7.3 KiB
title, shortTitle, intro, allowTitleToDifferFromFilename, product, versions, type, topics, redirect_from
| title | shortTitle | intro | allowTitleToDifferFromFilename | product | versions | type | topics | redirect_from | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quickstart for {% data variables.product.prodname_github_codespaces %} | Quickstart for {% data variables.product.prodname_codespaces %} | Try out {% data variables.product.prodname_github_codespaces %} in 5 minutes. | true | {% data reusables.gated-features.codespaces %} |
|
quick_start |
|
|
Introduction
In this guide, you'll create a codespace from a template repository and explore some of the essential features available to you within the codespace.
From this quickstart, you'll learn how to create a codespace, connect to a forwarded port to view your running application, use version control in a codespace, and personalize your setup with extensions.
For more information on exactly how {% data variables.product.prodname_github_codespaces %} works, see the companion guide "Deep dive into {% data variables.product.prodname_github_codespaces %}."
Creating your codespace
-
Navigate to the template repository and select Use this template.
-
Choose an owner for the new repository, enter a repository name, select your preferred privacy setting, and click Create repository from template.
-
Navigate to the main page of the newly created repository. Under the repository name, use the {% octicon "code" aria-label="The code icon" %} Code drop-down menu, and in the Codespaces tab, click Create codespace on main.
Running the application
Once your codespace is created, your repository will be automatically cloned into it. Now you can run the application and launch it in a browser.
-
When the terminal becomes available, enter the command
npm run dev. This example uses a Node.js project, and this command runs the script labeled "dev" in the package.json file, which starts up the web application defined in the sample repository.If you're following along with a different application type, enter the corresponding start command for that project.
-
When your application starts, the codespace recognizes the port the application is running on and displays a prompt to let you know it has been forwarded.
- Click Open in Browser to view your running application in a new tab.
Edit the application and view changes
-
Switch back to your codespace and open the haikus.json file by double-clicking it in the Explorer.
-
Edit the
textfield of the first haiku to personalize the application with your own haiku. -
Go back to the running application tab in your browser and refresh to see your changes.
{% octicon "light-bulb" aria-label="The lightbulb icon" %} If you've closed the tab, open the Ports panel and click the Open in browser icon for the running port.
Committing and pushing your changes
Now that you've made a few changes, you can use the integrated terminal or the source view to commit and push the changes back to the remote.
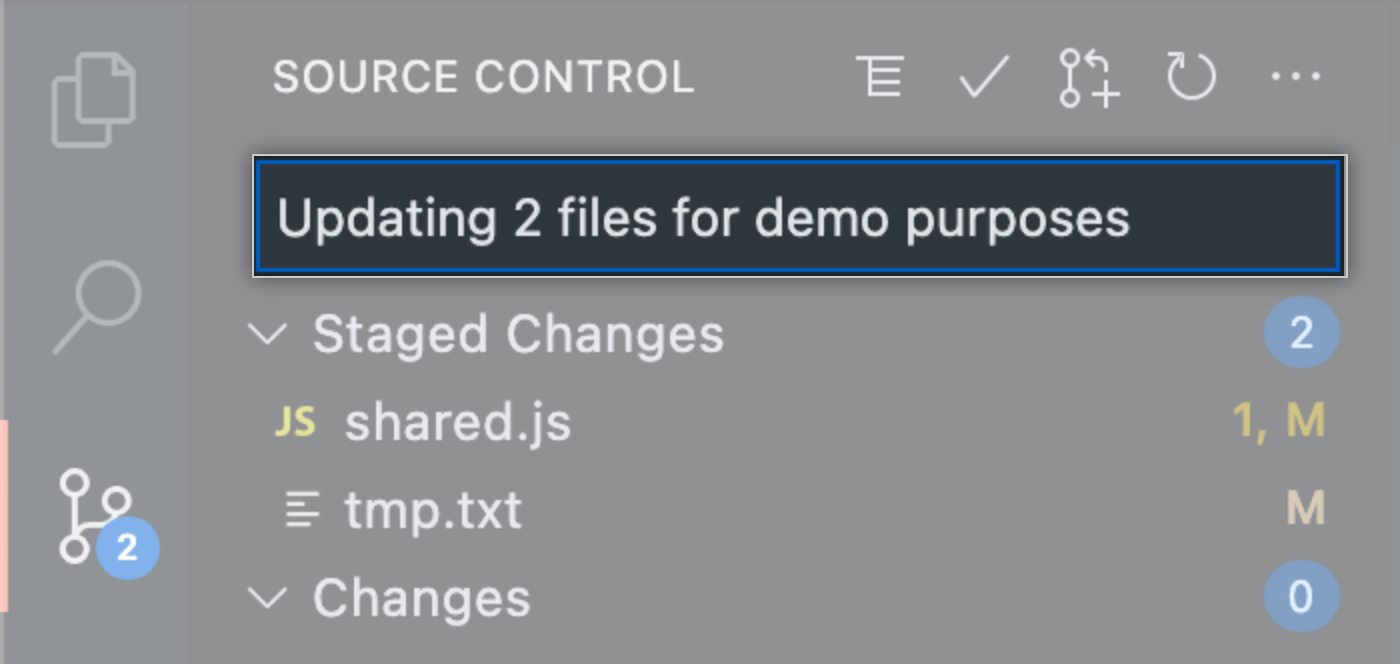
{% data reusables.codespaces.source-control-display-dark %}
-
To stage your changes, click + next to the file you've changed, or next to Changes if you've changed multiple files and you want to stage them all.
-
Type a commit message describing the change you've made.
-
To commit your staged changes, click the check mark at the top the source control side bar.
You can push the changes you've made. This applies those changes to the upstream branch on the remote repository. You might want to do this if you're not yet ready to create a pull request, or if you prefer to create a pull request on {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}.
-
At the top of the side bar, click the ellipsis (...).
-
In the drop-down menu, click Push.
-
Go back to your new repository on {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} and view the haikus.json file. Check that the change you made in your codespace has been successfully pushed to the repository.
Personalizing with an extension
Within a codespace, you have access to the {% data variables.product.prodname_vscode_marketplace %}. For this example, you'll install an extension that alters the theme, but you can install any extension that is useful for your workflow.
{% note %}
Note: If you have Settings Sync turned on, any changes you make to your editor setup in the current codespace, such as changing your theme or keyboard bindings, are automatically synced to any other codespaces you open and any instances of {% data variables.product.prodname_vscode %} that are signed into your {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} account.
{% endnote %}
-
In the left sidebar, click the Extensions icon.
-
In the search bar, enter
fairyflossand install the fairyfloss extension. -
Click Install in Codespaces.
-
Select the
fairyflosstheme by selecting it from the list.
Next Steps
You've successfully created, personalized, and run your first application within a codespace but there's so much more to explore! Here are some helpful resources for taking your next steps with {% data variables.product.prodname_codespaces %}.
- Deep dive: This quickstart presented some of the features of {% data variables.product.prodname_codespaces %}. The deep dive looks at these areas from a technical standpoint.
- Setting up your project for {% data variables.product.prodname_codespaces %}: These guides provide information on setting up your project to use {% data variables.product.prodname_codespaces %} with specific languages.
- Configuring {% data variables.product.prodname_codespaces %} for your project: This guide provides details on creating a custom configuration for {% data variables.product.prodname_codespaces %} for your project.