||
|
|
d940aca06d | ||
|
|
beb97b1d9f | ||
|
|
e7e9923cfb | ||
|
|
b5482fcd4b |
@@ -101,11 +101,20 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"subscription_id ='<subscription-id>'\n",
|
||||
"resource_group ='<resource-group>'\n",
|
||||
"workspace_name = '<workspace-name>'\n",
|
||||
"subscription_id = os.environ.get(\"SUBSCRIPTION_ID\", \"<my-subscription-id>\")\n",
|
||||
"resource_group = os.environ.get(\"RESOURCE_GROUP\", \"<my-resource-group>\")\n",
|
||||
"workspace_name = os.environ.get(\"WORKSPACE_NAME\", \"<my-workspace-name>\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" ws = Workspace(subscription_id = subscription_id, resource_group = resource_group, workspace_name = workspace_name)\n",
|
||||
@@ -131,7 +140,7 @@
|
||||
"* Your subscription id\n",
|
||||
"* The resource group name\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Note**: As with other Azure services, there are limits on certain resources (for eg. BatchAI cluster size) associated with the Azure Machine Learning service. Please read [this article](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/service/how-to-manage-quotas) on the default limits and how to request more quota."
|
||||
"**Note**: As with other Azure services, there are limits on certain resources (for eg. AmlCompute quota) associated with the Azure Machine Learning service. Please read [this article](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/service/how-to-manage-quotas) on the default limits and how to request more quota."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -142,15 +151,6 @@
|
||||
"Specify a region where your workspace will be located from the list of [Azure Machine Learning regions](https://linktoregions)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"workspace_region = \"eastus2\""
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
@@ -159,10 +159,11 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"subscription_id = os.environ.get(\"SUBSCRIPTION_ID\", subscription_id)\n",
|
||||
"resource_group = os.environ.get(\"RESOURCE_GROUP\", resource_group)\n",
|
||||
"workspace_name = os.environ.get(\"WORKSPACE_NAME\", workspace_name)\n",
|
||||
"workspace_region = os.environ.get(\"WORKSPACE_REGION\", workspace_region)"
|
||||
"subscription_id = os.environ.get(\"SUBSCRIPTION_ID\", \"<my-subscription-id>\")\n",
|
||||
"resource_group = os.environ.get(\"RESOURCE_GROUP\", \"my-aml-resource-group\")\n",
|
||||
"workspace_name = os.environ.get(\"WORKSPACE_NAME\", \"my-first-workspace\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"workspace_region = os.environ.get(\"WORKSPACE_REGION\", \"eastus2\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -207,12 +208,88 @@
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Success!\n",
|
||||
"Great, you are ready to move on to the rest of the sample notebooks."
|
||||
"## Create compute resources for your training experiments\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Many of the subsequent examples use Azure Machine Learning managed compute (AmlCompute) to train models at scale. To create a **CPU** cluster now, run the cell below. The autoscale settings mean that the cluster will scale down to 0 nodes when inactive and up to 4 nodes when busy."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute_target import ComputeTargetException\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Choose a name for your CPU cluster\n",
|
||||
"cpu_cluster_name = \"cpucluster\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Verify that cluster does not exist already\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" cpu_cluster = ComputeTarget(workspace=ws, name=cpu_cluster_name)\n",
|
||||
" print('Found existing cluster, use it.')\n",
|
||||
"except ComputeTargetException:\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size='STANDARD_D2_V2',\n",
|
||||
" max_nodes=4)\n",
|
||||
" cpu_cluster = ComputeTarget.create(ws, cpu_cluster_name, compute_config)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"cpu_cluster.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"To create a **GPU** cluster, run the cell below. Note that your subscription must have sufficient quota for GPU VMs or the command will fail. To increase quota, see [these instructions](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-supportability/resource-manager-core-quotas-request). "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute_target import ComputeTargetException\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Choose a name for your GPU cluster\n",
|
||||
"gpu_cluster_name = \"gpucluster\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Check if cluster exists already\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" gpu_cluster = ComputeTarget(workspace=ws, name=gpu_cluster_name)\n",
|
||||
" print('Found existing cluster, use it.')\n",
|
||||
"except ComputeTargetException:\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size='STANDARD_NC6',\n",
|
||||
" max_nodes=4)\n",
|
||||
" gpu_cluster = ComputeTarget.create(ws, gpu_cluster_name, compute_config)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"gpu_cluster.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Success!\n",
|
||||
"Great, you are ready to move on to the rest of the sample notebooks. A good place to start is the [01.train-model tutorial](./tutorials/01.train-model.ipynb) to learn how to train and then deploy an image classification model."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": []
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "roastala"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.6",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
@@ -228,7 +305,7 @@
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
"version": "3.6.2"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Prerequisites\n",
|
||||
"1. Make sure you go through the [00. Installation and Configuration](00.configuration.ipynb) Notebook first if you haven't. \n",
|
||||
"1. Make sure you go through the [00. Installation and Configuration](../../00.configuration.ipynb) Notebook first if you haven't. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"2. Install following pre-requisite libraries to your conda environment and restart notebook.\n",
|
||||
"```shell\n",
|
||||
@@ -525,8 +525,7 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"myenv = CondaDependencies()\n",
|
||||
"myenv.add_conda_package(\"scikit-learn\")\n",
|
||||
"myenv = CondaDependencies.create(conda_packages=[\"scikit-learn\"])\n",
|
||||
"print(myenv.serialize_to_string())\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with open(\"myenv.yml\",\"w\") as f:\n",
|
||||
@@ -680,7 +679,7 @@
|
||||
"# score the entire test set.\n",
|
||||
"test_samples = json.dumps({'data': X_test.tolist()})\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"result = json.loads(service.run(input_data = test_samples))['result']\n",
|
||||
"result = service.run(input_data = test_samples)\n",
|
||||
"residual = result - y_test"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -778,13 +777,6 @@
|
||||
"%%time\n",
|
||||
"service.delete()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": []
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
@@ -808,7 +800,7 @@
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.4"
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -21,7 +21,9 @@ def run(raw_data):
|
||||
data = json.loads(raw_data)['data']
|
||||
data = np.array(data)
|
||||
result = model.predict(data)
|
||||
return json.dumps({"result": result.tolist()})
|
||||
|
||||
# you can return any data type as long as it is JSON-serializable
|
||||
return result.tolist()
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
result = str(e)
|
||||
return json.dumps({"error": result})
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -291,11 +291,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.runconfig import RunConfiguration\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"run_config_docker = RunConfiguration()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"run_config_docker.environment.python.user_managed_dependencies = False\n",
|
||||
"run_config_docker.auto_prepare_environment = True\n",
|
||||
"run_config_docker.environment.docker.enabled = True\n",
|
||||
@@ -303,7 +299,9 @@
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Specify conda dependencies with scikit-learn\n",
|
||||
"cd = CondaDependencies.create(conda_packages=['scikit-learn'])\n",
|
||||
"run_config_docker.environment.python.conda_dependencies = cd"
|
||||
"run_config_docker.environment.python.conda_dependencies = cd\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"src = ScriptRunConfig(source_directory=\"./\", script='train.py', run_config=run_config_docker)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -322,8 +320,17 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"src = ScriptRunConfig(source_directory=\"./\", script='train.py', run_config=run_config_docker)\n",
|
||||
"run = exp.submit(src)"
|
||||
"import subprocess\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Check if Docker is installed and Linux containers are enables\n",
|
||||
"if subprocess.run(\"docker -v\", shell=True) == 0:\n",
|
||||
" out = subprocess.check_output(\"docker system info\", shell=True, encoding=\"ascii\").split(\"\\n\")\n",
|
||||
" if not \"OSType: linux\" in out:\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Switch Docker engine to use Linux containers.\")\n",
|
||||
" else:\n",
|
||||
" run = exp.submit(src)\n",
|
||||
"else:\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Docker engine not installed.\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -190,6 +190,16 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create Linux DSVM as a compute target\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Note**: To streamline the compute that Azure Machine Learning creates, we are making updates to support creating only single to multi-node AmlCompute. The DSVMCompute class will be deprecated in a later release, but the DSVM can be created using the below single line command and then attached(like any VM) using the sample code below. Also note, that we only support Linux VMs and the commands below will spin a Linux VM only.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"```shell\n",
|
||||
"# create a DSVM in your resource group\n",
|
||||
"# note you need to be at least a contributor to the resource group in order to execute this command successfully.\n",
|
||||
"(myenv) $ az vm create --resource-group <resource_group_name> --name <some_vm_name> --image microsoft-dsvm:linux-data-science-vm-ubuntu:linuxdsvmubuntu:latest --admin-username <username> --admin-password <password> --generate-ssh-keys --authentication-type password\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Note**: You can also use [this url](https://portal.azure.com/#create/microsoft-dsvm.linux-data-science-vm-ubuntulinuxdsvmubuntu) to create the VM using the Azure Portal\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Note**: If creation fails with a message about Marketplace purchase eligibilty, go to portal.azure.com, start creating DSVM there, and select \"Want to create programmatically\" to enable programmatic creation. Once you've enabled it, you can exit without actually creating VM.\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"**Note**: By default SSH runs on port 22 and you don't need to specify it. But if for security reasons you switch to a different port (such as 5022), you can specify the port number in the provisioning configuration object."
|
||||
@@ -613,7 +623,7 @@
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
"version": "3.6.2"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
|
||||
328
01.getting-started/06.logging-api/06.logging-api.ipynb
Normal file
328
01.getting-started/06.logging-api/06.logging-api.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,328 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# 06. Logging APIs\n",
|
||||
"This notebook showcase various ways to use the Azure Machine Learning service run logging APIs, and view the results in the Azure portal."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Prerequisites\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you go through the [00. Installation and Configuration](../../00.configuration.ipynb) Notebook first if you haven't. Also make sure you have tqdm and matplotlib installed in the current kernel.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"(myenv) $ conda install -y tqdm matplotlib\n",
|
||||
"```"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Validate Azure ML SDK installation and get version number for debugging purposes"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
"install"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Experiment, Run, Workspace\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Check core SDK version number\n",
|
||||
"print(\"SDK version:\", azureml.core.VERSION)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Initialize Workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Initialize a workspace object from persisted configuration."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
"create workspace"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"print('Workspace name: ' + ws.name, \n",
|
||||
" 'Azure region: ' + ws.location, \n",
|
||||
" 'Subscription id: ' + ws.subscription_id, \n",
|
||||
" 'Resource group: ' + ws.resource_group, sep='\\n')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Set experiment\n",
|
||||
"Create a new experiment (or get the one with such name)."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"exp = Experiment(workspace=ws, name='logging-api-test')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Log metrics\n",
|
||||
"We will start a run, and use the various logging APIs to record different types of metrics during the run."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from tqdm import tqdm\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# start logging for the run\n",
|
||||
"run = exp.start_logging()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# log a string value\n",
|
||||
"run.log(name='Name', value='Logging API run')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# log a numerical value\n",
|
||||
"run.log(name='Magic Number', value=42)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Log a list of values. Note this will generate a single-variable line chart.\n",
|
||||
"run.log_list(name='Fibonacci', value=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# create a dictionary to hold a table of values\n",
|
||||
"sines = {}\n",
|
||||
"sines['angle'] = []\n",
|
||||
"sines['sine'] = []\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for i in tqdm(range(-10, 10)):\n",
|
||||
" # log a metric value repeatedly, this will generate a single-variable line chart.\n",
|
||||
" run.log(name='Sigmoid', value=1 / (1 + np.exp(-i)))\n",
|
||||
" angle = i / 2.0\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # log a 2 (or more) values as a metric repeatedly. This will generate a 2-variable line chart if you have 2 numerical columns.\n",
|
||||
" run.log_row(name='Cosine Wave', angle=angle, cos=np.cos(angle))\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" sines['angle'].append(angle)\n",
|
||||
" sines['sine'].append(np.sin(angle))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# log a dictionary as a table, this will generate a 2-variable chart if you have 2 numerical columns\n",
|
||||
"run.log_table(name='Sine Wave', value=sines)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"run.complete()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Even after the run is marked completed, you can still log things."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Log an image\n",
|
||||
"This is how to log a _matplotlib_ pyplot object."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%matplotlib inline\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
|
||||
"angle = np.linspace(-3, 3, 50)\n",
|
||||
"plt.plot(angle, np.tanh(angle), label='tanh')\n",
|
||||
"plt.legend(fontsize=12)\n",
|
||||
"plt.title('Hyperbolic Tangent', fontsize=16)\n",
|
||||
"plt.grid(True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"run.log_image(name='Hyperbolic Tangent', plot=plt)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Upload a file"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"You can also upload an abitrary file. First, let's create a dummy file locally."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%%writefile myfile.txt\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This is a dummy file."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Now let's upload this file into the run record as a run artifact, and display the properties after the upload."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"props = run.upload_file(name='myfile_in_the_cloud.txt', path_or_stream='./myfile.txt')\n",
|
||||
"props.serialize()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Examine the run"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Now let's take a look at the run detail page in Azure portal. Make sure you checkout the various charts and plots generated/uploaded."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"run"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"You can get all the metrics in that run back."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"run.get_metrics()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"You can also see the files uploaded for this run."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"run.get_file_names()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"You can also download all the files locally."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"os.makedirs('files', exist_ok=True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for f in run.get_file_names():\n",
|
||||
" dest = os.path.join('files', f.split('/')[-1])\n",
|
||||
" print('Downloading file {} to {}...'.format(f, dest))\n",
|
||||
" run.download_file(f, dest) "
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "haining"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.6",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -192,9 +192,11 @@
|
||||
" data = json.loads(raw_data)['data']\n",
|
||||
" data = numpy.array(data)\n",
|
||||
" result = model.predict(data)\n",
|
||||
" # you can return any datatype as long as it is JSON-serializable\n",
|
||||
" return result.tolist()\n",
|
||||
" except Exception as e:\n",
|
||||
" result = str(e)\n",
|
||||
" return json.dumps({\"result\": result.tolist()})"
|
||||
" error = str(e)\n",
|
||||
" return error"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -387,13 +389,6 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"aci_service.delete()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": []
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
@@ -417,7 +412,7 @@
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.5"
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -122,9 +122,11 @@
|
||||
" data = json.loads(raw_data)['data']\n",
|
||||
" data = numpy.array(data)\n",
|
||||
" result = model.predict(data)\n",
|
||||
" # you can return any data type as long as it is JSON-serializable\n",
|
||||
" return result.tolist()\n",
|
||||
" except Exception as e:\n",
|
||||
" result = str(e)\n",
|
||||
" return json.dumps({\"result\": result.tolist()})"
|
||||
" error = str(e)\n",
|
||||
" return error"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -332,7 +334,7 @@
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.5"
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -156,11 +156,12 @@
|
||||
" inputs_dc.collect(data) #this call is saving our input data into our blob\n",
|
||||
" prediction_dc.collect(result)#this call is saving our prediction data into our blob\n",
|
||||
" print (\"saving prediction data\" + time.strftime(\"%H:%M:%S\"))\n",
|
||||
" return json.dumps({\"result\": result.tolist()})\n",
|
||||
" # you can return any data type as long as it is JSON-serializable\n",
|
||||
" return result.tolist()\n",
|
||||
" except Exception as e:\n",
|
||||
" result = str(e)\n",
|
||||
" print (result + time.strftime(\"%H:%M:%S\"))\n",
|
||||
" return json.dumps({\"error\": result})"
|
||||
" error = str(e)\n",
|
||||
" print (error + time.strftime(\"%H:%M:%S\"))\n",
|
||||
" return error"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -161,13 +161,12 @@
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" #Print statement for appinsights custom traces:\n",
|
||||
" print (\"saving prediction data\" + time.strftime(\"%H:%M:%S\"))\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" return json.dumps({\"result\": result.tolist()})\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # you can return any data type as long as it is JSON-serializable\n",
|
||||
" return result.tolist()\n",
|
||||
" except Exception as e:\n",
|
||||
" result = str(e)\n",
|
||||
" print (result + time.strftime(\"%H:%M:%S\"))\n",
|
||||
" return json.dumps({\"error\": result})"
|
||||
" error = str(e)\n",
|
||||
" print (error + time.strftime(\"%H:%M:%S\"))\n",
|
||||
" return error"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
22
README.md
22
README.md
@@ -1,10 +1,5 @@
|
||||
Get the full documentation for Azure Machine Learning service at:
|
||||
|
||||
https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/service/
|
||||
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
||||
# Sample notebooks for Azure Machine Learning service
|
||||
For full documentation for Azure Machine Learning service, visit **https://aka.ms/aml-docs**.
|
||||
# Sample Notebooks for Azure Machine Learning service
|
||||
|
||||
To run the notebooks in this repository use one of these methods:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,13 +17,24 @@ To run the notebooks in this repository use one of these methods:
|
||||
|
||||
## **Use your own notebook server**
|
||||
|
||||
Video walkthrough:
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://youtu.be/VIsXeTuW3FU)
|
||||
|
||||
1. Setup a Jupyter Notebook server and [install the Azure Machine Learning SDK](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/service/quickstart-create-workspace-with-python).
|
||||
1. Clone [this repository](https://aka.ms/aml-notebooks).
|
||||
1. You may need to install other packages for specific notebooks
|
||||
1. You may need to install other packages for specific notebook.
|
||||
- For example, to run the Azure Machine Learning Data Prep notebooks, install the extra dataprep SDK:
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install --upgrade azureml-dataprep
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. Start your notebook server.
|
||||
1. Follow the instructions in the [00.configuration](00.configuration.ipynb) notebook to create and connect to a workspace.
|
||||
1. Open one of the sample notebooks.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> Note: **Looking for automated machine learning samples?**
|
||||
> For your convenience, you can use an installation script instead of the steps below for the automated ML notebooks. Go to the [automl folder README](automl/README.md) and follow the instructions. The script installs all packages needed for notebooks in that folder.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -140,7 +140,7 @@
|
||||
"|-|-|\n",
|
||||
"|**task**|classification or regression|\n",
|
||||
"|**primary_metric**|This is the metric that you want to optimize. Classification supports the following primary metrics: <br><i>accuracy</i><br><i>AUC_weighted</i><br><i>balanced_accuracy</i><br><i>average_precision_score_weighted</i><br><i>precision_score_weighted</i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**max_time_sec**|Time limit in seconds for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iteration_timeout_minutes**|Time limit in minutes for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iterations**|Number of iterations. In each iteration AutoML trains a specific pipeline with the data.|\n",
|
||||
"|**n_cross_validations**|Number of cross validation splits.|\n",
|
||||
"|**X**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features]|\n",
|
||||
@@ -157,8 +157,8 @@
|
||||
"automl_config = AutoMLConfig(task = 'classification',\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'automl_errors.log',\n",
|
||||
" primary_metric = 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" max_time_sec = 3600,\n",
|
||||
" iterations = 50,\n",
|
||||
" iteration_timeout_minutes = 60,\n",
|
||||
" iterations = 25,\n",
|
||||
" n_cross_validations = 3,\n",
|
||||
" verbosity = logging.INFO,\n",
|
||||
" X = X_train, \n",
|
||||
@@ -246,7 +246,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(local_run).show() "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -143,7 +143,7 @@
|
||||
"|-|-|\n",
|
||||
"|**task**|classification or regression|\n",
|
||||
"|**primary_metric**|This is the metric that you want to optimize. Regression supports the following primary metrics: <br><i>spearman_correlation</i><br><i>normalized_root_mean_squared_error</i><br><i>r2_score</i><br><i>normalized_mean_absolute_error</i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**max_time_sec**|Time limit in seconds for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iteration_timeout_minutes**|Time limit in minutes for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iterations**|Number of iterations. In each iteration AutoML trains a specific pipeline with the data.|\n",
|
||||
"|**n_cross_validations**|Number of cross validation splits.|\n",
|
||||
"|**X**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features]|\n",
|
||||
@@ -158,7 +158,7 @@
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_config = AutoMLConfig(task = 'regression',\n",
|
||||
" max_time_sec = 600,\n",
|
||||
" iteration_timeout_minutes = 10,\n",
|
||||
" iterations = 10,\n",
|
||||
" primary_metric = 'spearman_correlation',\n",
|
||||
" n_cross_validations = 5,\n",
|
||||
@@ -221,7 +221,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(local_run).show() "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -128,7 +128,7 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import DsvmCompute\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"dsvm_name = 'mydsvm'\n",
|
||||
"dsvm_name = 'mydsvma'\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute = DsvmCompute(ws, dsvm_name)\n",
|
||||
" print('Found an existing DSVM.')\n",
|
||||
@@ -192,10 +192,10 @@
|
||||
"|Property|Description|\n",
|
||||
"|-|-|\n",
|
||||
"|**primary_metric**|This is the metric that you want to optimize. Classification supports the following primary metrics: <br><i>accuracy</i><br><i>AUC_weighted</i><br><i>balanced_accuracy</i><br><i>average_precision_score_weighted</i><br><i>precision_score_weighted</i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**max_time_sec**|Time limit in seconds for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iteration_timeout_minutes**|Time limit in minutes for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iterations**|Number of iterations. In each iteration AutoML trains a specific pipeline with the data.|\n",
|
||||
"|**n_cross_validations**|Number of cross validation splits.|\n",
|
||||
"|**concurrent_iterations**|Maximum number of iterations to execute in parallel. This should be less than the number of cores on the DSVM.|"
|
||||
"|**max_concurrent_iterations**|Maximum number of iterations to execute in parallel. This should be less than the number of cores on the DSVM.|"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -205,12 +205,12 @@
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_settings = {\n",
|
||||
" \"max_time_sec\": 600,\n",
|
||||
" \"iteration_timeout_minutes\": 10,\n",
|
||||
" \"iterations\": 20,\n",
|
||||
" \"n_cross_validations\": 5,\n",
|
||||
" \"primary_metric\": 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" \"preprocess\": False,\n",
|
||||
" \"concurrent_iterations\": 2,\n",
|
||||
" \"max_concurrent_iterations\": 2,\n",
|
||||
" \"verbosity\": logging.INFO\n",
|
||||
"}\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
@@ -286,7 +286,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(remote_run).show() "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -130,29 +130,25 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import BatchAiCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Choose a name for your cluster.\n",
|
||||
"batchai_cluster_name = \"mybatchai\"\n",
|
||||
"batchai_cluster_name = \"cpucluster\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"found = False\n",
|
||||
"# Check if this compute target already exists in the workspace.\n",
|
||||
"for ct_name, ct in ws.compute_targets().items():\n",
|
||||
" print(ct.name, ct.type)\n",
|
||||
" if (ct.name == batchai_cluster_name and ct.type == 'BatchAI'):\n",
|
||||
"cts = ws.compute_targets\n",
|
||||
"if batchai_cluster_name in cts and cts[batchai_cluster_name].type == 'BatchAI':\n",
|
||||
" found = True\n",
|
||||
" print('Found existing compute target.')\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = ct\n",
|
||||
" break\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = cts[batchai_cluster_name]\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"if not found:\n",
|
||||
" print('Creating a new compute target...')\n",
|
||||
" provisioning_config = BatchAiCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size = \"STANDARD_D2_V2\", # for GPU, use \"STANDARD_NC6\"\n",
|
||||
" provisioning_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size = \"STANDARD_D2_V2\", # for GPU, use \"STANDARD_NC6\"\n",
|
||||
" #vm_priority = 'lowpriority', # optional\n",
|
||||
" autoscale_enabled = True,\n",
|
||||
" cluster_min_nodes = 1, \n",
|
||||
" cluster_max_nodes = 4)\n",
|
||||
" max_nodes = 6)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # Create the cluster.\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = ComputeTarget.create(ws, batchai_cluster_name, provisioning_config)\n",
|
||||
@@ -217,10 +213,10 @@
|
||||
"|Property|Description|\n",
|
||||
"|-|-|\n",
|
||||
"|**primary_metric**|This is the metric that you want to optimize. Classification supports the following primary metrics: <br><i>accuracy</i><br><i>AUC_weighted</i><br><i>balanced_accuracy</i><br><i>average_precision_score_weighted</i><br><i>precision_score_weighted</i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**max_time_sec**|Time limit in seconds for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iteration_timeout_minutes**|Time limit in minutes for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iterations**|Number of iterations. In each iteration AutoML trains a specific pipeline with the data.|\n",
|
||||
"|**n_cross_validations**|Number of cross validation splits.|\n",
|
||||
"|**concurrent_iterations**|Maximum number of iterations that would be executed in parallel. This should be less than the number of cores on the DSVM.|"
|
||||
"|**max_concurrent_iterations**|Maximum number of iterations that would be executed in parallel. This should be less than the number of cores on the DSVM.|"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -230,12 +226,12 @@
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_settings = {\n",
|
||||
" \"max_time_sec\": 120,\n",
|
||||
" \"iteration_timeout_minutes\": 2,\n",
|
||||
" \"iterations\": 20,\n",
|
||||
" \"n_cross_validations\": 5,\n",
|
||||
" \"primary_metric\": 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" \"preprocess\": False,\n",
|
||||
" \"concurrent_iterations\": 5,\n",
|
||||
" \"max_concurrent_iterations\": 5,\n",
|
||||
" \"verbosity\": logging.INFO\n",
|
||||
"}\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
@@ -312,7 +308,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(remote_run).show() "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -137,22 +137,22 @@
|
||||
"# Add your VM information below\n",
|
||||
"# If a compute with the specified compute_name already exists, it will be used and the dsvm_ip_addr, dsvm_ssh_port, \n",
|
||||
"# dsvm_username and dsvm_password will be ignored.\n",
|
||||
"compute_name = 'mydsvm'\n",
|
||||
"compute_name = 'mydsvmb'\n",
|
||||
"dsvm_ip_addr = '<<ip_addr>>'\n",
|
||||
"dsvm_ssh_port = 22\n",
|
||||
"dsvm_username = '<<username>>'\n",
|
||||
"dsvm_password = '<<password>>'\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"if compute_name in ws.compute_targets():\n",
|
||||
"if compute_name in ws.compute_targets:\n",
|
||||
" print('Using existing compute.')\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute = ws.compute_targets()[compute_name]\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute = ws.compute_targets[compute_name]\n",
|
||||
"else:\n",
|
||||
" RemoteCompute.attach(workspace=ws, name=compute_name, address=dsvm_ip_addr, username=dsvm_username, password=dsvm_password, ssh_port=dsvm_ssh_port)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" while ws.compute_targets()[compute_name].provisioning_state == 'Creating':\n",
|
||||
" while ws.compute_targets[compute_name].provisioning_state == 'Creating':\n",
|
||||
" time.sleep(1)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute = ws.compute_targets()[compute_name]\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute = ws.compute_targets[compute_name]\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" if dsvm_compute.provisioning_state == 'Failed':\n",
|
||||
" print('Attached failed.')\n",
|
||||
@@ -243,10 +243,10 @@
|
||||
"|Property|Description|\n",
|
||||
"|-|-|\n",
|
||||
"|**primary_metric**|This is the metric that you want to optimize. Classification supports the following primary metrics: <br><i>accuracy</i><br><i>AUC_weighted</i><br><i>balanced_accuracy</i><br><i>average_precision_score_weighted</i><br><i>precision_score_weighted</i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**max_time_sec**|Time limit in seconds for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iteration_timeout_minutes**|Time limit in minutes for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iterations**|Number of iterations. In each iteration AutoML trains a specific pipeline with the data.|\n",
|
||||
"|**n_cross_validations**|Number of cross validation splits.|\n",
|
||||
"|**concurrent_iterations**|Maximum number of iterations that would be executed in parallel. This should be less than the number of cores on the DSVM.|\n",
|
||||
"|**max_concurrent_iterations**|Maximum number of iterations that would be executed in parallel. This should be less than the number of cores on the DSVM.|\n",
|
||||
"|**preprocess**|Setting this to *True* enables AutoML to perform preprocessing on the input to handle *missing data*, and to perform some common *feature extraction*.|\n",
|
||||
"|**max_cores_per_iteration**|Indicates how many cores on the compute target would be used to train a single pipeline.<br>Default is *1*; you can set it to *-1* to use all cores.|"
|
||||
]
|
||||
@@ -258,8 +258,8 @@
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_settings = {\n",
|
||||
" \"max_time_sec\": 3600,\n",
|
||||
" \"iterations\": 10,\n",
|
||||
" \"iteration_timeout_minutes\": 60,\n",
|
||||
" \"iterations\": 4,\n",
|
||||
" \"n_cross_validations\": 5,\n",
|
||||
" \"primary_metric\": 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" \"preprocess\": True,\n",
|
||||
@@ -312,10 +312,20 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(remote_run).show() "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Wait until the run finishes.\n",
|
||||
"remote_run.wait_for_completion(show_output = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -155,18 +155,18 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Configure AutoML\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Instantiate an `AutoMLConfig` object to specify the settings and data used to run the experiment. This includes setting `exit_score`, which should cause the run to complete before the `iterations` count is reached.\n",
|
||||
"Instantiate an `AutoMLConfig` object to specify the settings and data used to run the experiment. This includes setting `experiment_exit_score`, which should cause the run to complete before the `iterations` count is reached.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"|Property|Description|\n",
|
||||
"|-|-|\n",
|
||||
"|**task**|classification or regression|\n",
|
||||
"|**primary_metric**|This is the metric that you want to optimize. Classification supports the following primary metrics: <br><i>accuracy</i><br><i>AUC_weighted</i><br><i>balanced_accuracy</i><br><i>average_precision_score_weighted</i><br><i>precision_score_weighted</i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**max_time_sec**|Time limit in seconds for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iteration_timeout_minutes**|Time limit in minutes for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iterations**|Number of iterations. In each iteration AutoML trains a specific pipeline with the data.|\n",
|
||||
"|**n_cross_validations**|Number of cross validation splits.|\n",
|
||||
"|**preprocess**|Setting this to *True* enables AutoML to perform preprocessing on the input to handle *missing data*, and to perform some common *feature extraction*.|\n",
|
||||
"|**exit_score**|*double* value indicating the target for *primary_metric*. <br>Once the target is surpassed the run terminates.|\n",
|
||||
"|**blacklist_algos**|*List* of *strings* indicating machine learning algorithms for AutoML to avoid in this run.<br><br> Allowed values for **Classification**<br><i>LogisticRegression</i><br><i>SGDClassifierWrapper</i><br><i>NBWrapper</i><br><i>BernoulliNB</i><br><i>SVCWrapper</i><br><i>LinearSVMWrapper</i><br><i>KNeighborsClassifier</i><br><i>DecisionTreeClassifier</i><br><i>RandomForestClassifier</i><br><i>ExtraTreesClassifier</i><br><i>LightGBMClassifier</i><br><br>Allowed values for **Regression**<br><i>ElasticNet<i><br><i>GradientBoostingRegressor<i><br><i>DecisionTreeRegressor<i><br><i>KNeighborsRegressor<i><br><i>LassoLars<i><br><i>SGDRegressor<i><br><i>RandomForestRegressor<i><br><i>ExtraTreesRegressor<i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**experiment_exit_score**|*double* value indicating the target for *primary_metric*. <br>Once the target is surpassed the run terminates.|\n",
|
||||
"|**blacklist_models**|*List* of *strings* indicating machine learning algorithms for AutoML to avoid in this run.<br><br> Allowed values for **Classification**<br><i>LogisticRegression</i><br><i>SGD</i><br><i>MultinomialNaiveBayes</i><br><i>BernoulliNaiveBayes</i><br><i>SVM</i><br><i>LinearSVM</i><br><i>KNN</i><br><i>DecisionTree</i><br><i>RandomForest</i><br><i>ExtremeRandomTrees</i><br><i>LightGBM</i><br><i>GradientBoosting</i><br><i>TensorFlowDNN</i><br><i>TensorFlowLinearClassifier</i><br><br>Allowed values for **Regression**<br><i>ElasticNet</i><br><i>GradientBoosting</i><br><i>DecisionTree</i><br><i>KNN</i><br><i>LassoLars</i><br><i>SGD</i><br><i>RandomForest</i><br><i>ExtremeRandomTrees</i><br><i>LightGBM</i><br><i>TensorFlowLinearRegressor</i><br><i>TensorFlowDNN</i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**X**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features]|\n",
|
||||
"|**y**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, ], [n_samples, n_classes]<br>Multi-class targets. An indicator matrix turns on multilabel classification. This should be an array of integers.|\n",
|
||||
"|**path**|Relative path to the project folder. AutoML stores configuration files for the experiment under this folder. You can specify a new empty folder.|"
|
||||
@@ -181,12 +181,12 @@
|
||||
"automl_config = AutoMLConfig(task = 'classification',\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'automl_errors.log',\n",
|
||||
" primary_metric = 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" max_time_sec = 3600,\n",
|
||||
" iteration_timeout_minutes = 60,\n",
|
||||
" iterations = 20,\n",
|
||||
" n_cross_validations = 5,\n",
|
||||
" preprocess = True,\n",
|
||||
" exit_score = 0.9984,\n",
|
||||
" blacklist_algos = ['KNeighborsClassifier','LinearSVMWrapper'],\n",
|
||||
" experiment_exit_score = 0.9984,\n",
|
||||
" blacklist_models = ['KNN','LinearSVM'],\n",
|
||||
" verbosity = logging.INFO,\n",
|
||||
" X = X_train, \n",
|
||||
" y = y_train,\n",
|
||||
@@ -236,7 +236,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(local_run).show() "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,384 +0,0 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# AutoML 06: Custom CV Splits and Handling Sparse Data\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this example we use the scikit-learn's [20newsgroup](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.datasets.fetch_20newsgroups.html) to showcase how you can use AutoML for handling sparse data and how to specify custom cross validations splits.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you have executed the [00.configuration](00.configuration.ipynb) before running this notebook.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this notebook you will learn how to:\n",
|
||||
"1. Create an `Experiment` in an existing `Workspace`.\n",
|
||||
"2. Configure AutoML using `AutoMLConfig`.\n",
|
||||
"4. Train the model.\n",
|
||||
"5. Explore the results.\n",
|
||||
"6. Test the best fitted model.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In addition this notebook showcases the following features\n",
|
||||
"- **Custom CV** splits \n",
|
||||
"- Handling **sparse data** in the input"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create an Experiment\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"As part of the setup you have already created an Azure ML `Workspace` object. For AutoML you will need to create an `Experiment` object, which is a named object in a `Workspace` used to run experiments."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import logging\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"import random\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib import pyplot as plt\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn import datasets\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.experiment import Experiment\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.workspace import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl import AutoMLConfig\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl.run import AutoMLRun"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for the experiment\n",
|
||||
"experiment_name = 'automl-local-missing-data'\n",
|
||||
"# project folder\n",
|
||||
"project_folder = './sample_projects/automl-local-missing-data'\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"experiment = Experiment(ws, experiment_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"output = {}\n",
|
||||
"output['SDK version'] = azureml.core.VERSION\n",
|
||||
"output['Subscription ID'] = ws.subscription_id\n",
|
||||
"output['Workspace'] = ws.name\n",
|
||||
"output['Resource Group'] = ws.resource_group\n",
|
||||
"output['Location'] = ws.location\n",
|
||||
"output['Project Directory'] = project_folder\n",
|
||||
"output['Experiment Name'] = experiment.name\n",
|
||||
"pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', -1)\n",
|
||||
"pd.DataFrame(data=output, index=['']).T"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Diagnostics\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Opt-in diagnostics for better experience, quality, and security of future releases."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.telemetry import set_diagnostics_collection\n",
|
||||
"set_diagnostics_collection(send_diagnostics = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Creating Sparse Data"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import HashingVectorizer\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"remove = ('headers', 'footers', 'quotes')\n",
|
||||
"categories = [\n",
|
||||
" 'alt.atheism',\n",
|
||||
" 'talk.religion.misc',\n",
|
||||
" 'comp.graphics',\n",
|
||||
" 'sci.space',\n",
|
||||
"]\n",
|
||||
"data_train = fetch_20newsgroups(subset = 'train', categories = categories,\n",
|
||||
" shuffle = True, random_state = 42,\n",
|
||||
" remove = remove)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"X_train, X_valid, y_train, y_valid = train_test_split(data_train.data, data_train.target, test_size = 0.33, random_state = 42)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"vectorizer = HashingVectorizer(stop_words = 'english', alternate_sign = False,\n",
|
||||
" n_features = 2**16)\n",
|
||||
"X_train = vectorizer.transform(X_train)\n",
|
||||
"X_valid = vectorizer.transform(X_valid)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"summary_df = pd.DataFrame(index = ['No of Samples', 'No of Features'])\n",
|
||||
"summary_df['Train Set'] = [X_train.shape[0], X_train.shape[1]]\n",
|
||||
"summary_df['Validation Set'] = [X_valid.shape[0], X_valid.shape[1]]\n",
|
||||
"summary_df"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Configure AutoML\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Instantiate an `AutoMLConfig` object to specify the settings and data used to run the experiment.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"|Property|Description|\n",
|
||||
"|-|-|\n",
|
||||
"|**task**|classification or regression|\n",
|
||||
"|**primary_metric**|This is the metric that you want to optimize. Classification supports the following primary metrics: <br><i>accuracy</i><br><i>AUC_weighted</i><br><i>balanced_accuracy</i><br><i>average_precision_score_weighted</i><br><i>precision_score_weighted</i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**max_time_sec**|Time limit in seconds for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iterations**|Number of iterations. In each iteration AutoML trains a specific pipeline with the data.|\n",
|
||||
"|**preprocess**|Setting this to *True* enables AutoML to perform preprocessing on the input to handle *missing data*, and to perform some common *feature extraction*.<br>**Note:** If input data is sparse, you cannot use *True*.|\n",
|
||||
"|**X**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features]|\n",
|
||||
"|**y**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, ], [n_samples, n_classes]<br>Multi-class targets. An indicator matrix turns on multilabel classification. This should be an array of integers.|\n",
|
||||
"|**X_valid**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features] for the custom validation set.|\n",
|
||||
"|**y_valid**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, ], [n_samples, n_classes]<br>Multi-class targets. An indicator matrix turns on multilabel classification for the custom validation set.|\n",
|
||||
"|**path**|Relative path to the project folder. AutoML stores configuration files for the experiment under this folder. You can specify a new empty folder.|"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_config = AutoMLConfig(task = 'classification',\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'automl_errors.log',\n",
|
||||
" primary_metric = 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" max_time_sec = 3600,\n",
|
||||
" iterations = 5,\n",
|
||||
" preprocess = False,\n",
|
||||
" verbosity = logging.INFO,\n",
|
||||
" X = X_train, \n",
|
||||
" y = y_train,\n",
|
||||
" X_valid = X_valid, \n",
|
||||
" y_valid = y_valid, \n",
|
||||
" path = project_folder)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Train the Models\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Call the `submit` method on the experiment object and pass the run configuration. Execution of local runs is synchronous. Depending on the data and the number of iterations this can run for a while.\n",
|
||||
"In this example, we specify `show_output = True` to print currently running iterations to the console."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"local_run = experiment.submit(automl_config, show_output=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Explore the Results"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Widget for Monitoring Runs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The widget will first report a \"loading\" status while running the first iteration. After completing the first iteration, an auto-updating graph and table will be shown. The widget will refresh once per minute, so you should see the graph update as child runs complete.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Note:** The widget displays a link at the bottom. Use this link to open a web interface to explore the individual run details."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(local_run).show() "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Retrieve All Child Runs\n",
|
||||
"You can also use SDK methods to fetch all the child runs and see individual metrics that we log."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"children = list(local_run.get_children())\n",
|
||||
"metricslist = {}\n",
|
||||
"for run in children:\n",
|
||||
" properties = run.get_properties()\n",
|
||||
" metrics = {k: v for k, v in run.get_metrics().items() if isinstance(v, float)}\n",
|
||||
" metricslist[int(properties['iteration'])] = metrics\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"rundata = pd.DataFrame(metricslist).sort_index(1)\n",
|
||||
"rundata"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Retrieve the Best Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Below we select the best pipeline from our iterations. The `get_output` method returns the best run and the fitted model. The Model includes the pipeline and any pre-processing. Overloads on `get_output` allow you to retrieve the best run and fitted model for *any* logged metric or for a particular *iteration*."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Best Model Based on Any Other Metric\n",
|
||||
"Show the run and the model which has the smallest `accuracy` value:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# lookup_metric = \"accuracy\"\n",
|
||||
"# best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output(metric = lookup_metric)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Model from a Specific Iteration\n",
|
||||
"Show the run and the model from the third iteration:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# iteration = 3\n",
|
||||
"# best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output(iteration = iteration)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Testing the Best Fitted Model"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Load test data.\n",
|
||||
"from pandas_ml import ConfusionMatrix\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"data_test = fetch_20newsgroups(subset = 'test', categories = categories,\n",
|
||||
" shuffle = True, random_state = 42,\n",
|
||||
" remove = remove)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"X_test = vectorizer.transform(data_test.data)\n",
|
||||
"y_test = data_test.target\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Test our best pipeline.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"y_pred = fitted_model.predict(X_test)\n",
|
||||
"y_pred_strings = [data_test.target_names[i] for i in y_pred]\n",
|
||||
"y_test_strings = [data_test.target_names[i] for i in y_test]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"cm = ConfusionMatrix(y_test_strings, y_pred_strings)\n",
|
||||
"print(cm)\n",
|
||||
"cm.plot()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "savitam"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.6",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
384
automl/06.auto-ml-sparse-data-train-test-split.ipynb
Normal file
384
automl/06.auto-ml-sparse-data-train-test-split.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,384 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# AutoML 06: Train Test Split and Handling Sparse Data\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this example we use the scikit-learn's [20newsgroup](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.datasets.fetch_20newsgroups.html) to showcase how you can use AutoML for handling sparse data and how to specify custom cross validations splits.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you have executed the [00.configuration](00.configuration.ipynb) before running this notebook.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this notebook you will learn how to:\n",
|
||||
"1. Create an `Experiment` in an existing `Workspace`.\n",
|
||||
"2. Configure AutoML using `AutoMLConfig`.\n",
|
||||
"4. Train the model.\n",
|
||||
"5. Explore the results.\n",
|
||||
"6. Test the best fitted model.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In addition this notebook showcases the following features\n",
|
||||
"- Explicit train test splits \n",
|
||||
"- Handling **sparse data** in the input"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create an Experiment\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"As part of the setup you have already created an Azure ML `Workspace` object. For AutoML you will need to create an `Experiment` object, which is a named object in a `Workspace` used to run experiments."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import logging\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"import random\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib import pyplot as plt\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn import datasets\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.experiment import Experiment\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.workspace import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl import AutoMLConfig\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl.run import AutoMLRun"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for the experiment\n",
|
||||
"experiment_name = 'automl-local-missing-data'\n",
|
||||
"# project folder\n",
|
||||
"project_folder = './sample_projects/automl-local-missing-data'\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"experiment = Experiment(ws, experiment_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"output = {}\n",
|
||||
"output['SDK version'] = azureml.core.VERSION\n",
|
||||
"output['Subscription ID'] = ws.subscription_id\n",
|
||||
"output['Workspace'] = ws.name\n",
|
||||
"output['Resource Group'] = ws.resource_group\n",
|
||||
"output['Location'] = ws.location\n",
|
||||
"output['Project Directory'] = project_folder\n",
|
||||
"output['Experiment Name'] = experiment.name\n",
|
||||
"pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', -1)\n",
|
||||
"pd.DataFrame(data=output, index=['']).T"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Diagnostics\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Opt-in diagnostics for better experience, quality, and security of future releases."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.telemetry import set_diagnostics_collection\n",
|
||||
"set_diagnostics_collection(send_diagnostics = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Creating Sparse Data"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import HashingVectorizer\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"remove = ('headers', 'footers', 'quotes')\n",
|
||||
"categories = [\n",
|
||||
" 'alt.atheism',\n",
|
||||
" 'talk.religion.misc',\n",
|
||||
" 'comp.graphics',\n",
|
||||
" 'sci.space',\n",
|
||||
"]\n",
|
||||
"data_train = fetch_20newsgroups(subset = 'train', categories = categories,\n",
|
||||
" shuffle = True, random_state = 42,\n",
|
||||
" remove = remove)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"X_train, X_valid, y_train, y_valid = train_test_split(data_train.data, data_train.target, test_size = 0.33, random_state = 42)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"vectorizer = HashingVectorizer(stop_words = 'english', alternate_sign = False,\n",
|
||||
" n_features = 2**16)\n",
|
||||
"X_train = vectorizer.transform(X_train)\n",
|
||||
"X_valid = vectorizer.transform(X_valid)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"summary_df = pd.DataFrame(index = ['No of Samples', 'No of Features'])\n",
|
||||
"summary_df['Train Set'] = [X_train.shape[0], X_train.shape[1]]\n",
|
||||
"summary_df['Validation Set'] = [X_valid.shape[0], X_valid.shape[1]]\n",
|
||||
"summary_df"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Configure AutoML\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Instantiate an `AutoMLConfig` object to specify the settings and data used to run the experiment.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"|Property|Description|\n",
|
||||
"|-|-|\n",
|
||||
"|**task**|classification or regression|\n",
|
||||
"|**primary_metric**|This is the metric that you want to optimize. Classification supports the following primary metrics: <br><i>accuracy</i><br><i>AUC_weighted</i><br><i>balanced_accuracy</i><br><i>average_precision_score_weighted</i><br><i>precision_score_weighted</i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**iteration_timeout_minutes**|Time limit in minutes for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iterations**|Number of iterations. In each iteration AutoML trains a specific pipeline with the data.|\n",
|
||||
"|**preprocess**|Setting this to *True* enables AutoML to perform preprocessing on the input to handle *missing data*, and to perform some common *feature extraction*.<br>**Note:** If input data is sparse, you cannot use *True*.|\n",
|
||||
"|**X**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features]|\n",
|
||||
"|**y**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, ], [n_samples, n_classes]<br>Multi-class targets. An indicator matrix turns on multilabel classification. This should be an array of integers.|\n",
|
||||
"|**X_valid**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features] for the custom validation set.|\n",
|
||||
"|**y_valid**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, ], [n_samples, n_classes]<br>Multi-class targets. An indicator matrix turns on multilabel classification for the custom validation set.|\n",
|
||||
"|**path**|Relative path to the project folder. AutoML stores configuration files for the experiment under this folder. You can specify a new empty folder.|"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_config = AutoMLConfig(task = 'classification',\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'automl_errors.log',\n",
|
||||
" primary_metric = 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" iteration_timeout_minutes = 60,\n",
|
||||
" iterations = 5,\n",
|
||||
" preprocess = False,\n",
|
||||
" verbosity = logging.INFO,\n",
|
||||
" X = X_train, \n",
|
||||
" y = y_train,\n",
|
||||
" X_valid = X_valid, \n",
|
||||
" y_valid = y_valid, \n",
|
||||
" path = project_folder)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Train the Models\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Call the `submit` method on the experiment object and pass the run configuration. Execution of local runs is synchronous. Depending on the data and the number of iterations this can run for a while.\n",
|
||||
"In this example, we specify `show_output = True` to print currently running iterations to the console."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"local_run = experiment.submit(automl_config, show_output=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Explore the Results"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Widget for Monitoring Runs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The widget will first report a \"loading\" status while running the first iteration. After completing the first iteration, an auto-updating graph and table will be shown. The widget will refresh once per minute, so you should see the graph update as child runs complete.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Note:** The widget displays a link at the bottom. Use this link to open a web interface to explore the individual run details."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(local_run).show() "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Retrieve All Child Runs\n",
|
||||
"You can also use SDK methods to fetch all the child runs and see individual metrics that we log."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"children = list(local_run.get_children())\n",
|
||||
"metricslist = {}\n",
|
||||
"for run in children:\n",
|
||||
" properties = run.get_properties()\n",
|
||||
" metrics = {k: v for k, v in run.get_metrics().items() if isinstance(v, float)}\n",
|
||||
" metricslist[int(properties['iteration'])] = metrics\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"rundata = pd.DataFrame(metricslist).sort_index(1)\n",
|
||||
"rundata"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Retrieve the Best Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Below we select the best pipeline from our iterations. The `get_output` method returns the best run and the fitted model. The Model includes the pipeline and any pre-processing. Overloads on `get_output` allow you to retrieve the best run and fitted model for *any* logged metric or for a particular *iteration*."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Best Model Based on Any Other Metric\n",
|
||||
"Show the run and the model which has the smallest `accuracy` value:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# lookup_metric = \"accuracy\"\n",
|
||||
"# best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output(metric = lookup_metric)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Model from a Specific Iteration\n",
|
||||
"Show the run and the model from the third iteration:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# iteration = 3\n",
|
||||
"# best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output(iteration = iteration)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Testing the Best Fitted Model"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Load test data.\n",
|
||||
"from pandas_ml import ConfusionMatrix\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"data_test = fetch_20newsgroups(subset = 'test', categories = categories,\n",
|
||||
" shuffle = True, random_state = 42,\n",
|
||||
" remove = remove)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"X_test = vectorizer.transform(data_test.data)\n",
|
||||
"y_test = data_test.target\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Test our best pipeline.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"y_pred = fitted_model.predict(X_test)\n",
|
||||
"y_pred_strings = [data_test.target_names[i] for i in y_pred]\n",
|
||||
"y_test_strings = [data_test.target_names[i] for i in y_test]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"cm = ConfusionMatrix(y_test_strings, y_pred_strings)\n",
|
||||
"print(cm)\n",
|
||||
"cm.plot()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "savitam"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.6",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -116,10 +116,11 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"experiment_name = 'automl-local-classification' # Replace this with any project name from previous cell.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"proj = ws.experiments()[experiment_name]\n",
|
||||
"proj = ws.experiments[experiment_name]\n",
|
||||
"summary_df = pd.DataFrame(index = ['Type', 'Status', 'Primary Metric', 'Iterations', 'Compute', 'Name'])\n",
|
||||
"pattern = re.compile('^AutoML_[^_]*$')\n",
|
||||
"all_runs = list(proj.get_runs(properties={'azureml.runsource': 'automl'}))\n",
|
||||
"automl_runs_project = []\n",
|
||||
"for run in all_runs:\n",
|
||||
" if(pattern.match(run.id)):\n",
|
||||
" properties = run.get_properties()\n",
|
||||
@@ -130,6 +131,8 @@
|
||||
" else:\n",
|
||||
" iterations = properties['num_iterations']\n",
|
||||
" summary_df[run.id] = [amlsettings['task_type'], run.get_details()['status'], properties['primary_metric'], iterations, properties['target'], amlsettings['name']]\n",
|
||||
" if run.get_details()['status'] == 'Completed':\n",
|
||||
" automl_runs_project.append(run.id)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"from IPython.display import HTML\n",
|
||||
"projname_html = HTML(\"<h3>{}</h3>\".format(proj.name))\n",
|
||||
@@ -154,10 +157,10 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"run_id = '' # Filling your own run_id from above run ids\n",
|
||||
"run_id = automl_runs_project[0] # Replace with your own run_id from above run ids\n",
|
||||
"assert (run_id in summary_df.keys()), \"Run id not found! Please set run id to a value from above run ids\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"experiment = Experiment(ws, experiment_name)\n",
|
||||
"ml_run = AutoMLRun(experiment = experiment, run_id = run_id)\n",
|
||||
@@ -238,7 +241,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"iteration = 4 # Replace with an iteration number.\n",
|
||||
"iteration = 1 # Replace with an iteration number.\n",
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = ml_run.get_output(iteration = iteration)\n",
|
||||
"fitted_model"
|
||||
]
|
||||
@@ -296,7 +299,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"iteration = 4 # Replace with an iteration number.\n",
|
||||
"iteration = 1 # Replace with an iteration number.\n",
|
||||
"description = 'AutoML Model'\n",
|
||||
"tags = None\n",
|
||||
"ml_run.register_model(description = description, tags = tags, iteration = iteration)\n",
|
||||
|
||||
568
automl/08.auto-ml-remote-execution-with-DataStore.ipynb
Normal file
568
automl/08.auto-ml-remote-execution-with-DataStore.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,568 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# AutoML 08: Remote Execution with DataStore\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This sample accesses a data file on a remote DSVM through DataStore. Advantages of using data store are:\n",
|
||||
"1. DataStore secures the access details.\n",
|
||||
"2. DataStore supports read, write to blob and file store\n",
|
||||
"3. AutoML natively supports copying data from DataStore to DSVM\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you have executed the [00.configuration](00.configuration.ipynb) before running this notebook.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this notebook you would see\n",
|
||||
"1. Storing data in DataStore.\n",
|
||||
"2. get_data returning data from DataStore.\n",
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create Experiment\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"As part of the setup you have already created a <b>Workspace</b>. For AutoML you would need to create an <b>Experiment</b>. An <b>Experiment</b> is a named object in a <b>Workspace</b>, which is used to run experiments."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import logging\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"import random\n",
|
||||
"import time\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib import pyplot as plt\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn import datasets\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import DsvmCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.experiment import Experiment\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.workspace import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl import AutoMLConfig\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl.run import AutoMLRun"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for experiment\n",
|
||||
"experiment_name = 'automl-remote-datastore-file'\n",
|
||||
"# project folder\n",
|
||||
"project_folder = './sample_projects/automl-remote-dsvm-file'\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"experiment=Experiment(ws, experiment_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"output = {}\n",
|
||||
"output['SDK version'] = azureml.core.VERSION\n",
|
||||
"output['Subscription ID'] = ws.subscription_id\n",
|
||||
"output['Workspace'] = ws.name\n",
|
||||
"output['Resource Group'] = ws.resource_group\n",
|
||||
"output['Location'] = ws.location\n",
|
||||
"output['Project Directory'] = project_folder\n",
|
||||
"output['Experiment Name'] = experiment.name\n",
|
||||
"pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', -1)\n",
|
||||
"pd.DataFrame(data=output, index=['']).T"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Diagnostics\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Opt-in diagnostics for better experience, quality, and security of future releases"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.telemetry import set_diagnostics_collection\n",
|
||||
"set_diagnostics_collection(send_diagnostics=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create a Remote Linux DSVM\n",
|
||||
"Note: If creation fails with a message about Marketplace purchase eligibilty, go to portal.azure.com, start creating DSVM there, and select \"Want to create programmatically\" to enable programmatic creation. Once you've enabled it, you can exit without actually creating VM.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Note**: By default SSH runs on port 22 and you don't need to specify it. But if for security reasons you can switch to a different port (such as 5022), you can append the port number to the address. [Read more](https://render.githubusercontent.com/documentation/sdk/ssh-issue.md) on this."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"compute_target_name = 'mydsvmc'\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" while ws.compute_targets[compute_target_name].provisioning_state == 'Creating':\n",
|
||||
" time.sleep(1)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute = DsvmCompute(workspace=ws, name=compute_target_name)\n",
|
||||
" print('found existing:', dsvm_compute.name)\n",
|
||||
"except:\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_config = DsvmCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size=\"Standard_D2_v2\")\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute = DsvmCompute.create(ws, name=compute_target_name, provisioning_configuration=dsvm_config)\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Copy data file to local\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Download the data file.\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"mkdir data"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"df = pd.read_csv(\"https://automldemods.blob.core.windows.net/datasets/PlayaEvents2016,_1.6MB,_3.4k-rows.cleaned.2.tsv\",\n",
|
||||
" delimiter=\"\\t\", quotechar='\"')\n",
|
||||
"df.to_csv(\"data/data.tsv\", sep=\"\\t\", quotechar='\"', index=False)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Upload data to the cloud"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Now make the data accessible remotely by uploading that data from your local machine into Azure so it can be accessed for remote training. The datastore is a convenient construct associated with your workspace for you to upload/download data, and interact with it from your remote compute targets. It is backed by Azure blob storage account.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The data.tsv files are uploaded into a directory named data at the root of the datastore."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Workspace, Datastore\n",
|
||||
"#blob_datastore = Datastore(ws, blob_datastore_name)\n",
|
||||
"ds = ws.get_default_datastore()\n",
|
||||
"print(ds.datastore_type, ds.account_name, ds.container_name)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# ds.upload_files(\"data.tsv\")\n",
|
||||
"ds.upload(src_dir='./data', target_path='data', overwrite=True, show_progress=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Configure & Run\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"First let's create a DataReferenceConfigruation object to inform the system what data folder to download to the compute target.\n",
|
||||
"The path_on_compute should be an absolute path to ensure that the data files are downloaded only once. The get_data method should use this same path to access the data files."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.runconfig import DataReferenceConfiguration\n",
|
||||
"dr = DataReferenceConfiguration(datastore_name=ds.name, \n",
|
||||
" path_on_datastore='data', \n",
|
||||
" path_on_compute='/tmp/azureml_runs',\n",
|
||||
" mode='download', # download files from datastore to compute target\n",
|
||||
" overwrite=False)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.runconfig import RunConfiguration\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# create a new RunConfig object\n",
|
||||
"conda_run_config = RunConfiguration(framework=\"python\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Set compute target to the Linux DSVM\n",
|
||||
"conda_run_config.target = dsvm_compute\n",
|
||||
"# set the data reference of the run coonfiguration\n",
|
||||
"conda_run_config.data_references = {ds.name: dr}\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"cd = CondaDependencies.create(pip_packages=['azureml-sdk[automl]'], conda_packages=['numpy'])\n",
|
||||
"conda_run_config.environment.python.conda_dependencies = cd"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create Get Data File\n",
|
||||
"For remote executions you should author a get_data.py file containing a get_data() function. This file should be in the root directory of the project. You can encapsulate code to read data either from a blob storage or local disk in this file.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The *get_data()* function returns a [dictionary](README.md#getdata).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The read_csv uses the path_on_compute value specified in the DataReferenceConfiguration call plus the path_on_datastore folder and then the actual file name."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"if not os.path.exists(project_folder):\n",
|
||||
" os.makedirs(project_folder)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%%writefile $project_folder/get_data.py\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"from os.path import expanduser, join, dirname\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def get_data():\n",
|
||||
" # Burning man 2016 data\n",
|
||||
" df = pd.read_csv(\"/tmp/azureml_runs/data/data.tsv\", delimiter=\"\\t\", quotechar='\"')\n",
|
||||
" # get integer labels\n",
|
||||
" le = LabelEncoder()\n",
|
||||
" le.fit(df[\"Label\"].values)\n",
|
||||
" y = le.transform(df[\"Label\"].values)\n",
|
||||
" X = df.drop([\"Label\"], axis=1)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" X_train, _, y_train, _ = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.1, random_state=42)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" return { \"X\" : X_train.values, \"y\" : y_train }"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Instantiate AutoML <a class=\"anchor\" id=\"Instatiate-AutoML-Remote-DSVM\"></a>\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"You can specify automl_settings as **kwargs** as well. Also note that you can use the get_data() symantic for local excutions too. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"<i>Note: For Remote DSVM and Batch AI you cannot pass Numpy arrays directly to AutoMLConfig.</i>\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"|Property|Description|\n",
|
||||
"|-|-|\n",
|
||||
"|**primary_metric**|This is the metric that you want to optimize.<br> Classification supports the following primary metrics <br><i>accuracy</i><br><i>AUC_weighted</i><br><i>balanced_accuracy</i><br><i>average_precision_score_weighted</i><br><i>precision_score_weighted</i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**iteration_timeout_minutes**|Time limit in minutes for each iteration|\n",
|
||||
"|**iterations**|Number of iterations. In each iteration Auto ML trains a specific pipeline with the data|\n",
|
||||
"|**n_cross_validations**|Number of cross validation splits|\n",
|
||||
"|**max_concurrent_iterations**|Max number of iterations that would be executed in parallel. This should be less than the number of cores on the DSVM\n",
|
||||
"|**preprocess**| *True/False* <br>Setting this to *True* enables Auto ML to perform preprocessing <br>on the input to handle *missing data*, and perform some common *feature extraction*|\n",
|
||||
"|**max_cores_per_iteration**| Indicates how many cores on the compute target would be used to train a single pipeline.<br> Default is *1*, you can set it to *-1* to use all cores|"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_settings = {\n",
|
||||
" \"iteration_timeout_minutes\": 60,\n",
|
||||
" \"iterations\": 4,\n",
|
||||
" \"n_cross_validations\": 5,\n",
|
||||
" \"primary_metric\": 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" \"preprocess\": True,\n",
|
||||
" \"max_cores_per_iteration\": 1,\n",
|
||||
" \"verbosity\": logging.INFO\n",
|
||||
"}\n",
|
||||
"automl_config = AutoMLConfig(task = 'classification',\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'automl_errors.log',\n",
|
||||
" path=project_folder,\n",
|
||||
" run_configuration=conda_run_config,\n",
|
||||
" #compute_target = dsvm_compute,\n",
|
||||
" data_script = project_folder + \"/get_data.py\",\n",
|
||||
" **automl_settings\n",
|
||||
" )"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Training the Models <a class=\"anchor\" id=\"Training-the-model-Remote-DSVM\"></a>\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"For remote runs the execution is asynchronous, so you will see the iterations get populated as they complete. You can interact with the widgets/models even when the experiment is running to retreive the best model up to that point. Once you are satisfied with the model you can cancel a particular iteration or the whole run."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"remote_run = experiment.submit(automl_config, show_output=False)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Exploring the Results <a class=\"anchor\" id=\"Exploring-the-Results-Remote-DSVM\"></a>\n",
|
||||
"#### Widget for monitoring runs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The widget will sit on \"loading\" until the first iteration completed, then you will see an auto-updating graph and table show up. It refreshed once per minute, so you should see the graph update as child runs complete.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"You can click on a pipeline to see run properties and output logs. Logs are also available on the DSVM under /tmp/azureml_run/{iterationid}/azureml-logs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"NOTE: The widget displays a link at the bottom. This links to a web-ui to explore the individual run details."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(remote_run).show() "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Wait until the run finishes.\n",
|
||||
"remote_run.wait_for_completion(show_output = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Retrieve All Child Runs\n",
|
||||
"You can also use sdk methods to fetch all the child runs and see individual metrics that we log. "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"children = list(remote_run.get_children())\n",
|
||||
"metricslist = {}\n",
|
||||
"for run in children:\n",
|
||||
" properties = run.get_properties()\n",
|
||||
" metrics = {k: v for k, v in run.get_metrics().items() if isinstance(v, float)} \n",
|
||||
" metricslist[int(properties['iteration'])] = metrics\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"rundata = pd.DataFrame(metricslist).sort_index(1)\n",
|
||||
"rundata"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Canceling Runs\n",
|
||||
"You can cancel ongoing remote runs using the *cancel()* and *cancel_iteration()* functions"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Cancel the ongoing experiment and stop scheduling new iterations\n",
|
||||
"# remote_run.cancel()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Cancel iteration 1 and move onto iteration 2\n",
|
||||
"# remote_run.cancel_iteration(1)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Retrieve the Best Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Below we select the best pipeline from our iterations. The *get_output* method returns the best run and the fitted model. There are overloads on *get_output* that allow you to retrieve the best run and fitted model for *any* logged metric or a particular *iteration*."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = remote_run.get_output()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Best Model based on any other metric"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# lookup_metric = \"accuracy\"\n",
|
||||
"# best_run, fitted_model = remote_run.get_output(metric=lookup_metric)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Model from a specific iteration"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# iteration = 1\n",
|
||||
"# best_run, fitted_model = remote_run.get_output(iteration=iteration)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Testing the Best Fitted Model <a class=\"anchor\" id=\"Testing-the-Fitted-Model-Remote-DSVM\"></a>\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import sklearn\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder\n",
|
||||
"from pandas_ml import ConfusionMatrix\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"df = pd.read_csv(\"https://automldemods.blob.core.windows.net/datasets/PlayaEvents2016,_1.6MB,_3.4k-rows.cleaned.2.tsv\",\n",
|
||||
" delimiter=\"\\t\", quotechar='\"')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# get integer labels\n",
|
||||
"le = LabelEncoder()\n",
|
||||
"le.fit(df[\"Label\"].values)\n",
|
||||
"y = le.transform(df[\"Label\"].values)\n",
|
||||
"X = df.drop([\"Label\"], axis=1)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"_, X_test, _, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.1, random_state=42)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"ypred = fitted_model.predict(X_test.values)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"ypred_strings = le.inverse_transform(ypred)\n",
|
||||
"ytest_strings = le.inverse_transform(y_test)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"cm = ConfusionMatrix(ytest_strings, ypred_strings)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(cm)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"cm.plot()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "savitam"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.6",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -1,550 +0,0 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# AutoML 08: Remote Execution with DataStore\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This sample accesses a data file on a remote DSVM through DataStore. Advantages of using data store are:\n",
|
||||
"1. DataStore secures the access details.\n",
|
||||
"2. DataStore supports read, write to blob and file store\n",
|
||||
"3. AutoML natively supports copying data from DataStore to DSVM\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you have executed the [00.configuration](00.configuration.ipynb) before running this notebook.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this notebook you would see\n",
|
||||
"1. Storing data in DataStore.\n",
|
||||
"2. get_data returning data from DataStore.\n",
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create Experiment\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"As part of the setup you have already created a <b>Workspace</b>. For AutoML you would need to create an <b>Experiment</b>. An <b>Experiment</b> is a named object in a <b>Workspace</b>, which is used to run experiments."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import logging\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"import random\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib import pyplot as plt\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn import datasets\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.experiment import Experiment\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.workspace import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl import AutoMLConfig\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl.run import AutoMLRun"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for experiment\n",
|
||||
"experiment_name = 'automl-remote-datastore-file'\n",
|
||||
"# project folder\n",
|
||||
"project_folder = './sample_projects/automl-remote-dsvm-file'\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"experiment=Experiment(ws, experiment_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"output = {}\n",
|
||||
"output['SDK version'] = azureml.core.VERSION\n",
|
||||
"output['Subscription ID'] = ws.subscription_id\n",
|
||||
"output['Workspace'] = ws.name\n",
|
||||
"output['Resource Group'] = ws.resource_group\n",
|
||||
"output['Location'] = ws.location\n",
|
||||
"output['Project Directory'] = project_folder\n",
|
||||
"output['Experiment Name'] = experiment.name\n",
|
||||
"pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', -1)\n",
|
||||
"pd.DataFrame(data=output, index=['']).T"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Diagnostics\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Opt-in diagnostics for better experience, quality, and security of future releases"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.telemetry import set_diagnostics_collection\n",
|
||||
"set_diagnostics_collection(send_diagnostics=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create a Remote Linux DSVM\n",
|
||||
"Note: If creation fails with a message about Marketplace purchase eligibilty, go to portal.azure.com, start creating DSVM there, and select \"Want to create programmatically\" to enable programmatic creation. Once you've enabled it, you can exit without actually creating VM.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Note**: By default SSH runs on port 22 and you don't need to specify it. But if for security reasons you can switch to a different port (such as 5022), you can append the port number to the address. [Read more](https://render.githubusercontent.com/documentation/sdk/ssh-issue.md) on this."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import DsvmCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute_target import ComputeTargetException\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"compute_target_name = 'mydsvm'\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute = DsvmCompute(workspace=ws, name=compute_target_name)\n",
|
||||
" print('found existing:', dsvm_compute.name)\n",
|
||||
"except ComputeTargetException:\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_config = DsvmCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size=\"Standard_D2_v2\")\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute = DsvmCompute.create(ws, name=compute_target_name, provisioning_configuration=dsvm_config)\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Copy data file to local\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Download the data file.\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"mkdir data"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"df = pd.read_csv(\"https://automldemods.blob.core.windows.net/datasets/PlayaEvents2016,_1.6MB,_3.4k-rows.cleaned.2.tsv\",\n",
|
||||
" delimiter=\"\\t\", quotechar='\"')\n",
|
||||
"df.to_csv(\"data/data.tsv\", sep=\"\\t\", quotechar='\"', index=False)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Upload data to the cloud"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Now make the data accessible remotely by uploading that data from your local machine into Azure so it can be accessed for remote training. The datastore is a convenient construct associated with your workspace for you to upload/download data, and interact with it from your remote compute targets. It is backed by Azure blob storage account.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The data.tsv files are uploaded into a directory named data at the root of the datastore."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Workspace, Datastore\n",
|
||||
"#blob_datastore = Datastore(ws, blob_datastore_name)\n",
|
||||
"ds = ws.get_default_datastore()\n",
|
||||
"print(ds.datastore_type, ds.account_name, ds.container_name)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# ds.upload_files(\"data.tsv\")\n",
|
||||
"ds.upload(src_dir='./data', target_path='data', overwrite=True, show_progress=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Configure & Run\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"First let's create a DataReferenceConfigruation object to inform the system what data folder to download to the copmute target."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.runconfig import DataReferenceConfiguration\n",
|
||||
"dr = DataReferenceConfiguration(datastore_name=ds.name, \n",
|
||||
" path_on_datastore='data', \n",
|
||||
" mode='download', # download files from datastore to compute target\n",
|
||||
" overwrite=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.runconfig import RunConfiguration\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# create a new RunConfig object\n",
|
||||
"conda_run_config = RunConfiguration(framework=\"python\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Set compute target to the Linux DSVM\n",
|
||||
"conda_run_config.target = dsvm_compute.name\n",
|
||||
"# set the data reference of the run coonfiguration\n",
|
||||
"conda_run_config.data_references = {ds.name: dr}"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create Get Data File\n",
|
||||
"For remote executions you should author a get_data.py file containing a get_data() function. This file should be in the root directory of the project. You can encapsulate code to read data either from a blob storage or local disk in this file.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The *get_data()* function returns a [dictionary](README.md#getdata)."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"if not os.path.exists(project_folder):\n",
|
||||
" os.makedirs(project_folder)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%%writefile $project_folder/get_data.py\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"from os.path import expanduser, join, dirname\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def get_data():\n",
|
||||
" # Burning man 2016 data\n",
|
||||
" df = pd.read_csv(join(dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__)),\n",
|
||||
" os.environ[\"AZUREML_DATAREFERENCE_workspacefilestore\"],\n",
|
||||
" \"data.tsv\"), delimiter=\"\\t\", quotechar='\"')\n",
|
||||
" # get integer labels\n",
|
||||
" le = LabelEncoder()\n",
|
||||
" le.fit(df[\"Label\"].values)\n",
|
||||
" y = le.transform(df[\"Label\"].values)\n",
|
||||
" X = df.drop([\"Label\"], axis=1)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" X_train, _, y_train, _ = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.1, random_state=42)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" return { \"X\" : X_train.values, \"y\" : y_train }"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Instantiate AutoML <a class=\"anchor\" id=\"Instatiate-AutoML-Remote-DSVM\"></a>\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"You can specify automl_settings as **kwargs** as well. Also note that you can use the get_data() symantic for local excutions too. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"<i>Note: For Remote DSVM and Batch AI you cannot pass Numpy arrays directly to AutoMLConfig.</i>\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"|Property|Description|\n",
|
||||
"|-|-|\n",
|
||||
"|**primary_metric**|This is the metric that you want to optimize.<br> Classification supports the following primary metrics <br><i>accuracy</i><br><i>AUC_weighted</i><br><i>balanced_accuracy</i><br><i>average_precision_score_weighted</i><br><i>precision_score_weighted</i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**max_time_sec**|Time limit in seconds for each iteration|\n",
|
||||
"|**iterations**|Number of iterations. In each iteration Auto ML trains a specific pipeline with the data|\n",
|
||||
"|**n_cross_validations**|Number of cross validation splits|\n",
|
||||
"|**concurrent_iterations**|Max number of iterations that would be executed in parallel. This should be less than the number of cores on the DSVM\n",
|
||||
"|**preprocess**| *True/False* <br>Setting this to *True* enables Auto ML to perform preprocessing <br>on the input to handle *missing data*, and perform some common *feature extraction*|\n",
|
||||
"|**max_cores_per_iteration**| Indicates how many cores on the compute target would be used to train a single pipeline.<br> Default is *1*, you can set it to *-1* to use all cores|"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_settings = {\n",
|
||||
" \"max_time_sec\": 3600,\n",
|
||||
" \"iterations\": 10,\n",
|
||||
" \"n_cross_validations\": 5,\n",
|
||||
" \"primary_metric\": 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" \"preprocess\": True,\n",
|
||||
" \"max_cores_per_iteration\": 2,\n",
|
||||
" \"verbosity\": logging.INFO\n",
|
||||
"}\n",
|
||||
"automl_config = AutoMLConfig(task = 'classification',\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'automl_errors.log',\n",
|
||||
" path=project_folder,\n",
|
||||
" run_configuration=conda_run_config,\n",
|
||||
" #compute_target = dsvm_compute,\n",
|
||||
" data_script = project_folder + \"/get_data.py\",\n",
|
||||
" **automl_settings\n",
|
||||
" )"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Training the Models <a class=\"anchor\" id=\"Training-the-model-Remote-DSVM\"></a>\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"For remote runs the execution is asynchronous, so you will see the iterations get populated as they complete. You can interact with the widgets/models even when the experiment is running to retreive the best model up to that point. Once you are satisfied with the model you can cancel a particular iteration or the whole run."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"remote_run = experiment.submit(automl_config, show_output=False)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Exploring the Results <a class=\"anchor\" id=\"Exploring-the-Results-Remote-DSVM\"></a>\n",
|
||||
"#### Widget for monitoring runs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The widget will sit on \"loading\" until the first iteration completed, then you will see an auto-updating graph and table show up. It refreshed once per minute, so you should see the graph update as child runs complete.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"You can click on a pipeline to see run properties and output logs. Logs are also available on the DSVM under /tmp/azureml_run/{iterationid}/azureml-logs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"NOTE: The widget displays a link at the bottom. This links to a web-ui to explore the individual run details."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(remote_run).show() "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Retrieve All Child Runs\n",
|
||||
"You can also use sdk methods to fetch all the child runs and see individual metrics that we log. "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"children = list(remote_run.get_children())\n",
|
||||
"metricslist = {}\n",
|
||||
"for run in children:\n",
|
||||
" properties = run.get_properties()\n",
|
||||
" metrics = {k: v for k, v in run.get_metrics().items() if isinstance(v, float)} \n",
|
||||
" metricslist[int(properties['iteration'])] = metrics\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"rundata = pd.DataFrame(metricslist).sort_index(1)\n",
|
||||
"rundata"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Canceling Runs\n",
|
||||
"You can cancel ongoing remote runs using the *cancel()* and *cancel_iteration()* functions"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Cancel the ongoing experiment and stop scheduling new iterations\n",
|
||||
"remote_run.cancel()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Cancel iteration 1 and move onto iteration 2\n",
|
||||
"# remote_run.cancel_iteration(1)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Retrieve the Best Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Below we select the best pipeline from our iterations. The *get_output* method returns the best run and the fitted model. There are overloads on *get_output* that allow you to retrieve the best run and fitted model for *any* logged metric or a particular *iteration*."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = remote_run.get_output()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Best Model based on any other metric"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# lookup_metric = \"accuracy\"\n",
|
||||
"# best_run, fitted_model = remote_run.get_output(metric=lookup_metric)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Model from a specific iteration"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# iteration = 1\n",
|
||||
"# best_run, fitted_model = remote_run.get_output(iteration=iteration)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Testing the Best Fitted Model <a class=\"anchor\" id=\"Testing-the-Fitted-Model-Remote-DSVM\"></a>\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import sklearn\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder\n",
|
||||
"from pandas_ml import ConfusionMatrix\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"df = pd.read_csv(\"https://automldemods.blob.core.windows.net/datasets/PlayaEvents2016,_1.6MB,_3.4k-rows.cleaned.2.tsv\",\n",
|
||||
" delimiter=\"\\t\", quotechar='\"')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# get integer labels\n",
|
||||
"le = LabelEncoder()\n",
|
||||
"le.fit(df[\"Label\"].values)\n",
|
||||
"y = le.transform(df[\"Label\"].values)\n",
|
||||
"X = df.drop([\"Label\"], axis=1)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"_, X_test, _, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.1, random_state=42)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"ypred = fitted_model.predict(X_test.values)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"ypred_strings = le.inverse_transform(ypred)\n",
|
||||
"ytest_strings = le.inverse_transform(y_test)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"cm = ConfusionMatrix(ytest_strings, ypred_strings)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(cm)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"cm.plot()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "savitam"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.6",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -121,7 +121,7 @@
|
||||
"|-|-|\n",
|
||||
"|**task**|classification or regression|\n",
|
||||
"|**primary_metric**|This is the metric that you want to optimize. Classification supports the following primary metrics: <br><i>accuracy</i><br><i>AUC_weighted</i><br><i>balanced_accuracy</i><br><i>average_precision_score_weighted</i><br><i>precision_score_weighted</i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**max_time_sec**|Time limit in seconds for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iteration_timeout_minutes**|Time limit in minutes for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iterations**|Number of iterations. In each iteration AutoML trains a specific pipeline with the data.|\n",
|
||||
"|**n_cross_validations**|Number of cross validation splits.|\n",
|
||||
"|**X**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features]|\n",
|
||||
@@ -143,7 +143,7 @@
|
||||
" name = experiment_name,\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'automl_errors.log',\n",
|
||||
" primary_metric = 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" max_time_sec = 1200,\n",
|
||||
" iteration_timeout_minutes = 20,\n",
|
||||
" iterations = 10,\n",
|
||||
" n_cross_validations = 2,\n",
|
||||
" verbosity = logging.INFO,\n",
|
||||
@@ -226,6 +226,7 @@
|
||||
"import pickle\n",
|
||||
"import json\n",
|
||||
"import numpy\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.train.automl\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.externals import joblib\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.model import Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
@@ -298,15 +299,12 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%%writefile myenv.yml\n",
|
||||
"name: myenv\n",
|
||||
"channels:\n",
|
||||
" - defaults\n",
|
||||
"dependencies:\n",
|
||||
" - pip:\n",
|
||||
" - numpy==1.14.2\n",
|
||||
" - scikit-learn==0.19.2\n",
|
||||
" - azureml-sdk[notebooks,automl]==<<azureml-version>>"
|
||||
"from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"myenv = CondaDependencies.create(conda_packages=['numpy','scikit-learn'], pip_packages=['azureml-sdk[automl]'])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"conda_env_file_name = 'myenv.yml'\n",
|
||||
"myenv.save_to_file('.', conda_env_file_name)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -316,14 +314,14 @@
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Substitute the actual version number in the environment file.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"conda_env_file_name = 'myenv.yml'\n",
|
||||
"# This is not strictly needed in this notebook because the model should have been generated using the current SDK version.\n",
|
||||
"# However, we include this in case this code is used on an experiment from a previous SDK version.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with open(conda_env_file_name, 'r') as cefr:\n",
|
||||
" content = cefr.read()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with open(conda_env_file_name, 'w') as cefw:\n",
|
||||
" cefw.write(content.replace('<<azureml-version>>', dependencies['azureml-sdk']))\n",
|
||||
" cefw.write(content.replace(azureml.core.VERSION, dependencies['azureml-sdk']))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Substitute the actual model id in the script file.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
@@ -363,7 +361,10 @@
|
||||
" image_config = image_config, \n",
|
||||
" workspace = ws)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"image.wait_for_creation(show_output = True)"
|
||||
"image.wait_for_creation(show_output = True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"if image.creation_state == 'Failed':\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Image build log at: \" + image.image_build_log_uri)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -128,7 +128,7 @@
|
||||
"automl_classifier = AutoMLConfig(task = 'classification',\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'automl_errors.log',\n",
|
||||
" primary_metric = 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" max_time_sec = 3600,\n",
|
||||
" iteration_timeout_minutes = 60,\n",
|
||||
" iterations = 10,\n",
|
||||
" n_cross_validations = 2,\n",
|
||||
" verbosity = logging.INFO,\n",
|
||||
@@ -139,7 +139,7 @@
|
||||
"automl_sample_weight = AutoMLConfig(task = 'classification',\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'automl_errors.log',\n",
|
||||
" primary_metric = 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" max_time_sec = 3600,\n",
|
||||
" iteration_timeout_minutes = 60,\n",
|
||||
" iterations = 10,\n",
|
||||
" n_cross_validations = 2,\n",
|
||||
" verbosity = logging.INFO,\n",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -40,8 +40,7 @@
|
||||
"from azureml.core.experiment import Experiment\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.workspace import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl import AutoMLConfig\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl.run import AutoMLRun\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl.utilities import get_sdk_dependencies"
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl.run import AutoMLRun\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -63,29 +62,6 @@
|
||||
"set_diagnostics_collection(send_diagnostics = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Retrieve the SDK versions in the current environment"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"To retrieve the SDK versions in the current environment, run `get_sdk_dependencies`."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"get_sdk_dependencies()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,558 +0,0 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# AutoML 13: Prepare Data using `azureml.dataprep`\n",
|
||||
"In this example we showcase how you can use the `azureml.dataprep` SDK to load and prepare data for AutoML. `azureml.dataprep` can also be used standalone; full documentation can be found [here](https://github.com/Microsoft/PendletonDocs).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you have executed the [setup](00.configuration.ipynb) before running this notebook.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this notebook you will learn how to:\n",
|
||||
"1. Define data loading and preparation steps in a `Dataflow` using `azureml.dataprep`.\n",
|
||||
"2. Pass the `Dataflow` to AutoML for a local run.\n",
|
||||
"3. Pass the `Dataflow` to AutoML for a remote run."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Install `azureml.dataprep` SDK"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"!pip install azureml-dataprep"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Diagnostics\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Opt-in diagnostics for better experience, quality, and security of future releases."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.telemetry import set_diagnostics_collection\n",
|
||||
"set_diagnostics_collection(send_diagnostics = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create an Experiment\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"As part of the setup you have already created an Azure ML `Workspace` object. For AutoML you will need to create an `Experiment` object, which is a named object in a `Workspace` used to run experiments."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import logging\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import DsvmCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.experiment import Experiment\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.runconfig import CondaDependencies\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.runconfig import RunConfiguration\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.workspace import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.dataprep as dprep\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl import AutoMLConfig"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for experiment\n",
|
||||
"experiment_name = 'automl-dataprep-classification'\n",
|
||||
"# project folder\n",
|
||||
"project_folder = './sample_projects/automl-dataprep-classification'\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"experiment = Experiment(ws, experiment_name)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"output = {}\n",
|
||||
"output['SDK version'] = azureml.core.VERSION\n",
|
||||
"output['Subscription ID'] = ws.subscription_id\n",
|
||||
"output['Workspace Name'] = ws.name\n",
|
||||
"output['Resource Group'] = ws.resource_group\n",
|
||||
"output['Location'] = ws.location\n",
|
||||
"output['Project Directory'] = project_folder\n",
|
||||
"output['Experiment Name'] = experiment.name\n",
|
||||
"pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', -1)\n",
|
||||
"pd.DataFrame(data = output, index = ['']).T"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Loading Data using DataPrep"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# You can use `smart_read_file` which intelligently figures out delimiters and datatypes of a file.\n",
|
||||
"# The data referenced here was pulled from `sklearn.datasets.load_digits()`.\n",
|
||||
"simple_example_data_root = 'https://dprepdata.blob.core.windows.net/automl-notebook-data/'\n",
|
||||
"X = dprep.smart_read_file(simple_example_data_root + 'X.csv').skip(1) # Remove the header row.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# You can also use `read_csv` and `to_*` transformations to read (with overridable delimiter)\n",
|
||||
"# and convert column types manually.\n",
|
||||
"# Here we read a comma delimited file and convert all columns to integers.\n",
|
||||
"y = dprep.read_csv(simple_example_data_root + 'y.csv').to_long(dprep.ColumnSelector(term='.*', use_regex = True))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Review the Data Preparation Result\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"You can peek the result of a Dataflow at any range using `skip(i)` and `head(j)`. Doing so evaluates only `j` records for all the steps in the Dataflow, which makes it fast even against large datasets."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"X.skip(1).head(5)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Configure AutoML\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This creates a general AutoML settings object applicable for both local and remote runs."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_settings = {\n",
|
||||
" \"max_time_sec\" : 600,\n",
|
||||
" \"iterations\" : 2,\n",
|
||||
" \"primary_metric\" : 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" \"preprocess\" : False,\n",
|
||||
" \"verbosity\" : logging.INFO,\n",
|
||||
" \"n_cross_validations\": 3\n",
|
||||
"}"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Local Run"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Pass Data with `Dataflow` Objects\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The `Dataflow` objects captured above can be passed to the `submit` method for a local run. AutoML will retrieve the results from the `Dataflow` for model training."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_config = AutoMLConfig(task = 'classification',\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'automl_errors.log',\n",
|
||||
" X = X,\n",
|
||||
" y = y,\n",
|
||||
" **automl_settings)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"local_run = experiment.submit(automl_config, show_output = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Remote Run"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Create or Attach a Remote Linux DSVM"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"dsvm_name = 'mydsvm'\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute = DsvmCompute(ws, dsvm_name)\n",
|
||||
" print('Found existing DVSM.')\n",
|
||||
"except:\n",
|
||||
" print('Creating a new DSVM.')\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_config = DsvmCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size = \"Standard_D2_v2\")\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute = DsvmCompute.create(ws, name = dsvm_name, provisioning_configuration = dsvm_config)\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute.wait_for_completion(show_output = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Update Conda Dependency file to have AutoML and DataPrep SDK\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Currently the AutoML and DataPrep SDKs are not installed with the Azure ML SDK by default. To circumvent this limitation, we update the conda dependency file to add these dependencies."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"cd = CondaDependencies()\n",
|
||||
"cd.add_pip_package(pip_package='azureml-dataprep')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Create a `RunConfiguration` with DSVM name"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"run_config = RunConfiguration(conda_dependencies=cd)\n",
|
||||
"run_config.target = dsvm_compute\n",
|
||||
"run_config.auto_prepare_environment = True"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Pass Data with `Dataflow` Objects\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The `Dataflow` objects captured above can also be passed to the `submit` method for a remote run. AutoML will serialize the `Dataflow` object and send it to the remote compute target. The `Dataflow` will not be evaluated locally."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_config = AutoMLConfig(task = 'classification',\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'automl_errors.log',\n",
|
||||
" path = project_folder,\n",
|
||||
" run_configuration = run_config,\n",
|
||||
" X = X,\n",
|
||||
" y = y,\n",
|
||||
" **automl_settings)\n",
|
||||
"remote_run = experiment.submit(automl_config, show_output = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Explore the Results"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Widget for Monitoring Runs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The widget will first report a \"loading\" status while running the first iteration. After completing the first iteration, an auto-updating graph and table will be shown. The widget will refresh once per minute, so you should see the graph update as child runs complete.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Note:** The widget displays a link at the bottom. Use this link to open a web interface to explore the individual run details."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(local_run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Retrieve All Child Runs\n",
|
||||
"You can also use SDK methods to fetch all the child runs and see individual metrics that we log."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"children = list(local_run.get_children())\n",
|
||||
"metricslist = {}\n",
|
||||
"for run in children:\n",
|
||||
" properties = run.get_properties()\n",
|
||||
" metrics = {k: v for k, v in run.get_metrics().items() if isinstance(v, float)}\n",
|
||||
" metricslist[int(properties['iteration'])] = metrics\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"rundata = pd.DataFrame(metricslist).sort_index(1)\n",
|
||||
"rundata"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Retrieve the Best Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Below we select the best pipeline from our iterations. The `get_output` method returns the best run and the fitted model. Overloads on `get_output` allow you to retrieve the best run and fitted model for *any* logged metric or for a particular *iteration*."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output()\n",
|
||||
"print(best_run)\n",
|
||||
"print(fitted_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Best Model Based on Any Other Metric\n",
|
||||
"Show the run and the model that has the smallest `log_loss` value:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"lookup_metric = \"log_loss\"\n",
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output(metric = lookup_metric)\n",
|
||||
"print(best_run)\n",
|
||||
"print(fitted_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Model from a Specific Iteration\n",
|
||||
"Show the run and the model from the first iteration:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"iteration = 0\n",
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output(iteration = iteration)\n",
|
||||
"print(best_run)\n",
|
||||
"print(fitted_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Test the Best Fitted Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Load Test Data"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from sklearn import datasets\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"digits = datasets.load_digits()\n",
|
||||
"X_test = digits.data[:10, :]\n",
|
||||
"y_test = digits.target[:10]\n",
|
||||
"images = digits.images[:10]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Testing Our Best Fitted Model\n",
|
||||
"We will try to predict 2 digits and see how our model works."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#Randomly select digits and test\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib import pyplot as plt\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow\n",
|
||||
"import random\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for index in np.random.choice(len(y_test), 2, replace = False):\n",
|
||||
" print(index)\n",
|
||||
" predicted = fitted_model.predict(X_test[index:index + 1])[0]\n",
|
||||
" label = y_test[index]\n",
|
||||
" title = \"Label value = %d Predicted value = %d \" % (label, predicted)\n",
|
||||
" fig = plt.figure(1, figsize=(3,3))\n",
|
||||
" ax1 = fig.add_axes((0,0,.8,.8))\n",
|
||||
" ax1.set_title(title)\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(images[index], cmap = plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation = 'nearest')\n",
|
||||
" plt.show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Appendix"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Capture the `Dataflow` Objects for Later Use in AutoML\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"`Dataflow` objects are immutable and are composed of a list of data preparation steps. A `Dataflow` object can be branched at any point for further usage."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# sklearn.digits.data + target\n",
|
||||
"digits_complete = dprep.smart_read_file('https://dprepdata.blob.core.windows.net/automl-notebook-data/digits-complete.csv')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"`digits_complete` (sourced from `sklearn.datasets.load_digits()`) is forked into `dflow_X` to capture all the feature columns and `dflow_y` to capture the label column."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"digits_complete.to_pandas_dataframe().shape\n",
|
||||
"labels_column = 'Column64'\n",
|
||||
"dflow_X = digits_complete.drop_columns(columns = [labels_column])\n",
|
||||
"dflow_y = digits_complete.keep_columns(columns = [labels_column])"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "savitam"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.6",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.5"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
446
automl/13a.auto-ml-dataprep.ipynb
Normal file
446
automl/13a.auto-ml-dataprep.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,446 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# AutoML 13: Prepare Data using `azureml.dataprep` for Local Execution\n",
|
||||
"In this example we showcase how you can use the `azureml.dataprep` SDK to load and prepare data for AutoML. `azureml.dataprep` can also be used standalone; full documentation can be found [here](https://github.com/Microsoft/PendletonDocs).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you have executed the [setup](00.configuration.ipynb) before running this notebook.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this notebook you will learn how to:\n",
|
||||
"1. Define data loading and preparation steps in a `Dataflow` using `azureml.dataprep`.\n",
|
||||
"2. Pass the `Dataflow` to AutoML for a local run.\n",
|
||||
"3. Pass the `Dataflow` to AutoML for a remote run."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Diagnostics\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Opt-in diagnostics for better experience, quality, and security of future releases."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.telemetry import set_diagnostics_collection\n",
|
||||
"set_diagnostics_collection(send_diagnostics = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create an Experiment\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"As part of the setup you have already created an Azure ML `Workspace` object. For AutoML you will need to create an `Experiment` object, which is a named object in a `Workspace` used to run experiments."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import logging\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.experiment import Experiment\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.workspace import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.dataprep as dprep\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl import AutoMLConfig"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for experiment\n",
|
||||
"experiment_name = 'automl-dataprep-local'\n",
|
||||
"# project folder\n",
|
||||
"project_folder = './sample_projects/automl-dataprep-local'\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"experiment = Experiment(ws, experiment_name)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"output = {}\n",
|
||||
"output['SDK version'] = azureml.core.VERSION\n",
|
||||
"output['Subscription ID'] = ws.subscription_id\n",
|
||||
"output['Workspace Name'] = ws.name\n",
|
||||
"output['Resource Group'] = ws.resource_group\n",
|
||||
"output['Location'] = ws.location\n",
|
||||
"output['Project Directory'] = project_folder\n",
|
||||
"output['Experiment Name'] = experiment.name\n",
|
||||
"pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', -1)\n",
|
||||
"pd.DataFrame(data = output, index = ['']).T"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Loading Data using DataPrep"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# You can use `auto_read_file` which intelligently figures out delimiters and datatypes of a file.\n",
|
||||
"# The data referenced here was pulled from `sklearn.datasets.load_digits()`.\n",
|
||||
"simple_example_data_root = 'https://dprepdata.blob.core.windows.net/automl-notebook-data/'\n",
|
||||
"X = dprep.auto_read_file(simple_example_data_root + 'X.csv').skip(1) # Remove the header row.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# You can also use `read_csv` and `to_*` transformations to read (with overridable delimiter)\n",
|
||||
"# and convert column types manually.\n",
|
||||
"# Here we read a comma delimited file and convert all columns to integers.\n",
|
||||
"y = dprep.read_csv(simple_example_data_root + 'y.csv').to_long(dprep.ColumnSelector(term='.*', use_regex = True))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Review the Data Preparation Result\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"You can peek the result of a Dataflow at any range using `skip(i)` and `head(j)`. Doing so evaluates only `j` records for all the steps in the Dataflow, which makes it fast even against large datasets."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"X.skip(1).head(5)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Configure AutoML\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This creates a general AutoML settings object applicable for both local and remote runs."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_settings = {\n",
|
||||
" \"iteration_timeout_minutes\" : 10,\n",
|
||||
" \"iterations\" : 2,\n",
|
||||
" \"primary_metric\" : 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" \"preprocess\" : False,\n",
|
||||
" \"verbosity\" : logging.INFO,\n",
|
||||
" \"n_cross_validations\": 3\n",
|
||||
"}"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Local Run"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Pass Data with `Dataflow` Objects\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The `Dataflow` objects captured above can be passed to the `submit` method for a local run. AutoML will retrieve the results from the `Dataflow` for model training."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_config = AutoMLConfig(task = 'classification',\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'automl_errors.log',\n",
|
||||
" X = X,\n",
|
||||
" y = y,\n",
|
||||
" **automl_settings)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"local_run = experiment.submit(automl_config, show_output = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Explore the Results"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Widget for Monitoring Runs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The widget will first report a \"loading\" status while running the first iteration. After completing the first iteration, an auto-updating graph and table will be shown. The widget will refresh once per minute, so you should see the graph update as child runs complete.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Note:** The widget displays a link at the bottom. Use this link to open a web interface to explore the individual run details."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(local_run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Retrieve All Child Runs\n",
|
||||
"You can also use SDK methods to fetch all the child runs and see individual metrics that we log."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"children = list(local_run.get_children())\n",
|
||||
"metricslist = {}\n",
|
||||
"for run in children:\n",
|
||||
" properties = run.get_properties()\n",
|
||||
" metrics = {k: v for k, v in run.get_metrics().items() if isinstance(v, float)}\n",
|
||||
" metricslist[int(properties['iteration'])] = metrics\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"rundata = pd.DataFrame(metricslist).sort_index(1)\n",
|
||||
"rundata"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Retrieve the Best Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Below we select the best pipeline from our iterations. The `get_output` method returns the best run and the fitted model. Overloads on `get_output` allow you to retrieve the best run and fitted model for *any* logged metric or for a particular *iteration*."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output()\n",
|
||||
"print(best_run)\n",
|
||||
"print(fitted_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Best Model Based on Any Other Metric\n",
|
||||
"Show the run and the model that has the smallest `log_loss` value:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"lookup_metric = \"log_loss\"\n",
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output(metric = lookup_metric)\n",
|
||||
"print(best_run)\n",
|
||||
"print(fitted_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Model from a Specific Iteration\n",
|
||||
"Show the run and the model from the first iteration:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"iteration = 0\n",
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output(iteration = iteration)\n",
|
||||
"print(best_run)\n",
|
||||
"print(fitted_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Test the Best Fitted Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Load Test Data"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from sklearn import datasets\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"digits = datasets.load_digits()\n",
|
||||
"X_test = digits.data[:10, :]\n",
|
||||
"y_test = digits.target[:10]\n",
|
||||
"images = digits.images[:10]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Testing Our Best Fitted Model\n",
|
||||
"We will try to predict 2 digits and see how our model works."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#Randomly select digits and test\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib import pyplot as plt\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow\n",
|
||||
"import random\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for index in np.random.choice(len(y_test), 2, replace = False):\n",
|
||||
" print(index)\n",
|
||||
" predicted = fitted_model.predict(X_test[index:index + 1])[0]\n",
|
||||
" label = y_test[index]\n",
|
||||
" title = \"Label value = %d Predicted value = %d \" % (label, predicted)\n",
|
||||
" fig = plt.figure(1, figsize=(3,3))\n",
|
||||
" ax1 = fig.add_axes((0,0,.8,.8))\n",
|
||||
" ax1.set_title(title)\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(images[index], cmap = plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation = 'nearest')\n",
|
||||
" plt.show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Appendix"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Capture the `Dataflow` Objects for Later Use in AutoML\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"`Dataflow` objects are immutable and are composed of a list of data preparation steps. A `Dataflow` object can be branched at any point for further usage."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# sklearn.digits.data + target\n",
|
||||
"digits_complete = dprep.auto_read_file('https://dprepdata.blob.core.windows.net/automl-notebook-data/digits-complete.csv')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"`digits_complete` (sourced from `sklearn.datasets.load_digits()`) is forked into `dflow_X` to capture all the feature columns and `dflow_y` to capture the label column."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"digits_complete.to_pandas_dataframe().shape\n",
|
||||
"labels_column = 'Column64'\n",
|
||||
"dflow_X = digits_complete.drop_columns(columns = [labels_column])\n",
|
||||
"dflow_y = digits_complete.keep_columns(columns = [labels_column])"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "savitam"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.6",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.5"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
495
automl/13b.auto-ml-dataprep-remote-execution.ipynb
Normal file
495
automl/13b.auto-ml-dataprep-remote-execution.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,495 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# AutoML 13: Prepare Data using `azureml.dataprep` for Remote Execution (DSVM)\n",
|
||||
"In this example we showcase how you can use the `azureml.dataprep` SDK to load and prepare data for AutoML. `azureml.dataprep` can also be used standalone; full documentation can be found [here](https://github.com/Microsoft/PendletonDocs).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you have executed the [setup](00.configuration.ipynb) before running this notebook.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this notebook you will learn how to:\n",
|
||||
"1. Define data loading and preparation steps in a `Dataflow` using `azureml.dataprep`.\n",
|
||||
"2. Pass the `Dataflow` to AutoML for a local run.\n",
|
||||
"3. Pass the `Dataflow` to AutoML for a remote run."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Diagnostics\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Opt-in diagnostics for better experience, quality, and security of future releases."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.telemetry import set_diagnostics_collection\n",
|
||||
"set_diagnostics_collection(send_diagnostics = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create an Experiment\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"As part of the setup you have already created an Azure ML `Workspace` object. For AutoML you will need to create an `Experiment` object, which is a named object in a `Workspace` used to run experiments."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import logging\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"import time\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import DsvmCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.experiment import Experiment\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.workspace import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.dataprep as dprep\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl import AutoMLConfig"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for experiment\n",
|
||||
"experiment_name = 'automl-dataprep-remote-dsvm'\n",
|
||||
"# project folder\n",
|
||||
"project_folder = './sample_projects/automl-dataprep-remote-dsvm'\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"experiment = Experiment(ws, experiment_name)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"output = {}\n",
|
||||
"output['SDK version'] = azureml.core.VERSION\n",
|
||||
"output['Subscription ID'] = ws.subscription_id\n",
|
||||
"output['Workspace Name'] = ws.name\n",
|
||||
"output['Resource Group'] = ws.resource_group\n",
|
||||
"output['Location'] = ws.location\n",
|
||||
"output['Project Directory'] = project_folder\n",
|
||||
"output['Experiment Name'] = experiment.name\n",
|
||||
"pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', -1)\n",
|
||||
"pd.DataFrame(data = output, index = ['']).T"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Loading Data using DataPrep"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# You can use `auto_read_file` which intelligently figures out delimiters and datatypes of a file.\n",
|
||||
"# The data referenced here was pulled from `sklearn.datasets.load_digits()`.\n",
|
||||
"simple_example_data_root = 'https://dprepdata.blob.core.windows.net/automl-notebook-data/'\n",
|
||||
"X = dprep.auto_read_file(simple_example_data_root + 'X.csv').skip(1) # Remove the header row.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# You can also use `read_csv` and `to_*` transformations to read (with overridable delimiter)\n",
|
||||
"# and convert column types manually.\n",
|
||||
"# Here we read a comma delimited file and convert all columns to integers.\n",
|
||||
"y = dprep.read_csv(simple_example_data_root + 'y.csv').to_long(dprep.ColumnSelector(term='.*', use_regex = True))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Review the Data Preparation Result\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"You can peek the result of a Dataflow at any range using `skip(i)` and `head(j)`. Doing so evaluates only `j` records for all the steps in the Dataflow, which makes it fast even against large datasets."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"X.skip(1).head(5)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Configure AutoML\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This creates a general AutoML settings object applicable for both local and remote runs."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_settings = {\n",
|
||||
" \"iteration_timeout_minutes\" : 10,\n",
|
||||
" \"iterations\" : 2,\n",
|
||||
" \"primary_metric\" : 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" \"preprocess\" : False,\n",
|
||||
" \"verbosity\" : logging.INFO,\n",
|
||||
" \"n_cross_validations\": 3\n",
|
||||
"}"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Remote Run"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Create or Attach a Remote Linux DSVM"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"dsvm_name = 'mydsvmd'\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" while ws.compute_targets[dsvm_name].provisioning_state == 'Creating':\n",
|
||||
" time.sleep(1)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute = DsvmCompute(ws, dsvm_name)\n",
|
||||
" print('Found existing DVSM.')\n",
|
||||
"except:\n",
|
||||
" print('Creating a new DSVM.')\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_config = DsvmCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size = \"Standard_D2_v2\")\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute = DsvmCompute.create(ws, name = dsvm_name, provisioning_configuration = dsvm_config)\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute.wait_for_completion(show_output = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.runconfig import RunConfiguration\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"conda_run_config = RunConfiguration(framework=\"python\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"conda_run_config.target = dsvm_compute\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"cd = CondaDependencies.create(pip_packages=['azureml-sdk[automl]'], conda_packages=['numpy'])\n",
|
||||
"conda_run_config.environment.python.conda_dependencies = cd"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Pass Data with `Dataflow` Objects\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The `Dataflow` objects captured above can also be passed to the `submit` method for a remote run. AutoML will serialize the `Dataflow` object and send it to the remote compute target. The `Dataflow` will not be evaluated locally."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_config = AutoMLConfig(task = 'classification',\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'automl_errors.log',\n",
|
||||
" path = project_folder,\n",
|
||||
" run_configuration=conda_run_config,\n",
|
||||
" X = X,\n",
|
||||
" y = y,\n",
|
||||
" **automl_settings)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"remote_run = experiment.submit(automl_config, show_output = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Explore the Results"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Widget for Monitoring Runs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The widget will first report a \"loading\" status while running the first iteration. After completing the first iteration, an auto-updating graph and table will be shown. The widget will refresh once per minute, so you should see the graph update as child runs complete.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Note:** The widget displays a link at the bottom. Use this link to open a web interface to explore the individual run details."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(remote_run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Retrieve All Child Runs\n",
|
||||
"You can also use SDK methods to fetch all the child runs and see individual metrics that we log."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"children = list(remote_run.get_children())\n",
|
||||
"metricslist = {}\n",
|
||||
"for run in children:\n",
|
||||
" properties = run.get_properties()\n",
|
||||
" metrics = {k: v for k, v in run.get_metrics().items() if isinstance(v, float)}\n",
|
||||
" metricslist[int(properties['iteration'])] = metrics\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"rundata = pd.DataFrame(metricslist).sort_index(1)\n",
|
||||
"rundata"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Retrieve the Best Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Below we select the best pipeline from our iterations. The `get_output` method returns the best run and the fitted model. Overloads on `get_output` allow you to retrieve the best run and fitted model for *any* logged metric or for a particular *iteration*."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = remote_run.get_output()\n",
|
||||
"print(best_run)\n",
|
||||
"print(fitted_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Best Model Based on Any Other Metric\n",
|
||||
"Show the run and the model that has the smallest `log_loss` value:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"lookup_metric = \"log_loss\"\n",
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = remote_run.get_output(metric = lookup_metric)\n",
|
||||
"print(best_run)\n",
|
||||
"print(fitted_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Model from a Specific Iteration\n",
|
||||
"Show the run and the model from the first iteration:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"iteration = 0\n",
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = remote_run.get_output(iteration = iteration)\n",
|
||||
"print(best_run)\n",
|
||||
"print(fitted_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Test the Best Fitted Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Load Test Data"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from sklearn import datasets\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"digits = datasets.load_digits()\n",
|
||||
"X_test = digits.data[:10, :]\n",
|
||||
"y_test = digits.target[:10]\n",
|
||||
"images = digits.images[:10]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Testing Our Best Fitted Model\n",
|
||||
"We will try to predict 2 digits and see how our model works."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#Randomly select digits and test\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib import pyplot as plt\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow\n",
|
||||
"import random\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for index in np.random.choice(len(y_test), 2, replace = False):\n",
|
||||
" print(index)\n",
|
||||
" predicted = fitted_model.predict(X_test[index:index + 1])[0]\n",
|
||||
" label = y_test[index]\n",
|
||||
" title = \"Label value = %d Predicted value = %d \" % (label, predicted)\n",
|
||||
" fig = plt.figure(1, figsize=(3,3))\n",
|
||||
" ax1 = fig.add_axes((0,0,.8,.8))\n",
|
||||
" ax1.set_title(title)\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(images[index], cmap = plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation = 'nearest')\n",
|
||||
" plt.show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Appendix"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Capture the `Dataflow` Objects for Later Use in AutoML\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"`Dataflow` objects are immutable and are composed of a list of data preparation steps. A `Dataflow` object can be branched at any point for further usage."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# sklearn.digits.data + target\n",
|
||||
"digits_complete = dprep.auto_read_file('https://dprepdata.blob.core.windows.net/automl-notebook-data/digits-complete.csv')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"`digits_complete` (sourced from `sklearn.datasets.load_digits()`) is forked into `dflow_X` to capture all the feature columns and `dflow_y` to capture the label column."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"digits_complete.to_pandas_dataframe().shape\n",
|
||||
"labels_column = 'Column64'\n",
|
||||
"dflow_X = digits_complete.drop_columns(columns = [labels_column])\n",
|
||||
"dflow_y = digits_complete.keep_columns(columns = [labels_column])"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "savitam"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.6",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.5"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
374
automl/14.auto-ml-model-explanation.ipynb
Normal file
374
automl/14.auto-ml-model-explanation.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,374 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# AutoML 14: Explain classification model and visualize the explanation\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this example we use the sklearn's [iris dataset](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.datasets.load_iris.html) to showcase how you can use the AutoML Classifier for a simple classification problem.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you have executed the [00.configuration](00.configuration.ipynb) before running this notebook.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this notebook you would see\n",
|
||||
"1. Creating an Experiment in an existing Workspace\n",
|
||||
"2. Instantiating AutoMLConfig\n",
|
||||
"3. Training the Model using local compute and explain the model\n",
|
||||
"4. Visualization model's feature importance in widget\n",
|
||||
"5. Explore best model's explanation\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Install AzureML Explainer SDK "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"!pip install azureml_sdk[explain]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create Experiment\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"As part of the setup you have already created a <b>Workspace</b>. For AutoML you would need to create an <b>Experiment</b>. An <b>Experiment</b> is a named object in a <b>Workspace</b>, which is used to run experiments."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import logging\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"import random\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.experiment import Experiment\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.workspace import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl import AutoMLConfig\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl.run import AutoMLRun"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for experiment\n",
|
||||
"experiment_name = 'automl-local-classification'\n",
|
||||
"# project folder\n",
|
||||
"project_folder = './sample_projects/automl-local-classification-model-explanation'\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"experiment=Experiment(ws, experiment_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"output = {}\n",
|
||||
"output['SDK version'] = azureml.core.VERSION\n",
|
||||
"output['Subscription ID'] = ws.subscription_id\n",
|
||||
"output['Workspace Name'] = ws.name\n",
|
||||
"output['Resource Group'] = ws.resource_group\n",
|
||||
"output['Location'] = ws.location\n",
|
||||
"output['Project Directory'] = project_folder\n",
|
||||
"output['Experiment Name'] = experiment.name\n",
|
||||
"pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', -1)\n",
|
||||
"pd.DataFrame(data = output, index = ['']).T"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Diagnostics\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Opt-in diagnostics for better experience, quality, and security of future releases"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.telemetry import set_diagnostics_collection\n",
|
||||
"set_diagnostics_collection(send_diagnostics=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Load Iris Data Set"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from sklearn import datasets\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"iris = datasets.load_iris()\n",
|
||||
"y = iris.target\n",
|
||||
"X = iris.data\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"features = iris.feature_names\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n",
|
||||
"X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,\n",
|
||||
" y,\n",
|
||||
" test_size=0.1,\n",
|
||||
" random_state=100,\n",
|
||||
" stratify=y)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"X_train = pd.DataFrame(X_train, columns=features)\n",
|
||||
"X_test = pd.DataFrame(X_test, columns=features)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Instantiate Auto ML Config\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Instantiate a AutoMLConfig object. This defines the settings and data used to run the experiment.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"|Property|Description|\n",
|
||||
"|-|-|\n",
|
||||
"|**task**|classification or regression|\n",
|
||||
"|**primary_metric**|This is the metric that you want to optimize.<br> Classification supports the following primary metrics <br><i>accuracy</i><br><i>AUC_weighted</i><br><i>balanced_accuracy</i><br><i>average_precision_score_weighted</i><br><i>precision_score_weighted</i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**max_time_sec**|Time limit in minutes for each iterations|\n",
|
||||
"|**iterations**|Number of iterations. In each iteration Auto ML trains the data with a specific pipeline|\n",
|
||||
"|**X**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features]|\n",
|
||||
"|**y**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, ], [n_samples, n_classes]<br>Multi-class targets. An indicator matrix turns on multilabel classification. This should be an array of integers. |\n",
|
||||
"|**X_valid**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features]|\n",
|
||||
"|**y_valid**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, ], [n_samples, n_classes]|\n",
|
||||
"|**model_explainability**|Indicate to explain each trained pipeline or not |\n",
|
||||
"|**path**|Relative path to the project folder. AutoML stores configuration files for the experiment under this folder. You can specify a new empty folder. |"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_config = AutoMLConfig(task = 'classification',\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'automl_errors.log',\n",
|
||||
" primary_metric = 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" max_time_sec = 12000,\n",
|
||||
" iterations = 10,\n",
|
||||
" verbosity = logging.INFO,\n",
|
||||
" X = X_train, \n",
|
||||
" y = y_train,\n",
|
||||
" X_valid = X_test,\n",
|
||||
" y_valid = y_test,\n",
|
||||
" model_explainability=True,\n",
|
||||
" path=project_folder)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Training the Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"You can call the submit method on the experiment object and pass the run configuration. For Local runs the execution is synchronous. Depending on the data and number of iterations this can run for while.\n",
|
||||
"You will see the currently running iterations printing to the console."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"local_run = experiment.submit(automl_config, show_output=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Exploring the results"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Widget for monitoring runs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The widget will sit on \"loading\" until the first iteration completed, then you will see an auto-updating graph and table show up. It refreshed once per minute, so you should see the graph update as child runs complete.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"NOTE: The widget displays a link at the bottom. This links to a web-ui to explore the individual run details."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(local_run).show() "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"child_run = next(local_run.get_children())\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(child_run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Retrieve the Best Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Below we select the best pipeline from our iterations. The *get_output* method on automl_classifier returns the best run and the fitted model for the last *fit* invocation. There are overloads on *get_output* that allow you to retrieve the best run and fitted model for *any* logged metric or a particular *iteration*."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output()\n",
|
||||
"print(best_run)\n",
|
||||
"print(fitted_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Best Model 's explanation\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Retrieve the explanation from the best_run. And explanation information includes:\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"1.\tshap_values: The explanation information generated by shap lib\n",
|
||||
"2.\texpected_values: The expected value of the model applied to set of X_train data.\n",
|
||||
"3.\toverall_summary: The model level feature importance values sorted in descending order\n",
|
||||
"4.\toverall_imp: The feature names sorted in the same order as in overall_summary\n",
|
||||
"5.\tper_class_summary: The class level feature importance values sorted in descending order. Only available for the classification case\n",
|
||||
"6.\tper_class_imp: The feature names sorted in the same order as in per_class_summary. Only available for the classification case"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl.automlexplainer import retrieve_model_explanation\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"shap_values, expected_values, overall_summary, overall_imp, per_class_summary, per_class_imp = \\\n",
|
||||
" retrieve_model_explanation(best_run)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"print(overall_summary)\n",
|
||||
"print(overall_imp)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"print(per_class_summary)\n",
|
||||
"print(per_class_imp)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Beside retrieve the existed model explanation information, explain the model with different train/test data"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl.automlexplainer import explain_model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"shap_values, expected_values, overall_summary, overall_imp, per_class_summary, per_class_imp = \\\n",
|
||||
" explain_model(fitted_model, X_train, X_test)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"print(overall_summary)\n",
|
||||
"print(overall_imp)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "xif"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.6",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
423
automl/15a.auto-ml-classification-ensemble.ipynb
Normal file
423
automl/15a.auto-ml-classification-ensemble.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,423 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# AutoML 15a: Classification with ensembling on local compute\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this example we use the scikit-learn's [digit dataset](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.datasets.load_digits.html) to showcase how you can use AutoML for a simple classification problem.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you have executed the [00.configuration](00.configuration.ipynb) before running this notebook.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this notebook you will learn how to:\n",
|
||||
"1. Create an `Experiment` in an existing `Workspace`.\n",
|
||||
"2. Configure AutoML using `AutoMLConfig` which enables an extra ensembling iteration.\n",
|
||||
"3. Train the model using local compute.\n",
|
||||
"4. Explore the results.\n",
|
||||
"5. Test the best fitted model.\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create an Experiment\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"As part of the setup you have already created an Azure ML `Workspace` object. For AutoML you will need to create an `Experiment` object, which is a named object in a `Workspace` used to run experiments."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import logging\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"import random\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib import pyplot as plt\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn import datasets\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.experiment import Experiment\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.workspace import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl import AutoMLConfig\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl.run import AutoMLRun"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Choose a name for the experiment and specify the project folder.\n",
|
||||
"experiment_name = 'automl-local-classification'\n",
|
||||
"project_folder = './sample_projects/automl-local-classification'\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"experiment = Experiment(ws, experiment_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"output = {}\n",
|
||||
"output['SDK version'] = azureml.core.VERSION\n",
|
||||
"output['Subscription ID'] = ws.subscription_id\n",
|
||||
"output['Workspace Name'] = ws.name\n",
|
||||
"output['Resource Group'] = ws.resource_group\n",
|
||||
"output['Location'] = ws.location\n",
|
||||
"output['Project Directory'] = project_folder\n",
|
||||
"output['Experiment Name'] = experiment.name\n",
|
||||
"pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', -1)\n",
|
||||
"pd.DataFrame(data = output, index = ['']).T"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Diagnostics\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Opt-in diagnostics for better experience, quality, and security of future releases."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.telemetry import set_diagnostics_collection\n",
|
||||
"set_diagnostics_collection(send_diagnostics = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Load Training Data"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from sklearn import datasets\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"digits = datasets.load_digits()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Exclude the first 50 rows from training so that they can be used for test.\n",
|
||||
"X_train = digits.data[150:,:]\n",
|
||||
"y_train = digits.target[150:]\n",
|
||||
"X_valid = digits.data[50:150]\n",
|
||||
"y_valid = digits.target[50:150]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Configure AutoML\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Instantiate an `AutoMLConfig` object to specify the settings and data used to run the experiment.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"|Property|Description|\n",
|
||||
"|-|-|\n",
|
||||
"|**task**|classification or regression|\n",
|
||||
"|**primary_metric**|This is the metric that you want to optimize. Classification supports the following primary metrics: <br><i>accuracy</i><br><i>AUC_weighted</i><br><i>balanced_accuracy</i><br><i>average_precision_score_weighted</i><br><i>precision_score_weighted</i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**iteration_timeout_minutes**|Time limit in minutes for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iterations**|Number of iterations. In each iteration AutoML trains a specific pipeline with the data.|\n",
|
||||
"|**n_cross_validations**|Number of cross validation splits.|\n",
|
||||
"|**X**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features]|\n",
|
||||
"|**y**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, ], [n_samples, n_classes]<br>Multi-class targets. An indicator matrix turns on multilabel classification. This should be an array of integers.|\n",
|
||||
"|**X_valid**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features]|\n",
|
||||
"|**y_valid**|(sparse) array-like, shape = [n_samples, ], [n_samples, n_classes]<br>Multi-class targets. An indicator matrix turns on multilabel classification. This should be an array of integers.|\n",
|
||||
"|**enable_ensembling**|Flag to enable an ensembling iteration after all the other iterations complete.|\n",
|
||||
"|**ensemble_iterations**|Number of iterations during which we choose a fitted pipeline to be part of the final ensemble.|\n",
|
||||
"|**path**|Relative path to the project folder. AutoML stores configuration files for the experiment under this folder. You can specify a new empty folder.|"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_config = AutoMLConfig(task = 'classification',\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'classification.log',\n",
|
||||
" primary_metric = 'AUC_weighted',\n",
|
||||
" iteration_timeout_minutes = 60,\n",
|
||||
" iterations = 10,\n",
|
||||
" verbosity = logging.INFO,\n",
|
||||
" X = X_train, \n",
|
||||
" y = y_train,\n",
|
||||
" X_valid = X_valid,\n",
|
||||
" y_valid = y_valid,\n",
|
||||
" enable_ensembling = True,\n",
|
||||
" ensemble_iterations = 5,\n",
|
||||
" path = project_folder)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Train the Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Call the `submit` method on the experiment object and pass the run configuration. Execution of local runs is synchronous. Depending on the data and the number of iterations this can run for a while.\n",
|
||||
"In this example, we specify `show_output = True` to print currently running iterations to the console."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"local_run = experiment.submit(automl_config, show_output = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"local_run"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Optionally, you can continue an interrupted local run by calling `continue_experiment` without the `iterations` parameter, or run more iterations for a completed run by specifying the `iterations` parameter:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"local_run = local_run.continue_experiment(X = X_train, \n",
|
||||
" y = y_train,\n",
|
||||
" X_valid = X_valid,\n",
|
||||
" y_valid = y_valid,\n",
|
||||
" show_output = True,\n",
|
||||
" iterations = 5)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"local_run"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Explore the Results"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Widget for Monitoring Runs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The widget will first report a \"loading\" status while running the first iteration. After completing the first iteration, an auto-updating graph and table will be shown. The widget will refresh once per minute, so you should see the graph update as child runs complete.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Note:** The widget displays a link at the bottom. Use this link to open a web interface to explore the individual run details."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(local_run).show() "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Retrieve All Child Runs\n",
|
||||
"You can also use SDK methods to fetch all the child runs and see individual metrics that we log."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"children = list(local_run.get_children())\n",
|
||||
"metricslist = {}\n",
|
||||
"for run in children:\n",
|
||||
" properties = run.get_properties()\n",
|
||||
" metrics = {k: v for k, v in run.get_metrics().items() if isinstance(v, float)}\n",
|
||||
" metricslist[int(properties['iteration'])] = metrics\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"rundata = pd.DataFrame(metricslist).sort_index(1)\n",
|
||||
"rundata"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Retrieve the Best Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Below we select the best pipeline from our iterations. The `get_output` method on `automl_classifier` returns the best run and the fitted model for the last invocation. Overloads on `get_output` allow you to retrieve the best run and fitted model for *any* logged metric or for a particular *iteration*."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output()\n",
|
||||
"print(best_run)\n",
|
||||
"print(fitted_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Best Model Based on Any Other Metric\n",
|
||||
"Show the run and the model that has the smallest `log_loss` value:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"lookup_metric = \"log_loss\"\n",
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output(metric = lookup_metric)\n",
|
||||
"print(best_run)\n",
|
||||
"print(fitted_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Model from a Specific Iteration\n",
|
||||
"Show the run and the model from the third iteration:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"iteration = 3\n",
|
||||
"third_run, third_model = local_run.get_output(iteration = iteration)\n",
|
||||
"print(third_run)\n",
|
||||
"print(third_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Test the Best Fitted Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Load Test Data"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"digits = datasets.load_digits()\n",
|
||||
"X_test = digits.data[:10, :]\n",
|
||||
"y_test = digits.target[:10]\n",
|
||||
"images = digits.images[:10]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Testing Our Best Pipeline\n",
|
||||
"We will try to predict 2 digits and see how our model works."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Randomly select digits and test.\n",
|
||||
"for index in np.random.choice(len(y_test), 2, replace = False):\n",
|
||||
" print(index)\n",
|
||||
" predicted = fitted_model.predict(X_test[index:index + 1])[0]\n",
|
||||
" label = y_test[index]\n",
|
||||
" title = \"Label value = %d Predicted value = %d \" % (label, predicted)\n",
|
||||
" fig = plt.figure(1, figsize = (3,3))\n",
|
||||
" ax1 = fig.add_axes((0,0,.8,.8))\n",
|
||||
" ax1.set_title(title)\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(images[index], cmap = plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation = 'nearest')\n",
|
||||
" plt.show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "ratanase"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python [default]",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
449
automl/15b.auto-ml-regression-ensemble.ipynb
Normal file
449
automl/15b.auto-ml-regression-ensemble.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,449 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# AutoML 15b: Regression with ensembling on remote compute\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this example we use the scikit-learn's [diabetes dataset](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.datasets.load_diabetes.html) to showcase how you can use AutoML for a simple regression problem.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you have executed the [00.configuration](00.configuration.ipynb) before running this notebook.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this notebook you will learn how to:\n",
|
||||
"1. Create an `Experiment` in an existing `Workspace`.\n",
|
||||
"2. Configure AutoML using `AutoMLConfig`which enables an extra ensembling iteration.\n",
|
||||
"3. Train the model using remote compute.\n",
|
||||
"4. Explore the results.\n",
|
||||
"5. Test the best fitted model.\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create an Experiment\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"As part of the setup you have already created an Azure ML `Workspace` object. For AutoML you will need to create an `Experiment` object, which is a named object in a `Workspace` used to run experiments."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import logging\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"import random\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib import pyplot as plt\n",
|
||||
"from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn import datasets\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.experiment import Experiment\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.workspace import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl import AutoMLConfig\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.train.automl.run import AutoMLRun"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Choose a name for the experiment and specify the project folder.\n",
|
||||
"experiment_name = 'automl-local-regression'\n",
|
||||
"project_folder = './sample_projects/automl-local-regression'\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"experiment = Experiment(ws, experiment_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"output = {}\n",
|
||||
"output['SDK version'] = azureml.core.VERSION\n",
|
||||
"output['Subscription ID'] = ws.subscription_id\n",
|
||||
"output['Workspace Name'] = ws.name\n",
|
||||
"output['Resource Group'] = ws.resource_group\n",
|
||||
"output['Location'] = ws.location\n",
|
||||
"output['Project Directory'] = project_folder\n",
|
||||
"output['Experiment Name'] = experiment.name\n",
|
||||
"pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', -1)\n",
|
||||
"pd.DataFrame(data = output, index = ['']).T"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Diagnostics\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Opt-in diagnostics for better experience, quality, and security of future releases."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.telemetry import set_diagnostics_collection\n",
|
||||
"set_diagnostics_collection(send_diagnostics = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create a Remote Linux DSVM\n",
|
||||
"**Note:** If creation fails with a message about Marketplace purchase eligibilty, start creation of a DSVM through the [Azure portal](https://portal.azure.com), and select \"Want to create programmatically\" to enable programmatic creation. Once you've enabled this setting, you can exit the portal without actually creating the DSVM, and creation of the DSVM through the notebook should work."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import DsvmCompute\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"dsvm_name = 'mydsvm'\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute = DsvmCompute(ws, dsvm_name)\n",
|
||||
" print('Found an existing DSVM.')\n",
|
||||
"except:\n",
|
||||
" print('Creating a new DSVM.')\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_config = DsvmCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size = \"Standard_D2_v2\")\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute = DsvmCompute.create(ws, name = dsvm_name, provisioning_configuration = dsvm_config)\n",
|
||||
" dsvm_compute.wait_for_completion(show_output = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create Get Data File\n",
|
||||
"For remote executions you should author a `get_data.py` file containing a `get_data()` function. This file should be in the root directory of the project. You can encapsulate code to read data either from a blob storage or local disk in this file.\n",
|
||||
"In this example, the `get_data()` function returns data using scikit-learn's `diabetes` dataset."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"if not os.path.exists(project_folder):\n",
|
||||
" os.makedirs(project_folder)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%%writefile $project_folder/get_data.py\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Load the diabetes dataset, a well-known built-in small dataset that comes with scikit-learn.\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.datasets import load_diabetes\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def get_data():\n",
|
||||
" X, y = load_diabetes(return_X_y = True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" columns = ['age', 'gender', 'bmi', 'bp', 's1', 's2', 's3', 's4', 's5', 's6']\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" X_train, X_temp, y_train, y_temp = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 0)\n",
|
||||
" X_valid, X_test, y_valid, y_test = train_test_split(X_temp, y_temp, test_size = 0.5, random_state = 0)\n",
|
||||
" return { \"X\" : X_train, \"y\" : y_train, \"X_valid\": X_valid, \"y_valid\": y_valid }"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Configure AutoML\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Instantiate an `AutoMLConfig` object to specify the settings and data used to run the experiment.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"|Property|Description|\n",
|
||||
"|-|-|\n",
|
||||
"|**task**|classification or regression|\n",
|
||||
"|**primary_metric**|This is the metric that you want to optimize. Regression supports the following primary metrics: <br><i>spearman_correlation</i><br><i>normalized_root_mean_squared_error</i><br><i>r2_score</i><br><i>normalized_mean_absolute_error</i>|\n",
|
||||
"|**iteration_timeout_minutes**|Time limit in minutes for each iteration.|\n",
|
||||
"|**iterations**|Number of iterations. In each iteration AutoML trains a specific pipeline with the data.|\n",
|
||||
"|**enable_ensembling**|Flag to enable an ensembling iteration after all the other iterations complete.|\n",
|
||||
"|**ensemble_iterations**|Number of iterations during which we choose a fitted pipeline to be part of the final ensemble.|\n",
|
||||
"|**path**|Relative path to the project folder. AutoML stores configuration files for the experiment under this folder. You can specify a new empty folder.|"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"automl_config = AutoMLConfig(task = 'regression',\n",
|
||||
" iteration_timeout_minutes = 10,\n",
|
||||
" iterations = 20,\n",
|
||||
" primary_metric = 'spearman_correlation',\n",
|
||||
" debug_log = 'regression.log',\n",
|
||||
" verbosity = logging.INFO,\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = dsvm_compute,\n",
|
||||
" data_script = project_folder + \"/get_data.py\",\n",
|
||||
" enable_ensembling = True,\n",
|
||||
" ensemble_iterations = 5,\n",
|
||||
" path = project_folder)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Train the Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Call the `submit` method on the experiment object and pass the run configuration. Execution of local runs is synchronous. Depending on the data and the number of iterations this can run for a while.\n",
|
||||
"In this example, we specify `show_output = True` to print currently running iterations to the console."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"local_run = experiment.submit(automl_config, show_output = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"local_run"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Explore the Results"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Widget for Monitoring Runs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The widget will first report a \"loading\" status while running the first iteration. After completing the first iteration, an auto-updating graph and table will be shown. The widget will refresh once per minute, so you should see the graph update as child runs complete.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Note:** The widget displays a link at the bottom. Use this link to open a web interface to explore the individual run details."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(local_run).show() "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Retrieve All Child Runs\n",
|
||||
"You can also use SDK methods to fetch all the child runs and see individual metrics that we log."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"children = list(local_run.get_children())\n",
|
||||
"metricslist = {}\n",
|
||||
"for run in children:\n",
|
||||
" properties = run.get_properties()\n",
|
||||
" metrics = {k: v for k, v in run.get_metrics().items() if isinstance(v, float)}\n",
|
||||
" metricslist[int(properties['iteration'])] = metrics\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"rundata = pd.DataFrame(metricslist).sort_index(1)\n",
|
||||
"rundata"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Retrieve the Best Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Below we select the best pipeline from our iterations. The `get_output` method on `automl_classifier` returns the best run and the fitted model for the last invocation. Overloads on `get_output` allow you to retrieve the best run and fitted model for *any* logged metric or for a particular *iteration*."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output()\n",
|
||||
"print(best_run)\n",
|
||||
"print(fitted_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Best Model Based on Any Other Metric\n",
|
||||
"Show the run and the model that has the smallest `root_mean_squared_error` value."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"lookup_metric = \"root_mean_squared_error\"\n",
|
||||
"best_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output(metric = lookup_metric)\n",
|
||||
"print(best_run)\n",
|
||||
"print(fitted_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Test the Best Model (Ensemble)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Predict on training and test set, and calculate residual values."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from sklearn.datasets import load_diabetes\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"X, y = load_diabetes(return_X_y = True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"X_train, X_temp, y_train, y_temp = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 0)\n",
|
||||
"X_valid, X_test, y_valid, y_test = train_test_split(X_temp, y_temp, test_size = 0.5, random_state = 0)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"y_pred_train = fitted_model.predict(X_train)\n",
|
||||
"y_residual_train = y_train - y_pred_train\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"y_pred_test = fitted_model.predict(X_test)\n",
|
||||
"y_residual_test = y_test - y_pred_test"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%matplotlib inline\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn import datasets\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Set up a multi-plot chart.\n",
|
||||
"f, (a0, a1) = plt.subplots(1, 2, gridspec_kw = {'width_ratios':[1, 1], 'wspace':0, 'hspace': 0})\n",
|
||||
"f.suptitle('Regression Residual Values', fontsize = 18)\n",
|
||||
"f.set_figheight(6)\n",
|
||||
"f.set_figwidth(16)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Plot residual values of training set.\n",
|
||||
"a0.axis([0, 360, -200, 200])\n",
|
||||
"a0.plot(y_residual_train, 'bo', alpha = 0.5)\n",
|
||||
"a0.plot([-10,360],[0,0], 'r-', lw = 3)\n",
|
||||
"a0.text(16,170,'RMSE = {0:.2f}'.format(np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_train, y_pred_train))), fontsize = 12)\n",
|
||||
"a0.text(16,140,'R2 score = {0:.2f}'.format(r2_score(y_train, y_pred_train)), fontsize = 12)\n",
|
||||
"a0.set_xlabel('Training samples', fontsize = 12)\n",
|
||||
"a0.set_ylabel('Residual Values', fontsize = 12)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Plot a histogram.\n",
|
||||
"a0.hist(y_residual_train, orientation = 'horizontal', color = 'b', bins = 10, histtype = 'step');\n",
|
||||
"a0.hist(y_residual_train, orientation = 'horizontal', color = 'b', alpha = 0.2, bins = 10);\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Plot residual values of test set.\n",
|
||||
"a1.axis([0, 90, -200, 200])\n",
|
||||
"a1.plot(y_residual_test, 'bo', alpha = 0.5)\n",
|
||||
"a1.plot([-10,360],[0,0], 'r-', lw = 3)\n",
|
||||
"a1.text(5,170,'RMSE = {0:.2f}'.format(np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_test))), fontsize = 12)\n",
|
||||
"a1.text(5,140,'R2 score = {0:.2f}'.format(r2_score(y_test, y_pred_test)), fontsize = 12)\n",
|
||||
"a1.set_xlabel('Test samples', fontsize = 12)\n",
|
||||
"a1.set_yticklabels([])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Plot a histogram.\n",
|
||||
"a1.hist(y_residual_test, orientation = 'horizontal', color = 'b', bins = 10, histtype = 'step')\n",
|
||||
"a1.hist(y_residual_test, orientation = 'horizontal', color = 'b', alpha = 0.2, bins = 10)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"plt.show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "ratanase"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python [default]",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
172
automl/README.md
172
automl/README.md
@@ -1,24 +1,52 @@
|
||||
# Table of Contents
|
||||
1. [Auto ML Introduction](#introduction)
|
||||
2. [Running samples in a Local Conda environment](#localconda)
|
||||
3. [Auto ML SDK Sample Notebooks](#samples)
|
||||
4. [Documentation](#documentation)
|
||||
5. [Running using python command](#pythoncommand)
|
||||
6. [Troubleshooting](#troubleshooting)
|
||||
1. [Automated ML Introduction](#introduction)
|
||||
1. [Running samples in Azure Notebooks](#jupyter)
|
||||
1. [Running samples in a Local Conda environment](#localconda)
|
||||
1. [Automated ML SDK Sample Notebooks](#samples)
|
||||
1. [Documentation](#documentation)
|
||||
1. [Running using python command](#pythoncommand)
|
||||
1. [Troubleshooting](#troubleshooting)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="introduction"></a>
|
||||
# Automated ML introduction
|
||||
Automated machine learning (automated ML) builds high quality machine learning models for you by automating model and hyperparameter selection. Bring a labelled dataset that you want to build a model for, automated ML will give you a high quality machine learning model that you can use for predictions.
|
||||
|
||||
# Auto ML Introduction <a name="introduction"></a>
|
||||
AutoML builds high quality Machine Learning models for you by automating model and hyperparameter selection. Bring a labelled dataset that you want to build a model for, AutoML will give you a high quality machine learning model that you can use for predictions.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are new to Data Science, AutoML will help you get jumpstarted by simplifying machine learning model building. It abstracts you from needing to perform model selection, hyperparameter selection and in one step creates a high quality trained model for you to use.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are an experienced data scientist, AutoML will help increase your productivity by intelligently performing the model and hyperparameter selection for your training and generates high quality models much quicker than manually specifying several combinations of the parameters and running training jobs. AutoML provides visibility and access to all the training jobs and the performance characteristics of the models to help you further tune the pipeline if you desire.
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="jupyter"></a>
|
||||
## Running samples in Azure Notebooks - Jupyter based notebooks in the Azure cloud
|
||||
|
||||
# Running samples in a Local Conda environment <a name="localconda"></a>
|
||||
1. [](https://aka.ms/aml-clone-azure-notebooks)
|
||||
[Import sample notebooks ](https://aka.ms/aml-clone-azure-notebooks) into Azure Notebooks.
|
||||
1. Follow the instructions in the [../00.configuration](00.configuration.ipynb) notebook to create and connect to a workspace.
|
||||
1. Open one of the sample notebooks.
|
||||
|
||||
You can run these notebooks in Azure Notebooks without any extra installation. To run these notebook on your own notebook server, use these installation instructions.
|
||||
**Make sure the Azure Notebook kernel is set to `Python 3.6`** when you open a notebook.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
<a name="localconda"></a>
|
||||
## Running samples in a Local Conda environment
|
||||
|
||||
To run these notebook on your own notebook server, use these installation instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
The instructions below will install everything you need and then start a Jupyter notebook. To start your Jupyter notebook manually, use:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
conda activate azure_automl
|
||||
jupyter notebook
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or on Mac:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
source activate azure_automl
|
||||
jupyter notebook
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is best if you create a new conda environment locally to try this SDK, so it doesn't mess up with your existing Python environment.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Install mini-conda from [here](https://conda.io/miniconda.html), choose Python 3.7 or higher.
|
||||
- **Note**: if you already have conda installed, you can keep using it but it should be version 4.4.10 or later (as shown by: conda -V). If you have a previous version installed, you can update it using the command: conda update conda.
|
||||
@@ -29,7 +57,7 @@ There's no need to install mini-conda specifically.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Setup a new conda environment
|
||||
The **automl/automl_setup** script creates a new conda environment, installs the necessary packages, configures the widget and starts a jupyter notebook.
|
||||
It takes the conda environment name as an optional parameter. The default conda environment name is azure_automl. The exact command depends on the operating system. It can take about 30 minutes to execute.
|
||||
It takes the conda environment name as an optional parameter. The default conda environment name is azure_automl. The exact command depends on the operating system. It can take about 10 minutes to execute.
|
||||
## Windows
|
||||
Start a conda command windows, cd to the **automl** folder where the sample notebooks were extracted and then run:
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -48,19 +76,19 @@ bash automl_setup_mac.sh
|
||||
cd to the **automl** folder where the sample notebooks were extracted and then run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
automl_setup_linux.sh
|
||||
bash automl_setup_linux.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Running configuration.ipynb
|
||||
- Before running any samples you next need to run the configuration notebook. Click on 00.configuration.ipynb notebook
|
||||
- Please make sure you use the Python [conda env:azure_automl] kernel when running this notebook.
|
||||
- Execute the cells in the notebook to Register Machine Learning Services Resource Provider and create a workspace. (*instructions in notebook*)
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Running Samples
|
||||
- Please make sure you use the Python [conda env:azure_automl] kernel when trying the sample Notebooks.
|
||||
- Follow the instructions in the individual notebooks to explore various features in AutoML
|
||||
|
||||
# Auto ML SDK Sample Notebooks <a name="samples"></a>
|
||||
<a name="samples"></a>
|
||||
# Automated ML SDK Sample Notebooks
|
||||
- [00.configuration.ipynb](00.configuration.ipynb)
|
||||
- Register Machine Learning Services Resource Provider
|
||||
- Create new Azure ML Workspace
|
||||
@@ -87,7 +115,7 @@ automl_setup_linux.sh
|
||||
|
||||
- [03b.auto-ml-remote-batchai.ipynb](03b.auto-ml-remote-batchai.ipynb)
|
||||
- Dataset: scikit learn's [digit dataset](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.datasets.load_digits.html#sklearn.datasets.load_digits)
|
||||
- Example of using Auto ML for classification using a remote Batch AI compute for training
|
||||
- Example of using automated ML for classification using a remote Batch AI compute for training
|
||||
- Parallel execution of iterations
|
||||
- Async tracking of progress
|
||||
- Cancelling individual iterations or entire run
|
||||
@@ -106,7 +134,7 @@ automl_setup_linux.sh
|
||||
- Specify a target metrics to indicate stopping criteria
|
||||
- Handling Missing Data in the input
|
||||
|
||||
- [06.auto-ml-sparse-data-custom-cv-split.ipynb](06.auto-ml-sparse-data-custom-cv-split.ipynb)
|
||||
- [06.auto-ml-sparse-data-train-test-split.ipynb](06.auto-ml-sparse-data-train-test-split.ipynb)
|
||||
- Dataset: Scikit learn's [20newsgroup](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/datasets/twenty_newsgroups.html)
|
||||
- Handle sparse datasets
|
||||
- Specify custom train and validation set
|
||||
@@ -115,11 +143,11 @@ automl_setup_linux.sh
|
||||
- List all projects for the workspace
|
||||
- List all AutoML Runs for a given project
|
||||
- Get details for a AutoML Run. (Automl settings, run widget & all metrics)
|
||||
- Downlaod fitted pipeline for any iteration
|
||||
- Download fitted pipeline for any iteration
|
||||
|
||||
- [08.auto-ml-remote-execution-with-text-file-on-DSVM](08.auto-ml-remote-execution-with-text-file-on-DSVM.ipynb)
|
||||
- [08.auto-ml-remote-execution-with-DataStore.ipynb](08.auto-ml-remote-execution-with-DataStore.ipynb)
|
||||
- Dataset: scikit learn's [digit dataset](https://innovate.burningman.org/datasets-page/)
|
||||
- Download the data and store it in the DSVM to improve performance.
|
||||
- Download the data and store it in DataStore.
|
||||
|
||||
- [09.auto-ml-classification-with-deployment.ipynb](09.auto-ml-classification-with-deployment.ipynb)
|
||||
- Dataset: scikit learn's [digit dataset](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.datasets.load_digits.html#sklearn.datasets.load_digits)
|
||||
@@ -143,34 +171,76 @@ automl_setup_linux.sh
|
||||
- [13.auto-ml-dataprep.ipynb](13.auto-ml-dataprep.ipynb)
|
||||
- Using DataPrep for reading data
|
||||
|
||||
- [14a.auto-ml-classification-ensemble.ipynb](14a.auto-ml-classification-ensemble.ipynb)
|
||||
- Classification with ensembling
|
||||
- [14.auto-ml-model-explanation.ipynb](14.auto-ml-model-explanation.ipynb)
|
||||
- Dataset: sklearn's [iris dataset](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.datasets.load_iris.html)
|
||||
- Explaining the AutoML classification pipeline
|
||||
- Visualizing feature importance in widget
|
||||
|
||||
- [14b.auto-ml-regression-ensemble.ipynb](14b.auto-ml-regression-ensemble.ipynb)
|
||||
- Regression with ensembling
|
||||
- [15a.auto-ml-classification-ensemble.ipynb](15a.auto-ml-classification-ensemble.ipynb)
|
||||
- Dataset: scikit learn's [digit dataset](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.datasets.load_digits.html#sklearn.datasets.load_digits)
|
||||
- Enables an extra iteration for generating an Ensemble of models
|
||||
- Uses local compute for training
|
||||
|
||||
# Documentation <a name="documentation"></a>
|
||||
- [15b.auto-ml-regression-ensemble.ipynb](15b.auto-ml-regression-ensemble.ipynb)
|
||||
- Dataset: scikit learn's [diabetes dataset](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.datasets.load_diabetes.html)
|
||||
- Enables an extra iteration for generating an Ensemble of models
|
||||
- Uses remote Linux DSVM for training
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="documentation"></a>
|
||||
# Documentation
|
||||
## Table of Contents
|
||||
1. [Auto ML Settings ](#automlsettings)
|
||||
2. [Cross validation split options](#cvsplits)
|
||||
3. [Get Data Syntax](#getdata)
|
||||
4. [Data pre-processing and featurization](#preprocessing)
|
||||
1. [Automated ML Settings ](#automlsettings)
|
||||
1. [Cross validation split options](#cvsplits)
|
||||
1. [Get Data Syntax](#getdata)
|
||||
1. [Data pre-processing and featurization](#preprocessing)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="automlsettings"></a>
|
||||
## Automated ML Settings
|
||||
|
||||
## Auto ML Settings <a name="automlsettings"></a>
|
||||
|Property|Description|Default|
|
||||
|-|-|-|
|
||||
|**primary_metric**|This is the metric that you want to optimize.<br><br> Classification supports the following primary metrics <br><i>accuracy</i><br><i>AUC_weighted</i><br><i>balanced_accuracy</i><br><i>average_precision_score_weighted</i><br><i>precision_score_weighted</i><br><br> Regression supports the following primary metrics <br><i>spearman_correlation</i><br><i>normalized_root_mean_squared_error</i><br><i>r2_score</i><br><i>normalized_mean_absolute_error</i><br><i>normalized_root_mean_squared_log_error</i>| Classification: accuracy <br><br> Regression: spearman_correlation
|
||||
|**max_time_sec**|Time limit in seconds for each iteration|None|
|
||||
|**iteration_timeout_minutes**|Time limit in minutes for each iteration|None|
|
||||
|**iterations**|Number of iterations. In each iteration trains the data with a specific pipeline. To get the best result, use at least 100. |100|
|
||||
|**n_cross_validations**|Number of cross validation splits|None|
|
||||
|**validation_size**|Size of validation set as percentage of all training samples|None|
|
||||
|**concurrent_iterations**|Max number of iterations that would be executed in parallel|1|
|
||||
|**max_concurrent_iterations**|Max number of iterations that would be executed in parallel|1|
|
||||
|**preprocess**|*True/False* <br>Setting this to *True* enables preprocessing <br>on the input to handle missing data, and perform some common feature extraction<br>*Note: If input data is Sparse you cannot use preprocess=True*|False|
|
||||
|**max_cores_per_iteration**| Indicates how many cores on the compute target would be used to train a single pipeline.<br> You can set it to *-1* to use all cores|1|
|
||||
|**exit_score**|*double* value indicating the target for *primary_metric*. <br> Once the target is surpassed the run terminates|None|
|
||||
|**blacklist_algos**|*Array* of *strings* indicating pipelines to ignore for Auto ML.<br><br> Allowed values for **Classification**<br><i>LogisticRegression</i><br><i>SGDClassifierWrapper</i><br><i>NBWrapper</i><br><i>BernoulliNB</i><br><i>SVCWrapper</i><br><i>LinearSVMWrapper</i><br><i>KNeighborsClassifier</i><br><i>DecisionTreeClassifier</i><br><i>RandomForestClassifier</i><br><i>ExtraTreesClassifier</i><br><i>gradient boosting</i><br><i>LightGBMClassifier</i><br><br>Allowed values for **Regression**<br><i>ElasticNet</i><br><i>GradientBoostingRegressor</i><br><i>DecisionTreeRegressor</i><br><i>KNeighborsRegressor</i><br><i>LassoLars</i><br><i>SGDRegressor</i><br><i>RandomForestRegressor</i><br><i>ExtraTreesRegressor</i>|None|
|
||||
|**experiment_exit_score**|*double* value indicating the target for *primary_metric*. <br> Once the target is surpassed the run terminates|None|
|
||||
|**blacklist_models**|*Array* of *strings* indicating models to ignore for Auto ML from the list of models.|None|
|
||||
|**whilelist_models**|*Array* of *strings* use only models listed for Auto ML from the list of models..|None|
|
||||
<a name="cvsplits"></a>
|
||||
## List of models for white list/blacklist
|
||||
**Classification**
|
||||
<br><i>LogisticRegression</i>
|
||||
<br><i>SGD</i>
|
||||
<br><i>MultinomialNaiveBayes</i>
|
||||
<br><i>BernoulliNaiveBayes</i>
|
||||
<br><i>SVM</i>
|
||||
<br><i>LinearSVM</i>
|
||||
<br><i>KNN</i>
|
||||
<br><i>DecisionTree</i>
|
||||
<br><i>RandomForest</i>
|
||||
<br><i>ExtremeRandomTrees</i>
|
||||
<br><i>LightGBM</i>
|
||||
<br><i>GradientBoosting</i>
|
||||
<br><i>TensorFlowDNN</i>
|
||||
<br><i>TensorFlowLinearClassifier</i>
|
||||
<br><br>**Regression**
|
||||
<br><i>ElasticNet</i>
|
||||
<br><i>GradientBoosting</i>
|
||||
<br><i>DecisionTree</i>
|
||||
<br><i>KNN</i>
|
||||
<br><i>LassoLars</i>
|
||||
<br><i>SGD</i>
|
||||
<br><i>RandomForest</i>
|
||||
<br><i>ExtremeRandomTrees</i>
|
||||
<br><i>LightGBM</i>
|
||||
<br><i>TensorFlowLinearRegressor</i>
|
||||
<br><i>TensorFlowDNN</i>
|
||||
|
||||
## Cross validation split options <a name="cvsplits"></a>
|
||||
## Cross validation split options
|
||||
### K-Folds Cross Validation
|
||||
Use *n_cross_validations* setting to specify the number of cross validations. The training data set will be randomly split into *n_cross_validations* folds of equal size. During each cross validation round, one of the folds will be used for validation of the model trained on the remaining folds. This process repeats for *n_cross_validations* rounds until each fold is used once as validation set. Finally, the average scores accross all *n_cross_validations* rounds will be reported, and the corresponding model will be retrained on the whole training data set.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -180,7 +250,8 @@ Use *validation_size* to specify the percentage of the training data set that sh
|
||||
### Custom train and validation set
|
||||
You can specify seperate train and validation set either through the get_data() or directly to the fit method.
|
||||
|
||||
## get_data() syntax <a name="getdata"></a>
|
||||
<a name="getdata"></a>
|
||||
## get_data() syntax
|
||||
The *get_data()* function can be used to return a dictionary with these values:
|
||||
|
||||
|Key|Type|Dependency|Mutually Exclusive with|Description|
|
||||
@@ -196,21 +267,23 @@ The *get_data()* function can be used to return a dictionary with these values:
|
||||
|columns|Array of strings|data_train||*Optional* Whitelist of columns to use for features|
|
||||
|cv_splits_indices|Array of integers|data_train||*Optional* List of indexes to split the data for cross validation|
|
||||
|
||||
## Data pre-processing and featurization <a name="preprocessing"></a>
|
||||
If you use "preprocess=True", the following data preprocessing steps are performed automatically for you:
|
||||
### 1. Dropping high cardinality or no variance features
|
||||
<a name="preprocessing"></a>
|
||||
## Data pre-processing and featurization
|
||||
If you use `preprocess=True`, the following data preprocessing steps are performed automatically for you:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Dropping high cardinality or no variance features
|
||||
- Features with no useful information are dropped from training and validation sets. These include features with all values missing, same value across all rows or with extremely high cardinality (e.g., hashes, IDs or GUIDs).
|
||||
### 2. Missing value imputation
|
||||
2. Missing value imputation
|
||||
- For numerical features, missing values are imputed with average of values in the column.
|
||||
- For categorical features, missing values are imputed with most frequent value.
|
||||
### 3. Generating additional features
|
||||
3. Generating additional features
|
||||
- For DateTime features: Year, Month, Day, Day of week, Day of year, Quarter, Week of the year, Hour, Minute, Second.
|
||||
- For Text features: Term frequency based on bi-grams and tri-grams, Count vectorizer.
|
||||
### 4. Transformations and encodings
|
||||
4. Transformations and encodings
|
||||
- Numeric features with very few unique values are transformed into categorical features.
|
||||
- Depending on cardinality of categorical features label encoding or (hashing) one-hot encoding is performed.
|
||||
|
||||
# Running using python command <a name="pythoncommand"></a>
|
||||
<a name="pythoncommand"></a>
|
||||
# Running using python command
|
||||
Jupyter notebook provides a File / Download as / Python (.py) option for saving the notebook as a Python file.
|
||||
You can then run this file using the python command.
|
||||
However, on Windows the file needs to be modified before it can be run.
|
||||
@@ -220,13 +293,14 @@ The following condition must be added to the main code in the file:
|
||||
|
||||
The main code of the file must be indented so that it is under this condition.
|
||||
|
||||
# Troubleshooting <a name="troubleshooting"></a>
|
||||
<a name="troubleshooting"></a>
|
||||
# Troubleshooting
|
||||
## Iterations fail and the log contains "MemoryError"
|
||||
This can be caused by insufficient memory on the DSVM. AutoML loads all training data into memory. So, the available memory should be more than the training data size.
|
||||
If you are using a remote DSVM, memory is needed for each concurrent iteration. The concurrent_iterations setting specifies the maximum concurrent iterations. For example, if the training data size is 8Gb and concurrent_iterations is set to 10, the minimum memory required is at least 80Gb.
|
||||
To resolve this issue, allocate a DSVM with more memory or reduce the value specified for concurrent_iterations.
|
||||
If you are using a remote DSVM, memory is needed for each concurrent iteration. The max_concurrent_iterations setting specifies the maximum concurrent iterations. For example, if the training data size is 8Gb and max_concurrent_iterations is set to 10, the minimum memory required is at least 80Gb.
|
||||
To resolve this issue, allocate a DSVM with more memory or reduce the value specified for max_concurrent_iterations.
|
||||
|
||||
## Iterations show as "Not Responding" in the RunDetails widget.
|
||||
This can be caused by too many concurrent iterations for a remote DSVM. Each concurrent iteration usually takes 100% of a core when it is running. Some iterations can use multiple cores. So, the concurrent_iterations setting should always be less than the number of cores of the DSVM.
|
||||
To resolve this issue, try reducing the value specified for the concurrent_iterations setting.
|
||||
This can be caused by too many concurrent iterations for a remote DSVM. Each concurrent iteration usually takes 100% of a core when it is running. Some iterations can use multiple cores. So, the max_concurrent_iterations setting should always be less than the number of cores of the DSVM.
|
||||
To resolve this issue, try reducing the value specified for the max_concurrent_iterations setting.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,16 +4,28 @@ dependencies:
|
||||
# Currently Azure ML only supports 3.5.2 and later.
|
||||
- python=3.6
|
||||
- nb_conda
|
||||
- matplotlib
|
||||
- numpy>=1.11.0,<1.16.0
|
||||
- matplotlib==2.1.0
|
||||
- numpy>=1.11.0,<1.15.0
|
||||
- cython
|
||||
- urllib3<1.24
|
||||
- scipy>=0.19.0,<0.20.0
|
||||
- scikit-learn>=0.18.0,<=0.19.1
|
||||
- pandas>=0.22.0,<0.23.0
|
||||
|
||||
# Required for azuremlftk
|
||||
- dill
|
||||
- pyodbc
|
||||
- statsmodels
|
||||
- numexpr
|
||||
- keras
|
||||
- distributed>=1.21.5,<1.24
|
||||
|
||||
- pip:
|
||||
|
||||
# Required for azuremlftk
|
||||
- https://azuremlpackages.blob.core.windows.net/forecasting/azuremlftk-0.1.18313.5a1-py3-none-any.whl
|
||||
|
||||
# Required packages for AzureML execution, history, and data preparation.
|
||||
- --extra-index-url https://pypi.python.org/simple
|
||||
- azureml-sdk[automl]
|
||||
- azureml-train-widgets
|
||||
- azureml-sdk[automl,notebooks]
|
||||
- pandas_ml
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
31
automl/automl_env_mac.yml
Normal file
31
automl/automl_env_mac.yml
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
name: azure_automl
|
||||
dependencies:
|
||||
# The python interpreter version.
|
||||
# Currently Azure ML only supports 3.5.2 and later.
|
||||
- python=3.6
|
||||
- nb_conda
|
||||
- matplotlib==2.1.0
|
||||
- numpy>=1.15.3
|
||||
- cython
|
||||
- urllib3<1.24
|
||||
- scipy>=0.19.0,<0.20.0
|
||||
- scikit-learn>=0.18.0,<=0.19.1
|
||||
- pandas>=0.22.0,<0.23.0
|
||||
|
||||
# Required for azuremlftk
|
||||
- dill
|
||||
- pyodbc
|
||||
- statsmodels
|
||||
- numexpr
|
||||
- keras
|
||||
- distributed>=1.21.5,<1.24
|
||||
|
||||
- pip:
|
||||
|
||||
# Required for azuremlftk
|
||||
- https://azuremlpackages.blob.core.windows.net/forecasting/azuremlftk-0.1.18313.5a1-py3-none-any.whl
|
||||
# Required packages for AzureML execution, history, and data preparation.
|
||||
- azureml-sdk[automl,notebooks]
|
||||
- pandas_ml
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,16 +1,21 @@
|
||||
@echo off
|
||||
set conda_env_name=%1
|
||||
set automl_env_file=%2
|
||||
set PIP_NO_WARN_SCRIPT_LOCATION=0
|
||||
|
||||
IF "%conda_env_name%"=="" SET conda_env_name="azure_automl"
|
||||
IF "%automl_env_file%"=="" SET automl_env_file="automl_env.yml"
|
||||
|
||||
IF NOT EXIST %automl_env_file% GOTO YmlMissing
|
||||
|
||||
call conda activate %conda_env_name% 2>nul:
|
||||
|
||||
if not errorlevel 1 (
|
||||
echo Upgrading azureml-sdk[automl] in existing conda environment %conda_env_name%
|
||||
call pip install --upgrade azureml-sdk[automl]
|
||||
call pip install --upgrade azureml-sdk[automl,notebooks]
|
||||
if errorlevel 1 goto ErrorExit
|
||||
) else (
|
||||
call conda env create -f automl_env.yml -n %conda_env_name%
|
||||
call conda env create -f %automl_env_file% -n %conda_env_name%
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
call conda activate %conda_env_name% 2>nul:
|
||||
@@ -18,10 +23,12 @@ if errorlevel 1 goto ErrorExit
|
||||
|
||||
call pip install psutil
|
||||
|
||||
call jupyter nbextension install --py azureml.train.widgets
|
||||
call python -m ipykernel install --user --name %conda_env_name% --display-name "Python (%conda_env_name%)"
|
||||
|
||||
call jupyter nbextension install --py azureml.widgets --user
|
||||
if errorlevel 1 goto ErrorExit
|
||||
|
||||
call jupyter nbextension enable --py azureml.train.widgets
|
||||
call jupyter nbextension enable --py azureml.widgets --user
|
||||
if errorlevel 1 goto ErrorExit
|
||||
|
||||
echo.
|
||||
@@ -36,6 +43,9 @@ jupyter notebook --log-level=50
|
||||
|
||||
goto End
|
||||
|
||||
:YmlMissing
|
||||
echo File %automl_env_file% not found.
|
||||
|
||||
:ErrorExit
|
||||
echo Install failed
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,21 +1,34 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
CONDA_ENV_NAME=$1
|
||||
AUTOML_ENV_FILE=$2
|
||||
PIP_NO_WARN_SCRIPT_LOCATION=0
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "$CONDA_ENV_NAME" == "" ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
CONDA_ENV_NAME="azure_automl"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "$AUTOML_ENV_FILE" == "" ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
AUTOML_ENV_FILE="automl_env.yml"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [ ! -f $AUTOML_ENV_FILE ]; then
|
||||
echo "File $AUTOML_ENV_FILE not found"
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if source activate $CONDA_ENV_NAME 2> /dev/null
|
||||
then
|
||||
echo "Upgrading azureml-sdk[automl] in existing conda environment" $CONDA_ENV_NAME
|
||||
pip install --upgrade azureml-sdk[automl]
|
||||
pip install --upgrade azureml-sdk[automl,notebooks]
|
||||
else
|
||||
conda env create -f automl_env.yml -n $CONDA_ENV_NAME &&
|
||||
conda env create -f $AUTOML_ENV_FILE -n $CONDA_ENV_NAME &&
|
||||
source activate $CONDA_ENV_NAME &&
|
||||
jupyter nbextension install --py azureml.train.widgets --user &&
|
||||
jupyter nbextension enable --py azureml.train.widgets --user &&
|
||||
python -m ipykernel install --user --name $CONDA_ENV_NAME --display-name "Python ($CONDA_ENV_NAME)" &&
|
||||
jupyter nbextension install --py azureml.widgets --user &&
|
||||
jupyter nbextension enable --py azureml.widgets --user &&
|
||||
echo "" &&
|
||||
echo "" &&
|
||||
echo "***************************************" &&
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,22 +1,36 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
CONDA_ENV_NAME=$1
|
||||
AUTOML_ENV_FILE=$2
|
||||
PIP_NO_WARN_SCRIPT_LOCATION=0
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "$CONDA_ENV_NAME" == "" ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
CONDA_ENV_NAME="azure_automl"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "$AUTOML_ENV_FILE" == "" ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
AUTOML_ENV_FILE="automl_env_mac.yml"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [ ! -f $AUTOML_ENV_FILE ]; then
|
||||
echo "File $AUTOML_ENV_FILE not found"
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if source activate $CONDA_ENV_NAME 2> /dev/null
|
||||
then
|
||||
echo "Upgrading azureml-sdk[automl] in existing conda environment" $CONDA_ENV_NAME
|
||||
pip install --upgrade azureml-sdk[automl]
|
||||
pip install --upgrade azureml-sdk[automl,notebooks]
|
||||
else
|
||||
conda env create -f automl_env.yml -n $CONDA_ENV_NAME &&
|
||||
conda env create -f $AUTOML_ENV_FILE -n $CONDA_ENV_NAME &&
|
||||
source activate $CONDA_ENV_NAME &&
|
||||
conda install lightgbm -c conda-forge -y &&
|
||||
jupyter nbextension install --py azureml.train.widgets --user &&
|
||||
jupyter nbextension enable --py azureml.train.widgets --user &&
|
||||
python -m ipykernel install --user --name $CONDA_ENV_NAME --display-name "Python ($CONDA_ENV_NAME)" &&
|
||||
jupyter nbextension install --py azureml.widgets --user &&
|
||||
jupyter nbextension enable --py azureml.widgets --user &&
|
||||
pip install numpy==1.15.3
|
||||
echo "" &&
|
||||
echo "" &&
|
||||
echo "***************************************" &&
|
||||
@@ -34,3 +48,4 @@ then
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
49
databricks/automl_adb_readme.md
Normal file
49
databricks/automl_adb_readme.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
**PREVIEW capability**
|
||||
|
||||
Automated ML now supports Azure Databricks as a local compute to perform training (**public preview**). Azure Databricks is a managed Spark offering on Azure and customers already use it for advanced analytics. It provides a collaborative Notebook based environment with CPU or GPU based compute cluster.
|
||||
- Customers who use Azure Databricks for advanced analytics can now use the same cluster to run automated machine learning experiments.
|
||||
- You can keep the data within the same cluster.
|
||||
- You can leverage the local worker nodes with autoscale and auto termination capabilities.
|
||||
- You can use multiple cores of your Azure Databricks cluster to perform simultenous training.
|
||||
- You can further tune the model generated by automated machine learning if you chose to.
|
||||
- Every run (including the best run) is available as a pipeline.
|
||||
- The model from the pipeline can be registered in Azure ML SDK workspace and then deployed to Azure managed compute (ACI or AKS) using the Azure Machine learning SDK.
|
||||
|
||||
**Create Azure Databricks Cluster:**
|
||||
|
||||
Select New Cluster and fill in following detail:
|
||||
- Cluster name: _yourclustername_
|
||||
- Cluster Mode: Any. **High Concurrency** preferred
|
||||
- Databricks Runtime: Any 4.x runtime.
|
||||
- Python version: **3**
|
||||
- Workers: 2 or higher.
|
||||
- Max. number of **concurrent iterations** in Automated ML settings is **<=** to the number of **worker nodes** in your Databricks cluster.
|
||||
- Worker node VM types: **Memory optimized VM** preferred.
|
||||
- Uncheck _Enable Autoscaling_
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
It will take few minutes to create the cluster. Please ensure that the cluster state is running before proceeding further.
|
||||
|
||||
**Install Azure ML with Automated ML SDK on your Azure Databricks cluster**
|
||||
|
||||
- Select Import library
|
||||
|
||||
- Source: Upload Python Egg or PyPI
|
||||
|
||||
- PyPi Name (_with_ Automated ML capability): **azureml-sdk[automl_databricks]**
|
||||
|
||||
- PyPi Name (_without_ Automated ML capability): **azureml-sdk[databricks]**
|
||||
|
||||
- Click Install Library
|
||||
|
||||
- Do not select _Attach automatically to all clusters_. In case you have selected earlier then you can go to your Home folder and deselect it.
|
||||
|
||||
- Select the check box _Attach_ next to your cluster name
|
||||
|
||||
(More details on how to attach and detach libs are here - [https://docs.databricks.com/user-guide/libraries.html#attach-a-library-to-a-cluster](https://docs.databricks.com/user-guide/libraries.html#attach-a-library-to-a-cluster) )
|
||||
|
||||
- Ensure that there are no errors until Status changes to _Attached_. It may take a couple of minutes.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note** - If you have the old build the please deselect it from cluster’s installed libs > move to trash. Install the new build and restart the cluster. And if still there is an issue then detach and reattach your cluster.
|
||||
|
||||
**Now you can run the Automated ML sample notebook on your Azure Databricks cluster. Please let us know your feedback.**
|
||||
2985
dataprep/getting-started.ipynb
Normal file
2985
dataprep/getting-started.ipynb
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
BIN
images/yt_cover.png
Normal file
BIN
images/yt_cover.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 26 KiB |
@@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
|
||||
# ONNX on Azure Machine Learning
|
||||
|
||||
These tutorials show how to create and deploy [ONNX](http://onnx.ai) models using Azure Machine Learning and the [ONNX Runtime](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/service/how-to-build-deploy-onnx).
|
||||
Once deployed as web services, you can ping the models with your own images to be analyzed!
|
||||
These tutorials show how to create and deploy [ONNX](http://onnx.ai) models in Azure Machine Learning environments using [ONNX Runtime](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/service/how-to-build-deploy-onnx) for inference. Once deployed as a web service, you can ping the model with your own set of images to be analyzed!
|
||||
|
||||
## Tutorials
|
||||
- [Obtain ONNX model from ONNX Model Zoo and deploy - ResNet50](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/blob/master/onnx/onnx-modelzoo-aml-deploy-resnet50.ipynb)
|
||||
- [Obtain ONNX model from ONNX Model Zoo and deploy with ONNX Runtime inference - Handwritten Digit Classification (MNIST)](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/blob/master/onnx/onnx-inference-mnist-deploy.ipynb)
|
||||
- [Obtain ONNX model from ONNX Model Zoo and deploy with ONNX Runtime inference - Facial Expression Recognition (Emotion FER+)](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/blob/master/onnx/onnx-inference-facial-emotion-recognition-deploy.ipynb)
|
||||
- [Obtain ONNX model from ONNX Model Zoo and deploy with ONNX Runtime inference - Image Recognition (ResNet50)](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/blob/master/onnx/onnx-modelzoo-aml-deploy-resnet50.ipynb)
|
||||
- [Convert ONNX model from CoreML and deploy - TinyYOLO](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/blob/master/onnx/onnx-convert-aml-deploy-tinyyolo.ipynb)
|
||||
- [Train ONNX model in PyTorch and deploy - MNIST](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/blob/master/onnx/onnx-train-pytorch-aml-deploy-mnist.ipynb)
|
||||
- [Handwritten Digit Classification (MNIST) using ONNX Runtime on AzureML](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/blob/master/onnx/onnx-inference-mnist.ipynb)
|
||||
- [Facial Expression Recognition using ONNX Runtime on AzureML](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/blob/master/onnx/onnx-inference-emotion-recognition.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Documentation
|
||||
- [ONNX Runtime Python API Documentation](http://aka.ms/onnxruntime-python)
|
||||
@@ -21,7 +21,8 @@ Once deployed as web services, you can ping the models with your own images to b
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Licensed under the MIT License.
|
||||
|
||||
## Acknowledgements
|
||||
These tutorials were developed by Vinitra Swamy and Prasanth Pulavarthi of the Microsoft AI Frameworks team and adapted for presentation at Microsoft Ignite 2018.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -59,8 +59,9 @@
|
||||
"You'll need to run the following commands to use this tutorial:\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"```sh\n",
|
||||
"pip install coremltools\n",
|
||||
"pip install onnxmltools\n",
|
||||
"pip install coremltools # use this on Linux and Mac\n",
|
||||
"pip install git+https://github.com/apple/coremltools # use this on Windows\n",
|
||||
"```"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -79,7 +80,10 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"!wget https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/coreml-models/TinyYOLO.mlmodel"
|
||||
"import urllib.request\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"onnx_model_url = \"https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/coreml-models/TinyYOLO.mlmodel\"\n",
|
||||
"urllib.request.urlretrieve(onnx_model_url, filename=\"TinyYOLO.mlmodel\")\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -173,9 +177,9 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"models = ws.models()\n",
|
||||
"for m in models:\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Name:\", m.name,\"\\tVersion:\", m.version, \"\\tDescription:\", m.description, m.tags)"
|
||||
"models = ws.models\n",
|
||||
"for name, m in models.items():\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Name:\", name,\"\\tVersion:\", m.version, \"\\tDescription:\", m.description, m.tags)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -244,7 +248,7 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"myenv = CondaDependencies.create(pip_packages=[\"numpy\",\"onnxruntime\"])\n",
|
||||
"myenv = CondaDependencies.create(pip_packages=[\"numpy\",\"onnxruntime\",\"azureml-core\"])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with open(\"myenv.yml\",\"w\") as f:\n",
|
||||
" f.write(myenv.serialize_to_string())"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,812 +0,0 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. \n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Facial Expression Recognition (Emotion FER+) using ONNX Runtime on Azure ML\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This example shows how to deploy an image classification neural network using the Facial Expression Recognition ([FER](https://www.kaggle.com/c/challenges-in-representation-learning-facial-expression-recognition-challenge/data)) dataset and Open Neural Network eXchange format ([ONNX](http://aka.ms/onnxdocarticle)) on the Azure Machine Learning platform. This tutorial will show you how to deploy a FER+ model from the [ONNX model zoo](https://github.com/onnx/models), use it to make predictions using ONNX Runtime Inference, and deploy it as a web service in Azure.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Throughout this tutorial, we will be referring to ONNX, a neural network exchange format used to represent deep learning models. With ONNX, AI developers can more easily move models between state-of-the-art tools (CNTK, PyTorch, Caffe, MXNet, TensorFlow) and choose the combination that is best for them. ONNX is developed and supported by a community of partners including Microsoft AI, Facebook, and Amazon. For more information, explore the [ONNX website](http://onnx.ai) and [open source files](https://github.com/onnx).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"[ONNX Runtime](https://aka.ms/onnxruntime-python) is the runtime engine that enables evaluation of trained machine learning (Traditional ML and Deep Learning) models with high performance and low resource utilization. We use the CPU version of ONNX Runtime in this tutorial, but will soon be releasing an additional tutorial for deploying this model using ONNX Runtime GPU.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Tutorial Objectives:\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"1. Describe the FER+ dataset and pretrained Convolutional Neural Net ONNX model for Emotion Recognition, stored in the ONNX model zoo.\n",
|
||||
"2. Deploy and run the pretrained FER+ ONNX model on an Azure Machine Learning instance\n",
|
||||
"3. Predict labels for test set data points in the cloud using ONNX Runtime and Azure ML"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Prerequisites\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### 1. Install Azure ML SDK and create a new workspace\n",
|
||||
"Please follow [Azure ML configuration notebook](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/blob/master/00.configuration.ipynb) to set up your environment.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### 2. Install additional packages needed for this Notebook\n",
|
||||
"You need to install the popular plotting library `matplotlib`, the image manipulation library `opencv`, and the `onnx` library in the conda environment where Azure Maching Learning SDK is installed.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"```sh\n",
|
||||
"(myenv) $ pip install matplotlib onnx opencv-python\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Debugging tip**: Make sure that to activate your virtual environment (myenv) before you re-launch this notebook using the `jupyter notebook` comand. Choose the respective Python kernel for your new virtual environment using the `Kernel > Change Kernel` menu above. If you have completed the steps correctly, the upper right corner of your screen should state `Python [conda env:myenv]` instead of `Python [default]`.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### 3. Download sample data and pre-trained ONNX model from ONNX Model Zoo.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In the following lines of code, we download [the trained ONNX Emotion FER+ model and corresponding test data](https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/master/emotion_ferplus) and place them in the same folder as this tutorial notebook. For more information about the FER+ dataset, please visit Microsoft Researcher Emad Barsoum's [FER+ source data repository](https://github.com/ebarsoum/FERPlus)."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# urllib is a built-in Python library to download files from URLs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Objective: retrieve the latest version of the ONNX Emotion FER+ model files from the\n",
|
||||
"# ONNX Model Zoo and save it in the same folder as this tutorial\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import urllib.request\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"onnx_model_url = \"https://www.cntk.ai/OnnxModels/emotion_ferplus/opset_7/emotion_ferplus.tar.gz\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"urllib.request.urlretrieve(onnx_model_url, filename=\"emotion_ferplus.tar.gz\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# the ! magic command tells our jupyter notebook kernel to run the following line of \n",
|
||||
"# code from the command line instead of the notebook kernel\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# We use tar and xvcf to unzip the files we just retrieved from the ONNX model zoo\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"!tar xvzf emotion_ferplus.tar.gz"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Deploy a VM with your ONNX model in the Cloud\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Load Azure ML workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"We begin by instantiating a workspace object from the existing workspace created earlier in the configuration notebook."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Check core SDK version number\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(\"SDK version:\", azureml.core.VERSION)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"print(ws.name, ws.location, ws.resource_group, sep = '\\n')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Registering your model with Azure ML"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model_dir = \"emotion_ferplus\" # replace this with the location of your model files\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# leave as is if it's in the same folder as this notebook"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.model import Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"model = Model.register(model_path = model_dir + \"/\" + \"model.onnx\",\n",
|
||||
" model_name = \"onnx_emotion\",\n",
|
||||
" tags = {\"onnx\": \"demo\"},\n",
|
||||
" description = \"FER+ emotion recognition CNN from ONNX Model Zoo\",\n",
|
||||
" workspace = ws)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Optional: Displaying your registered models\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This step is not required, so feel free to skip it."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"models = ws.models()\n",
|
||||
"for name, m in models.items():\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Name:\", name,\"\\tVersion:\", m.version, \"\\tDescription:\", m.description, m.tags)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### ONNX FER+ Model Methodology\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The image classification model we are using is pre-trained using Microsoft's deep learning cognitive toolkit, [CNTK](https://github.com/Microsoft/CNTK), from the [ONNX model zoo](http://github.com/onnx/models). The model zoo has many other models that can be deployed on cloud providers like AzureML without any additional training. To ensure that our cloud deployed model works, we use testing data from the well-known FER+ data set, provided as part of the [trained Emotion Recognition model](https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/master/emotion_ferplus) in the ONNX model zoo.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The original Facial Emotion Recognition (FER) Dataset was released in 2013 by Pierre-Luc Carrier and Aaron Courville as part of a [Kaggle Competition](https://www.kaggle.com/c/challenges-in-representation-learning-facial-expression-recognition-challenge/data), but some of the labels are not entirely appropriate for the expression. In the FER+ Dataset, each photo was evaluated by at least 10 croud sourced reviewers, creating a more accurate basis for ground truth. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"You can see the difference of label quality in the sample model input below. The FER labels are the first word below each image, and the FER+ labels are the second word below each image.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"***Input: Photos of cropped faces from FER+ Dataset***\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"***Task: Classify each facial image into its appropriate emotions in the emotion table***\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"``` emotion_table = {'neutral':0, 'happiness':1, 'surprise':2, 'sadness':3, 'anger':4, 'disgust':5, 'fear':6, 'contempt':7} ```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"***Output: Emotion prediction for input image***\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Remember, once the application is deployed in Azure ML, you can use your own images as input for the model to classify."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# for images and plots in this notebook\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt \n",
|
||||
"from IPython.display import Image\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# display images inline\n",
|
||||
"%matplotlib inline"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Model Description\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The FER+ model from the ONNX Model Zoo is summarized by the graphic below. You can see the entire workflow of our pre-trained model in the following image from Barsoum et. al's paper [\"Training Deep Networks for Facial Expression Recognition\n",
|
||||
"with Crowd-Sourced Label Distribution\"](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.01041.pdf), with our (64 x 64) input images and our output probabilities for each of the labels."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"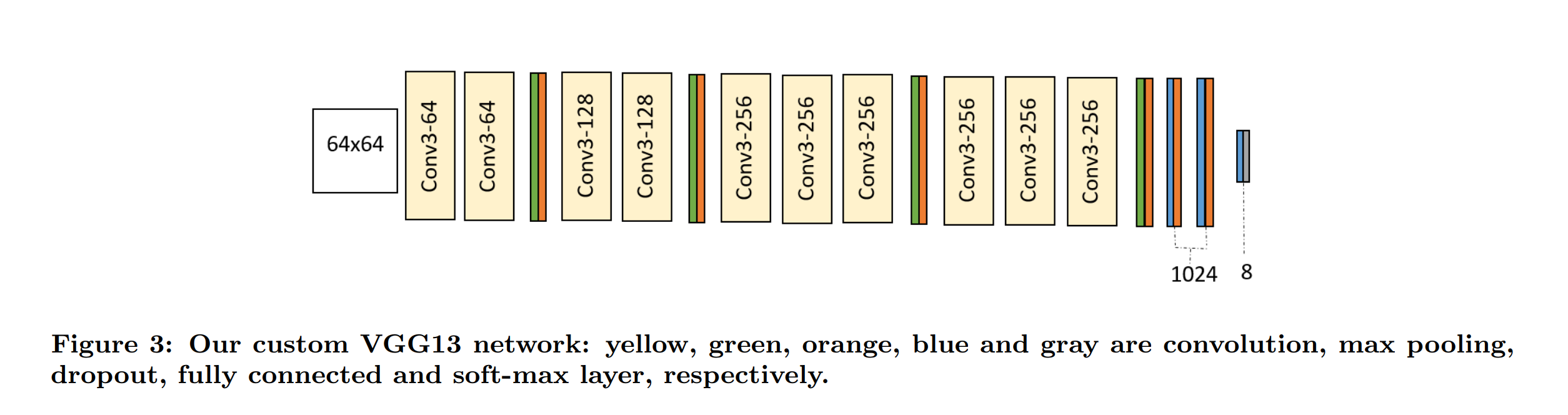"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Specify our Score and Environment Files"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"We are now going to deploy our ONNX Model on AML with inference in ONNX Runtime. We begin by writing a score.py file, which will help us run the model in our Azure ML virtual machine (VM), and then specify our environment by writing a yml file. You will also notice that we import the onnxruntime library to do runtime inference on our ONNX models (passing in input and evaluating out model's predicted output). More information on the API and commands can be found in the [ONNX Runtime documentation](https://aka.ms/onnxruntime).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Write Score File\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"A score file is what tells our Azure cloud service what to do. After initializing our model using azureml.core.model, we start an ONNX Runtime inference session to evaluate the data passed in on our function calls."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%%writefile score.py\n",
|
||||
"import json\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"import onnxruntime\n",
|
||||
"import sys\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.model import Model\n",
|
||||
"import time\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def init():\n",
|
||||
" global session, input_name, output_name\n",
|
||||
" model = Model.get_model_path(model_name = 'onnx_emotion')\n",
|
||||
" session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(model, None)\n",
|
||||
" input_name = session.get_inputs()[0].name\n",
|
||||
" output_name = session.get_outputs()[0].name \n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"def run(input_data):\n",
|
||||
" '''Purpose: evaluate test input in Azure Cloud using onnxruntime.\n",
|
||||
" We will call the run function later from our Jupyter Notebook \n",
|
||||
" so our azure service can evaluate our model input in the cloud. '''\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" try:\n",
|
||||
" # load in our data, convert to readable format\n",
|
||||
" data = np.array(json.loads(input_data)['data']).astype('float32')\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" start = time.time()\n",
|
||||
" r = session.run([output_name], {input_name : data})\n",
|
||||
" end = time.time()\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" result = emotion_map(postprocess(r[0]))\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" result_dict = {\"result\": result,\n",
|
||||
" \"time_in_sec\": [end - start]}\n",
|
||||
" except Exception as e:\n",
|
||||
" result_dict = {\"error\": str(e)}\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" return json.dumps(result_dict)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def emotion_map(classes, N=1):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Take the most probable labels (output of postprocess) and returns the \n",
|
||||
" top N emotional labels that fit the picture.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" emotion_table = {'neutral':0, 'happiness':1, 'surprise':2, 'sadness':3, \n",
|
||||
" 'anger':4, 'disgust':5, 'fear':6, 'contempt':7}\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" emotion_keys = list(emotion_table.keys())\n",
|
||||
" emotions = []\n",
|
||||
" for i in range(N):\n",
|
||||
" emotions.append(emotion_keys[classes[i]])\n",
|
||||
" return emotions\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def softmax(x):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Compute softmax values (probabilities from 0 to 1) for each possible label.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" x = x.reshape(-1)\n",
|
||||
" e_x = np.exp(x - np.max(x))\n",
|
||||
" return e_x / e_x.sum(axis=0)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def postprocess(scores):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"This function takes the scores generated by the network and \n",
|
||||
" returns the class IDs in decreasing order of probability.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" prob = softmax(scores)\n",
|
||||
" prob = np.squeeze(prob)\n",
|
||||
" classes = np.argsort(prob)[::-1]\n",
|
||||
" return classes"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Write Environment File"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"myenv = CondaDependencies()\n",
|
||||
"myenv.add_pip_package(\"numpy\")\n",
|
||||
"myenv.add_pip_package(\"azureml-core\")\n",
|
||||
"myenv.add_pip_package(\"onnxruntime\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with open(\"myenv.yml\",\"w\") as f:\n",
|
||||
" f.write(myenv.serialize_to_string())"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Create the Container Image\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This step will likely take a few minutes."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.image import ContainerImage\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"image_config = ContainerImage.image_configuration(execution_script = \"score.py\",\n",
|
||||
" runtime = \"python\",\n",
|
||||
" conda_file = \"myenv.yml\",\n",
|
||||
" description = \"Emotion ONNX Runtime container\",\n",
|
||||
" tags = {\"demo\": \"onnx\"})\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"image = ContainerImage.create(name = \"onnxtest\",\n",
|
||||
" # this is the model object\n",
|
||||
" models = [model],\n",
|
||||
" image_config = image_config,\n",
|
||||
" workspace = ws)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"image.wait_for_creation(show_output = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"In case you need to debug your code, the next line of code accesses the log file."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"print(image.image_build_log_uri)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"We're all done specifying what we want our virtual machine to do. Let's configure and deploy our container image.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Deploy the container image"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.webservice import AciWebservice\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aciconfig = AciWebservice.deploy_configuration(cpu_cores = 1, \n",
|
||||
" memory_gb = 1, \n",
|
||||
" tags = {'demo': 'onnx'}, \n",
|
||||
" description = 'ONNX for emotion recognition model')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.webservice import Webservice\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aci_service_name = 'onnx-demo-emotion'\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Service\", aci_service_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aci_service = Webservice.deploy_from_image(deployment_config = aciconfig,\n",
|
||||
" image = image,\n",
|
||||
" name = aci_service_name,\n",
|
||||
" workspace = ws)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aci_service.wait_for_deployment(True)\n",
|
||||
"print(aci_service.state)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"The following cell will likely take a few minutes to run as well."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"if aci_service.state != 'Healthy':\n",
|
||||
" # run this command for debugging.\n",
|
||||
" print(aci_service.get_logs())\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # If your deployment fails, make sure to delete your aci_service before trying again!\n",
|
||||
" # aci_service.delete()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Success!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"If you've made it this far, you've deployed a working VM with a facial emotion recognition model running in the cloud using Azure ML. Congratulations!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Let's see how well our model deals with our test images."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Testing and Evaluation\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Useful Helper Functions\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"We preprocess and postprocess our data (see score.py file) using the helper functions specified in the [ONNX FER+ Model page in the Model Zoo repository](https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/master/emotion_ferplus)."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"def emotion_map(classes, N=1):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Take the most probable labels (output of postprocess) and returns the \n",
|
||||
" top N emotional labels that fit the picture.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" emotion_table = {'neutral':0, 'happiness':1, 'surprise':2, 'sadness':3, \n",
|
||||
" 'anger':4, 'disgust':5, 'fear':6, 'contempt':7}\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" emotion_keys = list(emotion_table.keys())\n",
|
||||
" emotions = []\n",
|
||||
" for i in range(N):\n",
|
||||
" emotions.append(emotion_keys[classes[i]])\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" return emotions\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def softmax(x):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Compute softmax values (probabilities from 0 to 1) for each possible label.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" x = x.reshape(-1)\n",
|
||||
" e_x = np.exp(x - np.max(x))\n",
|
||||
" return e_x / e_x.sum(axis=0)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def postprocess(scores):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"This function takes the scores generated by the network and \n",
|
||||
" returns the class IDs in decreasing order of probability.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" prob = softmax(scores)\n",
|
||||
" prob = np.squeeze(prob)\n",
|
||||
" classes = np.argsort(prob)[::-1]\n",
|
||||
" return classes"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Load Test Data\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"These are already in your directory from your ONNX model download (from the model zoo).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Notice that our Model Zoo files have a .pb extension. This is because they are [protobuf files (Protocol Buffers)](https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/pythontutorial), so we need to read in our data through our ONNX TensorProto reader into a format we can work with, like numerical arrays."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# to manipulate our arrays\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# read in test data protobuf files included with the model\n",
|
||||
"import onnx\n",
|
||||
"from onnx import numpy_helper\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# to use parsers to read in our model/data\n",
|
||||
"import json\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"test_inputs = []\n",
|
||||
"test_outputs = []\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# read in 3 testing images from .pb files\n",
|
||||
"test_data_size = 3\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for i in np.arange(test_data_size):\n",
|
||||
" input_test_data = os.path.join(model_dir, 'test_data_set_{0}'.format(i), 'input_0.pb')\n",
|
||||
" output_test_data = os.path.join(model_dir, 'test_data_set_{0}'.format(i), 'output_0.pb')\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # convert protobuf tensors to np arrays using the TensorProto reader from ONNX\n",
|
||||
" tensor = onnx.TensorProto()\n",
|
||||
" with open(input_test_data, 'rb') as f:\n",
|
||||
" tensor.ParseFromString(f.read())\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" input_data = numpy_helper.to_array(tensor)\n",
|
||||
" test_inputs.append(input_data)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" with open(output_test_data, 'rb') as f:\n",
|
||||
" tensor.ParseFromString(f.read())\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" output_data = numpy_helper.to_array(tensor)\n",
|
||||
" output_processed = emotion_map(postprocess(output_data))[0]\n",
|
||||
" test_outputs.append(output_processed)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"nbpresent": {
|
||||
"id": "c3f2f57c-7454-4d3e-b38d-b0946cf066ea"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Show some sample images\n",
|
||||
"We use `matplotlib` to plot 3 test images from the dataset."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"nbpresent": {
|
||||
"id": "396d478b-34aa-4afa-9898-cdce8222a516"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"plt.figure(figsize = (20, 20))\n",
|
||||
"for test_image in np.arange(3):\n",
|
||||
" test_inputs[test_image].reshape(1, 64, 64)\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1, 8, test_image+1)\n",
|
||||
" plt.axhline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.axvline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 10, y = -10, s = test_outputs[test_image], fontsize = 18)\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(test_inputs[test_image].reshape(64, 64), cmap = plt.cm.gray)\n",
|
||||
"plt.show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Run evaluation / prediction"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6), frameon=False)\n",
|
||||
"plt.subplot(1, 8, 1)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 0, y = -30, s = \"True Label: \", fontsize = 13, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 0, y = -20, s = \"Result: \", fontsize = 13, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 0, y = -10, s = \"Inference Time: \", fontsize = 13, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 3, y = 14, s = \"Model Input\", fontsize = 12, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 6, y = 18, s = \"(64 x 64)\", fontsize = 12, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.imshow(np.ones((28,28)), cmap=plt.cm.Greys) \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for i in np.arange(test_data_size):\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" input_data = json.dumps({'data': test_inputs[i].tolist()})\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # predict using the deployed model\n",
|
||||
" r = json.loads(aci_service.run(input_data))\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" if \"error\" in r:\n",
|
||||
" print(r['error'])\n",
|
||||
" break\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" result = r['result'][0]\n",
|
||||
" time_ms = np.round(r['time_in_sec'][0] * 1000, 2)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" ground_truth = test_outputs[i]\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # compare actual value vs. the predicted values:\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1, 8, i+2)\n",
|
||||
" plt.axhline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.axvline('')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # use different color for misclassified sample\n",
|
||||
" font_color = 'red' if ground_truth != result else 'black'\n",
|
||||
" clr_map = plt.cm.Greys if ground_truth != result else plt.cm.gray\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # ground truth labels are in blue\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 10, y = -70, s = ground_truth, fontsize = 18, color = 'blue')\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # predictions are in black if correct, red if incorrect\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 10, y = -45, s = result, fontsize = 18, color = font_color)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 5, y = -22, s = str(time_ms) + ' ms', fontsize = 14, color = font_color)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(test_inputs[i].reshape(64, 64), cmap = clr_map)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"plt.show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Try classifying your own images!"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Preprocessing functions take your image and format it so it can be passed\n",
|
||||
"# as input into our ONNX model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import cv2\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def rgb2gray(rgb):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Convert the input image into grayscale\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" return np.dot(rgb[...,:3], [0.299, 0.587, 0.114])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def resize_img(img):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Resize image to MNIST model input dimensions\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" img = cv2.resize(img, dsize=(64, 64), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)\n",
|
||||
" img.resize((1, 1, 64, 64))\n",
|
||||
" return img\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def preprocess(img):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Resize input images and convert them to grayscale.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" if img.shape == (64, 64):\n",
|
||||
" img.resize((1, 1, 64, 64))\n",
|
||||
" return img\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" grayscale = rgb2gray(img)\n",
|
||||
" processed_img = resize_img(grayscale)\n",
|
||||
" return processed_img"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Replace the following string with your own path/test image\n",
|
||||
"# Make sure your image is square and the dimensions are equal (i.e. 100 * 100 pixels or 28 * 28 pixels)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Any PNG or JPG image file should work\n",
|
||||
"# Make sure to include the entire path with // instead of /\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# e.g. your_test_image = \"C://Users//vinitra.swamy//Pictures//emotion_test_images//img_1.png\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib.image as mpimg\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"if your_test_image != \"<path to file>\":\n",
|
||||
" img = mpimg.imread(your_test_image)\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1,3,1)\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(img, cmap = plt.cm.Greys)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Old Dimensions: \", img.shape)\n",
|
||||
" img = preprocess(img)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"New Dimensions: \", img.shape)\n",
|
||||
"else:\n",
|
||||
" img = None"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"if img is None:\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Add the path for your image data.\")\n",
|
||||
"else:\n",
|
||||
" input_data = json.dumps({'data': img.tolist()})\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" try:\n",
|
||||
" r = json.loads(aci_service.run(input_data))\n",
|
||||
" result = r['result'][0]\n",
|
||||
" time_ms = np.round(r['time_in_sec'][0] * 1000, 2)\n",
|
||||
" except Exception as e:\n",
|
||||
" print(str(e))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6))\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1,8,1)\n",
|
||||
" plt.axhline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.axvline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = -10, y = -40, s = \"Model prediction: \", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = -10, y = -25, s = \"Inference time: \", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 100, y = -40, s = str(result), fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 100, y = -25, s = str(time_ms) + \" ms\", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = -10, y = -10, s = \"Model Input image: \", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(img.reshape((64, 64)), cmap = plt.cm.gray) \n",
|
||||
" "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# remember to delete your service after you are done using it!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aci_service.delete()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Conclusion\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Congratulations!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this tutorial, you have:\n",
|
||||
"- familiarized yourself with ONNX Runtime inference and the pretrained models in the ONNX model zoo\n",
|
||||
"- understood a state-of-the-art convolutional neural net image classification model (FER+ in ONNX) and deployed it in the Azure ML cloud\n",
|
||||
"- ensured that your deep learning model is working perfectly (in the cloud) on test data, and checked it against some of your own!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Next steps:\n",
|
||||
"- If you have not already, check out another interesting ONNX/AML application that lets you set up a state-of-the-art [handwritten image classification model (MNIST)](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/tree/master/onnx/onnx-inference-mnist.ipynb) in the cloud! This tutorial deploys a pre-trained ONNX Computer Vision model for handwritten digit classification in an Azure ML virtual machine.\n",
|
||||
"- Keep an eye out for an updated version of this tutorial that uses ONNX Runtime GPU.\n",
|
||||
"- Contribute to our [open source ONNX repository on github](http://github.com/onnx/onnx) and/or add to our [ONNX model zoo](http://github.com/onnx/models)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "viswamy"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.6",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"msauthor": "vinitra.swamy"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
809
onnx/onnx-inference-facial-expression-recognition-deploy.ipynb
Normal file
809
onnx/onnx-inference-facial-expression-recognition-deploy.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,809 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. \n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Facial Expression Recognition (FER+) using ONNX Runtime on Azure ML\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This example shows how to deploy an image classification neural network using the Facial Expression Recognition ([FER](https://www.kaggle.com/c/challenges-in-representation-learning-facial-expression-recognition-challenge/data)) dataset and Open Neural Network eXchange format ([ONNX](http://aka.ms/onnxdocarticle)) on the Azure Machine Learning platform. This tutorial will show you how to deploy a FER+ model from the [ONNX model zoo](https://github.com/onnx/models), use it to make predictions using ONNX Runtime Inference, and deploy it as a web service in Azure.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Throughout this tutorial, we will be referring to ONNX, a neural network exchange format used to represent deep learning models. With ONNX, AI developers can more easily move models between state-of-the-art tools (CNTK, PyTorch, Caffe, MXNet, TensorFlow) and choose the combination that is best for them. ONNX is developed and supported by a community of partners including Microsoft AI, Facebook, and Amazon. For more information, explore the [ONNX website](http://onnx.ai) and [open source files](https://github.com/onnx).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"[ONNX Runtime](https://aka.ms/onnxruntime-python) is the runtime engine that enables evaluation of trained machine learning (Traditional ML and Deep Learning) models with high performance and low resource utilization. We use the CPU version of ONNX Runtime in this tutorial, but will soon be releasing an additional tutorial for deploying this model using ONNX Runtime GPU.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Tutorial Objectives:\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"1. Describe the FER+ dataset and pretrained Convolutional Neural Net ONNX model for Emotion Recognition, stored in the ONNX model zoo.\n",
|
||||
"2. Deploy and run the pretrained FER+ ONNX model on an Azure Machine Learning instance\n",
|
||||
"3. Predict labels for test set data points in the cloud using ONNX Runtime and Azure ML"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Prerequisites\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### 1. Install Azure ML SDK and create a new workspace\n",
|
||||
"Please follow [Azure ML configuration notebook](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/blob/master/00.configuration.ipynb) to set up your environment.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### 2. Install additional packages needed for this Notebook\n",
|
||||
"You need to install the popular plotting library `matplotlib`, the image manipulation library `opencv`, and the `onnx` library in the conda environment where Azure Maching Learning SDK is installed.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"```sh\n",
|
||||
"(myenv) $ pip install matplotlib onnx opencv-python\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Debugging tip**: Make sure that to activate your virtual environment (myenv) before you re-launch this notebook using the `jupyter notebook` comand. Choose the respective Python kernel for your new virtual environment using the `Kernel > Change Kernel` menu above. If you have completed the steps correctly, the upper right corner of your screen should state `Python [conda env:myenv]` instead of `Python [default]`.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### 3. Download sample data and pre-trained ONNX model from ONNX Model Zoo.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In the following lines of code, we download [the trained ONNX Emotion FER+ model and corresponding test data](https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/master/emotion_ferplus) and place them in the same folder as this tutorial notebook. For more information about the FER+ dataset, please visit Microsoft Researcher Emad Barsoum's [FER+ source data repository](https://github.com/ebarsoum/FERPlus)."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# urllib is a built-in Python library to download files from URLs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Objective: retrieve the latest version of the ONNX Emotion FER+ model files from the\n",
|
||||
"# ONNX Model Zoo and save it in the same folder as this tutorial\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import urllib.request\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"onnx_model_url = \"https://www.cntk.ai/OnnxModels/emotion_ferplus/opset_7/emotion_ferplus.tar.gz\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"urllib.request.urlretrieve(onnx_model_url, filename=\"emotion_ferplus.tar.gz\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# the ! magic command tells our jupyter notebook kernel to run the following line of \n",
|
||||
"# code from the command line instead of the notebook kernel\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# We use tar and xvcf to unzip the files we just retrieved from the ONNX model zoo\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"!tar xvzf emotion_ferplus.tar.gz"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Deploy a VM with your ONNX model in the Cloud\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Load Azure ML workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"We begin by instantiating a workspace object from the existing workspace created earlier in the configuration notebook."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Check core SDK version number\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(\"SDK version:\", azureml.core.VERSION)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"print(ws.name, ws.location, ws.resource_group, sep = '\\n')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Registering your model with Azure ML"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model_dir = \"emotion_ferplus\" # replace this with the location of your model files\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# leave as is if it's in the same folder as this notebook"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.model import Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"model = Model.register(model_path = model_dir + \"/\" + \"model.onnx\",\n",
|
||||
" model_name = \"onnx_emotion\",\n",
|
||||
" tags = {\"onnx\": \"demo\"},\n",
|
||||
" description = \"FER+ emotion recognition CNN from ONNX Model Zoo\",\n",
|
||||
" workspace = ws)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Optional: Displaying your registered models\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This step is not required, so feel free to skip it."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"models = ws.models\n",
|
||||
"for name, m in models.items():\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Name:\", name,\"\\tVersion:\", m.version, \"\\tDescription:\", m.description, m.tags)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### ONNX FER+ Model Methodology\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The image classification model we are using is pre-trained using Microsoft's deep learning cognitive toolkit, [CNTK](https://github.com/Microsoft/CNTK), from the [ONNX model zoo](http://github.com/onnx/models). The model zoo has many other models that can be deployed on cloud providers like AzureML without any additional training. To ensure that our cloud deployed model works, we use testing data from the well-known FER+ data set, provided as part of the [trained Emotion Recognition model](https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/master/emotion_ferplus) in the ONNX model zoo.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The original Facial Emotion Recognition (FER) Dataset was released in 2013 by Pierre-Luc Carrier and Aaron Courville as part of a [Kaggle Competition](https://www.kaggle.com/c/challenges-in-representation-learning-facial-expression-recognition-challenge/data), but some of the labels are not entirely appropriate for the expression. In the FER+ Dataset, each photo was evaluated by at least 10 croud sourced reviewers, creating a more accurate basis for ground truth. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"You can see the difference of label quality in the sample model input below. The FER labels are the first word below each image, and the FER+ labels are the second word below each image.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"***Input: Photos of cropped faces from FER+ Dataset***\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"***Task: Classify each facial image into its appropriate emotions in the emotion table***\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"``` emotion_table = {'neutral':0, 'happiness':1, 'surprise':2, 'sadness':3, 'anger':4, 'disgust':5, 'fear':6, 'contempt':7} ```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"***Output: Emotion prediction for input image***\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Remember, once the application is deployed in Azure ML, you can use your own images as input for the model to classify."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# for images and plots in this notebook\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt \n",
|
||||
"from IPython.display import Image\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# display images inline\n",
|
||||
"%matplotlib inline"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Model Description\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The FER+ model from the ONNX Model Zoo is summarized by the graphic below. You can see the entire workflow of our pre-trained model in the following image from Barsoum et. al's paper [\"Training Deep Networks for Facial Expression Recognition\n",
|
||||
"with Crowd-Sourced Label Distribution\"](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.01041.pdf), with our (64 x 64) input images and our output probabilities for each of the labels."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
""
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Specify our Score and Environment Files"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"We are now going to deploy our ONNX Model on AML with inference in ONNX Runtime. We begin by writing a score.py file, which will help us run the model in our Azure ML virtual machine (VM), and then specify our environment by writing a yml file. You will also notice that we import the onnxruntime library to do runtime inference on our ONNX models (passing in input and evaluating out model's predicted output). More information on the API and commands can be found in the [ONNX Runtime documentation](https://aka.ms/onnxruntime).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Write Score File\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"A score file is what tells our Azure cloud service what to do. After initializing our model using azureml.core.model, we start an ONNX Runtime inference session to evaluate the data passed in on our function calls."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%%writefile score.py\n",
|
||||
"import json\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"import onnxruntime\n",
|
||||
"import sys\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.model import Model\n",
|
||||
"import time\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def init():\n",
|
||||
" global session, input_name, output_name\n",
|
||||
" model = Model.get_model_path(model_name = 'onnx_emotion')\n",
|
||||
" session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(model, None)\n",
|
||||
" input_name = session.get_inputs()[0].name\n",
|
||||
" output_name = session.get_outputs()[0].name \n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"def run(input_data):\n",
|
||||
" '''Purpose: evaluate test input in Azure Cloud using onnxruntime.\n",
|
||||
" We will call the run function later from our Jupyter Notebook \n",
|
||||
" so our azure service can evaluate our model input in the cloud. '''\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" try:\n",
|
||||
" # load in our data, convert to readable format\n",
|
||||
" data = np.array(json.loads(input_data)['data']).astype('float32')\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" start = time.time()\n",
|
||||
" r = session.run([output_name], {input_name : data})\n",
|
||||
" end = time.time()\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" result = emotion_map(postprocess(r[0]))\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" result_dict = {\"result\": result,\n",
|
||||
" \"time_in_sec\": [end - start]}\n",
|
||||
" except Exception as e:\n",
|
||||
" result_dict = {\"error\": str(e)}\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" return json.dumps(result_dict)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def emotion_map(classes, N=1):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Take the most probable labels (output of postprocess) and returns the \n",
|
||||
" top N emotional labels that fit the picture.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" emotion_table = {'neutral':0, 'happiness':1, 'surprise':2, 'sadness':3, \n",
|
||||
" 'anger':4, 'disgust':5, 'fear':6, 'contempt':7}\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" emotion_keys = list(emotion_table.keys())\n",
|
||||
" emotions = []\n",
|
||||
" for i in range(N):\n",
|
||||
" emotions.append(emotion_keys[classes[i]])\n",
|
||||
" return emotions\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def softmax(x):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Compute softmax values (probabilities from 0 to 1) for each possible label.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" x = x.reshape(-1)\n",
|
||||
" e_x = np.exp(x - np.max(x))\n",
|
||||
" return e_x / e_x.sum(axis=0)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def postprocess(scores):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"This function takes the scores generated by the network and \n",
|
||||
" returns the class IDs in decreasing order of probability.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" prob = softmax(scores)\n",
|
||||
" prob = np.squeeze(prob)\n",
|
||||
" classes = np.argsort(prob)[::-1]\n",
|
||||
" return classes"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Write Environment File"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"myenv = CondaDependencies.create(pip_packages=[\"numpy\", \"onnxruntime\", \"azureml-core\"])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with open(\"myenv.yml\",\"w\") as f:\n",
|
||||
" f.write(myenv.serialize_to_string())"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Create the Container Image\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This step will likely take a few minutes."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.image import ContainerImage\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"image_config = ContainerImage.image_configuration(execution_script = \"score.py\",\n",
|
||||
" runtime = \"python\",\n",
|
||||
" conda_file = \"myenv.yml\",\n",
|
||||
" description = \"Emotion ONNX Runtime container\",\n",
|
||||
" tags = {\"demo\": \"onnx\"})\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"image = ContainerImage.create(name = \"onnximage\",\n",
|
||||
" # this is the model object\n",
|
||||
" models = [model],\n",
|
||||
" image_config = image_config,\n",
|
||||
" workspace = ws)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"image.wait_for_creation(show_output = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"In case you need to debug your code, the next line of code accesses the log file."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"print(image.image_build_log_uri)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"We're all done specifying what we want our virtual machine to do. Let's configure and deploy our container image.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Deploy the container image"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.webservice import AciWebservice\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aciconfig = AciWebservice.deploy_configuration(cpu_cores = 1, \n",
|
||||
" memory_gb = 1, \n",
|
||||
" tags = {'demo': 'onnx'}, \n",
|
||||
" description = 'ONNX for emotion recognition model')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.webservice import Webservice\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aci_service_name = 'onnx-demo-emotion'\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Service\", aci_service_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aci_service = Webservice.deploy_from_image(deployment_config = aciconfig,\n",
|
||||
" image = image,\n",
|
||||
" name = aci_service_name,\n",
|
||||
" workspace = ws)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aci_service.wait_for_deployment(True)\n",
|
||||
"print(aci_service.state)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"The following cell will likely take a few minutes to run as well."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"if aci_service.state != 'Healthy':\n",
|
||||
" # run this command for debugging.\n",
|
||||
" print(aci_service.get_logs())\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # If your deployment fails, make sure to delete your aci_service before trying again!\n",
|
||||
" # aci_service.delete()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Success!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"If you've made it this far, you've deployed a working VM with a facial emotion recognition model running in the cloud using Azure ML. Congratulations!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Let's see how well our model deals with our test images."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Testing and Evaluation\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Useful Helper Functions\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"We preprocess and postprocess our data (see score.py file) using the helper functions specified in the [ONNX FER+ Model page in the Model Zoo repository](https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/master/emotion_ferplus)."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"def emotion_map(classes, N=1):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Take the most probable labels (output of postprocess) and returns the \n",
|
||||
" top N emotional labels that fit the picture.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" emotion_table = {'neutral':0, 'happiness':1, 'surprise':2, 'sadness':3, \n",
|
||||
" 'anger':4, 'disgust':5, 'fear':6, 'contempt':7}\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" emotion_keys = list(emotion_table.keys())\n",
|
||||
" emotions = []\n",
|
||||
" for i in range(N):\n",
|
||||
" emotions.append(emotion_keys[classes[i]])\n",
|
||||
" return emotions\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def softmax(x):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Compute softmax values (probabilities from 0 to 1) for each possible label.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" x = x.reshape(-1)\n",
|
||||
" e_x = np.exp(x - np.max(x))\n",
|
||||
" return e_x / e_x.sum(axis=0)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def postprocess(scores):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"This function takes the scores generated by the network and \n",
|
||||
" returns the class IDs in decreasing order of probability.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" prob = softmax(scores)\n",
|
||||
" prob = np.squeeze(prob)\n",
|
||||
" classes = np.argsort(prob)[::-1]\n",
|
||||
" return classes"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Load Test Data\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"These are already in your directory from your ONNX model download (from the model zoo).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Notice that our Model Zoo files have a .pb extension. This is because they are [protobuf files (Protocol Buffers)](https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/pythontutorial), so we need to read in our data through our ONNX TensorProto reader into a format we can work with, like numerical arrays."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# to manipulate our arrays\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# read in test data protobuf files included with the model\n",
|
||||
"import onnx\n",
|
||||
"from onnx import numpy_helper\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# to use parsers to read in our model/data\n",
|
||||
"import json\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"test_inputs = []\n",
|
||||
"test_outputs = []\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# read in 3 testing images from .pb files\n",
|
||||
"test_data_size = 3\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for i in np.arange(test_data_size):\n",
|
||||
" input_test_data = os.path.join(model_dir, 'test_data_set_{0}'.format(i), 'input_0.pb')\n",
|
||||
" output_test_data = os.path.join(model_dir, 'test_data_set_{0}'.format(i), 'output_0.pb')\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # convert protobuf tensors to np arrays using the TensorProto reader from ONNX\n",
|
||||
" tensor = onnx.TensorProto()\n",
|
||||
" with open(input_test_data, 'rb') as f:\n",
|
||||
" tensor.ParseFromString(f.read())\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" input_data = numpy_helper.to_array(tensor)\n",
|
||||
" test_inputs.append(input_data)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" with open(output_test_data, 'rb') as f:\n",
|
||||
" tensor.ParseFromString(f.read())\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" output_data = numpy_helper.to_array(tensor)\n",
|
||||
" output_processed = emotion_map(postprocess(output_data[0]))[0]\n",
|
||||
" test_outputs.append(output_processed)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"nbpresent": {
|
||||
"id": "c3f2f57c-7454-4d3e-b38d-b0946cf066ea"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Show some sample images\n",
|
||||
"We use `matplotlib` to plot 3 test images from the dataset."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"nbpresent": {
|
||||
"id": "396d478b-34aa-4afa-9898-cdce8222a516"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"plt.figure(figsize = (20, 20))\n",
|
||||
"for test_image in np.arange(3):\n",
|
||||
" test_inputs[test_image].reshape(1, 64, 64)\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1, 8, test_image+1)\n",
|
||||
" plt.axhline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.axvline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 10, y = -10, s = test_outputs[test_image], fontsize = 18)\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(test_inputs[test_image].reshape(64, 64), cmap = plt.cm.gray)\n",
|
||||
"plt.show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Run evaluation / prediction"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6), frameon=False)\n",
|
||||
"plt.subplot(1, 8, 1)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 0, y = -30, s = \"True Label: \", fontsize = 13, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 0, y = -20, s = \"Result: \", fontsize = 13, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 0, y = -10, s = \"Inference Time: \", fontsize = 13, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 3, y = 14, s = \"Model Input\", fontsize = 12, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 6, y = 18, s = \"(64 x 64)\", fontsize = 12, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.imshow(np.ones((28,28)), cmap=plt.cm.Greys) \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for i in np.arange(test_data_size):\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" input_data = json.dumps({'data': test_inputs[i].tolist()})\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # predict using the deployed model\n",
|
||||
" r = json.loads(aci_service.run(input_data))\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" if \"error\" in r:\n",
|
||||
" print(r['error'])\n",
|
||||
" break\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" result = r['result'][0]\n",
|
||||
" time_ms = np.round(r['time_in_sec'][0] * 1000, 2)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" ground_truth = test_outputs[i]\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # compare actual value vs. the predicted values:\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1, 8, i+2)\n",
|
||||
" plt.axhline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.axvline('')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # use different color for misclassified sample\n",
|
||||
" font_color = 'red' if ground_truth != result else 'black'\n",
|
||||
" clr_map = plt.cm.Greys if ground_truth != result else plt.cm.gray\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # ground truth labels are in blue\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 10, y = -70, s = ground_truth, fontsize = 18, color = 'blue')\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # predictions are in black if correct, red if incorrect\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 10, y = -45, s = result, fontsize = 18, color = font_color)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 5, y = -22, s = str(time_ms) + ' ms', fontsize = 14, color = font_color)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(test_inputs[i].reshape(64, 64), cmap = clr_map)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"plt.show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Try classifying your own images!"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Preprocessing functions take your image and format it so it can be passed\n",
|
||||
"# as input into our ONNX model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import cv2\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def rgb2gray(rgb):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Convert the input image into grayscale\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" return np.dot(rgb[...,:3], [0.299, 0.587, 0.114])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def resize_img(img):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Resize image to MNIST model input dimensions\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" img = cv2.resize(img, dsize=(64, 64), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)\n",
|
||||
" img.resize((1, 1, 64, 64))\n",
|
||||
" return img\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def preprocess(img):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Resize input images and convert them to grayscale.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" if img.shape == (64, 64):\n",
|
||||
" img.resize((1, 1, 64, 64))\n",
|
||||
" return img\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" grayscale = rgb2gray(img)\n",
|
||||
" processed_img = resize_img(grayscale)\n",
|
||||
" return processed_img"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Replace the following string with your own path/test image\n",
|
||||
"# Make sure your image is square and the dimensions are equal (i.e. 100 * 100 pixels or 28 * 28 pixels)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Any PNG or JPG image file should work\n",
|
||||
"# Make sure to include the entire path with // instead of /\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# e.g. your_test_image = \"C:/Users/vinitra.swamy/Pictures/face.png\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"your_test_image = \"<path to file>\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib.image as mpimg\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"if your_test_image != \"<path to file>\":\n",
|
||||
" img = mpimg.imread(your_test_image)\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1,3,1)\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(img, cmap = plt.cm.Greys)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Old Dimensions: \", img.shape)\n",
|
||||
" img = preprocess(img)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"New Dimensions: \", img.shape)\n",
|
||||
"else:\n",
|
||||
" img = None"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"if img is None:\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Add the path for your image data.\")\n",
|
||||
"else:\n",
|
||||
" input_data = json.dumps({'data': img.tolist()})\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" try:\n",
|
||||
" r = json.loads(aci_service.run(input_data))\n",
|
||||
" result = r['result'][0]\n",
|
||||
" time_ms = np.round(r['time_in_sec'][0] * 1000, 2)\n",
|
||||
" except Exception as e:\n",
|
||||
" print(str(e))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6))\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1,8,1)\n",
|
||||
" plt.axhline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.axvline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = -10, y = -40, s = \"Model prediction: \", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = -10, y = -25, s = \"Inference time: \", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 100, y = -40, s = str(result), fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 100, y = -25, s = str(time_ms) + \" ms\", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = -10, y = -10, s = \"Model Input image: \", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(img.reshape((64, 64)), cmap = plt.cm.gray) \n",
|
||||
" "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# remember to delete your service after you are done using it!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# aci_service.delete()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Conclusion\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Congratulations!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this tutorial, you have:\n",
|
||||
"- familiarized yourself with ONNX Runtime inference and the pretrained models in the ONNX model zoo\n",
|
||||
"- understood a state-of-the-art convolutional neural net image classification model (FER+ in ONNX) and deployed it in the Azure ML cloud\n",
|
||||
"- ensured that your deep learning model is working perfectly (in the cloud) on test data, and checked it against some of your own!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Next steps:\n",
|
||||
"- If you have not already, check out another interesting ONNX/AML application that lets you set up a state-of-the-art [handwritten image classification model (MNIST)](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/tree/master/onnx/onnx-inference-mnist.ipynb) in the cloud! This tutorial deploys a pre-trained ONNX Computer Vision model for handwritten digit classification in an Azure ML virtual machine.\n",
|
||||
"- Keep an eye out for an updated version of this tutorial that uses ONNX Runtime GPU.\n",
|
||||
"- Contribute to our [open source ONNX repository on github](http://github.com/onnx/onnx) and/or add to our [ONNX model zoo](http://github.com/onnx/models)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "viswamy"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.6",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"msauthor": "vinitra.swamy"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
792
onnx/onnx-inference-mnist-deploy.ipynb
Normal file
792
onnx/onnx-inference-mnist-deploy.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,792 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. \n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Handwritten Digit Classification (MNIST) using ONNX Runtime on Azure ML\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This example shows how to deploy an image classification neural network using the Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology ([MNIST](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/)) dataset and Open Neural Network eXchange format ([ONNX](http://aka.ms/onnxdocarticle)) on the Azure Machine Learning platform. MNIST is a popular dataset consisting of 70,000 grayscale images. Each image is a handwritten digit of 28x28 pixels, representing number from 0 to 9. This tutorial will show you how to deploy a MNIST model from the [ONNX model zoo](https://github.com/onnx/models), use it to make predictions using ONNX Runtime Inference, and deploy it as a web service in Azure.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Throughout this tutorial, we will be referring to ONNX, a neural network exchange format used to represent deep learning models. With ONNX, AI developers can more easily move models between state-of-the-art tools (CNTK, PyTorch, Caffe, MXNet, TensorFlow) and choose the combination that is best for them. ONNX is developed and supported by a community of partners including Microsoft AI, Facebook, and Amazon. For more information, explore the [ONNX website](http://onnx.ai) and [open source files](https://github.com/onnx).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"[ONNX Runtime](https://aka.ms/onnxruntime-python) is the runtime engine that enables evaluation of trained machine learning (Traditional ML and Deep Learning) models with high performance and low resource utilization.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Tutorial Objectives:\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- Describe the MNIST dataset and pretrained Convolutional Neural Net ONNX model, stored in the ONNX model zoo.\n",
|
||||
"- Deploy and run the pretrained MNIST ONNX model on an Azure Machine Learning instance\n",
|
||||
"- Predict labels for test set data points in the cloud using ONNX Runtime and Azure ML"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Prerequisites\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### 1. Install Azure ML SDK and create a new workspace\n",
|
||||
"Please follow [Azure ML configuration notebook](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/blob/master/00.configuration.ipynb) to set up your environment.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### 2. Install additional packages needed for this tutorial notebook\n",
|
||||
"You need to install the popular plotting library `matplotlib`, the image manipulation library `opencv`, and the `onnx` library in the conda environment where Azure Maching Learning SDK is installed. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"```sh\n",
|
||||
"(myenv) $ pip install matplotlib onnx opencv-python\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Debugging tip**: Make sure that you run the \"jupyter notebook\" command to launch this notebook after activating your virtual environment. Choose the respective Python kernel for your new virtual environment using the `Kernel > Change Kernel` menu above. If you have completed the steps correctly, the upper right corner of your screen should state `Python [conda env:myenv]` instead of `Python [default]`.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### 3. Download sample data and pre-trained ONNX model from ONNX Model Zoo.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In the following lines of code, we download [the trained ONNX MNIST model and corresponding test data](https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/master/mnist) and place them in the same folder as this tutorial notebook. For more information about the MNIST dataset, please visit [Yan LeCun's website](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/)."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# urllib is a built-in Python library to download files from URLs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Objective: retrieve the latest version of the ONNX MNIST model files from the\n",
|
||||
"# ONNX Model Zoo and save it in the same folder as this tutorial\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import urllib.request\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"onnx_model_url = \"https://www.cntk.ai/OnnxModels/mnist/opset_7/mnist.tar.gz\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"urllib.request.urlretrieve(onnx_model_url, filename=\"mnist.tar.gz\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# the ! magic command tells our jupyter notebook kernel to run the following line of \n",
|
||||
"# code from the command line instead of the notebook kernel\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# We use tar and xvcf to unzip the files we just retrieved from the ONNX model zoo\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"!tar xvzf mnist.tar.gz"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Deploy a VM with your ONNX model in the Cloud\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Load Azure ML workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"We begin by instantiating a workspace object from the existing workspace created earlier in the configuration notebook."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Check core SDK version number\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(\"SDK version:\", azureml.core.VERSION)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"print(ws.name, ws.resource_group, ws.location, sep = '\\n')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Registering your model with Azure ML"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model_dir = \"mnist\" # replace this with the location of your model files\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# leave as is if it's in the same folder as this notebook"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.model import Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"model = Model.register(workspace = ws,\n",
|
||||
" model_path = model_dir + \"/\" + \"model.onnx\",\n",
|
||||
" model_name = \"mnist_1\",\n",
|
||||
" tags = {\"onnx\": \"demo\"},\n",
|
||||
" description = \"MNIST image classification CNN from ONNX Model Zoo\",)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Optional: Displaying your registered models\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This step is not required, so feel free to skip it."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"models = ws.models\n",
|
||||
"for name, m in models.items():\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Name:\", name,\"\\tVersion:\", m.version, \"\\tDescription:\", m.description, m.tags)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"nbpresent": {
|
||||
"id": "c3f2f57c-7454-4d3e-b38d-b0946cf066ea"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### ONNX MNIST Model Methodology\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The image classification model we are using is pre-trained using Microsoft's deep learning cognitive toolkit, [CNTK](https://github.com/Microsoft/CNTK), from the [ONNX model zoo](http://github.com/onnx/models). The model zoo has many other models that can be deployed on cloud providers like AzureML without any additional training. To ensure that our cloud deployed model works, we use testing data from the famous MNIST data set, provided as part of the [trained MNIST model](https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/master/mnist) in the ONNX model zoo.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"***Input: Handwritten Images from MNIST Dataset***\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"***Task: Classify each MNIST image into an appropriate digit***\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"***Output: Digit prediction for input image***\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Run the cell below to look at some of the sample images from the MNIST dataset that we used to train this ONNX model. Remember, once the application is deployed in Azure ML, you can use your own images as input for the model to classify!"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# for images and plots in this notebook\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt \n",
|
||||
"from IPython.display import Image\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# display images inline\n",
|
||||
"%matplotlib inline"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Image(url=\"http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_UpN7DfJA0j4/TJtUBWPk0SI/AAAAAAAAABY/oWPMtmqJn3k/s1600/mnist_originals.png\", width=200, height=200)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Specify our Score and Environment Files"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"We are now going to deploy our ONNX Model on AML with inference in ONNX Runtime. We begin by writing a score.py file, which will help us run the model in our Azure ML virtual machine (VM), and then specify our environment by writing a yml file. You will also notice that we import the onnxruntime library to do runtime inference on our ONNX models (passing in input and evaluating out model's predicted output). More information on the API and commands can be found in the [ONNX Runtime documentation](https://aka.ms/onnxruntime).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Write Score File\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"A score file is what tells our Azure cloud service what to do. After initializing our model using azureml.core.model, we start an ONNX Runtime inference session to evaluate the data passed in on our function calls."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%%writefile score.py\n",
|
||||
"import json\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"import onnxruntime\n",
|
||||
"import sys\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.model import Model\n",
|
||||
"import time\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def init():\n",
|
||||
" global session, input_name, output_name\n",
|
||||
" model = Model.get_model_path(model_name = 'mnist_1')\n",
|
||||
" session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(model, None)\n",
|
||||
" input_name = session.get_inputs()[0].name\n",
|
||||
" output_name = session.get_outputs()[0].name \n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"def run(input_data):\n",
|
||||
" '''Purpose: evaluate test input in Azure Cloud using onnxruntime.\n",
|
||||
" We will call the run function later from our Jupyter Notebook \n",
|
||||
" so our azure service can evaluate our model input in the cloud. '''\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" try:\n",
|
||||
" # load in our data, convert to readable format\n",
|
||||
" data = np.array(json.loads(input_data)['data']).astype('float32')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" start = time.time()\n",
|
||||
" r = session.run([output_name], {input_name: data})[0]\n",
|
||||
" end = time.time()\n",
|
||||
" result = choose_class(r[0])\n",
|
||||
" result_dict = {\"result\": [result],\n",
|
||||
" \"time_in_sec\": [end - start]}\n",
|
||||
" except Exception as e:\n",
|
||||
" result_dict = {\"error\": str(e)}\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" return json.dumps(result_dict)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def choose_class(result_prob):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"We use argmax to determine the right label to choose from our output\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" return int(np.argmax(result_prob, axis=0))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Write Environment File\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This step creates a YAML environment file that specifies which dependencies we would like to see in our Linux Virtual Machine."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"myenv = CondaDependencies.create(pip_packages=[\"numpy\", \"onnxruntime\", \"azureml-core\"])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with open(\"myenv.yml\",\"w\") as f:\n",
|
||||
" f.write(myenv.serialize_to_string())"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Create the Container Image\n",
|
||||
"This step will likely take a few minutes."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.image import ContainerImage\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"image_config = ContainerImage.image_configuration(execution_script = \"score.py\",\n",
|
||||
" runtime = \"python\",\n",
|
||||
" conda_file = \"myenv.yml\",\n",
|
||||
" description = \"MNIST ONNX Runtime container\",\n",
|
||||
" tags = {\"demo\": \"onnx\"}) \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"image = ContainerImage.create(name = \"onnximage\",\n",
|
||||
" # this is the model object\n",
|
||||
" models = [model],\n",
|
||||
" image_config = image_config,\n",
|
||||
" workspace = ws)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"image.wait_for_creation(show_output = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"In case you need to debug your code, the next line of code accesses the log file."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"print(image.image_build_log_uri)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"We're all done specifying what we want our virtual machine to do. Let's configure and deploy our container image.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Deploy the container image"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.webservice import AciWebservice\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aciconfig = AciWebservice.deploy_configuration(cpu_cores = 1, \n",
|
||||
" memory_gb = 1, \n",
|
||||
" tags = {'demo': 'onnx'}, \n",
|
||||
" description = 'ONNX for mnist model')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"The following cell will likely take a few minutes to run as well."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.webservice import Webservice\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aci_service_name = 'onnx-demo-mnist'\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Service\", aci_service_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aci_service = Webservice.deploy_from_image(deployment_config = aciconfig,\n",
|
||||
" image = image,\n",
|
||||
" name = aci_service_name,\n",
|
||||
" workspace = ws)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aci_service.wait_for_deployment(True)\n",
|
||||
"print(aci_service.state)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"if aci_service.state != 'Healthy':\n",
|
||||
" # run this command for debugging.\n",
|
||||
" print(aci_service.get_logs())\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # If your deployment fails, make sure to delete your aci_service or rename your service before trying again!\n",
|
||||
" # aci_service.delete()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Success!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"If you've made it this far, you've deployed a working VM with a handwritten digit classifier running in the cloud using Azure ML. Congratulations!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Let's see how well our model deals with our test images."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Testing and Evaluation\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Load Test Data\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"These are already in your directory from your ONNX model download (from the model zoo).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Notice that our Model Zoo files have a .pb extension. This is because they are [protobuf files (Protocol Buffers)](https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/pythontutorial), so we need to read in our data through our ONNX TensorProto reader into a format we can work with, like numerical arrays."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# to manipulate our arrays\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# read in test data protobuf files included with the model\n",
|
||||
"import onnx\n",
|
||||
"from onnx import numpy_helper\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# to use parsers to read in our model/data\n",
|
||||
"import json\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"test_inputs = []\n",
|
||||
"test_outputs = []\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# read in 3 testing images from .pb files\n",
|
||||
"test_data_size = 3\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for i in np.arange(test_data_size):\n",
|
||||
" input_test_data = os.path.join(model_dir, 'test_data_set_{0}'.format(i), 'input_0.pb')\n",
|
||||
" output_test_data = os.path.join(model_dir, 'test_data_set_{0}'.format(i), 'output_0.pb')\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # convert protobuf tensors to np arrays using the TensorProto reader from ONNX\n",
|
||||
" tensor = onnx.TensorProto()\n",
|
||||
" with open(input_test_data, 'rb') as f:\n",
|
||||
" tensor.ParseFromString(f.read())\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" input_data = numpy_helper.to_array(tensor)\n",
|
||||
" test_inputs.append(input_data)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" with open(output_test_data, 'rb') as f:\n",
|
||||
" tensor.ParseFromString(f.read())\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" output_data = numpy_helper.to_array(tensor)\n",
|
||||
" test_outputs.append(output_data)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"if len(test_inputs) == test_data_size:\n",
|
||||
" print('Test data loaded successfully.')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"nbpresent": {
|
||||
"id": "c3f2f57c-7454-4d3e-b38d-b0946cf066ea"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Show some sample images\n",
|
||||
"We use `matplotlib` to plot 3 test images from the dataset."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"nbpresent": {
|
||||
"id": "396d478b-34aa-4afa-9898-cdce8222a516"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6))\n",
|
||||
"for test_image in np.arange(3):\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1, 15, test_image+1)\n",
|
||||
" plt.axhline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.axvline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(test_inputs[test_image].reshape(28, 28), cmap = plt.cm.Greys)\n",
|
||||
"plt.show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Run evaluation / prediction"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6), frameon=False)\n",
|
||||
"plt.subplot(1, 8, 1)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 0, y = -30, s = \"True Label: \", fontsize = 13, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 0, y = -20, s = \"Result: \", fontsize = 13, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 0, y = -10, s = \"Inference Time: \", fontsize = 13, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 3, y = 14, s = \"Model Input\", fontsize = 12, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 6, y = 18, s = \"(28 x 28)\", fontsize = 12, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.imshow(np.ones((28,28)), cmap=plt.cm.Greys) \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for i in np.arange(test_data_size):\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" input_data = json.dumps({'data': test_inputs[i].tolist()})\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # predict using the deployed model\n",
|
||||
" r = json.loads(aci_service.run(input_data))\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" if \"error\" in r:\n",
|
||||
" print(r['error'])\n",
|
||||
" break\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" result = r['result'][0]\n",
|
||||
" time_ms = np.round(r['time_in_sec'][0] * 1000, 2)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" ground_truth = int(np.argmax(test_outputs[i]))\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # compare actual value vs. the predicted values:\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1, 8, i+2)\n",
|
||||
" plt.axhline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.axvline('')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # use different color for misclassified sample\n",
|
||||
" font_color = 'red' if ground_truth != result else 'black'\n",
|
||||
" clr_map = plt.cm.gray if ground_truth != result else plt.cm.Greys\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # ground truth labels are in blue\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 10, y = -30, s = ground_truth, fontsize = 18, color = 'blue')\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # predictions are in black if correct, red if incorrect\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 10, y = -20, s = result, fontsize = 18, color = font_color)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 5, y = -10, s = str(time_ms) + ' ms', fontsize = 14, color = font_color)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(test_inputs[i].reshape(28, 28), cmap = clr_map)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"plt.show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Try classifying your own images!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Create your own handwritten image and pass it into the model."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Preprocessing functions take your image and format it so it can be passed\n",
|
||||
"# as input into our ONNX model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import cv2\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def rgb2gray(rgb):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Convert the input image into grayscale\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" return np.dot(rgb[...,:3], [0.299, 0.587, 0.114])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def resize_img(img):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Resize image to MNIST model input dimensions\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" img = cv2.resize(img, dsize=(28, 28), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)\n",
|
||||
" img.resize((1, 1, 28, 28))\n",
|
||||
" return img\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def preprocess(img):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Resize input images and convert them to grayscale.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" if img.shape == (28, 28):\n",
|
||||
" img.resize((1, 1, 28, 28))\n",
|
||||
" return img\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" grayscale = rgb2gray(img)\n",
|
||||
" processed_img = resize_img(grayscale)\n",
|
||||
" return processed_img"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Replace this string with your own path/test image\n",
|
||||
"# Make sure your image is square and the dimensions are equal (i.e. 100 * 100 pixels or 28 * 28 pixels)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Any PNG or JPG image file should work\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"your_test_image = \"<path to file>\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# e.g. your_test_image = \"C:/Users/vinitra.swamy/Pictures/handwritten_digit.png\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib.image as mpimg\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"if your_test_image != \"<path to file>\":\n",
|
||||
" img = mpimg.imread(your_test_image)\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1,3,1)\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(img, cmap = plt.cm.Greys)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Old Dimensions: \", img.shape)\n",
|
||||
" img = preprocess(img)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"New Dimensions: \", img.shape)\n",
|
||||
"else:\n",
|
||||
" img = None"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"if img is None:\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Add the path for your image data.\")\n",
|
||||
"else:\n",
|
||||
" input_data = json.dumps({'data': img.tolist()})\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" try:\n",
|
||||
" r = json.loads(aci_service.run(input_data))\n",
|
||||
" result = r['result'][0]\n",
|
||||
" time_ms = np.round(r['time_in_sec'][0] * 1000, 2)\n",
|
||||
" except Exception as e:\n",
|
||||
" print(str(e))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6))\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1, 15,1)\n",
|
||||
" plt.axhline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.axvline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = -100, y = -20, s = \"Model prediction: \", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = -100, y = -10, s = \"Inference time: \", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 0, y = -20, s = str(result), fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 0, y = -10, s = str(time_ms) + \" ms\", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = -100, y = 14, s = \"Input image: \", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(img.reshape(28, 28), cmap = plt.cm.gray) "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Optional: How does our ONNX MNIST model work? \n",
|
||||
"#### A brief explanation of Convolutional Neural Networks\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"A [convolutional neural network](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convolutional_neural_network) (CNN, or ConvNet) is a type of [feed-forward](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feedforward_neural_network) artificial neural network made up of neurons that have learnable weights and biases. The CNNs take advantage of the spatial nature of the data. In nature, we perceive different objects by their shapes, size and colors. For example, objects in a natural scene are typically edges, corners/vertices (defined by two of more edges), color patches etc. These primitives are often identified using different detectors (e.g., edge detection, color detector) or combination of detectors interacting to facilitate image interpretation (object classification, region of interest detection, scene description etc.) in real world vision related tasks. These detectors are also known as filters. Convolution is a mathematical operator that takes an image and a filter as input and produces a filtered output (representing say edges, corners, or colors in the input image). \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Historically, these filters are a set of weights that were often hand crafted or modeled with mathematical functions (e.g., [Gaussian](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gaussian_filter) / [Laplacian](http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/HIPR2/log.htm) / [Canny](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Canny_edge_detector) filter). The filter outputs are mapped through non-linear activation functions mimicking human brain cells called [neurons](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuron). Popular deep CNNs or ConvNets (such as [AlexNet](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AlexNet), [VGG](https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556), [Inception](http://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_2015/papers/Szegedy_Going_Deeper_With_2015_CVPR_paper.pdf), [ResNet](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385v1.pdf)) that are used for various [computer vision](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_vision) tasks have many of these architectural primitives (inspired from biology). \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Convolution Layer\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"A convolution layer is a set of filters. Each filter is defined by a weight (**W**) matrix, and bias ($b$).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"These filters are scanned across the image performing the dot product between the weights and corresponding input value ($x$). The bias value is added to the output of the dot product and the resulting sum is optionally mapped through an activation function. This process is illustrated in the following animation."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Image(url=\"https://www.cntk.ai/jup/cntk103d_conv2d_final.gif\", width= 200)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Model Description\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The MNIST model from the ONNX Model Zoo uses maxpooling to update the weights in its convolutions, summarized by the graphic below. You can see the entire workflow of our pre-trained model in the following image, with our input images and our output probabilities of each of our 10 labels. If you're interested in exploring the logic behind creating a Deep Learning model further, please look at the [training tutorial for our ONNX MNIST Convolutional Neural Network](https://github.com/Microsoft/CNTK/blob/master/Tutorials/CNTK_103D_MNIST_ConvolutionalNeuralNetwork.ipynb). "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Max-Pooling for Convolutional Neural Nets\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
""
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Pre-Trained Model Architecture\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
""
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# remember to delete your service after you are done using it!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# aci_service.delete()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Conclusion\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Congratulations!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this tutorial, you have:\n",
|
||||
"- familiarized yourself with ONNX Runtime inference and the pretrained models in the ONNX model zoo\n",
|
||||
"- understood a state-of-the-art convolutional neural net image classification model (MNIST in ONNX) and deployed it in Azure ML cloud\n",
|
||||
"- ensured that your deep learning model is working perfectly (in the cloud) on test data, and checked it against some of your own!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Next steps:\n",
|
||||
"- Check out another interesting application based on a Microsoft Research computer vision paper that lets you set up a [facial emotion recognition model](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/tree/master/onnx/onnx-inference-emotion-recognition.ipynb) in the cloud! This tutorial deploys a pre-trained ONNX Computer Vision model in an Azure ML virtual machine.\n",
|
||||
"- Contribute to our [open source ONNX repository on github](http://github.com/onnx/onnx) and/or add to our [ONNX model zoo](http://github.com/onnx/models)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "viswamy"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.6",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"msauthor": "vinitra.swamy"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -1,804 +0,0 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. \n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Handwritten Digit Classification (MNIST) using ONNX Runtime on Azure ML\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This example shows how to deploy an image classification neural network using the Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology ([MNIST](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/)) dataset and Open Neural Network eXchange format ([ONNX](http://aka.ms/onnxdocarticle)) on the Azure Machine Learning platform. MNIST is a popular dataset consisting of 70,000 grayscale images. Each image is a handwritten digit of 28x28 pixels, representing number from 0 to 9. This tutorial will show you how to deploy a MNIST model from the [ONNX model zoo](https://github.com/onnx/models), use it to make predictions using ONNX Runtime Inference, and deploy it as a web service in Azure.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Throughout this tutorial, we will be referring to ONNX, a neural network exchange format used to represent deep learning models. With ONNX, AI developers can more easily move models between state-of-the-art tools (CNTK, PyTorch, Caffe, MXNet, TensorFlow) and choose the combination that is best for them. ONNX is developed and supported by a community of partners including Microsoft AI, Facebook, and Amazon. For more information, explore the [ONNX website](http://onnx.ai) and [open source files](https://github.com/onnx).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"[ONNX Runtime](https://aka.ms/onnxruntime-python) is the runtime engine that enables evaluation of trained machine learning (Traditional ML and Deep Learning) models with high performance and low resource utilization.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Tutorial Objectives:\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- Describe the MNIST dataset and pretrained Convolutional Neural Net ONNX model, stored in the ONNX model zoo.\n",
|
||||
"- Deploy and run the pretrained MNIST ONNX model on an Azure Machine Learning instance\n",
|
||||
"- Predict labels for test set data points in the cloud using ONNX Runtime and Azure ML"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Prerequisites\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### 1. Install Azure ML SDK and create a new workspace\n",
|
||||
"Please follow [Azure ML configuration notebook](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/blob/master/00.configuration.ipynb) to set up your environment.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### 2. Install additional packages needed for this tutorial notebook\n",
|
||||
"You need to install the popular plotting library `matplotlib`, the image manipulation library `opencv`, and the `onnx` library in the conda environment where Azure Maching Learning SDK is installed. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"```sh\n",
|
||||
"(myenv) $ pip install matplotlib onnx opencv-python\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Debugging tip**: Make sure that you run the \"jupyter notebook\" command to launch this notebook after activating your virtual environment. Choose the respective Python kernel for your new virtual environment using the `Kernel > Change Kernel` menu above. If you have completed the steps correctly, the upper right corner of your screen should state `Python [conda env:myenv]` instead of `Python [default]`.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### 3. Download sample data and pre-trained ONNX model from ONNX Model Zoo.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In the following lines of code, we download [the trained ONNX MNIST model and corresponding test data](https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/master/mnist) and place them in the same folder as this tutorial notebook. For more information about the MNIST dataset, please visit [Yan LeCun's website](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/)."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# urllib is a built-in Python library to download files from URLs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Objective: retrieve the latest version of the ONNX MNIST model files from the\n",
|
||||
"# ONNX Model Zoo and save it in the same folder as this tutorial\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import urllib.request\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"onnx_model_url = \"https://www.cntk.ai/OnnxModels/mnist/opset_7/mnist.tar.gz\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"urllib.request.urlretrieve(onnx_model_url, filename=\"mnist.tar.gz\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# the ! magic command tells our jupyter notebook kernel to run the following line of \n",
|
||||
"# code from the command line instead of the notebook kernel\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# We use tar and xvcf to unzip the files we just retrieved from the ONNX model zoo\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"!tar xvzf mnist.tar.gz"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Deploy a VM with your ONNX model in the Cloud\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Load Azure ML workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"We begin by instantiating a workspace object from the existing workspace created earlier in the configuration notebook."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Check core SDK version number\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(\"SDK version:\", azureml.core.VERSION)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"print(ws.name, ws.resource_group, ws.location, sep = '\\n')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Registering your model with Azure ML"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model_dir = \"mnist\" # replace this with the location of your model files\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# leave as is if it's in the same folder as this notebook"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.model import Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"model = Model.register(workspace = ws,\n",
|
||||
" model_path = model_dir + \"/\" + \"model.onnx\",\n",
|
||||
" model_name = \"mnist_1\",\n",
|
||||
" tags = {\"onnx\": \"demo\"},\n",
|
||||
" description = \"MNIST image classification CNN from ONNX Model Zoo\",)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Optional: Displaying your registered models\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This step is not required, so feel free to skip it."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"models = ws.models()\n",
|
||||
"for name, m in models.items():\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Name:\", name,\"\\tVersion:\", m.version, \"\\tDescription:\", m.description, m.tags)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"nbpresent": {
|
||||
"id": "c3f2f57c-7454-4d3e-b38d-b0946cf066ea"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### ONNX MNIST Model Methodology\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The image classification model we are using is pre-trained using Microsoft's deep learning cognitive toolkit, [CNTK](https://github.com/Microsoft/CNTK), from the [ONNX model zoo](http://github.com/onnx/models). The model zoo has many other models that can be deployed on cloud providers like AzureML without any additional training. To ensure that our cloud deployed model works, we use testing data from the famous MNIST data set, provided as part of the [trained MNIST model](https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/master/mnist) in the ONNX model zoo.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"***Input: Handwritten Images from MNIST Dataset***\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"***Task: Classify each MNIST image into an appropriate digit***\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"***Output: Digit prediction for input image***\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Run the cell below to look at some of the sample images from the MNIST dataset that we used to train this ONNX model. Remember, once the application is deployed in Azure ML, you can use your own images as input for the model to classify!"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# for images and plots in this notebook\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt \n",
|
||||
"from IPython.display import Image\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# display images inline\n",
|
||||
"%matplotlib inline"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Image(url=\"http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_UpN7DfJA0j4/TJtUBWPk0SI/AAAAAAAAABY/oWPMtmqJn3k/s1600/mnist_originals.png\", width=200, height=200)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Specify our Score and Environment Files"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"We are now going to deploy our ONNX Model on AML with inference in ONNX Runtime. We begin by writing a score.py file, which will help us run the model in our Azure ML virtual machine (VM), and then specify our environment by writing a yml file. You will also notice that we import the onnxruntime library to do runtime inference on our ONNX models (passing in input and evaluating out model's predicted output). More information on the API and commands can be found in the [ONNX Runtime documentation](https://aka.ms/onnxruntime).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Write Score File\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"A score file is what tells our Azure cloud service what to do. After initializing our model using azureml.core.model, we start an ONNX Runtime inference session to evaluate the data passed in on our function calls."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%%writefile score.py\n",
|
||||
"import json\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"import onnxruntime\n",
|
||||
"import sys\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.model import Model\n",
|
||||
"import time\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def init():\n",
|
||||
" global session, input_name, output_name\n",
|
||||
" model = Model.get_model_path(model_name = 'mnist_1')\n",
|
||||
" session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(model, None)\n",
|
||||
" input_name = session.get_inputs()[0].name\n",
|
||||
" output_name = session.get_outputs()[0].name \n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"def run(input_data):\n",
|
||||
" '''Purpose: evaluate test input in Azure Cloud using onnxruntime.\n",
|
||||
" We will call the run function later from our Jupyter Notebook \n",
|
||||
" so our azure service can evaluate our model input in the cloud. '''\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" try:\n",
|
||||
" # load in our data, convert to readable format\n",
|
||||
" data = np.array(json.loads(input_data)['data']).astype('float32')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" start = time.time()\n",
|
||||
" r = session.run([output_name], {input_name: data})[0]\n",
|
||||
" end = time.time()\n",
|
||||
" result = choose_class(r[0])\n",
|
||||
" result_dict = {\"result\": [result],\n",
|
||||
" \"time_in_sec\": [end - start]}\n",
|
||||
" except Exception as e:\n",
|
||||
" result_dict = {\"error\": str(e)}\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" return json.dumps(result_dict)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def choose_class(result_prob):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"We use argmax to determine the right label to choose from our output\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" return int(np.argmax(result_prob, axis=0))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Write Environment File\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This step creates a YAML environment file that specifies which dependencies we would like to see in our Linux Virtual Machine."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"myenv = CondaDependencies()\n",
|
||||
"myenv.add_pip_package(\"numpy\")\n",
|
||||
"myenv.add_pip_package(\"azureml-core\")\n",
|
||||
"myenv.add_pip_package(\"onnxruntime\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with open(\"myenv.yml\",\"w\") as f:\n",
|
||||
" f.write(myenv.serialize_to_string())"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Create the Container Image\n",
|
||||
"This step will likely take a few minutes."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.image import ContainerImage\n",
|
||||
"help(ContainerImage.image_configuration)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.image import ContainerImage\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"image_config = ContainerImage.image_configuration(execution_script = \"score.py\",\n",
|
||||
" runtime = \"python\",\n",
|
||||
" conda_file = \"myenv.yml\",\n",
|
||||
" description = \"MNIST ONNX Runtime container\",\n",
|
||||
" tags = {\"demo\": \"onnx\"}) \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"image = ContainerImage.create(name = \"onnxtest\",\n",
|
||||
" # this is the model object\n",
|
||||
" models = [model],\n",
|
||||
" image_config = image_config,\n",
|
||||
" workspace = ws)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"image.wait_for_creation(show_output = True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"In case you need to debug your code, the next line of code accesses the log file."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"print(image.image_build_log_uri)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"We're all done specifying what we want our virtual machine to do. Let's configure and deploy our container image.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Deploy the container image"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.webservice import AciWebservice\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aciconfig = AciWebservice.deploy_configuration(cpu_cores = 1, \n",
|
||||
" memory_gb = 1, \n",
|
||||
" tags = {'demo': 'onnx'}, \n",
|
||||
" description = 'ONNX for mnist model')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"The following cell will likely take a few minutes to run as well."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.webservice import Webservice\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aci_service_name = 'onnx-demo-mnist20'\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Service\", aci_service_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aci_service = Webservice.deploy_from_image(deployment_config = aciconfig,\n",
|
||||
" image = image,\n",
|
||||
" name = aci_service_name,\n",
|
||||
" workspace = ws)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aci_service.wait_for_deployment(True)\n",
|
||||
"print(aci_service.state)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"if aci_service.state != 'Healthy':\n",
|
||||
" # run this command for debugging.\n",
|
||||
" print(aci_service.get_logs())\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # If your deployment fails, make sure to delete your aci_service or rename your service before trying again!\n",
|
||||
" # aci_service.delete()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Success!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"If you've made it this far, you've deployed a working VM with a handwritten digit classifier running in the cloud using Azure ML. Congratulations!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Let's see how well our model deals with our test images."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Testing and Evaluation\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Load Test Data\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"These are already in your directory from your ONNX model download (from the model zoo).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Notice that our Model Zoo files have a .pb extension. This is because they are [protobuf files (Protocol Buffers)](https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/pythontutorial), so we need to read in our data through our ONNX TensorProto reader into a format we can work with, like numerical arrays."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# to manipulate our arrays\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# read in test data protobuf files included with the model\n",
|
||||
"import onnx\n",
|
||||
"from onnx import numpy_helper\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# to use parsers to read in our model/data\n",
|
||||
"import json\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"test_inputs = []\n",
|
||||
"test_outputs = []\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# read in 3 testing images from .pb files\n",
|
||||
"test_data_size = 3\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for i in np.arange(test_data_size):\n",
|
||||
" input_test_data = os.path.join(model_dir, 'test_data_set_{0}'.format(i), 'input_0.pb')\n",
|
||||
" output_test_data = os.path.join(model_dir, 'test_data_set_{0}'.format(i), 'output_0.pb')\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # convert protobuf tensors to np arrays using the TensorProto reader from ONNX\n",
|
||||
" tensor = onnx.TensorProto()\n",
|
||||
" with open(input_test_data, 'rb') as f:\n",
|
||||
" tensor.ParseFromString(f.read())\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" input_data = numpy_helper.to_array(tensor)\n",
|
||||
" test_inputs.append(input_data)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" with open(output_test_data, 'rb') as f:\n",
|
||||
" tensor.ParseFromString(f.read())\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" output_data = numpy_helper.to_array(tensor)\n",
|
||||
" test_outputs.append(output_data)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"if len(test_inputs) == test_data_size:\n",
|
||||
" print('Test data loaded successfully.')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"nbpresent": {
|
||||
"id": "c3f2f57c-7454-4d3e-b38d-b0946cf066ea"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Show some sample images\n",
|
||||
"We use `matplotlib` to plot 3 test images from the dataset."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"nbpresent": {
|
||||
"id": "396d478b-34aa-4afa-9898-cdce8222a516"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6))\n",
|
||||
"for test_image in np.arange(3):\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1, 15, test_image+1)\n",
|
||||
" plt.axhline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.axvline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(test_inputs[test_image].reshape(28, 28), cmap = plt.cm.Greys)\n",
|
||||
"plt.show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Run evaluation / prediction"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6), frameon=False)\n",
|
||||
"plt.subplot(1, 8, 1)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 0, y = -30, s = \"True Label: \", fontsize = 13, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 0, y = -20, s = \"Result: \", fontsize = 13, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 0, y = -10, s = \"Inference Time: \", fontsize = 13, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 3, y = 14, s = \"Model Input\", fontsize = 12, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.text(x = 6, y = 18, s = \"(28 x 28)\", fontsize = 12, color = 'black')\n",
|
||||
"plt.imshow(np.ones((28,28)), cmap=plt.cm.Greys) \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for i in np.arange(test_data_size):\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" input_data = json.dumps({'data': test_inputs[i].tolist()})\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # predict using the deployed model\n",
|
||||
" r = json.loads(aci_service.run(input_data))\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" if \"error\" in r:\n",
|
||||
" print(r['error'])\n",
|
||||
" break\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" result = r['result'][0]\n",
|
||||
" time_ms = np.round(r['time_in_sec'][0] * 1000, 2)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" ground_truth = int(np.argmax(test_outputs[i]))\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # compare actual value vs. the predicted values:\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1, 8, i+2)\n",
|
||||
" plt.axhline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.axvline('')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # use different color for misclassified sample\n",
|
||||
" font_color = 'red' if ground_truth != result else 'black'\n",
|
||||
" clr_map = plt.cm.gray if ground_truth != result else plt.cm.Greys\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # ground truth labels are in blue\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 10, y = -30, s = ground_truth, fontsize = 18, color = 'blue')\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # predictions are in black if correct, red if incorrect\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 10, y = -20, s = result, fontsize = 18, color = font_color)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 5, y = -10, s = str(time_ms) + ' ms', fontsize = 14, color = font_color)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(test_inputs[i].reshape(28, 28), cmap = clr_map)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"plt.show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Try classifying your own images!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Create your own handwritten image and pass it into the model."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Preprocessing functions take your image and format it so it can be passed\n",
|
||||
"# as input into our ONNX model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import cv2\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def rgb2gray(rgb):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Convert the input image into grayscale\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" return np.dot(rgb[...,:3], [0.299, 0.587, 0.114])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def resize_img(img):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Resize image to MNIST model input dimensions\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" img = cv2.resize(img, dsize=(28, 28), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)\n",
|
||||
" img.resize((1, 1, 28, 28))\n",
|
||||
" return img\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def preprocess(img):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Resize input images and convert them to grayscale.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" if img.shape == (28, 28):\n",
|
||||
" img.resize((1, 1, 28, 28))\n",
|
||||
" return img\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" grayscale = rgb2gray(img)\n",
|
||||
" processed_img = resize_img(grayscale)\n",
|
||||
" return processed_img"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Replace this string with your own path/test image\n",
|
||||
"# Make sure your image is square and the dimensions are equal (i.e. 100 * 100 pixels or 28 * 28 pixels)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Any PNG or JPG image file should work\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# e.g. your_test_image = \"C:/Users/vinitra.swamy/Pictures/handwritten_digit.png\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib.image as mpimg\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"if your_test_image != \"<path to file>\":\n",
|
||||
" img = mpimg.imread(your_test_image)\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1,3,1)\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(img, cmap = plt.cm.Greys)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Old Dimensions: \", img.shape)\n",
|
||||
" img = preprocess(img)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"New Dimensions: \", img.shape)\n",
|
||||
"else:\n",
|
||||
" img = None"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"if img is None:\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Add the path for your image data.\")\n",
|
||||
"else:\n",
|
||||
" input_data = json.dumps({'data': img.tolist()})\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" try:\n",
|
||||
" r = json.loads(aci_service.run(input_data))\n",
|
||||
" result = r['result'][0]\n",
|
||||
" time_ms = np.round(r['time_in_sec'][0] * 1000, 2)\n",
|
||||
" except Exception as e:\n",
|
||||
" print(str(e))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6))\n",
|
||||
" plt.subplot(1, 15,1)\n",
|
||||
" plt.axhline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.axvline('')\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = -100, y = -20, s = \"Model prediction: \", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = -100, y = -10, s = \"Inference time: \", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 0, y = -20, s = str(result), fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = 0, y = -10, s = str(time_ms) + \" ms\", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.text(x = -100, y = 14, s = \"Input image: \", fontsize = 14)\n",
|
||||
" plt.imshow(img.reshape(28, 28), cmap = plt.cm.gray) "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Optional: How does our ONNX MNIST model work? \n",
|
||||
"#### A brief explanation of Convolutional Neural Networks\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"A [convolutional neural network](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convolutional_neural_network) (CNN, or ConvNet) is a type of [feed-forward](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feedforward_neural_network) artificial neural network made up of neurons that have learnable weights and biases. The CNNs take advantage of the spatial nature of the data. In nature, we perceive different objects by their shapes, size and colors. For example, objects in a natural scene are typically edges, corners/vertices (defined by two of more edges), color patches etc. These primitives are often identified using different detectors (e.g., edge detection, color detector) or combination of detectors interacting to facilitate image interpretation (object classification, region of interest detection, scene description etc.) in real world vision related tasks. These detectors are also known as filters. Convolution is a mathematical operator that takes an image and a filter as input and produces a filtered output (representing say edges, corners, or colors in the input image). \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Historically, these filters are a set of weights that were often hand crafted or modeled with mathematical functions (e.g., [Gaussian](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gaussian_filter) / [Laplacian](http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/HIPR2/log.htm) / [Canny](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Canny_edge_detector) filter). The filter outputs are mapped through non-linear activation functions mimicking human brain cells called [neurons](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuron). Popular deep CNNs or ConvNets (such as [AlexNet](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AlexNet), [VGG](https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556), [Inception](http://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_2015/papers/Szegedy_Going_Deeper_With_2015_CVPR_paper.pdf), [ResNet](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385v1.pdf)) that are used for various [computer vision](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_vision) tasks have many of these architectural primitives (inspired from biology). \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Convolution Layer\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"A convolution layer is a set of filters. Each filter is defined by a weight (**W**) matrix, and bias ($b$).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"These filters are scanned across the image performing the dot product between the weights and corresponding input value ($x$). The bias value is added to the output of the dot product and the resulting sum is optionally mapped through an activation function. This process is illustrated in the following animation."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Image(url=\"https://www.cntk.ai/jup/cntk103d_conv2d_final.gif\", width= 200)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Model Description\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The MNIST model from the ONNX Model Zoo uses maxpooling to update the weights in its convolutions, summarized by the graphic below. You can see the entire workflow of our pre-trained model in the following image, with our input images and our output probabilities of each of our 10 labels. If you're interested in exploring the logic behind creating a Deep Learning model further, please look at the [training tutorial for our ONNX MNIST Convolutional Neural Network](https://github.com/Microsoft/CNTK/blob/master/Tutorials/CNTK_103D_MNIST_ConvolutionalNeuralNetwork.ipynb). "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Max-Pooling for Convolutional Neural Nets\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
""
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Pre-Trained Model Architecture\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
""
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# remember to delete your service after you are done using it!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aci_service.delete()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Conclusion\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Congratulations!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this tutorial, you have:\n",
|
||||
"- familiarized yourself with ONNX Runtime inference and the pretrained models in the ONNX model zoo\n",
|
||||
"- understood a state-of-the-art convolutional neural net image classification model (MNIST in ONNX) and deployed it in Azure ML cloud\n",
|
||||
"- ensured that your deep learning model is working perfectly (in the cloud) on test data, and checked it against some of your own!\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Next steps:\n",
|
||||
"- Check out another interesting application based on a Microsoft Research computer vision paper that lets you set up a [facial emotion recognition model](https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks/tree/master/onnx/onnx-inference-emotion-recognition.ipynb) in the cloud! This tutorial deploys a pre-trained ONNX Computer Vision model in an Azure ML virtual machine.\n",
|
||||
"- Contribute to our [open source ONNX repository on github](http://github.com/onnx/onnx) and/or add to our [ONNX model zoo](http://github.com/onnx/models)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "viswamy"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.6",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"msauthor": "vinitra.swamy"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -56,11 +56,21 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Download pre-trained ONNX model from ONNX Model Zoo.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Download the [ResNet50v2 model and test data](https://s3.amazonaws.com/onnx-model-zoo/resnet/resnet50v2/resnet50v2.tar.gz) and place it in the same folder as this tutorial notebook. You can unzip the file through the following line of code.\n",
|
||||
"Download the [ResNet50v2 model and test data](https://s3.amazonaws.com/onnx-model-zoo/resnet/resnet50v2/resnet50v2.tar.gz) and extract it in the same folder as this tutorial notebook.\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import urllib.request\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"```sh\n",
|
||||
"(myenv) $ tar xvzf resnet50v2.tar.gz\n",
|
||||
"```"
|
||||
"onnx_model_url = \"https://s3.amazonaws.com/onnx-model-zoo/resnet/resnet50v2/resnet50v2.tar.gz\"\n",
|
||||
"urllib.request.urlretrieve(onnx_model_url, filename=\"resnet50v2.tar.gz\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"!tar xvzf resnet50v2.tar.gz"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -130,9 +140,9 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"models = ws.models()\n",
|
||||
"for m in models:\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Name:\", m.name,\"\\tVersion:\", m.version, \"\\tDescription:\", m.description, m.tags)"
|
||||
"models = ws.models\n",
|
||||
"for name, m in models.items():\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Name:\", name,\"\\tVersion:\", m.version, \"\\tDescription:\", m.description, m.tags)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -222,7 +232,7 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"myenv = CondaDependencies.create(pip_packages=[\"numpy\",\"onnxruntime\"])\n",
|
||||
"myenv = CondaDependencies.create(pip_packages=[\"numpy\",\"onnxruntime\",\"azureml-core\"])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with open(\"myenv.yml\",\"w\") as f:\n",
|
||||
" f.write(myenv.serialize_to_string())"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -76,9 +76,9 @@
|
||||
"## Train model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Create a remote compute target\n",
|
||||
"You will need to create a [compute target](https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/service/concept-azure-machine-learning-architecture#compute-target) to execute your training script on. In this tutorial, you create an [Azure Batch AI](https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/batch-ai/overview) cluster as your training compute resource. This code creates a cluster for you if it does not already exist in your workspace.\n",
|
||||
"You will need to create a [compute target](https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/service/concept-azure-machine-learning-architecture#compute-target) to execute your training script on. In this tutorial, you create AmlCompute as your training compute resource. This code creates new compute for you if it does not already exist in your workspace.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Creation of the cluster takes approximately 5 minutes.** If the cluster is already in your workspace this code will skip the cluster creation process."
|
||||
"**Creation of the compute takes approximately 5 minutes.** If the compute is already in your workspace this code will skip the creation process."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -87,7 +87,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, BatchAiCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute_target import ComputeTargetException\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for your cluster\n",
|
||||
@@ -98,10 +98,8 @@
|
||||
" print('Found existing compute target.')\n",
|
||||
"except ComputeTargetException:\n",
|
||||
" print('Creating a new compute target...')\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = BatchAiCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size='STANDARD_NC6', \n",
|
||||
" autoscale_enabled=True,\n",
|
||||
" cluster_min_nodes=0, \n",
|
||||
" cluster_max_nodes=4)\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size='STANDARD_NC6', \n",
|
||||
" max_nodes=4)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # create the cluster\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = ComputeTarget.create(ws, cluster_name, compute_config)\n",
|
||||
@@ -251,10 +249,26 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Alternatively, you can block until the script has completed training before running more code."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"run.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
@@ -318,9 +332,9 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"models = ws.models()\n",
|
||||
"for m in models:\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Name:\", m.name,\"\\tVersion:\", m.version, \"\\tDescription:\", m.description, m.tags)"
|
||||
"models = ws.models\n",
|
||||
"for name, m in models.items():\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Name:\", name,\"\\tVersion:\", m.version, \"\\tDescription:\", m.description, m.tags)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -392,7 +406,7 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"myenv = CondaDependencies.create(pip_packages=[\"numpy\",\"onnxruntime\"])\n",
|
||||
"myenv = CondaDependencies.create(pip_packages=[\"numpy\",\"onnxruntime\",\"azureml-core\"])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with open(\"myenv.yml\",\"w\") as f:\n",
|
||||
" f.write(myenv.serialize_to_string())"
|
||||
@@ -571,7 +585,7 @@
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.5.6"
|
||||
"version": "3.6.2"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"widgets": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-state+json": {
|
||||
@@ -583,7 +597,7 @@
|
||||
"state": {}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"d146cbdbd4e04710b3eebc15a66957ce": {
|
||||
"model_module": "azureml_train_widgets",
|
||||
"model_module": "azureml_widgets",
|
||||
"model_module_version": "1.0.0",
|
||||
"model_name": "ShowRunDetailsModel",
|
||||
"state": {
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -40,8 +40,8 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"!jupyter nbextension install --py --user azureml.train.widgets\n",
|
||||
"!jupyter nbextension enable --py --user azureml.train.widgets"
|
||||
"!jupyter nbextension install --py --user azureml.widgets\n",
|
||||
"!jupyter nbextension enable --py --user azureml.widgets"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
BIN
pipeline/20news.pkl
Normal file
BIN
pipeline/20news.pkl
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
48
pipeline/README.md
Normal file
48
pipeline/README.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
# Azure Machine Learning Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The [Azure Machine Learning Pipelines](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/service/concept-ml-pipelines) enables data scientists to create and manage multiple simple and complex workflows concurrently. A typical pipeline would have multiple tasks to prepare data, train, deploy and evaluate models. Individual steps in the pipeline can make use of diverse compute options (for example: CPU for data preparation and GPU for training) and languages.
|
||||
|
||||
The Python-based Azure Machine Learning Pipeline SDK provides interfaces to work with Azure Machine Learning Pipelines. To get started quickly, the SDK includes imperative constructs for sequencing and parallelization of steps. With the use of declarative data dependencies, optimized execution of the tasks can be achieved. The SDK can be easily used from Jupyter Notebook or any other preferred IDE. The SDK includes a framework of pre-built modules for common tasks such as data transfer and compute provisioning.
|
||||
|
||||
Data management and reuse across pipelines and pipeline runs is simplified using named and strictly versioned data sources and named inputs and outputs for processing tasks. Pipelines enable collaboration across teams of data scientists by recording all intermediate tasks and data.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why build pipelines?
|
||||
|
||||
With pipelines, you can optimize your workflow with simplicity, speed, portability, and reuse. When building pipelines with Azure Machine Learning, you can focus on what you know best — machine learning — rather than infrastructure.
|
||||
|
||||
Using distinct steps makes it possible to rerun only the steps you need as you tweak and test your workflow. Once the pipeline is designed, there is often more fine-tuning around the training loop of the pipeline. When you rerun a pipeline, the execution jumps to the steps that need to be rerun, such as an updated training script, and skips what hasn't changed. The same paradigm applies to unchanged scripts and metadata.
|
||||
|
||||
With Azure Machine Learning, you can use distinct toolkits and frameworks for each step in your pipeline. Azure coordinates between the various compute targets you use so that your intermediate data can be shared with the downstream compute targets easily.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Azure Machine Learning Pipelines Features
|
||||
Azure Machine Learning Pipelines optimize for simplicity, speed, and efficiency. The following key concepts make it possible for a data scientist to focus on ML rather than infrastructure.
|
||||
|
||||
**Unattended execution**: Schedule a few scripts to run in parallel or in sequence in a reliable and unattended manner. Since data prep and modeling can last days or weeks, you can now focus on other tasks while your pipeline is running.
|
||||
|
||||
**Mixed and diverse compute**: Use multiple pipelines that are reliably coordinated across heterogeneous and scalable computes and storages. Individual pipeline steps can be run on different compute targets, such as HDInsight, GPU Data Science VMs, and Databricks, to make efficient use of available compute options.
|
||||
|
||||
**Reusability**: Pipelines can be templatized for specific scenarios such as retraining and batch scoring. They can be triggered from external systems via simple REST calls.
|
||||
|
||||
**Tracking and versioning**: Instead of manually tracking data and result paths as you iterate, use the pipelines SDK to explicitly name and version your data sources, inputs, and outputs as well as manage scripts and data separately for increased productivity.
|
||||
|
||||
### Notebooks
|
||||
|
||||
In this directory, there are two types of notebooks:
|
||||
|
||||
* The first type of notebooks will introduce you to core Azure Machine Learning Pipelines features. The notebooks below belong in this category, and are designed to go in sequence:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [aml-pipelines-getting-started.ipynb](aml-pipelines-getting-started.ipynb)
|
||||
2. [aml-pipelines-with-data-dependency-steps.ipynb](aml-pipelines-with-data-dependency-steps.ipynb)
|
||||
3. [aml-pipelines-publish-and-run-using-rest-endpoint.ipynb](aml-pipelines-publish-and-run-using-rest-endpoint.ipynb)
|
||||
4. [aml-pipelines-data-transfer.ipynb](aml-pipelines-data-transfer.ipynb)
|
||||
5. [aml-pipelines-use-databricks-as-compute-target.ipynb](aml-pipelines-use-databricks-as-compute-target.ipynb)
|
||||
6. [aml-pipelines-use-adla-as-compute-target.ipynb](aml-pipelines-use-adla-as-compute-target.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
* The second type of notebooks illustrate more sophisticated scenarios, and are independent of each other. These notebooks include:
|
||||
- [pipeline-batch-scoring.ipynb](pipeline-batch-scoring.ipynb)
|
||||
- [pipeline-style-transfer.ipynb](pipeline-style-transfer.ipynb)
|
||||
BIN
pipeline/aml-pipelines-concept.png
Normal file
BIN
pipeline/aml-pipelines-concept.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 24 KiB |
336
pipeline/aml-pipelines-data-transfer.ipynb
Normal file
336
pipeline/aml-pipelines-data-transfer.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,336 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. \n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Azure Machine Learning Pipeline with DataTranferStep\n",
|
||||
"This notebook is used to demonstrate the use of DataTranferStep in Azure Machine Learning Pipeline.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In certain cases, you will need to transfer data from one data location to another. For example, your data may be in Files storage and you may want to move it to Blob storage. Or, if your data is in an ADLS account and you want to make it available in the Blob storage. The built-in **DataTransferStep** class helps you transfer data in these situations.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The below example shows how to move data in an ADLS account to Blob storage."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Azure Machine Learning and Pipeline SDK-specific imports"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, DatabricksCompute, DataFactoryCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.exceptions import ComputeTargetException\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Workspace, Run, Experiment\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core import Pipeline, PipelineData\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.steps import AdlaStep\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.datastore import Datastore\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.data.data_reference import DataReference\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.data.sql_data_reference import SqlDataReference\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core import attach_legacy_compute_target\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.data.stored_procedure_parameter import StoredProcedureParameter, StoredProcedureParameterType\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.steps import DataTransferStep\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Check core SDK version number\n",
|
||||
"print(\"SDK version:\", azureml.core.VERSION)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Initialize Workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Initialize a workspace object from persisted configuration. Make sure the config file is present at .\\config.json\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"If you don't have a config.json file, please go through the configuration Notebook located here:\n",
|
||||
"https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This sets you up with a working config file that has information on your workspace, subscription id, etc. "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
"create workspace"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"print(ws.name, ws.resource_group, ws.location, ws.subscription_id, sep = '\\n')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Register Datastores\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In the code cell below, you will need to fill in the appropriate values for the workspace name, datastore name, subscription id, resource group, store name, tenant id, client id, and client secret that are associated with your ADLS datastore. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"For background on registering your data store, consult this article:\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-lake-store/data-lake-store-service-to-service-authenticate-using-active-directory"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# un-comment the following and replace the strings with the \n",
|
||||
"# correct values for your ADLS datastore\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# workspace = \"<my-workspace-name>\"\n",
|
||||
"# datastore_name = \"<my-datastore-name>\" # ADLS datastore name\n",
|
||||
"# subscription_id = \"<my-subscription-id>\" # subscription id of ADLS account\n",
|
||||
"# resource_group = \"<my-resource-group>\" # resource group of ADLS account\n",
|
||||
"# store_name = \"<my-storename>\" # ADLS account name\n",
|
||||
"# tenant_id = \"<my-tenant-id>\" # tenant id of service principal\n",
|
||||
"# client_id = \"<my-client-id>\" # client id of service principal\n",
|
||||
"# client_secret = \"<my-client-secret>\" # the secret of service principal\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" adls_datastore = Datastore.get(ws, datastore_name)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"found datastore with name: %s\" % datastore_name)\n",
|
||||
"except:\n",
|
||||
" adls_datastore = Datastore.register_azure_data_lake(\n",
|
||||
" workspace=ws,\n",
|
||||
" datastore_name=datastore_name,\n",
|
||||
" subscription_id=subscription_id, # subscription id of ADLS account\n",
|
||||
" resource_group=resource_group, # resource group of ADLS account\n",
|
||||
" store_name=store_name, # ADLS account name\n",
|
||||
" tenant_id=tenant_id, # tenant id of service principal\n",
|
||||
" client_id=client_id, # client id of service principal\n",
|
||||
" client_secret=client_secret) # the secret of service principal\n",
|
||||
" print(\"registered datastore with name: %s\" % datastore_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# un-comment the following and replace the strings with the\n",
|
||||
"# correct values for your blob datastore\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# blob_datastore_name = \"<my-blob-datastore-name>\"\n",
|
||||
"# account_name = \"<my-blob-account-name>\"\n",
|
||||
"# container_name = \"<my-blob-container-name>\"\n",
|
||||
"# account_key = \"<my-blob-account-key>\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" blob_datastore = Datastore.get(ws, blob_datastore_name)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"found blob datastore with name: %s\" % blob_datastore_name)\n",
|
||||
"except:\n",
|
||||
" blob_datastore = Datastore.register_azure_blob_container(\n",
|
||||
" workspace=ws,\n",
|
||||
" datastore_name=blob_datastore_name,\n",
|
||||
" account_name=account_name, # Storage account name\n",
|
||||
" container_name=container_name, # Name of Azure blob container\n",
|
||||
" account_key=account_key) # Storage account key\"\n",
|
||||
" print(\"registered blob datastore with name: %s\" % blob_datastore_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# CLI:\n",
|
||||
"# az ml datastore register-blob -n <datastore-name> -a <account-name> -c <container-name> -k <account-key> [-t <sas-token>]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create DataReferences"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"adls_datastore = Datastore(workspace=ws, name=\"MyAdlsDatastore\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# adls\n",
|
||||
"adls_data_ref = DataReference(\n",
|
||||
" datastore=adls_datastore,\n",
|
||||
" data_reference_name=\"adls_test_data\",\n",
|
||||
" path_on_datastore=\"testdata\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"blob_datastore = Datastore(workspace=ws, name=\"MyBlobDatastore\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# blob data\n",
|
||||
"blob_data_ref = DataReference(\n",
|
||||
" datastore=blob_datastore,\n",
|
||||
" data_reference_name=\"blob_test_data\",\n",
|
||||
" path_on_datastore=\"testdata\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(\"obtained adls, blob data references\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Setup Data Factory Account"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"data_factory_name = 'adftest'\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def get_or_create_data_factory(workspace, factory_name):\n",
|
||||
" try:\n",
|
||||
" return DataFactoryCompute(workspace, factory_name)\n",
|
||||
" except ComputeTargetException as e:\n",
|
||||
" if 'ComputeTargetNotFound' in e.message:\n",
|
||||
" print('Data factory not found, creating...')\n",
|
||||
" provisioning_config = DataFactoryCompute.provisioning_configuration()\n",
|
||||
" data_factory = ComputeTarget.create(workspace, factory_name, provisioning_config)\n",
|
||||
" data_factory.wait_for_provisioning()\n",
|
||||
" return data_factory\n",
|
||||
" else:\n",
|
||||
" raise e\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"data_factory_compute = get_or_create_data_factory(ws, data_factory_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(\"setup data factory account complete\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# CLI:\n",
|
||||
"# Create: az ml computetarget setup datafactory -n <name>\n",
|
||||
"# BYOC: az ml computetarget attach datafactory -n <name> -i <resource-id>"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create a DataTransferStep"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"**DataTransferStep** is used to transfer data between Azure Blob, Azure Data Lake Store, and Azure SQL database.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- **name:** Name of module\n",
|
||||
"- **source_data_reference:** Input connection that serves as source of data transfer operation.\n",
|
||||
"- **destination_data_reference:** Input connection that serves as destination of data transfer operation.\n",
|
||||
"- **compute_target:** Azure Data Factory to use for transferring data.\n",
|
||||
"- **allow_reuse:** Whether the step should reuse results of previous DataTransferStep when run with same inputs. Set as False to force data to be transferred again.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Optional arguments to explicitly specify whether a path corresponds to a file or a directory. These are useful when storage contains both file and directory with the same name or when creating a new destination path.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- **source_reference_type:** An optional string specifying the type of source_data_reference. Possible values include: 'file', 'directory'. When not specified, we use the type of existing path or directory if it's a new path.\n",
|
||||
"- **destination_reference_type:** An optional string specifying the type of destination_data_reference. Possible values include: 'file', 'directory'. When not specified, we use the type of existing path or directory if it's a new path."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"transfer_adls_to_blob = DataTransferStep(\n",
|
||||
" name=\"transfer_adls_to_blob\",\n",
|
||||
" source_data_reference=adls_data_ref,\n",
|
||||
" destination_data_reference=blob_data_ref,\n",
|
||||
" compute_target=data_factory_compute)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(\"data transfer step created\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Build and Submit the Experiment"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"pipeline = Pipeline(\n",
|
||||
" description=\"data_transfer_101\",\n",
|
||||
" workspace=ws,\n",
|
||||
" steps=[transfer_adls_to_blob])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"pipeline_run = Experiment(ws, \"Data_Transfer_example\").submit(pipeline)\n",
|
||||
"pipeline_run.wait_for_completion()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### View Run Details"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(pipeline_run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Next: Databricks as a Compute Target\n",
|
||||
"To use Databricks as a compute target from Azure Machine Learning Pipeline, a DatabricksStep is used. This [notebook](./aml-pipelines-use-databricks-as-compute-target.ipynb) demonstrates the use of a DatabricksStep in an Azure Machine Learning Pipeline."
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "diray"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.7"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
631
pipeline/aml-pipelines-getting-started.ipynb
Normal file
631
pipeline/aml-pipelines-getting-started.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,631 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. \n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Azure Machine Learning Pipelines: Getting Started\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"## Overview\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Read [Azure Machine Learning Pipelines](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/service/concept-ml-pipelines) overview, or the [readme article](./README.md) on Azure Machine Learning Pipelines to get more information.\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This Notebook shows basic construction of a **pipeline** that runs jobs unattended in different compute clusters. "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Prerequisites and Azure Machine Learning Basics\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you go through the configuration Notebook located at https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks first if you haven't. This sets you up with a working config file that has information on your workspace, subscription id, etc. \n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Installing Packages\n",
|
||||
"These packages are used at later stages."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"!pip install pandas\n",
|
||||
"!pip install requests"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Enabling Widgets\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Install the following jupyter extensions to support Azure Machine Learning widgets."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"!pip install azureml.widgets\n",
|
||||
"!jupyter nbextension install --py --user azureml.widgets\n",
|
||||
"!jupyter nbextension enable --py --user azureml.widgets"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Azure Machine Learning Imports"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Workspace, Run, Experiment, Datastore\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import DataFactoryCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Check core SDK version number\n",
|
||||
"print(\"SDK version:\", azureml.core.VERSION)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Pipeline SDK-specific imports"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.data.data_reference import DataReference\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core import Pipeline, PipelineData, StepSequence\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.steps import PythonScriptStep\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.steps import DataTransferStep\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core import PublishedPipeline\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core.graph import PipelineParameter\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Pipeline SDK-specific imports completed\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Initialize Workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Initialize a [workspace](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-core/azureml.core.workspace(class%29) object from persisted configuration."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
"create workspace"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"print(ws.name, ws.resource_group, ws.location, ws.subscription_id, sep = '\\n')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Default datastore (Azure file storage)\n",
|
||||
"def_file_store = ws.get_default_datastore() \n",
|
||||
"# The above call is equivalent to Datastore(ws, \"workspacefilestore\") or simply Datastore(ws)\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Default datastore's name: {}\".format(def_file_store.name))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Blob storage associated with the workspace\n",
|
||||
"# The following call GETS the Azure Blob Store associated with your workspace.\n",
|
||||
"# Note that workspaceblobstore is **the name of this store and CANNOT BE CHANGED and must be used as is** \n",
|
||||
"def_blob_store = Datastore(ws, \"workspaceblobstore\")\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Blobstore's name: {}\".format(def_blob_store.name))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# project folder\n",
|
||||
"project_folder = '.'\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"print('Sample projects will be created in {}.'.format(project_folder))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Required data and script files for the the tutorial\n",
|
||||
"Sample files required to finish this tutorial are already copied to the project folder specified above. Even though the .py provided in the samples don't have much \"ML work,\" as a data scientist, you will work on this extensively as part of your work. To complete this tutorial, the contents of these files are not very important. The one-line files are for demostration purpose only."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Datastore concepts\n",
|
||||
"A [Datastore](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-core/azureml.core.datastore(class) is a place where data can be stored that is then made accessible to a compute either by means of mounting or copying the data to the compute target. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"A Datastore can either be backed by an Azure File Storage (default) or by an Azure Blob Storage.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this next step, we will upload the training and test set into the workspace's default storage (File storage), and another piece of data to Azure Blob Storage. When to use [Azure Blobs](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/storage-blobs-introduction), [Azure Files](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/files/storage-files-introduction), or [Azure Disks](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/linux/managed-disks-overview) is [detailed here](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/common/storage-decide-blobs-files-disks).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Please take good note of the concept of the datastore.**"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Upload data to default datastore\n",
|
||||
"Default datastore on workspace is the Azure File storage. The workspace has a Blob storage associated with it as well. Let's upload a file to each of these storages."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# get_default_datastore() gets the default Azure File Store associated with your workspace.\n",
|
||||
"# Here we are reusing the def_file_store object we obtained earlier\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# target_path is the directory at the destination\n",
|
||||
"def_file_store.upload_files(['./20news.pkl'], \n",
|
||||
" target_path = '20newsgroups', \n",
|
||||
" overwrite = True, \n",
|
||||
" show_progress = True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Here we are reusing the def_blob_store we created earlier\n",
|
||||
"def_blob_store.upload_files([\"./20news.pkl\"], target_path=\"20newsgroups\", overwrite=True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Upload calls completed\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### (Optional) See your files using Azure Portal\n",
|
||||
"Once you successfully uploaded the files, you can browse to them (or upload more files) using [Azure Portal](https://portal.azure.com). At the portal, make sure you have selected **AzureML Nursery** as your subscription (click *Resource Groups* and then select the subscription). Then look for your **Machine Learning Workspace** (it has your *alias* as the name). It has a link to your storage. Click on the storage link. It will take you to a page where you can see [Blobs](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/storage-blobs-introduction), [Files](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/files/storage-files-introduction), [Tables](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/tables/table-storage-overview), and [Queues](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/queues/storage-queues-introduction). We have just uploaded a file to the Blob storage and another one to the File storage. You should be able to see both of these files in their respective locations. "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Compute Targets\n",
|
||||
"A compute target specifies where to execute your program such as a remote Docker on a VM, or a cluster. A compute target needs to be addressable and accessible by you.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**You need at least one compute target to send your payload to. We are planning to use Azure Machine Learning Compute exclusively for this tutorial for all steps. However in some cases you may require multiple compute targets as some steps may run in one compute target like Azure Machine Learning Compute, and some other steps in the same pipeline could run in a different compute target.**\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"*The example belows show creating/retrieving/attaching to an Azure Machine Learning Compute instance.*"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### List of Compute Targets on the workspace"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"cts = ws.compute_targets\n",
|
||||
"for ct in cts:\n",
|
||||
" print(ct)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Retrieve or create a Azure Machine Learning compute\n",
|
||||
"Azure Machine Learning Compute is a service for provisioning and managing clusters of Azure virtual machines for running machine learning workloads. Let's create a new Azure Machine Learning Compute in the current workspace, if it doesn't already exist. We will then run the training script on this compute target.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"If we could not find the compute with the given name in the previous cell, then we will create a new compute here. We will create an Azure Machine Learning Compute containing **STANDARD_D2_V2 CPU VMs**. This process is broken down into the following steps:\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"1. Create the configuration\n",
|
||||
"2. Create the Azure Machine Learning compute\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**This process will take about 3 minutes and is providing only sparse output in the process. Please make sure to wait until the call returns before moving to the next cell.**"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aml_compute_target = \"aml-compute\"\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" aml_compute = AmlCompute(ws, aml_compute_target)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"found existing compute target.\")\n",
|
||||
"except:\n",
|
||||
" print(\"creating new compute target\")\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" provisioning_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size = \"STANDARD_D2_V2\",\n",
|
||||
" min_nodes = 1, \n",
|
||||
" max_nodes = 4) \n",
|
||||
" aml_compute = ComputeTarget.create(ws, aml_compute_target, provisioning_config)\n",
|
||||
" aml_compute.wait_for_completion(show_output=True, min_node_count=None, timeout_in_minutes=20)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"print(\"Azure Machine Learning Compute attached\")\n",
|
||||
"# For a more detailed view of current Azure Machine Learning Compute status, use the 'status' property \n",
|
||||
"print(aml_compute.status.serialize())"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"**Wait for this call to finish before proceeding (you will see the asterisk turning to a number).**\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Now that you have created the compute target, let's see what the workspace's compute_targets() function returns. You should now see one entry named 'amlcompute' of type AmlCompute."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"**Now that we have completed learning the basics of Azure Machine Learning (AML), let's go ahead and start understanding the Pipeline concepts.**"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Creating a Step in a Pipeline\n",
|
||||
"A Step is a unit of execution. Step typically needs a target of execution (compute target), a script to execute, and may require script arguments and inputs, and can produce outputs. The step also could take a number of other parameters. Azure Machine Learning Pipelines provides the following built-in Steps:\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- [**PythonScriptStep**](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-pipeline-steps/azureml.pipeline.steps.python_script_step.pythonscriptstep?view=azure-ml-py): Add a step to run a Python script in a Pipeline.\n",
|
||||
"- [**AdlaStep**](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-pipeline-steps/azureml.pipeline.steps.adla_step.adlastep?view=azure-ml-py): Adds a step to run U-SQL script using Azure Data Lake Analytics.\n",
|
||||
"- [**DataTransferStep**](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-pipeline-steps/azureml.pipeline.steps.data_transfer_step.datatransferstep?view=azure-ml-py): Transfers data between Azure Blob and Data Lake accounts.\n",
|
||||
"- [**DatabricksStep**](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-pipeline-steps/azureml.pipeline.steps.databricks_step.databricksstep?view=azure-ml-py): Adds a DataBricks notebook as a step in a Pipeline.\n",
|
||||
"- [**HyperDriveStep**](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-pipeline-steps/azureml.pipeline.steps.hyper_drive_step.hyperdrivestep?view=azure-ml-py): Creates a Hyper Drive step for Hyper Parameter Tuning in a Pipeline.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The following code will create a PythonScriptStep to be executed in the Azure Machine Learning Compute we created above using train.py, one of the files already made available in the project folder.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"A **PythonScriptStep** is a basic, built-in step to run a Python Script on a compute target. It takes a script name and optionally other parameters like arguments for the script, compute target, inputs and outputs. If no compute target is specified, default compute target for the workspace is used."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Uses default values for PythonScriptStep construct.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Syntax\n",
|
||||
"# PythonScriptStep(\n",
|
||||
"# script_name, \n",
|
||||
"# name=None, \n",
|
||||
"# arguments=None, \n",
|
||||
"# compute_target=None, \n",
|
||||
"# runconfig=None, \n",
|
||||
"# inputs=None, \n",
|
||||
"# outputs=None, \n",
|
||||
"# params=None, \n",
|
||||
"# source_directory=None, \n",
|
||||
"# allow_reuse=True, \n",
|
||||
"# version=None, \n",
|
||||
"# hash_paths=None)\n",
|
||||
"# This returns a Step\n",
|
||||
"step1 = PythonScriptStep(name=\"train_step\",\n",
|
||||
" script_name=\"train.py\", \n",
|
||||
" compute_target=aml_compute, \n",
|
||||
" source_directory=project_folder,\n",
|
||||
" allow_reuse=False)\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Step1 created\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"**Note:** In the above call to PythonScriptStep(), the flag *allow_reuse* determines whether the step should reuse previous results when run with the same settings/inputs. This flag's default value is *True*; the default is set to *True* because, when inputs and parameters have not changed, we typically do not want to re-run a given pipeline step. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"If *allow_reuse* is set to *False*, a new run will always be generated for this step during pipeline execution. The *allow_reuse* flag can come in handy in situations where you do *not* want to re-run a pipeline step."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Running a few steps in parallel\n",
|
||||
"Here we are looking at a simple scenario where we are running a few steps (all involving PythonScriptStep) in parallel. Running nodes in **parallel** is the default behavior for steps in a pipeline.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"We already have one step defined earlier. Let's define few more steps."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# All steps use files already available in the project_folder\n",
|
||||
"# All steps use the same Azure Machine Learning compute target as well\n",
|
||||
"step2 = PythonScriptStep(name=\"compare_step\",\n",
|
||||
" script_name=\"compare.py\", \n",
|
||||
" compute_target=aml_compute, \n",
|
||||
" source_directory=project_folder)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"step3 = PythonScriptStep(name=\"extract_step\",\n",
|
||||
" script_name=\"extract.py\", \n",
|
||||
" compute_target=aml_compute, \n",
|
||||
" source_directory=project_folder)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# list of steps to run\n",
|
||||
"steps = [step1, step2, step3]\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Step lists created\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Build the pipeline\n",
|
||||
"Once we have the steps (or steps collection), we can build the [pipeline](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-pipeline-core/azureml.pipeline.core.pipeline.pipeline?view=azure-ml-py). By deafult, all these steps will run in **parallel** once we submit the pipeline for run.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"A pipeline is created with a list of steps and a workspace. Submit a pipeline using [submit](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-core/azureml.core.experiment%28class%29?view=azure-ml-py#submit). When submit is called, a [PipelineRun](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-pipeline-core/azureml.pipeline.core.pipelinerun?view=azure-ml-py) is created which in turn creates [StepRun](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-pipeline-core/azureml.pipeline.core.steprun?view=azure-ml-py) objects for each step in the workflow."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Syntax\n",
|
||||
"# Pipeline(workspace, \n",
|
||||
"# steps, \n",
|
||||
"# description=None, \n",
|
||||
"# default_datastore_name=None, \n",
|
||||
"# default_source_directory=None, \n",
|
||||
"# resolve_closure=True, \n",
|
||||
"# _workflow_provider=None, \n",
|
||||
"# _service_endpoint=None)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"pipeline1 = Pipeline(workspace=ws, steps=steps)\n",
|
||||
"print (\"Pipeline is built\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Validate the pipeline\n",
|
||||
"You have the option to [validate](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-pipeline-core/azureml.pipeline.core.pipeline.pipeline?view=azure-ml-py#validate) the pipeline prior to submitting for run. The platform runs validation steps such as checking for circular dependencies and parameter checks etc. even if you do not explicitly call validate method."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"pipeline1.validate()\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Pipeline validation complete\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Submit the pipeline\n",
|
||||
"[Submitting](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-pipeline-core/azureml.pipeline.core.pipeline.pipeline?view=azure-ml-py#submit) the pipeline involves creating an [Experiment](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-core/azureml.core.experiment?view=azure-ml-py) object and providing the built pipeline for submission. "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Submit syntax\n",
|
||||
"# submit(experiment_name, \n",
|
||||
"# pipeline_parameters=None, \n",
|
||||
"# continue_on_node_failure=False, \n",
|
||||
"# regenerate_outputs=False)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"pipeline_run1 = Experiment(ws, 'Hello_World1').submit(pipeline1, regenerate_outputs=True)\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Pipeline is submitted for execution\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"**Note:** If regenerate_outputs is set to True, a new submit will always force generation of all step outputs, and disallow data reuse for any step of this run. Once this run is complete, however, subsequent runs may reuse the results of this run.\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Examine the pipeline run\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Use RunDetails Widget\n",
|
||||
"We are going to use the RunDetails widget to examine the run of the pipeline. You can click each row below to get more details on the step runs."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"RunDetails(pipeline_run1).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Use Pipeline SDK objects\n",
|
||||
"You can cycle through the node_run objects and examine job logs, stdout, and stderr of each of the steps."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"step_runs = pipeline_run1.get_children()\n",
|
||||
"for step_run in step_runs:\n",
|
||||
" status = step_run.get_status()\n",
|
||||
" print('Script:', step_run.name, 'status:', status)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # Change this if you want to see details even if the Step has succeeded.\n",
|
||||
" if status == \"Failed\":\n",
|
||||
" joblog = step_run.get_job_log()\n",
|
||||
" print('job log:', joblog)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Get additonal run details\n",
|
||||
"If you wait until the pipeline_run is finished, you may be able to get additional details on the run. **Since this is a blocking call, the following code is commented out.**"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#pipeline_run1.wait_for_completion()\n",
|
||||
"#for step_run in pipeline_run1.get_children():\n",
|
||||
"# print(\"{}: {}\".format(step_run.name, step_run.get_metrics()))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Running a few steps in sequence\n",
|
||||
"Now let's see how we run a few steps in sequence. We already have three steps defined earlier. Let's *reuse* those steps for this part.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"We will reuse step1, step2, step3, but build the pipeline in such a way that we chain step3 after step2 and step2 after step1. Note that there is no explicit data dependency between these steps, but still steps can be made dependent by using the [run_after](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-pipeline-core/azureml.pipeline.core.builder.pipelinestep?view=azure-ml-py#run-after) construct."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"step2.run_after(step1)\n",
|
||||
"step3.run_after(step2)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Try a loop\n",
|
||||
"#step2.run_after(step3)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Now, construct the pipeline using the steps.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# We can specify the \"final step\" in the chain, \n",
|
||||
"# Pipeline will take care of \"transitive closure\" and \n",
|
||||
"# figure out the implicit or explicit dependencies\n",
|
||||
"# https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/transitive-closure-of-a-graph/\n",
|
||||
"pipeline2 = Pipeline(workspace=ws, steps=[step3])\n",
|
||||
"print (\"Pipeline is built\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"pipeline2.validate()\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Simple validation complete\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"pipeline_run2 = Experiment(ws, 'Hello_World2').submit(pipeline2)\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Pipeline is submitted for execution\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"RunDetails(pipeline_run2).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Next: Pipelines with data dependency\n",
|
||||
"The next [notebook](./aml-pipelines-with-data-dependency-steps.ipynb) demostrates how to construct a pipeline with data dependency."
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "diray"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.7"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
358
pipeline/aml-pipelines-publish-and-run-using-rest-endpoint.ipynb
Normal file
358
pipeline/aml-pipelines-publish-and-run-using-rest-endpoint.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,358 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. \n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# How to Publish a Pipeline and Invoke the REST endpoint\n",
|
||||
"In this notebook, we will see how we can publish a pipeline and then invoke the REST endpoint."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Prerequisites and Azure Machine Learning Basics\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you go through the configuration Notebook located at https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks first if you haven't. This sets you up with a working config file that has information on your workspace, subscription id, etc. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Initialization Steps"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Workspace, Run, Experiment, Datastore\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import DataFactoryCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Check core SDK version number\n",
|
||||
"print(\"SDK version:\", azureml.core.VERSION)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.data.data_reference import DataReference\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core import Pipeline, PipelineData, StepSequence\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.steps import PythonScriptStep\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.steps import DataTransferStep\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core import PublishedPipeline\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core.graph import PipelineParameter\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Pipeline SDK-specific imports completed\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"print(ws.name, ws.resource_group, ws.location, ws.subscription_id, sep = '\\n')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Default datastore (Azure file storage)\n",
|
||||
"def_file_store = ws.get_default_datastore() \n",
|
||||
"print(\"Default datastore's name: {}\".format(def_file_store.name))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def_blob_store = Datastore(ws, \"workspaceblobstore\")\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Blobstore's name: {}\".format(def_blob_store.name))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# project folder\n",
|
||||
"project_folder = '.'"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Compute Targets\n",
|
||||
"#### Retrieve an already attached Azure Machine Learning Compute"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aml_compute_target = \"aml-compute\"\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" aml_compute = AmlCompute(ws, aml_compute_target)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"found existing compute target.\")\n",
|
||||
"except:\n",
|
||||
" print(\"creating new compute target\")\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" provisioning_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size = \"STANDARD_D2_V2\",\n",
|
||||
" min_nodes = 1, \n",
|
||||
" max_nodes = 4) \n",
|
||||
" aml_compute = ComputeTarget.create(ws, aml_compute_target, provisioning_config)\n",
|
||||
" aml_compute.wait_for_completion(show_output=True, min_node_count=None, timeout_in_minutes=20)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"print(aml_compute.status.serialize())\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Building Pipeline Steps with Inputs and Outputs\n",
|
||||
"As mentioned earlier, a step in the pipeline can take data as input. This data can be a data source that lives in one of the accessible data locations, or intermediate data produced by a previous step in the pipeline."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Reference the data uploaded to blob storage using DataReference\n",
|
||||
"# Assign the datasource to blob_input_data variable\n",
|
||||
"blob_input_data = DataReference(\n",
|
||||
" datastore=def_blob_store,\n",
|
||||
" data_reference_name=\"test_data\",\n",
|
||||
" path_on_datastore=\"20newsgroups/20news.pkl\")\n",
|
||||
"print(\"DataReference object created\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Define intermediate data using PipelineData\n",
|
||||
"processed_data1 = PipelineData(\"processed_data1\",datastore=def_blob_store)\n",
|
||||
"print(\"PipelineData object created\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Define a Step that consumes a datasource and produces intermediate data.\n",
|
||||
"In this step, we define a step that consumes a datasource and produces intermediate data.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Open `train.py` in the local machine and examine the arguments, inputs, and outputs for the script. That will give you a good sense of why the script argument names used below are important.** "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# trainStep consumes the datasource (Datareference) in the previous step\n",
|
||||
"# and produces processed_data1\n",
|
||||
"trainStep = PythonScriptStep(\n",
|
||||
" script_name=\"train.py\", \n",
|
||||
" arguments=[\"--input_data\", blob_input_data, \"--output_train\", processed_data1],\n",
|
||||
" inputs=[blob_input_data],\n",
|
||||
" outputs=[processed_data1],\n",
|
||||
" compute_target=aml_compute, \n",
|
||||
" source_directory=project_folder\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"print(\"trainStep created\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Define a Step that consumes intermediate data and produces intermediate data\n",
|
||||
"In this step, we define a step that consumes an intermediate data and produces intermediate data.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Open `extract.py` in the local machine and examine the arguments, inputs, and outputs for the script. That will give you a good sense of why the script argument names used below are important.** "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# extractStep to use the intermediate data produced by step4\n",
|
||||
"# This step also produces an output processed_data2\n",
|
||||
"processed_data2 = PipelineData(\"processed_data2\", datastore=def_blob_store)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"extractStep = PythonScriptStep(\n",
|
||||
" script_name=\"extract.py\",\n",
|
||||
" arguments=[\"--input_extract\", processed_data1, \"--output_extract\", processed_data2],\n",
|
||||
" inputs=[processed_data1],\n",
|
||||
" outputs=[processed_data2],\n",
|
||||
" compute_target=aml_compute, \n",
|
||||
" source_directory=project_folder)\n",
|
||||
"print(\"extractStep created\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Define a Step that consumes multiple intermediate data and produces intermediate data\n",
|
||||
"In this step, we define a step that consumes multiple intermediate data and produces intermediate data."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### PipelineParameter"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"This step also has a [PipelineParameter](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-pipeline-core/azureml.pipeline.core.graph.pipelineparameter?view=azure-ml-py) argument that help with calling the REST endpoint of the published pipeline."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# We will use this later in publishing pipeline\n",
|
||||
"pipeline_param = PipelineParameter(name=\"pipeline_arg\", default_value=10)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"**Open `compare.py` in the local machine and examine the arguments, inputs, and outputs for the script. That will give you a good sense of why the script argument names used below are important.**"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Now define step6 that takes two inputs (both intermediate data), and produce an output\n",
|
||||
"processed_data3 = PipelineData(\"processed_data3\", datastore=def_blob_store)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"compareStep = PythonScriptStep(\n",
|
||||
" script_name=\"compare.py\",\n",
|
||||
" arguments=[\"--compare_data1\", processed_data1, \"--compare_data2\", processed_data2, \"--output_compare\", processed_data3, \"--pipeline_param\", pipeline_param],\n",
|
||||
" inputs=[processed_data1, processed_data2],\n",
|
||||
" outputs=[processed_data3], \n",
|
||||
" compute_target=aml_compute, \n",
|
||||
" source_directory=project_folder)\n",
|
||||
"print(\"compareStep created\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Build the pipeline"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"pipeline1 = Pipeline(workspace=ws, steps=[compareStep])\n",
|
||||
"print (\"Pipeline is built\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"pipeline1.validate()\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Simple validation complete\") "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Publish the pipeline"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"published_pipeline1 = pipeline1.publish(name=\"My_New_Pipeline\", description=\"My Published Pipeline Description\")\n",
|
||||
"print(published_pipeline1.id)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Run published pipeline using its REST endpoint"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.authentication import AzureCliAuthentication\n",
|
||||
"import requests\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"cli_auth = AzureCliAuthentication()\n",
|
||||
"aad_token = cli_auth.get_authentication_header()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"rest_endpoint1 = published_pipeline1.endpoint\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(rest_endpoint1)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# specify the param when running the pipeline\n",
|
||||
"response = requests.post(rest_endpoint1, \n",
|
||||
" headers=aad_token, \n",
|
||||
" json={\"ExperimentName\": \"My_Pipeline1\",\n",
|
||||
" \"RunSource\": \"SDK\",\n",
|
||||
" \"ParameterAssignments\": {\"pipeline_arg\": 45}})\n",
|
||||
"run_id = response.json()[\"Id\"]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(run_id)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Next: Data Transfer\n",
|
||||
"The next [notebook](./aml-pipelines-data-transfer.ipynb) will showcase data transfer steps between different types of data stores."
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "diray"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.7"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
348
pipeline/aml-pipelines-use-adla-as-compute-target.ipynb
Normal file
348
pipeline/aml-pipelines-use-adla-as-compute-target.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,348 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. \n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# AML Pipeline with AdlaStep\n",
|
||||
"This notebook is used to demonstrate the use of AdlaStep in AML Pipeline."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## AML and Pipeline SDK-specific imports"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, DatabricksCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.exceptions import ComputeTargetException\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Workspace, Run, Experiment\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core import Pipeline, PipelineData\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.steps import AdlaStep\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.datastore import Datastore\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.data.data_reference import DataReference\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core import attach_legacy_compute_target\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Check core SDK version number\n",
|
||||
"print(\"SDK version:\", azureml.core.VERSION)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Initialize Workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Initialize a workspace object from persisted configuration. Make sure the config file is present at .\\config.json"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
"create workspace"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"print(ws.name, ws.resource_group, ws.location, ws.subscription_id, sep = '\\n')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"script_folder = '.'\n",
|
||||
"experiment_name = \"adla_101_experiment\"\n",
|
||||
"ws._initialize_folder(experiment_name=experiment_name, directory=script_folder)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Register Datastore"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# un-comment the following and replace the strings with the \n",
|
||||
"# correct values for your ADLS datastore\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# workspace=\"<my-workspace-name\"\n",
|
||||
"# datastore_name= \"<my-adls-datastore-name>\"\n",
|
||||
"# subscription_id = \"<my-subscription-id>\"\n",
|
||||
"# resource_group = \"<my-rg>\"\n",
|
||||
"# store_name = \"<my-sotrename>\"\n",
|
||||
"# tenant_id = \"<my-tenant>\"\n",
|
||||
"# client_id = \"<my-client-id>\"\n",
|
||||
"# client_secret = \"<my-client-secret>\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" adls_datastore = Datastore.get(ws, datastore_name)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"found datastore with name: %s\" % datastore_name)\n",
|
||||
"except:\n",
|
||||
" adls_datastore = Datastore.register_azure_data_lake(\n",
|
||||
" workspace=ws,\n",
|
||||
" datastore_name=datastore_name,\n",
|
||||
" subscription_id=subscription_id, # subscription id of ADLS account\n",
|
||||
" resource_group=resource_group, # resource group of ADLS account\n",
|
||||
" store_name=store_name, # ADLS account name\n",
|
||||
" tenant_id=tenant_id, # tenant id of service principal\n",
|
||||
" client_id=client_id, # client id of service principal\n",
|
||||
" client_secret=client_secret) # the secret of service principal\n",
|
||||
" print(\"registered datastore with name: %s\" % datastore_name)\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create DataReferences and PipelineData\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In the code cell below, replace datastorename with your default datastore name. Copy the file `testdata.txt` (located in the pipeline folder that this notebook is in) to the path on the datastore."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"datastorename = \"TestAdlsDatastore\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"adls_datastore = Datastore(workspace=ws, name=datastorename)\n",
|
||||
"script_input = DataReference(\n",
|
||||
" datastore=adls_datastore,\n",
|
||||
" data_reference_name=\"script_input\",\n",
|
||||
" path_on_datastore=\"testdata/testdata.txt\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"script_output = PipelineData(\"script_output\", datastore=adls_datastore)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Created Pipeline Data\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Setup Data Lake Account\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"ADLA can only use data that is located in the default data store associated with that ADLA account. Through Azure portal, check the name of the default data store corresponding to the ADLA account you are using below. Replace the value associated with `adla_compute_name` in the code cell below accordingly."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"adla_compute_name = 'testadl' # Replace this with your default compute\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, AdlaCompute\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def get_or_create_adla_compute(workspace, compute_name):\n",
|
||||
" try:\n",
|
||||
" return AdlaCompute(workspace, compute_name)\n",
|
||||
" except ComputeTargetException as e:\n",
|
||||
" if 'ComputeTargetNotFound' in e.message:\n",
|
||||
" print('adla compute not found, creating...')\n",
|
||||
" provisioning_config = AdlaCompute.provisioning_configuration()\n",
|
||||
" adla_compute = ComputeTarget.create(workspace, compute_name, provisioning_config)\n",
|
||||
" adla_compute.wait_for_completion()\n",
|
||||
" return adla_compute\n",
|
||||
" else:\n",
|
||||
" raise e\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"adla_compute = get_or_create_adla_compute(ws, adla_compute_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# CLI:\n",
|
||||
"# Create: az ml computetarget setup adla -n <name>\n",
|
||||
"# BYOC: az ml computetarget attach adla -n <name> -i <resource-id>"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Once the above code cell completes, run the below to check your ADLA compute status:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"print(\"ADLA compute state:{}\".format(adla_compute.provisioning_state))\n",
|
||||
"print(\"ADLA compute state:{}\".format(adla_compute.provisioning_errors))\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Using ADLA compute:{}\".format(adla_compute.cluster_resource_id))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create an AdlaStep"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"**AdlaStep** is used to run U-SQL script using Azure Data Lake Analytics.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- **name:** Name of module\n",
|
||||
"- **script_name:** name of U-SQL script\n",
|
||||
"- **inputs:** List of input port bindings\n",
|
||||
"- **outputs:** List of output port bindings\n",
|
||||
"- **adla_compute:** the ADLA compute to use for this job\n",
|
||||
"- **params:** Dictionary of name-value pairs to pass to U-SQL job *(optional)*\n",
|
||||
"- **degree_of_parallelism:** the degree of parallelism to use for this job *(optional)*\n",
|
||||
"- **priority:** the priority value to use for the current job *(optional)*\n",
|
||||
"- **runtime_version:** the runtime version of the Data Lake Analytics engine *(optional)*\n",
|
||||
"- **root_folder:** folder that contains the script, assemblies etc. *(optional)*\n",
|
||||
"- **hash_paths:** list of paths to hash to detect a change (script file is always hashed) *(optional)*"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"adla_step = AdlaStep(\n",
|
||||
" name='adla_script_step',\n",
|
||||
" script_name='test_adla_script.usql',\n",
|
||||
" inputs=[script_input],\n",
|
||||
" outputs=[script_output],\n",
|
||||
" compute_target=adla_compute)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Build and Submit the Experiment"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"pipeline = Pipeline(\n",
|
||||
" description=\"adla_102\",\n",
|
||||
" workspace=ws, \n",
|
||||
" steps=[adla_step],\n",
|
||||
" default_source_directory=script_folder)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"pipeline_run = Experiment(workspace, experiment_name).submit(pipeline)\n",
|
||||
"pipeline_run.wait_for_completion()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### View Run Details"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(pipeline_run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Examine the run\n",
|
||||
"You can cycle through the node_run objects and examine job logs, stdout, and stderr of each of the steps."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"step_runs = pipeline_run.get_children()\n",
|
||||
"for step_run in step_runs:\n",
|
||||
" status = step_run.get_status()\n",
|
||||
" print('node', step_run.name, 'status:', status)\n",
|
||||
" if status == \"Failed\":\n",
|
||||
" joblog = step_run.get_job_log()\n",
|
||||
" print('job log:', joblog)\n",
|
||||
" stdout_log = step_run.get_stdout_log()\n",
|
||||
" print('stdout log:', stdout_log)\n",
|
||||
" stderr_log = step_run.get_stderr_log()\n",
|
||||
" print('stderr log:', stderr_log)\n",
|
||||
" with open(\"logs-\" + step_run.name + \".txt\", \"w\") as f:\n",
|
||||
" f.write(joblog)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Job log written to logs-\"+ step_run.name + \".txt\")\n",
|
||||
" if status == \"Finished\":\n",
|
||||
" stdout_log = step_run.get_stdout_log()\n",
|
||||
" print('stdout log:', stdout_log)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "diray"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.7"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
651
pipeline/aml-pipelines-use-databricks-as-compute-target.ipynb
Normal file
651
pipeline/aml-pipelines-use-databricks-as-compute-target.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,651 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. \n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Using Databricks as a Compute Target from Azure Machine Learning Pipeline\n",
|
||||
"To use Databricks as a compute target from [Azure Machine Learning Pipeline](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/service/concept-ml-pipelines), a [DatabricksStep](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-pipeline-steps/azureml.pipeline.steps.databricks_step.databricksstep?view=azure-ml-py) is used. This notebook demonstrates the use of DatabricksStep in Azure Machine Learning Pipeline.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The notebook will show:\n",
|
||||
"1. Running an arbitrary Databricks notebook that the customer has in Databricks workspace\n",
|
||||
"2. Running an arbitrary Python script that the customer has in DBFS\n",
|
||||
"3. Running an arbitrary Python script that is available on local computer (will upload to DBFS, and then run in Databricks) \n",
|
||||
"4. Running a JAR job that the customer has in DBFS.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"## Before you begin:\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"1. **Create an Azure Databricks workspace** in the same subscription where you have your Azure Machine Learning workspace. You will need details of this workspace later on to define DatabricksStep. [Click here](https://ms.portal.azure.com/#blade/HubsExtension/Resources/resourceType/Microsoft.Databricks%2Fworkspaces) for more information.\n",
|
||||
"2. **Create PAT (access token)**: Manually create a Databricks access token at the Azure Databricks portal. See [this](https://docs.databricks.com/api/latest/authentication.html#generate-a-token) for more information.\n",
|
||||
"3. **Add demo notebook to ADB**: This notebook has a sample you can use as is. Launch Azure Databricks attached to your Azure Machine Learning workspace and add a new notebook. \n",
|
||||
"4. **Create/attach a Blob storage** for use from ADB"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Add demo notebook to ADB Workspace\n",
|
||||
"Copy and paste the below code to create a new notebook in your ADB workspace."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"# direct access\n",
|
||||
"dbutils.widgets.get(\"myparam\")\n",
|
||||
"p = getArgument(\"myparam\")\n",
|
||||
"print (\"Param -\\'myparam':\")\n",
|
||||
"print (p)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"dbutils.widgets.get(\"input\")\n",
|
||||
"i = getArgument(\"input\")\n",
|
||||
"print (\"Param -\\'input':\")\n",
|
||||
"print (i)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"dbutils.widgets.get(\"output\")\n",
|
||||
"o = getArgument(\"output\")\n",
|
||||
"print (\"Param -\\'output':\")\n",
|
||||
"print (o)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"n = i + \"/testdata.txt\"\n",
|
||||
"df = spark.read.csv(n)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"display (df)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"data = [('value1', 'value2')]\n",
|
||||
"df2 = spark.createDataFrame(data)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"z = o + \"/output.txt\"\n",
|
||||
"df2.write.csv(z)\n",
|
||||
"```"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Azure Machine Learning and Pipeline SDK-specific imports"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.runconfig import JarLibrary\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, DatabricksCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.exceptions import ComputeTargetException\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Workspace, Run, Experiment\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core import Pipeline, PipelineData\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.steps import DatabricksStep\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.datastore import Datastore\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.data.data_reference import DataReference\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Check core SDK version number\n",
|
||||
"print(\"SDK version:\", azureml.core.VERSION)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Initialize Workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Initialize a workspace object from persisted configuration. Make sure the config file is present at .\\config.json"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"print(ws.name, ws.resource_group, ws.location, ws.subscription_id, sep = '\\n')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Attach Databricks compute target\n",
|
||||
"Next, you need to add your Databricks workspace to Azure Machine Learning as a compute target and give it a name. You will use this name to refer to your Databricks workspace compute target inside Azure Machine Learning.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- **Resource Group** - The resource group name of your Azure Machine Learning workspace\n",
|
||||
"- **Databricks Workspace Name** - The workspace name of your Azure Databricks workspace\n",
|
||||
"- **Databricks Access Token** - The access token you created in ADB"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Replace with your account info before running.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# db_compute_name = \"<my-databricks_compute_name>\"\n",
|
||||
"# aml_resource_group = \"<my-aml-resource-group>\"\n",
|
||||
"# db_workspace_name = \"<my-databricks_workspace_name>\"\n",
|
||||
"# access_token = \"<my-databricks_access_token>\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" databricks_compute = ComputeTarget(workspace=ws, name=db_compute_name)\n",
|
||||
" print('Compute target {} already exists'.format(db_compute_name))\n",
|
||||
"except ComputeTargetException:\n",
|
||||
" print('compute not found')\n",
|
||||
" print('databricks_compute_name {}'.format(db_compute_name))\n",
|
||||
" print('databricks_resource_id {}'.format(db_workspace_name))\n",
|
||||
" print('databricks_access_token {}'.format(access_token))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" config = DatabricksCompute.attach_configuration(aml_resource_group, db_workspace_name, access_token)\n",
|
||||
" ComputeTarget.attach(ws, db_compute_name, config)\n",
|
||||
" databricks_compute.wait_for_completion(True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Data Connections with Inputs and Outputs\n",
|
||||
"The DatabricksStep supports Azure Bloband ADLS for inputs and outputs. You also will need to define a [Secrets](https://docs.azuredatabricks.net/user-guide/secrets/index.html) scope to enable authentication to external data sources such as Blob and ADLS from Databricks.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- Databricks documentation on [Azure Blob](https://docs.azuredatabricks.net/spark/latest/data-sources/azure/azure-storage.html)\n",
|
||||
"- Databricks documentation on [ADLS](https://docs.databricks.com/spark/latest/data-sources/azure/azure-datalake.html)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Type of Data Access\n",
|
||||
"Databricks allows to interact with Azure Blob and ADLS in two ways.\n",
|
||||
"- **Direct Access**: Databricks allows you to interact with Azure Blob or ADLS URIs directly. The input or output URIs will be mapped to a Databricks widget param in the Databricks notebook.\n",
|
||||
"- **Mouting**: You will be supplied with additional parameters and secrets that will enable you to mount your ADLS or Azure Blob input or output location in your Databricks notebook."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Direct Access: Python sample code\n",
|
||||
"If you have a data reference named \"input\" it will represent the URI of the input and you can access it directly in the Databricks python notebook like so:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"dbutils.widgets.get(\"input\")\n",
|
||||
"y = getArgument(\"input\")\n",
|
||||
"df = spark.read.csv(y)\n",
|
||||
"```"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Mounting: Python sample code for Azure Blob\n",
|
||||
"Given an Azure Blob data reference named \"input\" the following widget params will be made available in the Databricks notebook:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"# This contains the input URI\n",
|
||||
"dbutils.widgets.get(\"input\")\n",
|
||||
"myinput_uri = getArgument(\"input\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# How to get the input datastore name inside ADB notebook\n",
|
||||
"# This contains the name of a Databricks secret (in the predefined \"amlscope\" secret scope) \n",
|
||||
"# that contians an access key or sas for the Azure Blob input (this name is obtained by appending \n",
|
||||
"# the name of the input with \"_blob_secretname\". \n",
|
||||
"dbutils.widgets.get(\"input_blob_secretname\") \n",
|
||||
"myinput_blob_secretname = getArgument(\"input_blob_secretname\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# This contains the required configuration for mounting\n",
|
||||
"dbutils.widgets.get(\"input_blob_config\")\n",
|
||||
"myinput_blob_config = getArgument(\"input_blob_config\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Usage\n",
|
||||
"dbutils.fs.mount(\n",
|
||||
" source = myinput_uri,\n",
|
||||
" mount_point = \"/mnt/input\",\n",
|
||||
" extra_configs = {myinput_blob_config:dbutils.secrets.get(scope = \"amlscope\", key = myinput_blob_secretname)})\n",
|
||||
"```"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Mounting: Python sample code for ADLS\n",
|
||||
"Given an ADLS data reference named \"input\" the following widget params will be made available in the Databricks notebook:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"# This contains the input URI\n",
|
||||
"dbutils.widgets.get(\"input\") \n",
|
||||
"myinput_uri = getArgument(\"input\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# This contains the client id for the service principal \n",
|
||||
"# that has access to the adls input\n",
|
||||
"dbutils.widgets.get(\"input_adls_clientid\") \n",
|
||||
"myinput_adls_clientid = getArgument(\"input_adls_clientid\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# This contains the name of a Databricks secret (in the predefined \"amlscope\" secret scope) \n",
|
||||
"# that contains the secret for the above mentioned service principal\n",
|
||||
"dbutils.widgets.get(\"input_adls_secretname\") \n",
|
||||
"myinput_adls_secretname = getArgument(\"input_adls_secretname\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# This contains the refresh url for the mounting configs\n",
|
||||
"dbutils.widgets.get(\"input_adls_refresh_url\") \n",
|
||||
"myinput_adls_refresh_url = getArgument(\"input_adls_refresh_url\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Usage \n",
|
||||
"configs = {\"dfs.adls.oauth2.access.token.provider.type\": \"ClientCredential\",\n",
|
||||
" \"dfs.adls.oauth2.client.id\": myinput_adls_clientid,\n",
|
||||
" \"dfs.adls.oauth2.credential\": dbutils.secrets.get(scope = \"amlscope\", key =myinput_adls_secretname),\n",
|
||||
" \"dfs.adls.oauth2.refresh.url\": myinput_adls_refresh_url}\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"dbutils.fs.mount(\n",
|
||||
" source = myinput_uri,\n",
|
||||
" mount_point = \"/mnt/output\",\n",
|
||||
" extra_configs = configs)\n",
|
||||
"```"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Use Databricks from Azure Machine Learning Pipeline\n",
|
||||
"To use Databricks as a compute target from Azure Machine Learning Pipeline, a DatabricksStep is used. Let's define a datasource (via DataReference) and intermediate data (via PipelineData) to be used in DatabricksStep."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Use the default blob storage\n",
|
||||
"def_blob_store = Datastore(ws, \"workspaceblobstore\")\n",
|
||||
"print('Datastore {} will be used'.format(def_blob_store.name))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# We are uploading a sample file in the local directory to be used as a datasource\n",
|
||||
"def_blob_store.upload_files([\"./testdata.txt\"], target_path=\"dbtest\", overwrite=False)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"step_1_input = DataReference(datastore=def_blob_store, path_on_datastore=\"dbtest\",\n",
|
||||
" data_reference_name=\"input\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"step_1_output = PipelineData(\"output\", datastore=def_blob_store)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Add a DatabricksStep\n",
|
||||
"Adds a Databricks notebook as a step in a Pipeline.\n",
|
||||
"- ***name:** Name of the Module\n",
|
||||
"- **inputs:** List of input connections for data consumed by this step. Fetch this inside the notebook using dbutils.widgets.get(\"input\")\n",
|
||||
"- **outputs:** List of output port definitions for outputs produced by this step. Fetch this inside the notebook using dbutils.widgets.get(\"output\")\n",
|
||||
"- **spark_version:** Version of spark for the databricks run cluster. default value: 4.0.x-scala2.11\n",
|
||||
"- **node_type:** Azure vm node types for the databricks run cluster. default value: Standard_D3_v2\n",
|
||||
"- **num_workers:** Number of workers for the databricks run cluster\n",
|
||||
"- **autoscale:** The autoscale configuration for the databricks run cluster\n",
|
||||
"- **spark_env_variables:** Spark environment variables for the databricks run cluster (dictionary of {str:str}). default value: {'PYSPARK_PYTHON': '/databricks/python3/bin/python3'}\n",
|
||||
"- ***notebook_path:** Path to the notebook in the databricks instance.\n",
|
||||
"- **notebook_params:** Parameters for the databricks notebook (dictionary of {str:str}). Fetch this inside the notebook using dbutils.widgets.get(\"myparam\")\n",
|
||||
"- **run_name:** Name in databricks for this run\n",
|
||||
"- **timeout_seconds:** Timeout for the databricks run\n",
|
||||
"- **maven_libraries:** maven libraries for the databricks run\n",
|
||||
"- **pypi_libraries:** pypi libraries for the databricks run\n",
|
||||
"- **egg_libraries:** egg libraries for the databricks run\n",
|
||||
"- **jar_libraries:** jar libraries for the databricks run\n",
|
||||
"- **rcran_libraries:** rcran libraries for the databricks run\n",
|
||||
"- **databricks_compute:** Azure Databricks compute\n",
|
||||
"- **databricks_compute_name:** Name of Azure Databricks compute\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\\* *denotes required fields* \n",
|
||||
"*You must provide exactly one of num_workers or autoscale paramaters* \n",
|
||||
"*You must provide exactly one of databricks_compute or databricks_compute_name parameters*"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"<a id='notebook_howto'></a>"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### 1. Running the demo notebook already added to the Databricks workspace\n",
|
||||
"The commented out code in the below cell assumes that you have created a notebook called `demo_notebook` in Azure Databricks under your user folder so you can use `notebook_path = \"/Users/you@company.com/demo_notebook\"`:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# notebook_path = \"/Users/you@company.com/demo_notebook\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"dbNbStep = DatabricksStep(\n",
|
||||
" name=\"DBNotebookInWS\",\n",
|
||||
" inputs=[step_1_input],\n",
|
||||
" outputs=[step_1_output],\n",
|
||||
" num_workers=1,\n",
|
||||
" notebook_path=notebook_path,\n",
|
||||
" notebook_params={'myparam': 'testparam'},\n",
|
||||
" run_name='DB_Notebook_demo',\n",
|
||||
" compute_target=databricks_compute,\n",
|
||||
" allow_reuse=False\n",
|
||||
")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Build and submit the Experiment"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"steps = [dbNbStep]\n",
|
||||
"pipeline = Pipeline(workspace=ws, steps=steps)\n",
|
||||
"pipeline_run = Experiment(ws, 'DB_Notebook_demo').submit(pipeline)\n",
|
||||
"pipeline_run.wait_for_completion()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### View Run Details"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(pipeline_run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### 2. Running a Python script that is already added in DBFS\n",
|
||||
"To run a Python script that is already uploaded to DBFS, follow the instructions below. You will first upload the Python script to DBFS using the [CLI](https://docs.azuredatabricks.net/user-guide/dbfs-databricks-file-system.html).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The commented out code in the below cell assumes that you have uploaded `train-db-dbfs.py` to the root folder in DBFS. You can upload `train-db-dbfs.py` to the root folder in DBFS using this commandline so you can use `python_script_path = \"dbfs:/train-db-dbfs.py\"`:\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"dbfs cp ./train-db-dbfs.py dbfs:/train-db-dbfs.py\n",
|
||||
"```"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"python_script_path = \"dbfs:/train-db-dbfs.py\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"dbPythonInDbfsStep = DatabricksStep(\n",
|
||||
" name=\"DBPythonInDBFS\",\n",
|
||||
" inputs=[step_1_input],\n",
|
||||
" num_workers=1,\n",
|
||||
" python_script_path=python_script_path,\n",
|
||||
" python_script_params={'--input_data'},\n",
|
||||
" run_name='DB_Python_demo',\n",
|
||||
" compute_target=databricks_compute,\n",
|
||||
" allow_reuse=False\n",
|
||||
")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Build and submit the Experiment"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"steps = [dbPythonInDbfsStep]\n",
|
||||
"pipeline = Pipeline(workspace=ws, steps=steps)\n",
|
||||
"pipeline_run = Experiment(ws, 'DB_Python_demo').submit(pipeline)\n",
|
||||
"pipeline_run.wait_for_completion()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### View Run Details"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(pipeline_run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### 3. Running a Python script in Databricks that currenlty is in local computer\n",
|
||||
"To run a Python script that is currently in your local computer, follow the instructions below. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The commented out code below code assumes that you have `train-db-local.py` in the `scripts` subdirectory under the current working directory.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this case, the Python script will be uploaded first to DBFS, and then the script will be run in Databricks."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"python_script_name = \"train-db-local.py\"\n",
|
||||
"source_directory = \".\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"dbPythonInLocalMachineStep = DatabricksStep(\n",
|
||||
" name=\"DBPythonInLocalMachine\",\n",
|
||||
" inputs=[step_1_input],\n",
|
||||
" num_workers=1,\n",
|
||||
" python_script_name=python_script_name,\n",
|
||||
" source_directory=source_directory,\n",
|
||||
" run_name='DB_Python_Local_demo',\n",
|
||||
" compute_target=databricks_compute,\n",
|
||||
" allow_reuse=False\n",
|
||||
")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Build and submit the Experiment"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"steps = [dbPythonInLocalMachineStep]\n",
|
||||
"pipeline = Pipeline(workspace=ws, steps=steps)\n",
|
||||
"pipeline_run = Experiment(ws, 'DB_Python_Local_demo').submit(pipeline)\n",
|
||||
"pipeline_run.wait_for_completion()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### View Run Details"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(pipeline_run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### 4. Running a JAR job that is alreay added in DBFS\n",
|
||||
"To run a JAR job that is already uploaded to DBFS, follow the instructions below. You will first upload the JAR file to DBFS using the [CLI](https://docs.azuredatabricks.net/user-guide/dbfs-databricks-file-system.html).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The commented out code in the below cell assumes that you have uploaded `train-db-dbfs.jar` to the root folder in DBFS. You can upload `train-db-dbfs.jar` to the root folder in DBFS using this commandline so you can use `jar_library_dbfs_path = \"dbfs:/train-db-dbfs.jar\"`:\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"dbfs cp ./train-db-dbfs.jar dbfs:/train-db-dbfs.jar\n",
|
||||
"```"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"main_jar_class_name = \"com.microsoft.aeva.Main\"\n",
|
||||
"jar_library_dbfs_path = \"dbfs:/train-db-dbfs.jar\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"dbJarInDbfsStep = DatabricksStep(\n",
|
||||
" name=\"DBJarInDBFS\",\n",
|
||||
" inputs=[step_1_input],\n",
|
||||
" num_workers=1,\n",
|
||||
" main_class_name=main_jar_class_name,\n",
|
||||
" jar_params={'arg1', 'arg2'},\n",
|
||||
" run_name='DB_JAR_demo',\n",
|
||||
" jar_libraries=[JarLibrary(jar_library_dbfs_path)],\n",
|
||||
" compute_target=databricks_compute,\n",
|
||||
" allow_reuse=False\n",
|
||||
")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Build and submit the Experiment"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"steps = [dbJarInDbfsStep]\n",
|
||||
"pipeline = Pipeline(workspace=ws, steps=steps)\n",
|
||||
"pipeline_run = Experiment(ws, 'DB_JAR_demo').submit(pipeline)\n",
|
||||
"pipeline_run.wait_for_completion()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### View Run Details"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(pipeline_run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Next: ADLA as a Compute Target\n",
|
||||
"To use ADLA as a compute target from Azure Machine Learning Pipeline, a AdlaStep is used. This [notebook](./aml-pipelines-use-adla-as-compute-target.ipynb) demonstrates the use of AdlaStep in Azure Machine Learning Pipeline."
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "diray"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.7"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
409
pipeline/aml-pipelines-with-data-dependency-steps.ipynb
Normal file
409
pipeline/aml-pipelines-with-data-dependency-steps.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,409 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. \n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Azure Machine Learning Pipelines with Data Dependency\n",
|
||||
"In this notebook, we will see how we can build a pipeline with implicit data dependancy."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Prerequisites and Azure Machine Learning Basics\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you go through the configuration Notebook located at https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks first if you haven't. This sets you up with a working config file that has information on your workspace, subscription id, etc. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Azure Machine Learning and Pipeline SDK-specific Imports"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import azureml.core\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Workspace, Run, Experiment, Datastore\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import DataFactoryCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Check core SDK version number\n",
|
||||
"print(\"SDK version:\", azureml.core.VERSION)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.data.data_reference import DataReference\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core import Pipeline, PipelineData, StepSequence\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.steps import PythonScriptStep\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.steps import DataTransferStep\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core import PublishedPipeline\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core.graph import PipelineParameter\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Pipeline SDK-specific imports completed\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Initialize Workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Initialize a [workspace](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-core/azureml.core.workspace(class%29) object from persisted configuration."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
"create workspace"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"print(ws.name, ws.resource_group, ws.location, ws.subscription_id, sep = '\\n')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Default datastore (Azure file storage)\n",
|
||||
"def_file_store = ws.get_default_datastore() \n",
|
||||
"print(\"Default datastore's name: {}\".format(def_file_store.name))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def_blob_store = Datastore(ws, \"workspaceblobstore\")\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Blobstore's name: {}\".format(def_blob_store.name))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# project folder\n",
|
||||
"project_folder = '.'\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"print('Sample projects will be created in {}.'.format(project_folder))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Required data and script files for the the tutorial\n",
|
||||
"Sample files required to finish this tutorial are already copied to the project folder specified above. Even though the .py provided in the samples don't have much \"ML work,\" as a data scientist, you will work on this extensively as part of your work. To complete this tutorial, the contents of these files are not very important. The one-line files are for demostration purpose only."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Compute Targets\n",
|
||||
"See the list of Compute Targets on the workspace."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"cts = ws.compute_targets\n",
|
||||
"for ct in cts:\n",
|
||||
" print(ct)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Retrieve or create a Aml compute\n",
|
||||
"Azure Machine Learning Compute is a service for provisioning and managing clusters of Azure virtual machines for running machine learning workloads. Let's create a new Aml Compute in the current workspace, if it doesn't already exist. We will then run the training script on this compute target."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"aml_compute_target = \"aml-compute\"\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" aml_compute = AmlCompute(ws, aml_compute_target)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"found existing compute target.\")\n",
|
||||
"except:\n",
|
||||
" print(\"creating new compute target\")\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" provisioning_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size = \"STANDARD_D2_V2\",\n",
|
||||
" min_nodes = 1, \n",
|
||||
" max_nodes = 4) \n",
|
||||
" aml_compute = ComputeTarget.create(ws, aml_compute_target, provisioning_config)\n",
|
||||
" aml_compute.wait_for_completion(show_output=True, min_node_count=None, timeout_in_minutes=20)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"print(\"Aml Compute attached\")\n",
|
||||
"# For a more detailed view of current AmlCompute status, use the 'status' property \n",
|
||||
"print(aml_compute.status.serialize())"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"**Wait for this call to finish before proceeding (you will see the asterisk turning to a number).**\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Now that you have created the compute target, let's see what the workspace's compute_targets() function returns. You should now see one entry named 'amlcompute' of type AmlCompute."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Building Pipeline Steps with Inputs and Outputs\n",
|
||||
"As mentioned earlier, a step in the pipeline can take data as input. This data can be a data source that lives in one of the accessible data locations, or intermediate data produced by a previous step in the pipeline.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Datasources\n",
|
||||
"Datasource is represented by **[DataReference](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-core/azureml.data.data_reference.datareference?view=azure-ml-py)** object and points to data that lives in or is accessible from Datastore. DataReference could be a pointer to a file or a directory."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Reference the data uploaded to blob storage using DataReference\n",
|
||||
"# Assign the datasource to blob_input_data variable\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# DataReference(datastore, \n",
|
||||
"# data_reference_name=None, \n",
|
||||
"# path_on_datastore=None, \n",
|
||||
"# mode='mount', \n",
|
||||
"# path_on_compute=None, \n",
|
||||
"# overwrite=False)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"blob_input_data = DataReference(\n",
|
||||
" datastore=def_blob_store,\n",
|
||||
" data_reference_name=\"test_data\",\n",
|
||||
" path_on_datastore=\"20newsgroups/20news.pkl\")\n",
|
||||
"print(\"DataReference object created\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Intermediate/Output Data\n",
|
||||
"Intermediate data (or output of a Step) is represented by **[PipelineData](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/python/api/azureml-pipeline-core/azureml.pipeline.core.pipelinedata?view=azure-ml-py)** object. PipelineData can be produced by one step and consumed in another step by providing the PipelineData object as an output of one step and the input of one or more steps.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### Constructing PipelineData\n",
|
||||
"- **name:** [*Required*] Name of the data item within the pipeline graph\n",
|
||||
"- **datastore_name:** Name of the Datastore to write this output to\n",
|
||||
"- **output_name:** Name of the output\n",
|
||||
"- **output_mode:** Specifies \"upload\" or \"mount\" modes for producing output (default: mount)\n",
|
||||
"- **output_path_on_compute:** For \"upload\" mode, the path to which the module writes this output during execution\n",
|
||||
"- **output_overwrite:** Flag to overwrite pre-existing data"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Define intermediate data using PipelineData\n",
|
||||
"# Syntax\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# PipelineData(name, \n",
|
||||
"# datastore=None, \n",
|
||||
"# output_name=None, \n",
|
||||
"# output_mode='mount', \n",
|
||||
"# output_path_on_compute=None, \n",
|
||||
"# output_overwrite=None, \n",
|
||||
"# data_type=None, \n",
|
||||
"# is_directory=None)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Naming the intermediate data as processed_data1 and assigning it to the variable processed_data1.\n",
|
||||
"processed_data1 = PipelineData(\"processed_data1\",datastore=def_blob_store)\n",
|
||||
"print(\"PipelineData object created\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Pipelines steps using datasources and intermediate data\n",
|
||||
"Machine learning pipelines have many steps and these steps could use or reuse datasources and intermediate data. Here's how we construct such a pipeline:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Define a Step that consumes a datasource and produces intermediate data.\n",
|
||||
"In this step, we define a step that consumes a datasource and produces intermediate data.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Open `train.py` in the local machine and examine the arguments, inputs, and outputs for the script. That will give you a good sense of why the script argument names used below are important.** "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# step4 consumes the datasource (Datareference) in the previous step\n",
|
||||
"# and produces processed_data1\n",
|
||||
"trainStep = PythonScriptStep(\n",
|
||||
" script_name=\"train.py\", \n",
|
||||
" arguments=[\"--input_data\", blob_input_data, \"--output_train\", processed_data1],\n",
|
||||
" inputs=[blob_input_data],\n",
|
||||
" outputs=[processed_data1],\n",
|
||||
" compute_target=aml_compute, \n",
|
||||
" source_directory=project_folder\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"print(\"trainStep created\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Define a Step that consumes intermediate data and produces intermediate data\n",
|
||||
"In this step, we define a step that consumes an intermediate data and produces intermediate data.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Open `extract.py` in the local machine and examine the arguments, inputs, and outputs for the script. That will give you a good sense of why the script argument names used below are important.** "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# step5 to use the intermediate data produced by step4\n",
|
||||
"# This step also produces an output processed_data2\n",
|
||||
"processed_data2 = PipelineData(\"processed_data2\", datastore=def_blob_store)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"extractStep = PythonScriptStep(\n",
|
||||
" script_name=\"extract.py\",\n",
|
||||
" arguments=[\"--input_extract\", processed_data1, \"--output_extract\", processed_data2],\n",
|
||||
" inputs=[processed_data1],\n",
|
||||
" outputs=[processed_data2],\n",
|
||||
" compute_target=aml_compute, \n",
|
||||
" source_directory=project_folder)\n",
|
||||
"print(\"extractStep created\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Define a Step that consumes multiple intermediate data and produces intermediate data\n",
|
||||
"In this step, we define a step that consumes multiple intermediate data and produces intermediate data.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Open `compare.py` in the local machine and examine the arguments, inputs, and outputs for the script. That will give you a good sense of why the script argument names used below are important.**"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Now define step6 that takes two inputs (both intermediate data), and produce an output\n",
|
||||
"processed_data3 = PipelineData(\"processed_data3\", datastore=def_blob_store)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"compareStep = PythonScriptStep(\n",
|
||||
" script_name=\"compare.py\",\n",
|
||||
" arguments=[\"--compare_data1\", processed_data1, \"--compare_data2\", processed_data2, \"--output_compare\", processed_data3],\n",
|
||||
" inputs=[processed_data1, processed_data2],\n",
|
||||
" outputs=[processed_data3], \n",
|
||||
" compute_target=aml_compute, \n",
|
||||
" source_directory=project_folder)\n",
|
||||
"print(\"compareStep created\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### Build the pipeline"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"pipeline1 = Pipeline(workspace=ws, steps=[compareStep])\n",
|
||||
"print (\"Pipeline is built\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"pipeline1.validate()\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Simple validation complete\") "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"pipeline_run1 = Experiment(ws, 'Data_dependency').submit(pipeline1)\n",
|
||||
"print(\"Pipeline is submitted for execution\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"RunDetails(pipeline_run1).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Next: Publishing the Pipeline and calling it from the REST endpoint\n",
|
||||
"See this [notebook](./aml-pipelines-publish-and-run-using-rest-endpoint.ipynb) to understand how the pipeline is published and you can call the REST endpoint to run the pipeline."
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "diray"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.7"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
119
pipeline/batch_scoring.py
Normal file
119
pipeline/batch_scoring.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
|
||||
# Copyright (c) Microsoft. All rights reserved.
|
||||
# Licensed under the MIT license.
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import datetime
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import tensorflow as tf
|
||||
from math import ceil
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import shutil
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.slim.python.slim.nets import inception_v3
|
||||
from azureml.core.model import Model
|
||||
|
||||
slim = tf.contrib.slim
|
||||
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Start a tensorflow model serving")
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--model_name', dest="model_name", required=True)
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--label_dir', dest="label_dir", required=True)
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--dataset_path', dest="dataset_path", required=True)
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--output_dir', dest="output_dir", required=True)
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--batch_size', dest="batch_size", type=int, required=True)
|
||||
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
image_size = 299
|
||||
num_channel = 3
|
||||
|
||||
# create output directory if it does not exist
|
||||
os.makedirs(args.output_dir, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_class_label_dict(label_file):
|
||||
label = []
|
||||
proto_as_ascii_lines = tf.gfile.GFile(label_file).readlines()
|
||||
for l in proto_as_ascii_lines:
|
||||
label.append(l.rstrip())
|
||||
return label
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DataIterator:
|
||||
def __init__(self, data_dir):
|
||||
self.file_paths = []
|
||||
image_list = os.listdir(data_dir)
|
||||
# total_size = len(image_list)
|
||||
self.file_paths = [data_dir + '/' + file_name.rstrip() for file_name in image_list]
|
||||
|
||||
self.labels = [1 for file_name in self.file_paths]
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def size(self):
|
||||
return len(self.labels)
|
||||
|
||||
def input_pipeline(self, batch_size):
|
||||
images_tensor = tf.convert_to_tensor(self.file_paths, dtype=tf.string)
|
||||
labels_tensor = tf.convert_to_tensor(self.labels, dtype=tf.int64)
|
||||
input_queue = tf.train.slice_input_producer([images_tensor, labels_tensor], shuffle=False)
|
||||
labels = input_queue[1]
|
||||
images_content = tf.read_file(input_queue[0])
|
||||
|
||||
image_reader = tf.image.decode_jpeg(images_content, channels=num_channel, name="jpeg_reader")
|
||||
float_caster = tf.cast(image_reader, tf.float32)
|
||||
new_size = tf.constant([image_size, image_size], dtype=tf.int32)
|
||||
images = tf.image.resize_images(float_caster, new_size)
|
||||
images = tf.divide(tf.subtract(images, [0]), [255])
|
||||
|
||||
image_batch, label_batch = tf.train.batch([images, labels], batch_size=batch_size, capacity=5 * batch_size)
|
||||
return image_batch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main(_):
|
||||
# start_time = datetime.datetime.now()
|
||||
label_file_name = os.path.join(args.label_dir, "labels.txt")
|
||||
label_dict = get_class_label_dict(label_file_name)
|
||||
classes_num = len(label_dict)
|
||||
test_feeder = DataIterator(data_dir=args.dataset_path)
|
||||
total_size = len(test_feeder.labels)
|
||||
count = 0
|
||||
# get model from model registry
|
||||
model_path = Model.get_model_path(args.model_name)
|
||||
with tf.Session() as sess:
|
||||
test_images = test_feeder.input_pipeline(batch_size=args.batch_size)
|
||||
with slim.arg_scope(inception_v3.inception_v3_arg_scope()):
|
||||
input_images = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [args.batch_size, image_size, image_size, num_channel])
|
||||
logits, _ = inception_v3.inception_v3(input_images,
|
||||
num_classes=classes_num,
|
||||
is_training=False)
|
||||
probabilities = tf.argmax(logits, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
|
||||
sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer())
|
||||
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
|
||||
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
|
||||
saver = tf.train.Saver()
|
||||
saver.restore(sess, model_path)
|
||||
out_filename = os.path.join(args.output_dir, "result-labels.txt")
|
||||
with open(out_filename, "w") as result_file:
|
||||
i = 0
|
||||
while count < total_size and not coord.should_stop():
|
||||
test_images_batch = sess.run(test_images)
|
||||
file_names_batch = test_feeder.file_paths[i * args.batch_size:
|
||||
min(test_feeder.size, (i + 1) * args.batch_size)]
|
||||
results = sess.run(probabilities, feed_dict={input_images: test_images_batch})
|
||||
new_add = min(args.batch_size, total_size - count)
|
||||
count += new_add
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
for j in range(new_add):
|
||||
result_file.write(os.path.basename(file_names_batch[j]) + ": " + label_dict[results[j]] + "\n")
|
||||
result_file.flush()
|
||||
coord.request_stop()
|
||||
coord.join(threads)
|
||||
|
||||
# copy the file to artifacts
|
||||
shutil.copy(out_filename, "./outputs/")
|
||||
# Move the processed data out of the blob so that the next run can process the data.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
tf.app.run()
|
||||
22
pipeline/compare.py
Normal file
22
pipeline/compare.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
# Copyright (c) Microsoft. All rights reserved.
|
||||
# Licensed under the MIT license.
|
||||
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
print("In compare.py")
|
||||
print("As a data scientist, this is where I use my compare code.")
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser("compare")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--compare_data1", type=str, help="compare_data1 data")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--compare_data2", type=str, help="compare_data2 data")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--output_compare", type=str, help="output_compare directory")
|
||||
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
print("Argument 1: %s" % args.compare_data1)
|
||||
print("Argument 2: %s" % args.compare_data2)
|
||||
print("Argument 3: %s" % args.output_compare)
|
||||
|
||||
if not (args.output_compare is None):
|
||||
os.makedirs(args.output_compare, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
print("%s created" % args.output_compare)
|
||||
21
pipeline/extract.py
Normal file
21
pipeline/extract.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
# Copyright (c) Microsoft. All rights reserved.
|
||||
# Licensed under the MIT license.
|
||||
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
print("In extract.py")
|
||||
print("As a data scientist, this is where I use my extract code.")
|
||||
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser("extract")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--input_extract", type=str, help="input_extract data")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--output_extract", type=str, help="output_extract directory")
|
||||
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
print("Argument 1: %s" % args.input_extract)
|
||||
print("Argument 2: %s" % args.output_extract)
|
||||
|
||||
if not (args.output_extract is None):
|
||||
os.makedirs(args.output_extract, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
print("%s created" % args.output_extract)
|
||||
@@ -5,7 +5,6 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -13,7 +12,15 @@
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"This notebook demonstrates how to run batch scoring job. __[Inception-V3 model](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.00567)__ and unlabeled images from __[ImageNet](http://image-net.org/)__ dataset will be used. It registers a pretrained inception model in model registry then uses the model to do batch scoring on images in a blob container."
|
||||
"# Using Azure Machine Learning Pipelines for batch prediction\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this notebook we will demonstrate how to run a batch scoring job using Azure Machine Learning pipelines. Our example job will be to take an already-trained image classification model, and run that model on some unlabeled images. The image classification model that we'll use is the __[Inception-V3 model](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.00567)__ and we'll run this model on unlabeled images from the __[ImageNet](http://image-net.org/)__ dataset. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The outline of this notebook is as follows:\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- Register the pretrained inception model into the model registry. \n",
|
||||
"- Store the dataset images in a blob container.\n",
|
||||
"- Use the registered model to do batch scoring on the images in the data blob container."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -21,7 +28,24 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Prerequisites\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you go through the [00. Installation and Configuration](./00.configuration.ipynb) Notebook first if you haven't.\n"
|
||||
"Make sure you go through the configuration Notebook located at https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks first if you haven't. This sets you up with a working config file that has information on your workspace, subscription id, etc. "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Datastore\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Experiment\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import AmlCompute, ComputeTarget\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.datastore import Datastore\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.runconfig import CondaDependencies, RunConfiguration\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.data.data_reference import DataReference\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core import Pipeline, PipelineData\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.steps import PythonScriptStep"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -37,13 +61,28 @@
|
||||
"print('Workspace name: ' + ws.name, \n",
|
||||
" 'Azure region: ' + ws.location, \n",
|
||||
" 'Subscription id: ' + ws.subscription_id, \n",
|
||||
" 'Resource group: ' + ws.resource_group, sep = '\\n')\n",
|
||||
" 'Resource group: ' + ws.resource_group, sep = '\\n')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Set up machine learning resources"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Set up datastores\n",
|
||||
"First, let’s access the datastore that has the model, labels, and images. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Also create a Project and attach to Workspace\n",
|
||||
"scripts_folder = \"scripts\"\n",
|
||||
"### Create a datastore that points to a blob container containing sample images\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"if not os.path.isdir(scripts_folder):\n",
|
||||
" os.mkdir(scripts_folder)"
|
||||
"We have created a public blob container `sampledata` on an account named `pipelinedata`, containing images from the ImageNet evaluation set. In the next step, we create a datastore with the name `images_datastore`, which points to this container. In the call to `register_azure_blob_container` below, setting the `overwrite` flag to `True` overwrites any datastore that was created previously with that name. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This step can be changed to point to your blob container by providing your own `datastore_name`, `container_name`, and `account_name`."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -52,19 +91,72 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import BatchAiCompute, ComputeTarget\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.datastore import Datastore\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.data.data_reference import DataReference\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core import Pipeline, PipelineData\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.steps import PythonScriptStep\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.runconfig import CondaDependencies, RunConfiguration"
|
||||
"account_name = \"pipelinedata\"\n",
|
||||
"datastore_name=\"images_datastore\"\n",
|
||||
"container_name=\"sampledata\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"batchscore_blob = Datastore.register_azure_blob_container(ws, \n",
|
||||
" datastore_name=datastore_name, \n",
|
||||
" container_name= container_name, \n",
|
||||
" account_name=account_name, \n",
|
||||
" overwrite=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create and attach Compute targets\n",
|
||||
"Next, let’s specify the default datastore for the outputs."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"def_data_store = ws.get_default_datastore()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Configure data references\n",
|
||||
"Now you need to add references to the data, as inputs to the appropriate pipeline steps in your pipeline. A data source in a pipeline is represented by a DataReference object. The DataReference object points to data that lives in, or is accessible from, a datastore. We need DataReference objects corresponding to the following: the directory containing the input images, the directory in which the pretrained model is stored, the directory containing the labels, and the output directory."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"input_images = DataReference(datastore=batchscore_blob, \n",
|
||||
" data_reference_name=\"input_images\",\n",
|
||||
" path_on_datastore=\"batchscoring/images\",\n",
|
||||
" mode=\"download\"\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
"model_dir = DataReference(datastore=batchscore_blob, \n",
|
||||
" data_reference_name=\"input_model\",\n",
|
||||
" path_on_datastore=\"batchscoring/models\",\n",
|
||||
" mode=\"download\" \n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
"label_dir = DataReference(datastore=batchscore_blob, \n",
|
||||
" data_reference_name=\"input_labels\",\n",
|
||||
" path_on_datastore=\"batchscoring/labels\",\n",
|
||||
" mode=\"download\" \n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
"output_dir = PipelineData(name=\"scores\", \n",
|
||||
" datastore=def_data_store, \n",
|
||||
" output_path_on_compute=\"batchscoring/results\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Create and attach Compute targets\n",
|
||||
"Use the below code to create and attach Compute targets. "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -74,171 +166,51 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Batch AI compute\n",
|
||||
"cluster_name = \"gpu-cluster\"\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" cluster = BatchAiCompute(ws, cluster_name)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"found existing cluster.\")\n",
|
||||
"except:\n",
|
||||
" print(\"creating new cluster\")\n",
|
||||
" provisioning_config = BatchAiCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size = \"STANDARD_NC6\",\n",
|
||||
" autoscale_enabled = True,\n",
|
||||
" cluster_min_nodes = 0, \n",
|
||||
" cluster_max_nodes = 1)\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for your cluster\n",
|
||||
"aml_compute_name = os.environ.get(\"AML_COMPUTE_NAME\", \"gpu-cluster\")\n",
|
||||
"cluster_min_nodes = os.environ.get(\"AML_COMPUTE_MIN_NODES\", 0)\n",
|
||||
"cluster_max_nodes = os.environ.get(\"AML_COMPUTE_MAX_NODES\", 1)\n",
|
||||
"vm_size = os.environ.get(\"AML_COMPUTE_SKU\", \"STANDARD_NC6\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"if aml_compute_name in ws.compute_targets:\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = ws.compute_targets[aml_compute_name]\n",
|
||||
" if compute_target and type(compute_target) is AmlCompute:\n",
|
||||
" print('found compute target. just use it. ' + aml_compute_name)\n",
|
||||
"else:\n",
|
||||
" print('creating a new compute target...')\n",
|
||||
" provisioning_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size = vm_size, # NC6 is GPU-enabled\n",
|
||||
" vm_priority = 'lowpriority', # optional\n",
|
||||
" min_nodes = cluster_min_nodes, \n",
|
||||
" max_nodes = cluster_max_nodes)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # create the cluster\n",
|
||||
" cluster = ComputeTarget.create(ws, cluster_name, provisioning_config)\n",
|
||||
" cluster.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)"
|
||||
" compute_target = ComputeTarget.create(ws, aml_compute_name, provisioning_config)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # can poll for a minimum number of nodes and for a specific timeout. \n",
|
||||
" # if no min node count is provided it will use the scale settings for the cluster\n",
|
||||
" compute_target.wait_for_completion(show_output=True, min_node_count=None, timeout_in_minutes=20)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # For a more detailed view of current Azure Machine Learning Compute status, use the 'status' property \n",
|
||||
" print(compute_target.status.serialize())"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Python scripts to run"
|
||||
"## Prepare the Model"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Python scripts that run the batch scoring. `batchai_score.py` takes input images in `dataset_path`, pretrained models in `model_dir` and outputs a `results-label.txt` to `output_dir`."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%%writefile $scripts_folder/batchai_score.py\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"import argparse\n",
|
||||
"import datetime,time\n",
|
||||
"import tensorflow as tf\n",
|
||||
"from math import ceil\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"import shutil\n",
|
||||
"from tensorflow.contrib.slim.python.slim.nets import inception_v3\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.model import Model\n",
|
||||
"### Download the Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"slim = tf.contrib.slim\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=\"Start a tensorflow model serving\")\n",
|
||||
"parser.add_argument('--model_name', dest=\"model_name\", required=True)\n",
|
||||
"parser.add_argument('--label_dir', dest=\"label_dir\", required=True)\n",
|
||||
"parser.add_argument('--dataset_path', dest=\"dataset_path\", required=True)\n",
|
||||
"parser.add_argument('--output_dir', dest=\"output_dir\", required=True)\n",
|
||||
"parser.add_argument('--batch_size', dest=\"batch_size\", type=int, required=True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"args = parser.parse_args()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"image_size = 299\n",
|
||||
"num_channel = 3\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# create output directory if it does not exist\n",
|
||||
"os.makedirs(args.output_dir, exist_ok=True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def get_class_label_dict(label_file):\n",
|
||||
" label = []\n",
|
||||
" proto_as_ascii_lines = tf.gfile.GFile(label_file).readlines()\n",
|
||||
" for l in proto_as_ascii_lines:\n",
|
||||
" label.append(l.rstrip())\n",
|
||||
" return label\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"class DataIterator:\n",
|
||||
" def __init__(self, data_dir):\n",
|
||||
" self.file_paths = []\n",
|
||||
" image_list = os.listdir(data_dir)\n",
|
||||
" total_size = len(image_list)\n",
|
||||
" self.file_paths = [data_dir + '/' + file_name.rstrip() for file_name in image_list ]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" self.labels = [1 for file_name in self.file_paths]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" @property\n",
|
||||
" def size(self):\n",
|
||||
" return len(self.labels)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" def input_pipeline(self, batch_size):\n",
|
||||
" images_tensor = tf.convert_to_tensor(self.file_paths, dtype=tf.string)\n",
|
||||
" labels_tensor = tf.convert_to_tensor(self.labels, dtype=tf.int64)\n",
|
||||
" input_queue = tf.train.slice_input_producer([images_tensor, labels_tensor], shuffle=False)\n",
|
||||
" labels = input_queue[1]\n",
|
||||
" images_content = tf.read_file(input_queue[0])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" image_reader = tf.image.decode_jpeg(images_content, channels=num_channel, name=\"jpeg_reader\")\n",
|
||||
" float_caster = tf.cast(image_reader, tf.float32)\n",
|
||||
" new_size = tf.constant([image_size, image_size], dtype=tf.int32)\n",
|
||||
" images = tf.image.resize_images(float_caster, new_size)\n",
|
||||
" images = tf.divide(tf.subtract(images, [0]), [255])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" image_batch, label_batch = tf.train.batch([images, labels], batch_size=batch_size, capacity=5 * batch_size)\n",
|
||||
" return image_batch\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def main(_):\n",
|
||||
" start_time = datetime.datetime.now()\n",
|
||||
" label_file_name = os.path.join(args.label_dir, \"labels.txt\")\n",
|
||||
" label_dict = get_class_label_dict(label_file_name)\n",
|
||||
" classes_num = len(label_dict)\n",
|
||||
" test_feeder = DataIterator(data_dir=args.dataset_path)\n",
|
||||
" total_size = len(test_feeder.labels)\n",
|
||||
" count = 0\n",
|
||||
" # get model from model registry\n",
|
||||
" model_path = Model.get_model_path(args.model_name)\n",
|
||||
" with tf.Session() as sess:\n",
|
||||
" test_images = test_feeder.input_pipeline(batch_size=args.batch_size)\n",
|
||||
" with slim.arg_scope(inception_v3.inception_v3_arg_scope()):\n",
|
||||
" input_images = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [args.batch_size, image_size, image_size, num_channel])\n",
|
||||
" logits, _ = inception_v3.inception_v3(input_images,\n",
|
||||
" num_classes=classes_num,\n",
|
||||
" is_training=False)\n",
|
||||
" probabilities = tf.argmax(logits, 1)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())\n",
|
||||
" sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer())\n",
|
||||
" coord = tf.train.Coordinator()\n",
|
||||
" threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)\n",
|
||||
" saver = tf.train.Saver()\n",
|
||||
" saver.restore(sess, model_path)\n",
|
||||
" out_filename = os.path.join(args.output_dir, \"result-labels.txt\")\n",
|
||||
" with open(out_filename, \"w\") as result_file:\n",
|
||||
" i = 0\n",
|
||||
" while count < total_size and not coord.should_stop():\n",
|
||||
" test_images_batch = sess.run(test_images)\n",
|
||||
" file_names_batch = test_feeder.file_paths[i*args.batch_size: min(test_feeder.size, (i+1)*args.batch_size)]\n",
|
||||
" results = sess.run(probabilities, feed_dict={input_images: test_images_batch})\n",
|
||||
" new_add = min(args.batch_size, total_size-count)\n",
|
||||
" count += new_add\n",
|
||||
" i += 1\n",
|
||||
" for j in range(new_add):\n",
|
||||
" result_file.write(os.path.basename(file_names_batch[j]) + \": \" + label_dict[results[j]] + \"\\n\")\n",
|
||||
" result_file.flush()\n",
|
||||
" coord.request_stop()\n",
|
||||
" coord.join(threads)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # copy the file to artifacts\n",
|
||||
" shutil.copy(out_filename, \"./outputs/\")\n",
|
||||
" # Move the processed data out of the blob so that the next run can process the data.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"if __name__ == \"__main__\":\n",
|
||||
" tf.app.run()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Prepare Model and Input data"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Download Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Download and extract model from http://download.tensorflow.org/models/inception_v3_2016_08_28.tar.gz to `\"models\"`"
|
||||
"Download and extract the model from http://download.tensorflow.org/models/inception_v3_2016_08_28.tar.gz to `\"models\"`"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -272,99 +244,7 @@
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Create a datastore that points to blob container containing sample images\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"We have created a public blob container `sampledata` on an account named `pipelinedata` containing images from ImageNet evaluation set. In the next step, we create a datastore with name `images_datastore` that points to this container. The `overwrite=True` step overwrites any datastore that was created previously with that name. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This step can be changed to point to your blob container by providing an additional `account_key` parameter with `account_name`. "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"account_name = \"pipelinedata\"\n",
|
||||
"sample_data = Datastore.register_azure_blob_container(ws, datastore_name=\"images_datastore\", container_name=\"sampledata\", \n",
|
||||
" account_name=account_name, \n",
|
||||
" overwrite=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Output datastore"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"We write the outputs to the default datastore"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"default_ds = ws.get_default_datastore()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Specify where the data is stored or will be written to"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.data.data_reference import DataReference\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core import Pipeline, PipelineData\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Datastore\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Experiment"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"input_images = DataReference(datastore=sample_data, \n",
|
||||
" data_reference_name=\"input_images\",\n",
|
||||
" path_on_datastore=\"batchscoring/images\",\n",
|
||||
" mode=\"download\"\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
"model_dir = DataReference(datastore=sample_data, \n",
|
||||
" data_reference_name=\"input_model\",\n",
|
||||
" path_on_datastore=\"batchscoring/models\",\n",
|
||||
" mode=\"download\" \n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
"label_dir = DataReference(datastore=sample_data, \n",
|
||||
" data_reference_name=\"input_labels\",\n",
|
||||
" path_on_datastore=\"batchscoring/labels\",\n",
|
||||
" mode=\"download\" \n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
"output_dir = PipelineData(name=\"scores\", \n",
|
||||
" datastore_name=default_ds.name, \n",
|
||||
" output_path_on_compute=\"batchscoring/results\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Register the model with Workspace"
|
||||
"### Register the model with Workspace"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -390,7 +270,40 @@
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Specify environment to run the script"
|
||||
"## Write your scoring script"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"To do the scoring, we use a batch scoring script `batch_scoring.py`, which is located in the same directory that this notebook is in. You can take a look at this script to see how you might modify it for your custom batch scoring task.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The python script `batch_scoring.py` takes input images, applies the image classification model to these images, and outputs a classification result to a results file.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"The script `batch_scoring.py` takes the following parameters:\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- `--model_name`: the name of the model being used, which is expected to be in the `model_dir` directory\n",
|
||||
"- `--label_dir` : the directory holding the `labels.txt` file \n",
|
||||
"- `--dataset_path`: the directory containing the input images\n",
|
||||
"- `--output_dir` : the script will run the model on the data and output a `results-label.txt` to this directory\n",
|
||||
"- `--batch_size` : the batch size used in running the model.\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Build and run the batch scoring pipeline\n",
|
||||
"You have everything you need to build the pipeline. Let’s put all these together."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Specify the environment to run the script\n",
|
||||
"Specify the conda dependencies for your script. You will need this object when you create the pipeline step later on."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -399,27 +312,23 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"cd = CondaDependencies.create(pip_packages=[\"tensorflow-gpu==1.4.0\", \"azureml-defaults\"])\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.runconfig import DEFAULT_GPU_IMAGE\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"cd = CondaDependencies.create(pip_packages=[\"tensorflow-gpu==1.10.0\", \"azureml-defaults\"])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Runconfig\n",
|
||||
"batchai_run_config = RunConfiguration(conda_dependencies=cd)\n",
|
||||
"batchai_run_config.environment.docker.enabled = True\n",
|
||||
"batchai_run_config.environment.docker.gpu_support = True\n",
|
||||
"batchai_run_config.environment.docker.base_image = \"microsoft/mmlspark:gpu-0.12\"\n",
|
||||
"batchai_run_config.environment.spark.precache_packages = False"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Steps to run"
|
||||
"amlcompute_run_config = RunConfiguration(conda_dependencies=cd)\n",
|
||||
"amlcompute_run_config.environment.docker.enabled = True\n",
|
||||
"amlcompute_run_config.environment.docker.gpu_support = True\n",
|
||||
"amlcompute_run_config.environment.docker.base_image = DEFAULT_GPU_IMAGE\n",
|
||||
"amlcompute_run_config.environment.spark.precache_packages = False"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Specify the parameters for your pipeline\n",
|
||||
"A subset of the parameters to the python script can be given as input when we re-run a `PublishedPipeline`. In the current example, we define `batch_size` taken by the script as such parameter."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -433,6 +342,14 @@
|
||||
"batch_size_param = PipelineParameter(name=\"param_batch_size\", default_value=20)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Create the pipeline step\n",
|
||||
"Create the pipeline step using the script, environment configuration, and parameters. Specify the compute target you already attached to your workspace as the target of execution of the script. We will use PythonScriptStep to create the pipeline step."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
@@ -442,21 +359,28 @@
|
||||
"inception_model_name = \"inception_v3.ckpt\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"batch_score_step = PythonScriptStep(\n",
|
||||
" name=\"batch ai scoring\",\n",
|
||||
" script_name=\"batchai_score.py\",\n",
|
||||
" name=\"batch_scoring\",\n",
|
||||
" script_name=\"batch_scoring.py\",\n",
|
||||
" arguments=[\"--dataset_path\", input_images, \n",
|
||||
" \"--model_name\", \"inception\",\n",
|
||||
" \"--label_dir\", label_dir, \n",
|
||||
" \"--output_dir\", output_dir, \n",
|
||||
" \"--batch_size\", batch_size_param],\n",
|
||||
" target=cluster,\n",
|
||||
" compute_target=compute_target,\n",
|
||||
" inputs=[input_images, label_dir],\n",
|
||||
" outputs=[output_dir],\n",
|
||||
" runconfig=batchai_run_config,\n",
|
||||
" source_directory=scripts_folder\n",
|
||||
" runconfig=amlcompute_run_config\n",
|
||||
")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Run the pipeline\n",
|
||||
"At this point you can run the pipeline and examine the output it produced. "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
@@ -471,7 +395,7 @@
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Monitor run"
|
||||
"### Monitor the run"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -480,7 +404,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(pipeline_run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -497,7 +421,7 @@
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Download and review output"
|
||||
"### Download and review output"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -526,14 +450,15 @@
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Publish a pipeline and rerun using a REST call"
|
||||
"## Publish a pipeline and rerun using a REST call"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create a published pipeline"
|
||||
"### Create a published pipeline\n",
|
||||
"Once you are satisfied with the outcome of the run, you can publish the pipeline to run it with different input values later. When you publish a pipeline, you will get a REST endpoint that accepts invoking of the pipeline with the set of parameters you have already incorporated above using PipelineParameter."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -543,7 +468,7 @@
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"published_pipeline = pipeline_run.publish_pipeline(\n",
|
||||
" name=\"Inception v3 scoring\", description=\"Batch scoring using Inception v3 model\", version=\"1.0\")\n",
|
||||
" name=\"Inception_v3_scoring\", description=\"Batch scoring using Inception v3 model\", version=\"1.0\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"published_id = published_pipeline.id"
|
||||
]
|
||||
@@ -552,14 +477,14 @@
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Rerun using REST call"
|
||||
"## Rerun the pipeline using the REST endpoint"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Get AAD token"
|
||||
"### Get AAD token"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -579,7 +504,7 @@
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Run published pipeline using its REST endpoint"
|
||||
"### Run published pipeline"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -590,9 +515,12 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core import PublishedPipeline\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"rest_endpoint = PublishedPipeline.get_endpoint(published_id, ws)\n",
|
||||
"rest_endpoint = published_pipeline.endpoint\n",
|
||||
"# specify batch size when running the pipeline\n",
|
||||
"response = requests.post(rest_endpoint, headers=aad_token, json={\"param_batch_size\": 50})\n",
|
||||
"response = requests.post(rest_endpoint, \n",
|
||||
" headers=aad_token, \n",
|
||||
" json={\"ExperimentName\": \"batch_scoring\",\n",
|
||||
" \"ParameterAssignments\": {\"param_batch_size\": 50}})\n",
|
||||
"run_id = response.json()[\"Id\"]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -600,7 +528,7 @@
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Monitor the new run"
|
||||
"### Monitor the new run"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -610,7 +538,7 @@
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core.run import PipelineRun\n",
|
||||
"published_pipeline_run = PipelineRun(ws.experiments()[\"batch_scoring\"], run_id)\n",
|
||||
"published_pipeline_run = PipelineRun(ws.experiments[\"batch_scoring\"], run_id)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(published_pipeline_run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
@@ -623,9 +551,9 @@
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.6",
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python36"
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
@@ -637,7 +565,7 @@
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
"version": "3.6.7"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
|
||||
610
pipeline/pipeline-style-transfer.ipynb
Normal file
610
pipeline/pipeline-style-transfer.ipynb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,610 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Licensed under the MIT License."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Neural style transfer on video\n",
|
||||
"Using modified code from `pytorch`'s neural style [example](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/advanced/neural_style_tutorial.html), we show how to setup a pipeline for doing style transfer on video. The pipeline has following steps:\n",
|
||||
"1. Split a video into images\n",
|
||||
"2. Run neural style on each image using one of the provided models (from `pytorch` pretrained models for this example).\n",
|
||||
"3. Stitch the image back into a video."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Prerequisites\n",
|
||||
"Make sure you go through the configuration Notebook located at https://github.com/Azure/MachineLearningNotebooks first if you haven't. This sets you up with a working config file that has information on your workspace, subscription id, etc. "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Initialize Workspace\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Initialize a workspace object from persisted configuration."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core import Workspace, Run, Experiment\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"print('Workspace name: ' + ws.name, \n",
|
||||
" 'Azure region: ' + ws.location, \n",
|
||||
" 'Subscription id: ' + ws.subscription_id, \n",
|
||||
" 'Resource group: ' + ws.resource_group, sep = '\\n')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"scripts_folder = \"scripts_folder\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"if not os.path.isdir(scripts_folder):\n",
|
||||
" os.mkdir(scripts_folder)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import AmlCompute, ComputeTarget\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.datastore import Datastore\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.data.data_reference import DataReference\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core import Pipeline, PipelineData\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.steps import PythonScriptStep, MpiStep\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.runconfig import CondaDependencies, RunConfiguration"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Create or use existing compute"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"cpu_cluster_name = \"cpucluster\"\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" cpu_cluster = AmlCompute(ws, cpu_cluster_name)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"found existing cluster.\")\n",
|
||||
"except:\n",
|
||||
" print(\"creating new cluster\")\n",
|
||||
" provisioning_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size = \"STANDARD_D2_v2\",\n",
|
||||
" max_nodes = 1)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # create the cluster\n",
|
||||
" cpu_cluster = ComputeTarget.create(ws, cpu_cluster_name, provisioning_config)\n",
|
||||
" cpu_cluster.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"# AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"gpu_cluster_name = \"gpucluster\"\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" gpu_cluster = AmlCompute(ws, gpu_cluster_name)\n",
|
||||
" print(\"found existing cluster.\")\n",
|
||||
"except:\n",
|
||||
" print(\"creating new cluster\")\n",
|
||||
" provisioning_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size = \"STANDARD_NC6\",\n",
|
||||
" max_nodes = 3)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # create the cluster\n",
|
||||
" gpu_cluster = ComputeTarget.create(ws, gpu_cluster_name, provisioning_config)\n",
|
||||
" gpu_cluster.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Python Scripts\n",
|
||||
"We use an edited version of `neural_style_mpi.py` (original is [here](https://github.com/pytorch/examples/blob/master/fast_neural_style/neural_style/neural_style_mpi.py)). Scripts to split and stitch the video are thin wrappers to calls to `ffmpeg`. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"We install `ffmpeg` through conda dependencies."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import shutil\n",
|
||||
"shutil.copy(\"neural_style_mpi.py\", scripts_folder)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%%writefile $scripts_folder/process_video.py\n",
|
||||
"import argparse\n",
|
||||
"import glob\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"import subprocess\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=\"Process input video\")\n",
|
||||
"parser.add_argument('--input_video', required=True)\n",
|
||||
"parser.add_argument('--output_audio', required=True)\n",
|
||||
"parser.add_argument('--output_images', required=True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"args = parser.parse_args()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"os.makedirs(args.output_audio, exist_ok=True)\n",
|
||||
"os.makedirs(args.output_images, exist_ok=True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"subprocess.run(\"ffmpeg -i {} {}/video.aac\"\n",
|
||||
" .format(args.input_video, args.output_audio),\n",
|
||||
" shell=True, check=True\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"subprocess.run(\"ffmpeg -i {} {}/%05d_video.jpg -hide_banner\"\n",
|
||||
" .format(args.input_video, args.output_images),\n",
|
||||
" shell=True, check=True\n",
|
||||
" )"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%%writefile $scripts_folder/stitch_video.py\n",
|
||||
"import argparse\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"import subprocess\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=\"Process input video\")\n",
|
||||
"parser.add_argument('--images_dir', required=True)\n",
|
||||
"parser.add_argument('--input_audio', required=True)\n",
|
||||
"parser.add_argument('--output_dir', required=True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"args = parser.parse_args()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"os.makedirs(args.output_dir, exist_ok=True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"subprocess.run(\"ffmpeg -framerate 30 -i {}/%05d_video.jpg -c:v libx264 -profile:v high -crf 20 -pix_fmt yuv420p \"\n",
|
||||
" \"-y {}/video_without_audio.mp4\"\n",
|
||||
" .format(args.images_dir, args.output_dir),\n",
|
||||
" shell=True, check=True\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"subprocess.run(\"ffmpeg -i {}/video_without_audio.mp4 -i {}/video.aac -map 0:0 -map 1:0 -vcodec \"\n",
|
||||
" \"copy -acodec copy -y {}/video_with_audio.mp4\"\n",
|
||||
" .format(args.output_dir, args.input_audio, args.output_dir),\n",
|
||||
" shell=True, check=True\n",
|
||||
" )"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# datastore for input video\n",
|
||||
"account_name = \"happypathspublic\"\n",
|
||||
"video_ds = Datastore.register_azure_blob_container(ws, \"videos\", \"videos\",\n",
|
||||
" account_name=account_name, overwrite=True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# datastore for models\n",
|
||||
"models_ds = Datastore.register_azure_blob_container(ws, \"models\", \"styletransfer\", \n",
|
||||
" account_name=\"pipelinedata\", \n",
|
||||
" overwrite=True)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"# downloaded models from https://pytorch.org/tutorials/advanced/neural_style_tutorial.html are kept here\n",
|
||||
"models_dir = DataReference(data_reference_name=\"models\", datastore=models_ds, \n",
|
||||
" path_on_datastore=\"saved_models\", mode=\"download\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# the default blob store attached to a workspace\n",
|
||||
"default_datastore = ws.get_default_datastore()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Sample video"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"orangutan_video = DataReference(datastore=video_ds,\n",
|
||||
" data_reference_name=\"video\",\n",
|
||||
" path_on_datastore=\"orangutan.mp4\", mode=\"download\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"cd = CondaDependencies()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"cd.add_channel(\"conda-forge\")\n",
|
||||
"cd.add_conda_package(\"ffmpeg\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"cd.add_channel(\"pytorch\")\n",
|
||||
"cd.add_conda_package(\"pytorch\")\n",
|
||||
"cd.add_conda_package(\"torchvision\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Runconfig\n",
|
||||
"amlcompute_run_config = RunConfiguration(conda_dependencies=cd)\n",
|
||||
"amlcompute_run_config.environment.docker.enabled = True\n",
|
||||
"amlcompute_run_config.environment.docker.gpu_support = True\n",
|
||||
"amlcompute_run_config.environment.docker.base_image = \"pytorch/pytorch\"\n",
|
||||
"amlcompute_run_config.environment.spark.precache_packages = False"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ffmpeg_audio = PipelineData(name=\"ffmpeg_audio\", datastore=default_datastore)\n",
|
||||
"ffmpeg_images = PipelineData(name=\"ffmpeg_images\", datastore=default_datastore)\n",
|
||||
"processed_images = PipelineData(name=\"processed_images\", datastore=default_datastore)\n",
|
||||
"output_video = PipelineData(name=\"output_video\", datastore=default_datastore)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Define tweakable parameters to pipeline\n",
|
||||
"These parameters can be changed when the pipeline is published and rerun from a REST call"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core.graph import PipelineParameter\n",
|
||||
"# create a parameter for style (one of \"candy\", \"mosaic\", \"rain_princess\", \"udnie\") to transfer the images to\n",
|
||||
"style_param = PipelineParameter(name=\"style\", default_value=\"mosaic\")\n",
|
||||
"# create a parameter for the number of nodes to use in step no. 2 (style transfer)\n",
|
||||
"nodecount_param = PipelineParameter(name=\"nodecount\", default_value=1)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"split_video_step = PythonScriptStep(\n",
|
||||
" name=\"split video\",\n",
|
||||
" script_name=\"process_video.py\",\n",
|
||||
" arguments=[\"--input_video\", orangutan_video,\n",
|
||||
" \"--output_audio\", ffmpeg_audio,\n",
|
||||
" \"--output_images\", ffmpeg_images,\n",
|
||||
" ],\n",
|
||||
" compute_target=cpu_cluster,\n",
|
||||
" inputs=[orangutan_video],\n",
|
||||
" outputs=[ffmpeg_images, ffmpeg_audio],\n",
|
||||
" runconfig=amlcompute_run_config,\n",
|
||||
" source_directory=scripts_folder\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# create a MPI step for distributing style transfer step across multiple nodes in AmlCompute \n",
|
||||
"# using 'nodecount_param' PipelineParameter\n",
|
||||
"distributed_style_transfer_step = MpiStep(\n",
|
||||
" name=\"mpi style transfer\",\n",
|
||||
" script_name=\"neural_style_mpi.py\",\n",
|
||||
" arguments=[\"--content-dir\", ffmpeg_images,\n",
|
||||
" \"--output-dir\", processed_images,\n",
|
||||
" \"--model-dir\", models_dir,\n",
|
||||
" \"--style\", style_param,\n",
|
||||
" \"--cuda\", 1\n",
|
||||
" ],\n",
|
||||
" compute_target=gpu_cluster,\n",
|
||||
" node_count=nodecount_param, \n",
|
||||
" process_count_per_node=1,\n",
|
||||
" inputs=[models_dir, ffmpeg_images],\n",
|
||||
" outputs=[processed_images],\n",
|
||||
" pip_packages=[\"mpi4py\", \"torch\", \"torchvision\"],\n",
|
||||
" runconfig=amlcompute_run_config,\n",
|
||||
" use_gpu=True,\n",
|
||||
" source_directory=scripts_folder\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"stitch_video_step = PythonScriptStep(\n",
|
||||
" name=\"stitch\",\n",
|
||||
" script_name=\"stitch_video.py\",\n",
|
||||
" arguments=[\"--images_dir\", processed_images, \n",
|
||||
" \"--input_audio\", ffmpeg_audio, \n",
|
||||
" \"--output_dir\", output_video],\n",
|
||||
" compute_target=cpu_cluster,\n",
|
||||
" inputs=[processed_images, ffmpeg_audio],\n",
|
||||
" outputs=[output_video],\n",
|
||||
" runconfig=amlcompute_run_config,\n",
|
||||
" source_directory=scripts_folder\n",
|
||||
")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Run the pipeline"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"pipeline = Pipeline(workspace=ws, steps=[stitch_video_step])\n",
|
||||
"# submit the pipeline and provide values for the PipelineParameters used in the pipeline\n",
|
||||
"pipeline_run = Experiment(ws, 'style_transfer').submit(pipeline, pipeline_params={\"style\": \"mosaic\", \"nodecount\": 3})"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Monitor using widget"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(pipeline_run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Downloads the video in `output_video` folder"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Download output video"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"def download_video(run, target_dir=None):\n",
|
||||
" stitch_run = run.find_step_run(\"stitch\")[0]\n",
|
||||
" port_data = stitch_run.get_output_data(\"output_video\")\n",
|
||||
" port_data.download(target_dir, show_progress=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"pipeline_run.wait_for_completion()\n",
|
||||
"download_video(pipeline_run, \"output_video_mosaic\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Publish pipeline"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"published_pipeline = pipeline_run.publish_pipeline(\n",
|
||||
" name=\"batch score style transfer\", description=\"style transfer\", version=\"1.0\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"published_id = published_pipeline.id"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Re-run pipeline through REST calls for other styles"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Get AAD token"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.authentication import AzureCliAuthentication\n",
|
||||
"import requests\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"cli_auth = AzureCliAuthentication()\n",
|
||||
"aad_token = cli_auth.get_authentication_header()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Get endpoint URL"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"rest_endpoint = published_pipeline.endpoint"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Send request and monitor"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# run the pipeline using PipelineParameter values style='candy' and nodecount=2\n",
|
||||
"response = requests.post(rest_endpoint, \n",
|
||||
" headers=aad_token,\n",
|
||||
" json={\"ExperimentName\": \"style_transfer\",\n",
|
||||
" \"ParameterAssignments\": {\"style\": \"candy\", \"nodecount\": 2}}) \n",
|
||||
"run_id = response.json()[\"Id\"]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core.run import PipelineRun\n",
|
||||
"published_pipeline_run_candy = PipelineRun(ws.experiments[\"style_transfer\"], run_id)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(published_pipeline_run_candy).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# run the pipeline using PipelineParameter values style='rain_princess' and nodecount=3\n",
|
||||
"response = requests.post(rest_endpoint, \n",
|
||||
" headers=aad_token,\n",
|
||||
" json={\"ExperimentName\": \"style_transfer\",\n",
|
||||
" \"ParameterAssignments\": {\"style\": \"rain_princess\", \"nodecount\": 3}}) \n",
|
||||
"run_id = response.json()[\"Id\"]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core.run import PipelineRun\n",
|
||||
"published_pipeline_run_rain = PipelineRun(ws.experiments[\"style_transfer\"], run_id)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(published_pipeline_run_rain).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# run the pipeline using PipelineParameter values style='udnie' and nodecount=4\n",
|
||||
"response = requests.post(rest_endpoint, \n",
|
||||
" headers=aad_token,\n",
|
||||
" json={\"ExperimentName\": \"style_transfer\",\n",
|
||||
" \"ParameterAssignments\": {\"style\": \"udnie\", \"nodecount\": 4}}) \n",
|
||||
"run_id = response.json()[\"Id\"]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.pipeline.core.run import PipelineRun\n",
|
||||
"published_pipeline_run_udnie = PipelineRun(ws.experiments[\"style_transfer\"], run_id)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(published_pipeline_run_udnie).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Download output from re-run"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"published_pipeline_run_candy.wait_for_completion()\n",
|
||||
"published_pipeline_run_rain.wait_for_completion()\n",
|
||||
"published_pipeline_run_udnie.wait_for_completion()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"download_video(published_pipeline_run_candy, target_dir=\"output_video_candy\")\n",
|
||||
"download_video(published_pipeline_run_rain, target_dir=\"output_video_rain_princess\")\n",
|
||||
"download_video(published_pipeline_run_udnie, target_dir=\"output_video_udnie\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"authors": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "hichando"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.7"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
12
pipeline/test_adla_script.usql
Normal file
12
pipeline/test_adla_script.usql
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
||||
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS oneboxtest01;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@resourcereader =
|
||||
EXTRACT query string
|
||||
FROM "@@script_input@@"
|
||||
USING Extractors.Csv();
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
OUTPUT @resourcereader
|
||||
TO "@@script_output@@"
|
||||
USING Outputters.Csv();
|
||||
1
pipeline/testdata.txt
Normal file
1
pipeline/testdata.txt
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
Test1
|
||||
5
pipeline/train-db-dbfs.py
Normal file
5
pipeline/train-db-dbfs.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
# Copyright (c) Microsoft. All rights reserved.
|
||||
# Licensed under the MIT license.
|
||||
|
||||
print("In train.py")
|
||||
print("As a data scientist, this is where I use my training code.")
|
||||
5
pipeline/train-db-local.py
Normal file
5
pipeline/train-db-local.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
# Copyright (c) Microsoft. All rights reserved.
|
||||
# Licensed under the MIT license.
|
||||
|
||||
print("In train.py")
|
||||
print("As a data scientist, this is where I use my training code.")
|
||||
22
pipeline/train.py
Normal file
22
pipeline/train.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
# Copyright (c) Microsoft. All rights reserved.
|
||||
# Licensed under the MIT license.
|
||||
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
print("In train.py")
|
||||
print("As a data scientist, this is where I use my training code.")
|
||||
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser("train")
|
||||
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--input_data", type=str, help="input data")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--output_train", type=str, help="output_train directory")
|
||||
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
print("Argument 1: %s" % args.input_data)
|
||||
print("Argument 2: %s" % args.output_train)
|
||||
|
||||
if not (args.output_train is None):
|
||||
os.makedirs(args.output_train, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
print("%s created" % args.output_train)
|
||||
14
pr.md
14
pr.md
@@ -12,6 +12,18 @@
|
||||
## Community Blogs
|
||||
- [Power Bat – How Spektacom is Powering the Game of Cricket with Microsoft AI](https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/machinelearning/2018/10/11/power-bat-how-spektacom-is-powering-the-game-of-cricket-with-microsoft-ai/)
|
||||
|
||||
## Ignite 2018 Public Preview Launch Sessions
|
||||
- [AI with Azure Machine Learning services: Simplifying the data science process](https://myignite.techcommunity.microsoft.com/sessions/66248)
|
||||
- [AI TechTalk: Azure Machine Learning SDK - a walkthrough](https://myignite.techcommunity.microsoft.com/sessions/66265)
|
||||
- [AI for an intelligent cloud and intelligent edge: Discover, deploy, and manage with Azure ML services](https://myignite.techcommunity.microsoft.com/sessions/65389)
|
||||
- [Generating high quality models efficiently using Automated ML and Hyperparameter Tuning](https://myignite.techcommunity.microsoft.com/sessions/66245)
|
||||
- [AI for pros: Deep learning with PyTorch using the Azure Data Science Virtual Machine and scaling training with Azure ML](https://myignite.techcommunity.microsoft.com/sessions/66244)
|
||||
|
||||
## Get-started Videos on YouTube
|
||||
- [Get started with Python SDK](https://youtu.be/VIsXeTuW3FU)
|
||||
- [Get started from Azure Portal](https://youtu.be/lCkYUHV86Mk)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Third Party Articles
|
||||
- [Azure’s new machine learning features embrace Python](https://www.infoworld.com/article/3306840/azure/azures-new-machine-learning-features-embrace-python.html) (InfoWorld)
|
||||
- [How to use Azure ML in Windows 10](https://www.infoworld.com/article/3308381/azure/how-to-use-azure-ml-in-windows-10.html) (InfoWorld)
|
||||
@@ -24,7 +36,7 @@
|
||||
## Community Projects
|
||||
- [Fashion MNIST](https://github.com/amynic/azureml-sdk-fashion)
|
||||
- Keras on Databricks
|
||||
- Samples from CSS
|
||||
- [Samples from CSS](https://github.com/Azure/AMLSamples)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Azure Machine Learning Studio Resources
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -434,12 +434,13 @@
|
||||
"from azureml.core.image import Image\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.webservice import Webservice\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.contrib.brainwave import BrainwaveWebservice, BrainwaveImage\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.exceptions import WebserviceException\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"model_name = \"catsanddogs-resnet50-model\"\n",
|
||||
"image_name = \"catsanddogs-resnet50-image\"\n",
|
||||
"service_name = \"modelbuild-service\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"registered_model = Model.register(ws, service_def_path, model_name)\n",
|
||||
"registered_model = Model.register(ws, model_def_path, model_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"image_config = BrainwaveImage.image_configuration()\n",
|
||||
"deployment_config = BrainwaveWebservice.deploy_configuration()\n",
|
||||
@@ -448,8 +449,10 @@
|
||||
" service = Webservice(ws, service_name)\n",
|
||||
" service.delete()\n",
|
||||
" service = Webservice.deploy_from_model(ws, service_name, [registered_model], image_config, deployment_config)\n",
|
||||
" service.wait_for_deployment(True)\n",
|
||||
"except WebserviceException:\n",
|
||||
" service = Webservice.deploy_from_model(ws, service_name, [registered_model], image_config, deployment_config)"
|
||||
" service = Webservice.deploy_from_model(ws, service_name, [registered_model], image_config, deployment_config)\n",
|
||||
" service.wait_for_deployment(True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -80,7 +80,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.contrib.brainwave.models import QuantizedResnet50, Resnet50\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.contrib.brainwave.models import QuantizedResnet50\n",
|
||||
"model_path = os.path.expanduser('~/models')\n",
|
||||
"model = QuantizedResnet50(model_path, is_frozen = True)\n",
|
||||
"feature_tensor = model.import_graph_def(image_tensors)\n",
|
||||
@@ -198,7 +198,7 @@
|
||||
" image_config = BrainwaveImage.image_configuration()\n",
|
||||
" deployment_config = BrainwaveWebservice.deploy_configuration()\n",
|
||||
" service = Webservice.deploy_from_model(ws, service_name, [registered_model], image_config, deployment_config)\n",
|
||||
" service.wait_for_deployment(true)"
|
||||
" service.wait_for_deployment(True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -265,9 +265,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"service.delete()\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"registered_model.delete()"
|
||||
"service.delete()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -404,7 +404,7 @@
|
||||
" image_config = BrainwaveImage.image_configuration()\n",
|
||||
" deployment_config = BrainwaveWebservice.deploy_configuration()\n",
|
||||
" service = Webservice.deploy_from_model(ws, service_name, [registered_model], image_config, deployment_config)\n",
|
||||
" service.wait_for_deployment(true)"
|
||||
" service.wait_for_deployment(True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -511,7 +511,7 @@
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"New BSD License\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Copyright (c) 2007\u00e2\u20ac\u201c2018 The scikit-learn developers.\n",
|
||||
"Copyright (c) 2007–2018 The scikit-learn developers.\n",
|
||||
"All rights reserved.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
|
||||
Binary file not shown.
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 61 KiB |
@@ -104,7 +104,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, BatchAiCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute_target import ComputeTargetException\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for your cluster\n",
|
||||
@@ -115,10 +115,8 @@
|
||||
" print('Found existing compute target.')\n",
|
||||
"except ComputeTargetException:\n",
|
||||
" print('Creating a new compute target...')\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = BatchAiCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size='STANDARD_NC6', \n",
|
||||
" autoscale_enabled=True,\n",
|
||||
" cluster_min_nodes=0, \n",
|
||||
" cluster_max_nodes=4)\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size='STANDARD_NC6', \n",
|
||||
" max_nodes=6)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # create the cluster\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = ComputeTarget.create(ws, cluster_name, compute_config)\n",
|
||||
@@ -333,7 +331,7 @@
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"script_params = {\n",
|
||||
" '--data_dir': ds_data,\n",
|
||||
" '--num_epochs': 25,\n",
|
||||
" '--num_epochs': 10,\n",
|
||||
" '--output_dir': './outputs'\n",
|
||||
"}\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
@@ -387,10 +385,26 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Alternatively, you can block until the script has completed training before running more code."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"run.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
@@ -431,7 +445,7 @@
|
||||
" policy=early_termination_policy,\n",
|
||||
" primary_metric_name='best_val_acc',\n",
|
||||
" primary_metric_goal=PrimaryMetricGoal.MAXIMIZE,\n",
|
||||
" max_total_runs=20,\n",
|
||||
" max_total_runs=8,\n",
|
||||
" max_concurrent_runs=4)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -466,11 +480,27 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(hyperdrive_run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Or block until the HyperDrive sweep has completed:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"hyperdrive_run.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
@@ -546,7 +576,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Create environment file\n",
|
||||
"Then, we will need to create an environment file (`myenv.yml`) that specifies all of the scoring script's package dependencies. This file is used to ensure that all of those dependencies are installed in the Docker image by AML. In this case, we need to specify `torch`, `torchvision`, `pillow`, and `azureml-sdk`."
|
||||
"Then, we will need to create an environment file (`myenv.yml`) that specifies all of the scoring script's package dependencies. This file is used to ensure that all of those dependencies are installed in the Docker image by AML. In this case, we need to specify `azureml-core`, `torch` and `torchvision`."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -555,16 +585,14 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%%writefile myenv.yml\n",
|
||||
"name: myenv\n",
|
||||
"channels:\n",
|
||||
" - defaults\n",
|
||||
"dependencies:\n",
|
||||
" - pip:\n",
|
||||
" - torch\n",
|
||||
" - torchvision\n",
|
||||
" - pillow\n",
|
||||
" - azureml-core"
|
||||
"from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"myenv = CondaDependencies.create(pip_packages=['azureml-core', 'torch', 'torchvision'])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with open(\"myenv.yml\",\"w\") as f:\n",
|
||||
" f.write(myenv.serialize_to_string())\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"print(myenv.serialize_to_string())"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -616,25 +644,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Deploy the registered model\n",
|
||||
"Finally, let's deploy a web service from our registered model. First, retrieve the model from your workspace."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.model import Model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"model = Model(ws, name='pytorch-hymenoptera')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Then, deploy the web service using the ACI config and image config files created in the previous steps. We pass the `model` object in a list to the `models` parameter. If you would like to deploy more than one registered model, append the additional models to this list."
|
||||
"Finally, let's deploy a web service from our registered model. Deploy the web service using the ACI config and image config files created in the previous steps. We pass the `model` object in a list to the `models` parameter. If you would like to deploy more than one registered model, append the additional models to this list."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -710,18 +720,10 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import os, json, base64\n",
|
||||
"from io import BytesIO\n",
|
||||
"import os, json\n",
|
||||
"from PIL import Image\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def imgToBase64(img):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Convert pillow image to base64-encoded image\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" imgio = BytesIO()\n",
|
||||
" img.save(imgio, 'JPEG')\n",
|
||||
" img_str = base64.b64encode(imgio.getvalue())\n",
|
||||
" return img_str.decode('utf-8')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"test_img = os.path.join('hymenoptera_data', 'val', 'bees', '10870992_eebeeb3a12.jpg') #arbitary image from val dataset\n",
|
||||
"plt.imshow(Image.open(test_img))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
@@ -732,18 +734,42 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"base64Img = imgToBase64(Image.open(test_img))\n",
|
||||
"import torch\n",
|
||||
"from torchvision import transforms\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"result = service.run(input_data=json.dumps({'data': base64Img}))\n",
|
||||
"print(json.loads(result))"
|
||||
"def preprocess(image_file):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Preprocess the input image.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" data_transforms = transforms.Compose([\n",
|
||||
" transforms.Resize(256),\n",
|
||||
" transforms.CenterCrop(224),\n",
|
||||
" transforms.ToTensor(),\n",
|
||||
" transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])\n",
|
||||
" ])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" image = Image.open(image_file)\n",
|
||||
" image = data_transforms(image).float()\n",
|
||||
" image = torch.tensor(image)\n",
|
||||
" image = image.unsqueeze(0)\n",
|
||||
" return image.numpy()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"input_data = preprocess(test_img)\n",
|
||||
"result = service.run(input_data=json.dumps({'data': input_data.tolist()}))\n",
|
||||
"print(result)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Delete web service\n",
|
||||
"Once you no longer need the web service, you should delete it."
|
||||
"## Clean up\n",
|
||||
"Once you no longer need the web service, you can delete it with a simple API call."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -777,7 +803,7 @@
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
"version": "3.6.2"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"msauthor": "minxia"
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,35 +5,10 @@ import torch
|
||||
import torch.nn as nn
|
||||
from torchvision import transforms
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import base64
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
from azureml.core.model import Model
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess_image(image_file):
|
||||
"""Preprocess the input image."""
|
||||
data_transforms = transforms.Compose([
|
||||
transforms.Resize(256),
|
||||
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
|
||||
transforms.ToTensor(),
|
||||
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
image = Image.open(image_file)
|
||||
image = data_transforms(image).float()
|
||||
image = torch.tensor(image)
|
||||
image = image.unsqueeze(0)
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def base64ToImg(base64ImgString):
|
||||
base64Img = base64ImgString.encode('utf-8')
|
||||
decoded_img = base64.b64decode(base64Img)
|
||||
return BytesIO(decoded_img)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def init():
|
||||
global model
|
||||
model_path = Model.get_model_path('pytorch-hymenoptera')
|
||||
@@ -42,16 +17,15 @@ def init():
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def run(input_data):
|
||||
img = base64ToImg(json.loads(input_data)['data'])
|
||||
img = preprocess_image(img)
|
||||
input_data = torch.tensor(json.loads(input_data)['data'])
|
||||
|
||||
# get prediction
|
||||
output = model(img)
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
output = model(input_data)
|
||||
classes = ['ants', 'bees']
|
||||
softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
|
||||
pred_probs = softmax(model(img)).detach().numpy()[0]
|
||||
pred_probs = softmax(output).numpy()[0]
|
||||
index = torch.argmax(output, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
result = json.dumps({"label": classes[index], "probability": str(pred_probs[index])})
|
||||
result = {"label": classes[index], "probability": str(pred_probs[index])}
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -59,6 +59,7 @@ def train_model(model, criterion, optimizer, scheduler, num_epochs, data_dir):
|
||||
dataloaders, dataset_sizes, class_names = load_data(data_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
|
||||
|
||||
since = time.time()
|
||||
|
||||
best_model_wts = copy.deepcopy(model.state_dict())
|
||||
@@ -146,12 +147,15 @@ def fine_tune_model(num_epochs, data_dir, learning_rate, momentum):
|
||||
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
|
||||
|
||||
# Observe that all parameters are being optimized
|
||||
optimizer_ft = optim.SGD(model_ft.parameters(), lr=learning_rate, momentum=momentum)
|
||||
optimizer_ft = optim.SGD(model_ft.parameters(),
|
||||
lr=learning_rate, momentum=momentum)
|
||||
|
||||
# Decay LR by a factor of 0.1 every 7 epochs
|
||||
exp_lr_scheduler = lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer_ft, step_size=7, gamma=0.1)
|
||||
exp_lr_scheduler = lr_scheduler.StepLR(
|
||||
optimizer_ft, step_size=7, gamma=0.1)
|
||||
|
||||
model = train_model(model_ft, criterion, optimizer_ft, exp_lr_scheduler, num_epochs, data_dir)
|
||||
model = train_model(model_ft, criterion, optimizer_ft,
|
||||
exp_lr_scheduler, num_epochs, data_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
return model
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -159,15 +163,19 @@ def fine_tune_model(num_epochs, data_dir, learning_rate, momentum):
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
# get command-line arguments
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--data_dir', type=str, help='directory of training data')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--num_epochs', type=int, default=25, help='number of epochs to train')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--data_dir', type=str,
|
||||
help='directory of training data')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--num_epochs', type=int, default=25,
|
||||
help='number of epochs to train')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--output_dir', type=str, help='output directory')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--learning_rate', type=float, default=0.001, help='learning rate')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--learning_rate', type=float,
|
||||
default=0.001, help='learning rate')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--momentum', type=float, default=0.9, help='momentum')
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
print("data directory is: " + args.data_dir)
|
||||
model = fine_tune_model(args.num_epochs, args.data_dir, args.learning_rate, args.momentum)
|
||||
model = fine_tune_model(args.num_epochs, args.data_dir,
|
||||
args.learning_rate, args.momentum)
|
||||
os.makedirs(args.output_dir, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
torch.save(model, os.path.join(args.output_dir, 'model.pt'))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -103,7 +103,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, BatchAiCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute_target import ComputeTargetException\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for your cluster\n",
|
||||
@@ -114,10 +114,8 @@
|
||||
" print('Found existing compute target.')\n",
|
||||
"except ComputeTargetException:\n",
|
||||
" print('Creating a new compute target...')\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = BatchAiCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size='STANDARD_NC6', \n",
|
||||
" autoscale_enabled=True,\n",
|
||||
" cluster_min_nodes=0, \n",
|
||||
" cluster_max_nodes=4)\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size='STANDARD_NC6', \n",
|
||||
" max_nodes=6)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # create the cluster\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = ComputeTarget.create(ws, cluster_name, compute_config)\n",
|
||||
@@ -264,7 +262,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
1
training/03.train-hyperparameter-tune-deploy-with-tensorflow/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
1
training/03.train-hyperparameter-tune-deploy-with-tensorflow/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
/data/
|
||||
@@ -225,9 +225,23 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Upload MNIST dataset to default datastore \n",
|
||||
"A [datastore](https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/service/how-to-access-data) is a place where data can be stored that is then made accessible to a Run either by means of mounting or copying the data to the compute target. A datastore can either be backed by an Azure Blob Storage or and Azure File Share (ADLS will be supported in the future). For simple data handling, each workspace provides a default datastore that can be used, in case the data is not already in Blob Storage or File Share.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this next step, we will upload the training and test set into the workspace's default datastore, which we will then later be mount on a Batch AI cluster for training.\n"
|
||||
"A [datastore](https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/service/how-to-access-data) is a place where data can be stored that is then made accessible to a Run either by means of mounting or copying the data to the compute target. A datastore can either be backed by an Azure Blob Storage or and Azure File Share (ADLS will be supported in the future). For simple data handling, each workspace provides a default datastore that can be used, in case the data is not already in Blob Storage or File Share."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ds = ws.get_default_datastore()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"In this next step, we will upload the training and test set into the workspace's default datastore, which we will then later be mount on a Batch AI cluster for training."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -236,7 +250,6 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ds = ws.get_default_datastore()\n",
|
||||
"ds.upload(src_dir='./data/mnist', target_path='mnist', overwrite=True, show_progress=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -252,7 +265,7 @@
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"If we could not find the cluster with the given name in the previous cell, then we will create a new cluster here. We will create a Batch AI Cluster of `STANDARD_D2_V2` CPU VMs. This process is broken down into 3 steps:\n",
|
||||
"If we could not find the cluster with the given name in the previous cell, then we will create a new cluster here. We will create a Batch AI Cluster of `STANDARD_NC6` GPU VMs. This process is broken down into 3 steps:\n",
|
||||
"1. create the configuration (this step is local and only takes a second)\n",
|
||||
"2. create the Batch AI cluster (this step will take about **20 seconds**)\n",
|
||||
"3. provision the VMs to bring the cluster to the initial size (of 1 in this case). This step will take about **3-5 minutes** and is providing only sparse output in the process. Please make sure to wait until the call returns before moving to the next cell"
|
||||
@@ -264,7 +277,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, BatchAiCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute_target import ComputeTargetException\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for your cluster\n",
|
||||
@@ -273,17 +286,15 @@
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" # look for the existing cluster by name\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = ComputeTarget(workspace=ws, name=cluster_name)\n",
|
||||
" if type(compute_target) is BatchAiCompute:\n",
|
||||
" if type(compute_target) is AmlCompute:\n",
|
||||
" print('Found existing compute target {}.'.format(cluster_name))\n",
|
||||
" else:\n",
|
||||
" print('{} exists but it is not a Batch AI cluster. Please choose a different name.'.format(cluster_name))\n",
|
||||
"except ComputeTargetException:\n",
|
||||
" print('Creating a new compute target...')\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = BatchAiCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size=\"STANDARD_NC6\", # GPU-based VM\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size=\"STANDARD_NC6\", # GPU-based VM\n",
|
||||
" #vm_priority='lowpriority', # optional\n",
|
||||
" autoscale_enabled=True,\n",
|
||||
" cluster_min_nodes=0, \n",
|
||||
" cluster_max_nodes=4)\n",
|
||||
" max_nodes=6)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # create the cluster\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = ComputeTarget.create(ws, cluster_name, compute_config)\n",
|
||||
@@ -300,7 +311,7 @@
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Now that you have created the compute target, let's see what the workspace's `compute_targets()` function returns. You should now see one entry named 'gpucluster' of type BatchAI."
|
||||
"Now that you have created the compute target, let's see what the workspace's `compute_targets` property returns. You should now see one entry named 'gpucluster' of type BatchAI."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -309,7 +320,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"compute_targets = ws.compute_targets()\n",
|
||||
"compute_targets = ws.compute_targets\n",
|
||||
"for name, ct in compute_targets.items():\n",
|
||||
" print(name, ct.type, ct.provisioning_state)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
@@ -432,7 +443,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"run = exp.submit(config=est)"
|
||||
"run = exp.submit(est)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -460,7 +471,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -480,6 +491,15 @@
|
||||
"run"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"run.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
@@ -728,9 +748,10 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"htc = HyperDriveRunConfig(estimator=est, \n",
|
||||
" hyperparameter_sampling=ps, \n",
|
||||
" policy=policy, \n",
|
||||
" primary_metric_name='validation_acc', \n",
|
||||
" primary_metric_goal=PrimaryMetricGoal.MAXIMIZE, \n",
|
||||
" max_total_runs=20,\n",
|
||||
" max_total_runs=8,\n",
|
||||
" max_concurrent_runs=4)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -766,6 +787,15 @@
|
||||
"RunDetails(htr).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"htr.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
@@ -796,7 +826,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"print(best_run.get_file_names()"
|
||||
"print(best_run.get_file_names())"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -859,7 +889,7 @@
|
||||
" # make prediction\n",
|
||||
" out = output.eval(session=sess, feed_dict={X: data})\n",
|
||||
" y_hat = np.argmax(out, axis=1)\n",
|
||||
" return json.dumps(y_hat.tolist())"
|
||||
" return y_hat.tolist()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -1011,7 +1041,7 @@
|
||||
"test_samples = bytes(test_samples, encoding='utf8')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# predict using the deployed model\n",
|
||||
"result = json.loads(service.run(input_data = test_samples))\n",
|
||||
"result = service.run(input_data=test_samples)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# compare actual value vs. the predicted values:\n",
|
||||
"i = 0\n",
|
||||
@@ -1079,15 +1109,15 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"models = ws.models()\n",
|
||||
"models = ws.models\n",
|
||||
"for name, model in models.items():\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Model: {}, ID: {}\".format(name, model.id))\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"images = ws.images()\n",
|
||||
"images = ws.images\n",
|
||||
"for name, image in images.items():\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Image: {}, location: {}\".format(name, image.image_location))\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"webservices = ws.webservices()\n",
|
||||
"webservices = ws.webservices\n",
|
||||
"for name, webservice in webservices.items():\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Webservice: {}, scoring URI: {}\".format(name, webservice.scoring_uri))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
@@ -1108,23 +1138,6 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"service.delete()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"We can also delete the computer cluster. But remember if you set the `cluster_min_nodes` value to 0 when you created the cluster, once the jobs are finished, all nodes are deleted automatically. So you don't have to delete the cluster itself since it won't incur any cost. Next time you submit jobs to it, the cluster will then automatically \"grow\" up to the `cluster_min_nodes` which is set to 4."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# delete the cluster if you need to.\n",
|
||||
"compute_target.delete()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
@@ -1150,505 +1163,7 @@
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbpresent": {
|
||||
"slides": {
|
||||
"05bb34ad-74b0-42b3-9654-8357d1ba9c99": {
|
||||
"id": "05bb34ad-74b0-42b3-9654-8357d1ba9c99",
|
||||
"prev": "851089af-9725-40c9-8f0b-9bf892b2b1fe",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"23fb396d-50f9-4770-adb3-0d6abcb40767": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "2039d2d5-aca6-4f25-a12f-df9ae6529cae",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "23fb396d-50f9-4770-adb3-0d6abcb40767"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"11bebe14-d1dc-476d-a31a-5828b9c3adf0": {
|
||||
"id": "11bebe14-d1dc-476d-a31a-5828b9c3adf0",
|
||||
"prev": "502648cb-26fe-496b-899f-84c8fe1dcbc0",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"a42499db-623e-4414-bea2-ff3617fd8fc5": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "4788c040-27a2-4dc1-8ed0-378a99b3a255",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "a42499db-623e-4414-bea2-ff3617fd8fc5"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"134f92d0-6389-4226-af51-1134ae8e8278": {
|
||||
"id": "134f92d0-6389-4226-af51-1134ae8e8278",
|
||||
"prev": "36b8728c-32ad-4941-be03-5cef51cdc430",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"b6d82a77-2d58-4b9e-a375-3103214b826c": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "7ab0e6d0-1f1c-451b-8ac5-687da44a8287",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "b6d82a77-2d58-4b9e-a375-3103214b826c"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"282a2421-697b-4fd0-9485-755abf5a0c18": {
|
||||
"id": "282a2421-697b-4fd0-9485-755abf5a0c18",
|
||||
"prev": "a8b9ceb9-b38f-4489-84df-b644c6fe28f2",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"522fec96-abe7-4a34-bd34-633733afecc8": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "d58e7785-c2ee-4a45-8e3d-4c538bf8075a",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "522fec96-abe7-4a34-bd34-633733afecc8"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"2dfec088-8a70-411a-9199-904ef3fa2383": {
|
||||
"id": "2dfec088-8a70-411a-9199-904ef3fa2383",
|
||||
"prev": "282a2421-697b-4fd0-9485-755abf5a0c18",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"0535fcb6-3a2b-4b46-98a7-3ebb1a38c47e": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "c377ea0c-0cd9-4345-9be2-e20fb29c94c3",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "0535fcb6-3a2b-4b46-98a7-3ebb1a38c47e"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"36a814c9-c540-4a6d-92d9-c03553d3d2c2": {
|
||||
"id": "36a814c9-c540-4a6d-92d9-c03553d3d2c2",
|
||||
"prev": "b52e4d09-5186-44e5-84db-3371c087acde",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"8bfba503-9907-43f0-b1a6-46a0b4311793": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "d5e4a56c-dfac-4346-be83-1c15b503deac",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "8bfba503-9907-43f0-b1a6-46a0b4311793"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"36b8728c-32ad-4941-be03-5cef51cdc430": {
|
||||
"id": "36b8728c-32ad-4941-be03-5cef51cdc430",
|
||||
"prev": "05bb34ad-74b0-42b3-9654-8357d1ba9c99",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"a36a5bdf-7f62-49b0-8634-e155a98851dc": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "e33dfc47-e7df-4623-a7a6-ab6bcf944629",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "a36a5bdf-7f62-49b0-8634-e155a98851dc"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"3f136f2a-f14c-4a4b-afea-13380556a79c": {
|
||||
"id": "3f136f2a-f14c-4a4b-afea-13380556a79c",
|
||||
"prev": "54cb8dfd-a89c-4922-867b-3c87d8b67cd3",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"80ecf237-d1b0-401e-83d2-6d04b7fcebd3": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "7debeb2b-ecea-414f-9b50-49657abb3e6a",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "80ecf237-d1b0-401e-83d2-6d04b7fcebd3"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"502648cb-26fe-496b-899f-84c8fe1dcbc0": {
|
||||
"id": "502648cb-26fe-496b-899f-84c8fe1dcbc0",
|
||||
"prev": "3f136f2a-f14c-4a4b-afea-13380556a79c",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"4c83bb4d-2a52-41ba-a77f-0c6efebd83a6": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "dbd22f6b-6d49-4005-b8fe-422ef8ef1d42",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "4c83bb4d-2a52-41ba-a77f-0c6efebd83a6"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"54cb8dfd-a89c-4922-867b-3c87d8b67cd3": {
|
||||
"id": "54cb8dfd-a89c-4922-867b-3c87d8b67cd3",
|
||||
"prev": "aa224267-f885-4c0c-95af-7bacfcc186d9",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"0848f0a7-032d-46c7-b35c-bfb69c83f961": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "3c32c557-d0e8-4bb3-a61a-aa51a767cd4e",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "0848f0a7-032d-46c7-b35c-bfb69c83f961"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"636b563c-faee-4c9e-a6a3-f46a905bfa82": {
|
||||
"id": "636b563c-faee-4c9e-a6a3-f46a905bfa82",
|
||||
"prev": "c5f59b98-a227-4344-9d6d-03abdd01c6aa",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"9c64f662-05dc-4b14-9cdc-d450b96f4368": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "70640ac0-7041-47a8-9a7f-e871defd74b2",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "9c64f662-05dc-4b14-9cdc-d450b96f4368"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"793cec2f-8413-484d-aa1e-388fd2b53a45": {
|
||||
"id": "793cec2f-8413-484d-aa1e-388fd2b53a45",
|
||||
"prev": "c66f3dfd-2d27-482b-be78-10ba733e826b",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"d08f9cfa-3b8d-4fb4-91ba-82d9858ea93e": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "dd56113e-e3db-41ae-91b7-2472ed194308",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "d08f9cfa-3b8d-4fb4-91ba-82d9858ea93e"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"83e912ff-260a-4391-8a12-331aba098506": {
|
||||
"id": "83e912ff-260a-4391-8a12-331aba098506",
|
||||
"prev": "fe5a0732-69f5-462a-8af6-851f84a9fdec",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"2fefcf5f-ea20-4604-a528-5e6c91bcb100": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "c3f2f57c-7454-4d3e-b38d-b0946cf066ea",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "2fefcf5f-ea20-4604-a528-5e6c91bcb100"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"851089af-9725-40c9-8f0b-9bf892b2b1fe": {
|
||||
"id": "851089af-9725-40c9-8f0b-9bf892b2b1fe",
|
||||
"prev": "636b563c-faee-4c9e-a6a3-f46a905bfa82",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"31c9dda5-fdf4-45e2-bcb7-12aa0f30e1d8": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "8408b90e-6cdd-44d1-86d3-648c23f877ac",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "31c9dda5-fdf4-45e2-bcb7-12aa0f30e1d8"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"87ab653d-e804-470f-bde9-c67caaa0f354": {
|
||||
"id": "87ab653d-e804-470f-bde9-c67caaa0f354",
|
||||
"prev": "a8c2d446-caee-42c8-886a-ed98f4935d78",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"bc3aeb56-c465-4868-a1ea-2de82584de98": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "59f52294-4a25-4c92-bab8-3b07f0f44d15",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "bc3aeb56-c465-4868-a1ea-2de82584de98"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"8b887c97-83bc-4395-83ac-f6703cbe243d": {
|
||||
"id": "8b887c97-83bc-4395-83ac-f6703cbe243d",
|
||||
"prev": "36a814c9-c540-4a6d-92d9-c03553d3d2c2",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"9d0bc72a-cb13-483f-a572-2bf60d0d145f": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "75499c85-d0a1-43db-8244-25778b9b2736",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "9d0bc72a-cb13-483f-a572-2bf60d0d145f"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"a8b9ceb9-b38f-4489-84df-b644c6fe28f2": {
|
||||
"id": "a8b9ceb9-b38f-4489-84df-b644c6fe28f2",
|
||||
"prev": null,
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"f741ed94-3f24-4427-b615-3ab8753e5814": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "bf74d2e9-2708-49b1-934b-e0ede342f475",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "f741ed94-3f24-4427-b615-3ab8753e5814"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"a8c2d446-caee-42c8-886a-ed98f4935d78": {
|
||||
"id": "a8c2d446-caee-42c8-886a-ed98f4935d78",
|
||||
"prev": "2dfec088-8a70-411a-9199-904ef3fa2383",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"f03457d8-b2a7-4e14-9a73-cab80c5b815d": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "edaa7f2f-2439-4148-b57a-8c794c0945ec",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "f03457d8-b2a7-4e14-9a73-cab80c5b815d"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"aa224267-f885-4c0c-95af-7bacfcc186d9": {
|
||||
"id": "aa224267-f885-4c0c-95af-7bacfcc186d9",
|
||||
"prev": "793cec2f-8413-484d-aa1e-388fd2b53a45",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"0d7ac442-5e1d-49a5-91b3-1432d72449d8": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "4d6826fe-2cb8-4468-85ed-a242a1ce7155",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "0d7ac442-5e1d-49a5-91b3-1432d72449d8"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"b52e4d09-5186-44e5-84db-3371c087acde": {
|
||||
"id": "b52e4d09-5186-44e5-84db-3371c087acde",
|
||||
"prev": "134f92d0-6389-4226-af51-1134ae8e8278",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"7af7d997-80b2-497d-bced-ef8341763439": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "376882ec-d469-4fad-9462-18e4bbea64ca",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "7af7d997-80b2-497d-bced-ef8341763439"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"c5f59b98-a227-4344-9d6d-03abdd01c6aa": {
|
||||
"id": "c5f59b98-a227-4344-9d6d-03abdd01c6aa",
|
||||
"prev": "83e912ff-260a-4391-8a12-331aba098506",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"7268abff-0540-4c06-aefc-c386410c0953": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "396d478b-34aa-4afa-9898-cdce8222a516",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "7268abff-0540-4c06-aefc-c386410c0953"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"c66f3dfd-2d27-482b-be78-10ba733e826b": {
|
||||
"id": "c66f3dfd-2d27-482b-be78-10ba733e826b",
|
||||
"prev": "8b887c97-83bc-4395-83ac-f6703cbe243d",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"6cbe8e0e-8645-41a1-8a38-e44acb81be4b": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "7594c7c7-b808-48f7-9500-d7830a07968a",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "6cbe8e0e-8645-41a1-8a38-e44acb81be4b"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"d22045e5-7e3e-452e-bc7b-c6c4a893da8e": {
|
||||
"id": "d22045e5-7e3e-452e-bc7b-c6c4a893da8e",
|
||||
"prev": "ec41f96a-63a3-4825-9295-f4657a440ddb",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"24e2a3a9-bf65-4dab-927f-0bf6ffbe581d": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "defe921f-8097-44c3-8336-8af6700804a7",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "24e2a3a9-bf65-4dab-927f-0bf6ffbe581d"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"d24c958c-e419-4e4d-aa9c-d228a8ca55e4": {
|
||||
"id": "d24c958c-e419-4e4d-aa9c-d228a8ca55e4",
|
||||
"prev": "11bebe14-d1dc-476d-a31a-5828b9c3adf0",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"25312144-9faa-4680-bb8e-6307ea71370f": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "bed09a92-9a7a-473b-9464-90e479883a3e",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "25312144-9faa-4680-bb8e-6307ea71370f"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"ec41f96a-63a3-4825-9295-f4657a440ddb": {
|
||||
"id": "ec41f96a-63a3-4825-9295-f4657a440ddb",
|
||||
"prev": "87ab653d-e804-470f-bde9-c67caaa0f354",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"22e8be98-c254-4d04-b0e4-b9b5ae46eefe": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "bc70f780-c240-4779-96f3-bc5ef9a37d59",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "22e8be98-c254-4d04-b0e4-b9b5ae46eefe"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"fe5a0732-69f5-462a-8af6-851f84a9fdec": {
|
||||
"id": "fe5a0732-69f5-462a-8af6-851f84a9fdec",
|
||||
"prev": "d22045e5-7e3e-452e-bc7b-c6c4a893da8e",
|
||||
"regions": {
|
||||
"671b89f5-fa9c-4bc1-bdeb-6e0a4ce8939b": {
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"height": 0.8,
|
||||
"width": 0.8,
|
||||
"x": 0.1,
|
||||
"y": 0.1
|
||||
},
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"cell": "fd46e2ab-4ab6-4001-b536-1f323525d7d3",
|
||||
"part": "whole"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "671b89f5-fa9c-4bc1-bdeb-6e0a4ce8939b"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"themes": {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
"msauthor": "minxia"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ n_h1 = args.n_hidden_1
|
||||
n_h2 = args.n_hidden_2
|
||||
n_outputs = 10
|
||||
learning_rate = args.learning_rate
|
||||
n_epochs = 50
|
||||
n_epochs = 20
|
||||
batch_size = args.batch_size
|
||||
|
||||
with tf.name_scope('network'):
|
||||
|
||||
2
training/04.distributed-tensorflow-with-horovod/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
2
training/04.distributed-tensorflow-with-horovod/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
/data/
|
||||
/tf-distr-hvd/
|
||||
@@ -102,7 +102,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, BatchAiCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute_target import ComputeTargetException\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for your cluster\n",
|
||||
@@ -113,10 +113,8 @@
|
||||
" print('Found existing compute target')\n",
|
||||
"except ComputeTargetException:\n",
|
||||
" print('Creating a new compute target...')\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = BatchAiCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size='STANDARD_NC6', \n",
|
||||
" autoscale_enabled=True,\n",
|
||||
" cluster_min_nodes=0, \n",
|
||||
" cluster_max_nodes=4)\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size='STANDARD_NC6', \n",
|
||||
" max_nodes=6)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # create the cluster\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = ComputeTarget.create(ws, cluster_name, compute_config)\n",
|
||||
@@ -169,7 +167,7 @@
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Each workspace is associated with a default datastore. In this tutorial, we will upload the training data to this default datastore. The below code will upload the contents of the data directory to the path `./data` on the default datastore."
|
||||
"Each workspace is associated with a default datastore. In this tutorial, we will upload the training data to this default datastore."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -179,8 +177,22 @@
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ds = ws.get_default_datastore()\n",
|
||||
"print(ds.datastore_type, ds.account_name, ds.container_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(ds.datastore_type, ds.account_name, ds.container_name)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Upload the contents of the data directory to the path `./data` on the default datastore."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ds.upload(src_dir='data', target_path='data', overwrite=True, show_progress=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -223,6 +235,8 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"project_folder = './tf-distr-hvd'\n",
|
||||
"os.makedirs(project_folder, exist_ok=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
@@ -335,7 +349,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
1
training/05.distributed-tensorflow-with-parameter-server/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
1
training/05.distributed-tensorflow-with-parameter-server/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
/tf-distr-ps/
|
||||
@@ -102,7 +102,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, BatchAiCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute_target import ComputeTargetException\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for your cluster\n",
|
||||
@@ -113,10 +113,8 @@
|
||||
" print('Found existing compute target.')\n",
|
||||
"except ComputeTargetException:\n",
|
||||
" print('Creating a new compute target...')\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = BatchAiCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size='STANDARD_NC6', \n",
|
||||
" autoscale_enabled=True,\n",
|
||||
" cluster_min_nodes=0, \n",
|
||||
" cluster_max_nodes=4)\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size='STANDARD_NC6', \n",
|
||||
" max_nodes=6)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # create the cluster\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = ComputeTarget.create(ws, cluster_name, compute_config)\n",
|
||||
@@ -209,7 +207,8 @@
|
||||
"from azureml.train.dnn import TensorFlow\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"script_params={\n",
|
||||
" '--num_gpus': 1\n",
|
||||
" '--num_gpus': 1,\n",
|
||||
" '--train_steps': 500\n",
|
||||
"}\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"estimator = TensorFlow(source_directory=project_folder,\n",
|
||||
@@ -245,7 +244,7 @@
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"run = experiment.submit(estimator)\n",
|
||||
"print(run.get_details())"
|
||||
"print(run)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -262,7 +261,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -102,7 +102,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, BatchAiCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute_target import ComputeTargetException\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for your cluster\n",
|
||||
@@ -113,10 +113,8 @@
|
||||
" print('Found existing compute target.')\n",
|
||||
"except ComputeTargetException:\n",
|
||||
" print('Creating a new compute target...')\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = BatchAiCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size='STANDARD_NC6', \n",
|
||||
" autoscale_enabled=True,\n",
|
||||
" cluster_min_nodes=0, \n",
|
||||
" cluster_max_nodes=4)\n",
|
||||
" compute_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size='STANDARD_NC6', \n",
|
||||
" max_nodes=6)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # create the cluster\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = ComputeTarget.create(ws, cluster_name, compute_config)\n",
|
||||
@@ -283,7 +281,7 @@
|
||||
"from azureml.train.estimator import *\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"script_params = {\n",
|
||||
" '--num_epochs': 50,\n",
|
||||
" '--num_epochs': 20,\n",
|
||||
" '--data_dir': ds_data.as_mount(),\n",
|
||||
" '--output_dir': './outputs'\n",
|
||||
"}\n",
|
||||
@@ -341,7 +339,7 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,321 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
|
||||
# Licensed under the MIT License.
|
||||
# Script adapted from:
|
||||
# 1. https://github.com/Microsoft/CNTK/blob/v2.0/Tutorials/CNTK_103A_MNIST_DataLoader.ipynb
|
||||
# 2. https://github.com/Microsoft/CNTK/blob/v2.0/Tutorials/CNTK_103C_MNIST_MultiLayerPerceptron.ipynb
|
||||
# ===================================================================================================
|
||||
"""Train a CNTK multi-layer perceptron on the MNIST dataset."""
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
import gzip
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import shutil
|
||||
import struct
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
import cntk as C
|
||||
from azureml.core.run import Run
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
|
||||
run = Run.get_submitted_run()
|
||||
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
||||
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--learning_rate', type=float, default=0.001, help='learning rate')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--num_hidden_layers', type=int, default=2, help='number of hidden layers')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--minibatch_size', type=int, default=64, help='minibatchsize')
|
||||
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
# Functions to load MNIST images and unpack into train and test set.
|
||||
# - loadData reads image data and formats into a 28x28 long array
|
||||
# - loadLabels reads the corresponding labels data, 1 for each image
|
||||
# - load packs the downloaded image and labels data into a combined format to be read later by
|
||||
# CNTK text reader
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def loadData(src, cimg):
|
||||
print('Downloading ' + src)
|
||||
gzfname, h = urlretrieve(src, './delete.me')
|
||||
print('Done.')
|
||||
try:
|
||||
with gzip.open(gzfname) as gz:
|
||||
n = struct.unpack('I', gz.read(4))
|
||||
# Read magic number.
|
||||
if n[0] != 0x3080000:
|
||||
raise Exception('Invalid file: unexpected magic number.')
|
||||
# Read number of entries.
|
||||
n = struct.unpack('>I', gz.read(4))[0]
|
||||
if n != cimg:
|
||||
raise Exception('Invalid file: expected {0} entries.'.format(cimg))
|
||||
crow = struct.unpack('>I', gz.read(4))[0]
|
||||
ccol = struct.unpack('>I', gz.read(4))[0]
|
||||
if crow != 28 or ccol != 28:
|
||||
raise Exception('Invalid file: expected 28 rows/cols per image.')
|
||||
# Read data.
|
||||
res = np.fromstring(gz.read(cimg * crow * ccol), dtype=np.uint8)
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
os.remove(gzfname)
|
||||
return res.reshape((cimg, crow * ccol))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def loadLabels(src, cimg):
|
||||
print('Downloading ' + src)
|
||||
gzfname, h = urlretrieve(src, './delete.me')
|
||||
print('Done.')
|
||||
try:
|
||||
with gzip.open(gzfname) as gz:
|
||||
n = struct.unpack('I', gz.read(4))
|
||||
# Read magic number.
|
||||
if n[0] != 0x1080000:
|
||||
raise Exception('Invalid file: unexpected magic number.')
|
||||
# Read number of entries.
|
||||
n = struct.unpack('>I', gz.read(4))
|
||||
if n[0] != cimg:
|
||||
raise Exception('Invalid file: expected {0} rows.'.format(cimg))
|
||||
# Read labels.
|
||||
res = np.fromstring(gz.read(cimg), dtype=np.uint8)
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
os.remove(gzfname)
|
||||
return res.reshape((cimg, 1))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def try_download(dataSrc, labelsSrc, cimg):
|
||||
data = loadData(dataSrc, cimg)
|
||||
labels = loadLabels(labelsSrc, cimg)
|
||||
return np.hstack((data, labels))
|
||||
|
||||
# Save the data files into a format compatible with CNTK text reader
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def savetxt(filename, ndarray):
|
||||
dir = os.path.dirname(filename)
|
||||
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(dir):
|
||||
os.makedirs(dir)
|
||||
|
||||
if not os.path.isfile(filename):
|
||||
print("Saving", filename)
|
||||
with open(filename, 'w') as f:
|
||||
labels = list(map(' '.join, np.eye(10, dtype=np.uint).astype(str)))
|
||||
for row in ndarray:
|
||||
row_str = row.astype(str)
|
||||
label_str = labels[row[-1]]
|
||||
feature_str = ' '.join(row_str[:-1])
|
||||
f.write('|labels {} |features {}\n'.format(label_str, feature_str))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print("File already exists", filename)
|
||||
|
||||
# Read a CTF formatted text (as mentioned above) using the CTF deserializer from a file
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def create_reader(path, is_training, input_dim, num_label_classes):
|
||||
return C.io.MinibatchSource(C.io.CTFDeserializer(path, C.io.StreamDefs(
|
||||
labels=C.io.StreamDef(field='labels', shape=num_label_classes, is_sparse=False),
|
||||
features=C.io.StreamDef(field='features', shape=input_dim, is_sparse=False)
|
||||
)), randomize=is_training, max_sweeps=C.io.INFINITELY_REPEAT if is_training else 1)
|
||||
|
||||
# Defines a utility that prints the training progress
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def print_training_progress(trainer, mb, frequency, verbose=1):
|
||||
training_loss = "NA"
|
||||
eval_error = "NA"
|
||||
|
||||
if mb % frequency == 0:
|
||||
training_loss = trainer.previous_minibatch_loss_average
|
||||
eval_error = trainer.previous_minibatch_evaluation_average
|
||||
if verbose:
|
||||
print("Minibatch: {0}, Loss: {1:.4f}, Error: {2:.2f}%".format(mb, training_loss, eval_error * 100))
|
||||
|
||||
return mb, training_loss, eval_error
|
||||
|
||||
# Create the network architecture
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def create_model(features):
|
||||
with C.layers.default_options(init=C.layers.glorot_uniform(), activation=C.ops.relu):
|
||||
h = features
|
||||
for _ in range(num_hidden_layers):
|
||||
h = C.layers.Dense(hidden_layers_dim)(h)
|
||||
r = C.layers.Dense(num_output_classes, activation=None)(h)
|
||||
return r
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
run = Run.get_submitted_run()
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from urllib.request import urlretrieve
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
from urllib import urlretrieve
|
||||
|
||||
# Select the right target device when this script is being used:
|
||||
if 'TEST_DEVICE' in os.environ:
|
||||
if os.environ['TEST_DEVICE'] == 'cpu':
|
||||
C.device.try_set_default_device(C.device.cpu())
|
||||
else:
|
||||
C.device.try_set_default_device(C.device.gpu(0))
|
||||
|
||||
# URLs for the train image and labels data
|
||||
url_train_image = 'http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz'
|
||||
url_train_labels = 'http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'
|
||||
num_train_samples = 60000
|
||||
|
||||
print("Downloading train data")
|
||||
train = try_download(url_train_image, url_train_labels, num_train_samples)
|
||||
|
||||
url_test_image = 'http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz'
|
||||
url_test_labels = 'http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'
|
||||
num_test_samples = 10000
|
||||
|
||||
print("Downloading test data")
|
||||
test = try_download(url_test_image, url_test_labels, num_test_samples)
|
||||
|
||||
# Save the train and test files (prefer our default path for the data
|
||||
rank = os.environ.get("OMPI_COMM_WORLD_RANK")
|
||||
data_dir = os.path.join("outputs", "MNIST")
|
||||
sentinel_path = os.path.join(data_dir, "complete.txt")
|
||||
if rank == '0':
|
||||
print('Writing train text file...')
|
||||
savetxt(os.path.join(data_dir, "Train-28x28_cntk_text.txt"), train)
|
||||
|
||||
print('Writing test text file...')
|
||||
savetxt(os.path.join(data_dir, "Test-28x28_cntk_text.txt"), test)
|
||||
with open(sentinel_path, 'w+') as f:
|
||||
f.write("download complete")
|
||||
|
||||
print('Done with downloading data.')
|
||||
else:
|
||||
while not os.path.exists(sentinel_path):
|
||||
time.sleep(0.01)
|
||||
|
||||
# Ensure we always get the same amount of randomness
|
||||
np.random.seed(0)
|
||||
|
||||
# Define the data dimensions
|
||||
input_dim = 784
|
||||
num_output_classes = 10
|
||||
|
||||
# Ensure the training and test data is generated and available for this tutorial.
|
||||
# We search in two locations in the toolkit for the cached MNIST data set.
|
||||
data_found = False
|
||||
for data_dir in [os.path.join("..", "Examples", "Image", "DataSets", "MNIST"),
|
||||
os.path.join("data_" + str(rank), "MNIST"),
|
||||
os.path.join("outputs", "MNIST")]:
|
||||
train_file = os.path.join(data_dir, "Train-28x28_cntk_text.txt")
|
||||
test_file = os.path.join(data_dir, "Test-28x28_cntk_text.txt")
|
||||
if os.path.isfile(train_file) and os.path.isfile(test_file):
|
||||
data_found = True
|
||||
break
|
||||
if not data_found:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Please generate the data by completing CNTK 103 Part A")
|
||||
print("Data directory is {0}".format(data_dir))
|
||||
|
||||
num_hidden_layers = args.num_hidden_layers
|
||||
hidden_layers_dim = 400
|
||||
|
||||
input = C.input_variable(input_dim)
|
||||
label = C.input_variable(num_output_classes)
|
||||
|
||||
z = create_model(input)
|
||||
# Scale the input to 0-1 range by dividing each pixel by 255.
|
||||
z = create_model(input / 255.0)
|
||||
|
||||
loss = C.cross_entropy_with_softmax(z, label)
|
||||
label_error = C.classification_error(z, label)
|
||||
|
||||
# Instantiate the trainer object to drive the model training
|
||||
learning_rate = args.learning_rate
|
||||
lr_schedule = C.learning_rate_schedule(learning_rate, C.UnitType.minibatch)
|
||||
learner = C.sgd(z.parameters, lr_schedule)
|
||||
trainer = C.Trainer(z, (loss, label_error), [learner])
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize the parameters for the trainer
|
||||
minibatch_size = args.minibatch_size
|
||||
num_samples_per_sweep = 60000
|
||||
num_sweeps_to_train_with = 10
|
||||
num_minibatches_to_train = (num_samples_per_sweep * num_sweeps_to_train_with) / minibatch_size
|
||||
|
||||
# Create the reader to training data set
|
||||
reader_train = create_reader(train_file, True, input_dim, num_output_classes)
|
||||
|
||||
# Map the data streams to the input and labels.
|
||||
input_map = {
|
||||
label: reader_train.streams.labels,
|
||||
input: reader_train.streams.features
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the trainer on and perform model training
|
||||
training_progress_output_freq = 500
|
||||
|
||||
errors = []
|
||||
losses = []
|
||||
for i in range(0, int(num_minibatches_to_train)):
|
||||
# Read a mini batch from the training data file
|
||||
data = reader_train.next_minibatch(minibatch_size, input_map=input_map)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train_minibatch(data)
|
||||
batchsize, loss, error = print_training_progress(trainer, i, training_progress_output_freq, verbose=1)
|
||||
if (error != 'NA') and (loss != 'NA'):
|
||||
errors.append(float(error))
|
||||
losses.append(float(loss))
|
||||
|
||||
# log the losses
|
||||
if rank == '0':
|
||||
run.log_list("Loss", losses)
|
||||
run.log_list("Error", errors)
|
||||
|
||||
# Read the training data
|
||||
reader_test = create_reader(test_file, False, input_dim, num_output_classes)
|
||||
|
||||
test_input_map = {
|
||||
label: reader_test.streams.labels,
|
||||
input: reader_test.streams.features,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Test data for trained model
|
||||
test_minibatch_size = 512
|
||||
num_samples = 10000
|
||||
num_minibatches_to_test = num_samples // test_minibatch_size
|
||||
test_result = 0.0
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(num_minibatches_to_test):
|
||||
# We are loading test data in batches specified by test_minibatch_size
|
||||
# Each data point in the minibatch is a MNIST digit image of 784 dimensions
|
||||
# with one pixel per dimension that we will encode / decode with the
|
||||
# trained model.
|
||||
data = reader_test.next_minibatch(test_minibatch_size,
|
||||
input_map=test_input_map)
|
||||
|
||||
eval_error = trainer.test_minibatch(data)
|
||||
test_result = test_result + eval_error
|
||||
|
||||
# Average of evaluation errors of all test minibatches
|
||||
print("Average test error: {0:.2f}%".format((test_result * 100) / num_minibatches_to_test))
|
||||
|
||||
out = C.softmax(z)
|
||||
|
||||
# Read the data for evaluation
|
||||
reader_eval = create_reader(test_file, False, input_dim, num_output_classes)
|
||||
|
||||
eval_minibatch_size = 25
|
||||
eval_input_map = {input: reader_eval.streams.features}
|
||||
|
||||
data = reader_test.next_minibatch(eval_minibatch_size, input_map=test_input_map)
|
||||
|
||||
img_label = data[label].asarray()
|
||||
img_data = data[input].asarray()
|
||||
predicted_label_prob = [out.eval(img_data[i]) for i in range(len(img_data))]
|
||||
|
||||
# Find the index with the maximum value for both predicted as well as the ground truth
|
||||
pred = [np.argmax(predicted_label_prob[i]) for i in range(len(predicted_label_prob))]
|
||||
gtlabel = [np.argmax(img_label[i]) for i in range(len(img_label))]
|
||||
|
||||
print("Label :", gtlabel[:25])
|
||||
print("Predicted:", pred)
|
||||
|
||||
# save model to outputs folder
|
||||
z.save('outputs/cntk.model')
|
||||
@@ -176,13 +176,13 @@
|
||||
"from azureml.core.script_run_config import ScriptRunConfig\n",
|
||||
"import tensorflow as tf\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"logs_dir = os.curdir + os.sep + \"logs\"\n",
|
||||
"tensorflow_logs_dir = os.path.join(logs_dir, \"tensorflow\")\n",
|
||||
"logs_dir = os.path.join(os.curdir, \"logs\")\n",
|
||||
"data_dir = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.curdir, \"mnist_data\"))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"if not path.exists(tensorflow_logs_dir):\n",
|
||||
" makedirs(tensorflow_logs_dir)\n",
|
||||
"if not path.exists(data_dir):\n",
|
||||
" makedirs(data_dir)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"os.environ[\"TEST_TMPDIR\"] = logs_dir\n",
|
||||
"os.environ[\"TEST_TMPDIR\"] = data_dir\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Writing logs to ./logs results in their being uploaded to Artifact Service,\n",
|
||||
"# and thus, made accessible to our Tensorboard instance.\n",
|
||||
@@ -191,15 +191,15 @@
|
||||
"# Create an experiment\n",
|
||||
"exp = Experiment(ws, experiment_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"script = ScriptRunConfig(exp_dir,\n",
|
||||
" script=\"mnist_with_summaries.py\",\n",
|
||||
" run_config=run_config)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# If you would like the run to go for longer, add --max_steps 5000 to the arguments list:\n",
|
||||
"# arguments_list += [\"--max_steps\", \"5000\"]\n",
|
||||
"kwargs = {}\n",
|
||||
"kwargs['arguments_list'] = arguments_list\n",
|
||||
"run = exp.submit(script, kwargs)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"script = ScriptRunConfig(exp_dir,\n",
|
||||
" script=\"mnist_with_summaries.py\",\n",
|
||||
" run_config=run_config,\n",
|
||||
" arguments=arguments_list)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"run = exp.submit(script)\n",
|
||||
"# You can also wait for the run to complete\n",
|
||||
"# run.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)\n",
|
||||
"runs.append(run)"
|
||||
@@ -367,23 +367,21 @@
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import BatchAiCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"clust_name = ws.name + \"cpu\"\n",
|
||||
"clust_name = \"cpucluster\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"try:\n",
|
||||
" # If you already have a cluster named this, we don't need to make a new one.\n",
|
||||
" cts = ws.compute_targets() \n",
|
||||
" cts = ws.compute_targets \n",
|
||||
" compute_target = cts[clust_name]\n",
|
||||
" assert compute_target.type == 'BatchAI'\n",
|
||||
"except:\n",
|
||||
" # Let's make a new one here.\n",
|
||||
" provisioning_config = BatchAiCompute.provisioning_configuration(cluster_max_nodes=2, \n",
|
||||
" autoscale_enabled=True, \n",
|
||||
" cluster_min_nodes=1,\n",
|
||||
" vm_size='Standard_D11_V2')\n",
|
||||
" provisioning_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(max_nodes=6, \n",
|
||||
" vm_size='STANDARD_D2_V2')\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" compute_target = BatchAiCompute.create(ws, clust_name, provisioning_config)\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = AmlCompute.create(ws, clust_name, provisioning_config)\n",
|
||||
"compute_target.wait_for_completion(show_output=True, min_node_count=1, timeout_in_minutes=20)\n",
|
||||
"print(compute_target.name)\n",
|
||||
"# For a more detailed view of current BatchAI cluster status, use the 'status' property \n",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,52 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Training ML models with Azure ML SDK
|
||||
These notebook tutorials cover the various scenarios for training machine learning and deep learning models with Azure Machine Learning.
|
||||
|
||||
## Sample notebooks
|
||||
- [01.train-hyperparameter-tune-deploy-with-pytorch](./01.train-hyperparameter-tune-deploy-with-pytorch/01.train-hyperparameter-tune-deploy-with-pytorch.ipynb)
|
||||
Train, hyperparameter tune, and deploy a PyTorch image classification model that distinguishes bees vs. ants using transfer learning. Azure ML concepts covered:
|
||||
- Create a remote compute target (Batch AI cluster)
|
||||
- Upload training data using `Datastore`
|
||||
- Run a single-node `PyTorch` training job
|
||||
- Hyperparameter tune model with HyperDrive
|
||||
- Find and register the best model
|
||||
- Deploy model to ACI
|
||||
- [02.distributed-pytorch-with-horovod](./02.distributed-pytorch-with-horovod/02.distributed-pytorch-with-horovod.ipynb)
|
||||
Train a PyTorch model on the MNIST dataset using distributed training with Horovod. Azure ML concepts covered:
|
||||
- Create a remote compute target (Batch AI cluster)
|
||||
- Run a two-node distributed `PyTorch` training job using Horovod
|
||||
- [03.train-hyperparameter-tun-deploy-with-tensorflow](./03.train-hyperparameter-tune-deploy-with-tensorflow/03.train-hyperparameter-tune-deploy-with-tensorflow.ipynb)
|
||||
Train, hyperparameter tune, and deploy a TensorFlow model on the MNIST dataset. Azure ML concepts covered:
|
||||
- Create a remote compute target (Batch AI cluster)
|
||||
- Upload training data using `Datastore`
|
||||
- Run a single-node `TensorFlow` training job
|
||||
- Leverage features of the `Run` object
|
||||
- Download the trained model
|
||||
- Hyperparameter tune model with HyperDrive
|
||||
- Find and register the best model
|
||||
- Deploy model to ACI
|
||||
- [04.distributed-tensorflow-with-horovod](./04.distributed-tensorflow-with-horovod/04.distributed-tensorflow-with-horovod.ipynb)
|
||||
Train a TensorFlow word2vec model using distributed training with Horovod. Azure ML concepts covered:
|
||||
- Create a remote compute target (Batch AI cluster)
|
||||
- Upload training data using `Datastore`
|
||||
- Run a two-node distributed `TensorFlow` training job using Horovod
|
||||
- [05.distributed-tensorflow-with-parameter-server](./05.distributed-tensorflow-with-parameter-server/05.distributed-tensorflow-with-parameter-server.ipynb)
|
||||
Train a TensorFlow model on the MNIST dataset using native distributed TensorFlow (parameter server). Azure ML concepts covered:
|
||||
- Create a remote compute target (Batch AI cluster)
|
||||
- Run a two workers, one parameter server distributed `TensorFlow` training job
|
||||
- [06.distributed-cntk-with-custom-docker](./06.distributed-cntk-with-custom-docker/06.distributed-cntk-with-custom-docker.ipynb)
|
||||
Train a CNTK model on the MNIST dataset using the Azure ML base `Estimator` with custom Docker image and distributed training. Azure ML concepts covered:
|
||||
- Create a remote compute target (Batch AI cluster)
|
||||
- Upload training data using `Datastore`
|
||||
- Run a base `Estimator` training job using a custom Docker image from Docker Hub
|
||||
- Distributed CNTK two-node training job via MPI using base `Estimator`
|
||||
|
||||
- [07.tensorboard](./07.tensorboard/07.tensorboard.ipynb)
|
||||
Train a TensorFlow MNIST model locally, on a DSVM, and on Batch AI and view the logs live on TensorBoard. Azure ML concepts covered:
|
||||
- Run the training job locally with Azure ML and run TensorBoard locally. Start (and stop) an Azure ML `TensorBoard` object to stream and view the logs
|
||||
- Run the training job on a remote DSVM and stream the logs to TensorBoard
|
||||
- Run the training job on a remote Batch AI cluster and stream the logs to TensorBoard
|
||||
- Start a `Tensorboard` instance that displays the logs from all three above runs in one
|
||||
- [08.export-run-history-to-tensorboard](./08.export-run-history-to-tensorboard/08.export-run-history-to-tensorboard.ipynb)
|
||||
- Start an Azure ML `Experiment` and log metrics to `Run` history
|
||||
- Export the `Run` history logs to TensorBoard logs
|
||||
- View the logs in TensorBoard
|
||||
@@ -64,7 +64,7 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%matplotlib inline\n",
|
||||
"%matplotlib notebook\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
|
||||
@@ -131,9 +131,9 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Create remote compute target\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Azure Azure ML Managed Compute is a managed service that enables data scientists to train machine learning models on clusters of Azure virtual machines, including VMs with GPU support. In this tutorial, you create an Azure Managed Compute cluster as your training environment. This code creates a cluster for you if it does not already exist in your workspace. \n",
|
||||
"Azure Machine Learning Managed Compute(AmlCompute) is a managed service that enables data scientists to train machine learning models on clusters of Azure virtual machines, including VMs with GPU support. In this tutorial, you create AmlCompute as your training environment. This code creates compute for you if it does not already exist in your workspace. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" **Creation of the cluster takes approximately 5 minutes.** If the cluster is already in the workspace this code uses it and skips the creation process."
|
||||
" **Creation of the compute takes approximately 5 minutes.** If the compute is already in the workspace this code uses it and skips the creation process."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -147,32 +147,31 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import BatchAiCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import AmlCompute\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# choose a name for your cluster\n",
|
||||
"batchai_cluster_name = os.environ.get(\"BATCHAI_CLUSTER_NAME\", ws.name + \"gpu\")\n",
|
||||
"cluster_min_nodes = os.environ.get(\"BATCHAI_CLUSTER_MIN_NODES\", 1)\n",
|
||||
"cluster_max_nodes = os.environ.get(\"BATCHAI_CLUSTER_MAX_NODES\", 3)\n",
|
||||
"vm_size = os.environ.get(\"BATCHAI_CLUSTER_SKU\", \"STANDARD_NC6\")\n",
|
||||
"autoscale_enabled = os.environ.get(\"BATCHAI_CLUSTER_AUTOSCALE_ENABLED\", True)\n",
|
||||
"compute_name = os.environ.get(\"BATCHAI_CLUSTER_NAME\", \"cpucluster\")\n",
|
||||
"compute_min_nodes = os.environ.get(\"BATCHAI_CLUSTER_MIN_NODES\", 0)\n",
|
||||
"compute_max_nodes = os.environ.get(\"BATCHAI_CLUSTER_MAX_NODES\", 4)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# This example uses CPU VM. For using GPU VM, set SKU to STANDARD_NC6\n",
|
||||
"vm_size = os.environ.get(\"BATCHAI_CLUSTER_SKU\", \"STANDARD_D2_V2\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"if batchai_cluster_name in ws.compute_targets():\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = ws.compute_targets()[batchai_cluster_name]\n",
|
||||
" if compute_target and type(compute_target) is BatchAiCompute:\n",
|
||||
" print('found compute target. just use it. ' + batchai_cluster_name)\n",
|
||||
"if compute_name in ws.compute_targets:\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = ws.compute_targets[compute_name]\n",
|
||||
" if compute_target and type(compute_target) is AmlCompute:\n",
|
||||
" print('found compute target. just use it. ' + compute_name)\n",
|
||||
"else:\n",
|
||||
" print('creating a new compute target...')\n",
|
||||
" provisioning_config = BatchAiCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size = vm_size, # NC6 is GPU-enabled\n",
|
||||
" vm_priority = 'lowpriority', # optional\n",
|
||||
" autoscale_enabled = autoscale_enabled,\n",
|
||||
" cluster_min_nodes = cluster_min_nodes, \n",
|
||||
" cluster_max_nodes = cluster_max_nodes)\n",
|
||||
" provisioning_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size = vm_size,\n",
|
||||
" min_nodes = compute_min_nodes, \n",
|
||||
" max_nodes = compute_max_nodes)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # create the cluster\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = ComputeTarget.create(ws, batchai_cluster_name, provisioning_config)\n",
|
||||
" compute_target = ComputeTarget.create(ws, compute_name, provisioning_config)\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" # can poll for a minimum number of nodes and for a specific timeout. \n",
|
||||
" # if no min node count is provided it will use the scale settings for the cluster\n",
|
||||
@@ -201,13 +200,6 @@
|
||||
"Download the MNIST dataset and save the files into a `data` directory locally. Images and labels for both training and testing are downloaded."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
@@ -578,7 +570,7 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -717,7 +709,7 @@
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.6"
|
||||
"version": "3.6.2"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"msauthor": "sgilley"
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -97,7 +97,7 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%matplotlib inline\n",
|
||||
"%matplotlib notebook\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
|
||||
@@ -134,7 +134,7 @@
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"ws = Workspace.from_config()\n",
|
||||
"model=Model(ws, 'sklearn_mnist')\n",
|
||||
"model.download(target_dir = '.')\n",
|
||||
"model.download(target_dir='.', exists_ok=True)\n",
|
||||
"import os \n",
|
||||
"# verify the downloaded model file\n",
|
||||
"os.stat('./sklearn_mnist_model.pkl')"
|
||||
@@ -296,7 +296,8 @@
|
||||
" data = np.array(json.loads(raw_data)['data'])\n",
|
||||
" # make prediction\n",
|
||||
" y_hat = model.predict(data)\n",
|
||||
" return json.dumps(y_hat.tolist())"
|
||||
" # you can return any data type as long as it is JSON-serializable\n",
|
||||
" return y_hat.tolist()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -480,7 +481,7 @@
|
||||
"test_samples = bytes(test_samples, encoding='utf8')\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# predict using the deployed model\n",
|
||||
"result = json.loads(service.run(input_data=test_samples))\n",
|
||||
"result = service.run(input_data=test_samples)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# compare actual value vs. the predicted values:\n",
|
||||
"i = 0\n",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -264,7 +264,7 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from azureml.train.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n",
|
||||
"RunDetails(local_run).show()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -393,7 +393,7 @@
|
||||
"> * Review training results\n",
|
||||
"> * Register the best model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Learn more about [how to configure settings for automatic training](https://aka.ms/aml-how-configure-auto) or [how to use automatic training on a remote resource](https://aka.ms/aml-how-to-auto-remote)."
|
||||
"Learn more about [how to configure settings for automatic training](https://aka.ms/aml-how-to-configure-auto) or [how to use automatic training on a remote resource](https://aka.ms/aml-how-to-auto-remote)."
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user