Merge branch 'main' into fix-nav
This commit is contained in:
@@ -52,6 +52,32 @@ The default {% data variables.product.prodname_codeql_workflow %} uses the `pull
|
||||
|
||||
For more information about the `pull_request` event, see "[Workflow syntax for {% data variables.product.prodname_actions %}](/actions/reference/workflow-syntax-for-github-actions#onpushpull_requestbranchestags)."
|
||||
|
||||
#### Avoiding unnecessary scans of pull requests
|
||||
|
||||
You might want to avoid a code scan being triggered on specific pull requests targeted against the default branch, irrespective of which files have been changed. You can configure this by specifying `on:pull_request:paths-ignore` or `on:pull_request:paths` in the {% data variables.product.prodname_code_scanning %} workflow. For example, if the only changes in a pull request are to files with the file extensions `.md` or `.txt` you can use the following `paths-ignore` array.
|
||||
|
||||
``` yaml
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches: [main, protected]
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
branches: [main]
|
||||
paths-ignore:
|
||||
- '**/*.md'
|
||||
- '**/*.txt'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Notes**
|
||||
|
||||
* `on:pull_request:paths-ignore` and `on:pull_request:paths` set conditions that determine whether the actions in the workflow will run on a pull request. They don't determine what files will be analyzed when the actions _are_ run. When a pull request contains any files that are not matched by `on:pull_request:paths-ignore` or `on:pull_request:paths`, the workflow runs the actions and scans all of the files changed in the pull request, including those matched by `on:pull_request:paths-ignore` or `on:pull_request:paths`, unless the files have been excluded. For information on how to exclude files from analysis, see "[Specifying directories to scan](#specifying-directories-to-scan)."
|
||||
* For {% data variables.product.prodname_codeql %} {% data variables.product.prodname_code_scanning %} workflow files, don't use the `paths-ignore` or `paths` keywords with the `on:push` event as this is likely to cause missing analyses. For accurate results, {% data variables.product.prodname_codeql %} {% data variables.product.prodname_code_scanning %} needs to be able to compare new changes with the analysis of the previous commit.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
|
||||
For more information about using `on:pull_request:paths-ignore` and `on:pull_request:paths` to determine when a workflow will run for a pull request, see "[Workflow syntax for {% data variables.product.prodname_actions %}](/actions/reference/workflow-syntax-for-github-actions#onpushpull_requestpaths)."
|
||||
|
||||
#### Scanning on a schedule
|
||||
|
||||
If you use the default {% data variables.product.prodname_codeql_workflow %}, the workflow will scan the code in your repository once a week, in addition to the scans triggered by events. To adjust this schedule, edit the `cron` value in the workflow. For more information, see "[Workflow syntax for {% data variables.product.prodname_actions %}](/actions/reference/workflow-syntax-for-github-actions#onschedule)."
|
||||
@@ -235,13 +261,13 @@ If you only want to run custom queries, you can disable the default security que
|
||||
|
||||
#### Specifying directories to scan
|
||||
|
||||
For the interpreted languages that {% data variables.product.prodname_codeql %} supports (Python and JavaScript/TypeScript), you can restrict {% data variables.product.prodname_code_scanning %} to files in specific directories by adding a `paths` array to the configuration file. You can exclude the files in specific directories from scans by adding a `paths-ignore` array.
|
||||
For the interpreted languages that {% data variables.product.prodname_codeql %} supports (Python and JavaScript/TypeScript), you can restrict {% data variables.product.prodname_code_scanning %} to files in specific directories by adding a `paths` array to the configuration file. You can exclude the files in specific directories from analysis by adding a `paths-ignore` array.
|
||||
|
||||
``` yaml
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- src
|
||||
paths-ignore:
|
||||
- node_modules
|
||||
- src/node_modules
|
||||
- '**/*.test.js'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -254,7 +280,7 @@ paths-ignore:
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
|
||||
For C/C++, C#, and Java, if you want to limit {% data variables.product.prodname_code_scanning %} to specific directories in your project, you must specify appropriate build steps in the workflow. The commands you need to use to exclude a directory from the build will depend on your build system. For more information, see "[Configuring the {% data variables.product.prodname_codeql %} workflow for compiled languages](/github/finding-security-vulnerabilities-and-errors-in-your-code/configuring-the-codeql-workflow-for-compiled-languages#adding-build-steps-for-a-compiled-language)."
|
||||
For compiled languages, if you want to limit {% data variables.product.prodname_code_scanning %} to specific directories in your project, you must specify appropriate build steps in the workflow. The commands you need to use to exclude a directory from the build will depend on your build system. For more information, see "[Configuring the {% data variables.product.prodname_codeql %} workflow for compiled languages](/github/finding-security-vulnerabilities-and-errors-in-your-code/configuring-the-codeql-workflow-for-compiled-languages#adding-build-steps-for-a-compiled-language)."
|
||||
|
||||
You can quickly analyze small portions of a monorepo when you modify code in specific directories. You'll need to both exclude directories in your build steps and use the `paths-ignore` and `paths` keywords for [`on.<push|pull_request>`](/actions/reference/workflow-syntax-for-github-actions#onpushpull_requestpaths) in your workflow.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,42 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: About labels
|
||||
intro: 'Labels on {% data variables.product.product_name %} help you organize and prioritize your work. You can apply labels to issues and pull requests to signify priority, category, or any other information you find useful.'
|
||||
redirect_from:
|
||||
- /articles/about-labels
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
free-pro-team: '*'
|
||||
enterprise-server: '*'
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Labels are tied to the repository they are created in. Once a label exists, you can use it on any issue or pull request within that repository. For more information, see "[Creating a label](/articles/creating-a-label/)."
|
||||
|
||||
Anyone with read access to a repository can view and search the repository’s labels. To create, edit, apply, or delete a label, you must have write access to the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
### Using default labels
|
||||
|
||||
{% data variables.product.product_name %} provides default labels in every new repository. You can use these default labels to help create a standard workflow in a repository:
|
||||
|
||||
Label | Description
|
||||
--- | ---
|
||||
`bug` | Indicates an unexpected problem or unintended behavior
|
||||
`documentation` | Indicates a need for improvements or additions to documentation
|
||||
`duplicate` | Indicates similar issues or pull requests
|
||||
`enhancement` | Indicates new feature requests
|
||||
`good first issue` | Indicates a good issue for first-time contributors
|
||||
`help wanted` | Indicates that a maintainer wants help on an issue or pull request
|
||||
`invalid` | Indicates that an issue or pull request is no longer relevant
|
||||
`question` | Indicates that an issue or pull request needs more information
|
||||
`wontfix` | Indicates that work won't continue on an issue or pull request
|
||||
|
||||
Default labels are included in every new repository when the repository is created, but you can edit or delete the labels later. For more information, see "[Deleting a label](/articles/deleting-a-label/)."
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
Organization owners can customize the default labels for repositories in their organization. For more information, see "[Managing default labels for repositories in your organization](/articles/managing-default-labels-for-repositories-in-your-organization)."
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
### Further reading
|
||||
|
||||
- "[Encouraging helpful contributions to your project with labels](/github/building-a-strong-community/encouraging-helpful-contributions-to-your-project-with-labels)"
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
@@ -1,29 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Applying labels to issues and pull requests
|
||||
intro: 'In repositories where you have write access, you can assign labels to issues and pull requests to help organize your projects.'
|
||||
redirect_from:
|
||||
- /articles/customizing-issue-labels/
|
||||
- /articles/applying-labels-to-issues-and-pull-requests
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
free-pro-team: '*'
|
||||
enterprise-server: '*'
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
{% tip %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** You can apply up to a maximum of 100 labels to issues and pull requests.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endtip %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.sidebar-issue-pr %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.select-items-in-issue-or-pr-list %}
|
||||
4. In the upper-right corner, click **Label**, then start typing the name of an existing label. Click the label's name to associate it with the selected items. You can also apply a label in the Labels drop-down menu within an issue or pull request.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Further reading
|
||||
|
||||
- "[About labels](/articles/about-labels)"
|
||||
- "[Filtering issues and pull requests by labels](/articles/filtering-issues-and-pull-requests-by-labels)"
|
||||
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Creating a label
|
||||
intro: 'In repositories where you have write access, you can create labels to organize issues and pull requests.'
|
||||
redirect_from:
|
||||
- /articles/creating-and-editing-labels-for-issues-and-pull-requests/
|
||||
- /articles/creating-a-label
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
free-pro-team: '*'
|
||||
enterprise-server: '*'
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
{% tip %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** You can also create a label in the Labels drop-down menu within an issue or pull request.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endtip %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.sidebar-issue-pr %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.labels %}
|
||||
4. To the right of the search field, click **New label**.
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.name-label %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.label-description %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.label-color-randomizer %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.create-label %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Further reading
|
||||
|
||||
- "[About labels](/articles/about-labels)"
|
||||
- "[Applying labels to issues and pull requests](/articles/applying-labels-to-issues-and-pull-requests)"
|
||||
- "[Editing a label](/articles/editing-a-label)"
|
||||
- "[Filtering issues and pull requests by labels](/articles/filtering-issues-and-pull-requests-by-labels)"{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
- "[Managing default labels for repositories in your organization](/articles/managing-default-labels-for-repositories-in-your-organization)"
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
@@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Deleting a label
|
||||
intro: 'In repositories where you have write access, you can delete a label if you no longer need it to classify issues or pull requests.'
|
||||
redirect_from:
|
||||
- /articles/deleting-a-label
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
free-pro-team: '*'
|
||||
enterprise-server: '*'
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Deleting a label will remove the label from any issues or pull requests where it's been applied.
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.sidebar-issue-pr %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.labels %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.delete-label %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Further reading
|
||||
|
||||
- "[Applying labels to issues and pull requests](/articles/applying-labels-to-issues-and-pull-requests)"
|
||||
- "[Filtering issues and pull requests by labels](/articles/filtering-issues-and-pull-requests-by-labels)"{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
- "[Managing default labels for repositories in your organization](/articles/managing-default-labels-for-repositories-in-your-organization)"
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
@@ -1,29 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Editing a label
|
||||
intro: 'In repositories where you have write access, you can edit the name, color, and description of an existing label.'
|
||||
redirect_from:
|
||||
- /articles/editing-a-label
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
free-pro-team: '*'
|
||||
enterprise-server: '*'
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.sidebar-issue-pr %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.labels %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.edit-label %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.name-label %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.label-description %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.label-color-randomizer %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.save-label %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Further reading
|
||||
|
||||
- "[About labels](/articles/about-labels)"
|
||||
- "[Creating a label](/articles/creating-a-label)"
|
||||
- "[Deleting a label](/articles/deleting-a-label)"
|
||||
- "[Applying labels to issues and pull requests](/articles/applying-labels-to-issues-and-pull-requests)"
|
||||
- "[Filtering issues and pull requests by labels](/articles/filtering-issues-and-pull-requests-by-labels)"{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
- "[Managing default labels for repositories in your organization](/articles/managing-default-labels-for-repositories-in-your-organization)"
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ versions:
|
||||
|
||||
### Table of Contents
|
||||
|
||||
{% topic_link_in_list /managing-your-work-with-issues %}
|
||||
{% topic_link_in_list /managing-your-work-with-issues-and-pull-requests %}
|
||||
{% link_in_list /about-issues %}
|
||||
{% link_in_list /creating-an-issue %}
|
||||
<!-- if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.15" -->
|
||||
@@ -27,6 +27,7 @@ versions:
|
||||
{% link_in_list /pinning-an-issue-to-your-repository %}
|
||||
<!-- endif -->
|
||||
{% link_in_list /creating-a-permanent-link-to-a-code-snippet %}
|
||||
{% link_in_list /managing-labels %}
|
||||
{% link_in_list /about-task-lists %}
|
||||
{% link_in_list /about-automation-for-issues-and-pull-requests-with-query-parameters %}
|
||||
{% link_in_list /file-attachments-on-issues-and-pull-requests %}
|
||||
@@ -35,12 +36,6 @@ versions:
|
||||
{% link_in_list /disabling-issues %}
|
||||
{% link_in_list /linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue %}
|
||||
{% link_in_list /about-duplicate-issues-and-pull-requests %}
|
||||
{% topic_link_in_list /labeling-issues-and-pull-requests %}
|
||||
{% link_in_list /about-labels %}
|
||||
{% link_in_list /creating-a-label %}
|
||||
{% link_in_list /applying-labels-to-issues-and-pull-requests %}
|
||||
{% link_in_list /editing-a-label %}
|
||||
{% link_in_list /deleting-a-label %}
|
||||
{% topic_link_in_list /managing-project-boards %}
|
||||
{% link_in_list /about-project-boards %}
|
||||
{% link_in_list /creating-a-project-board %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Labeling issues and pull requests
|
||||
intro: 'You can manage your work on {% data variables.product.product_name %} by creating labels to categorize issues and pull requests.'
|
||||
mapTopic: true
|
||||
redirect_from:
|
||||
- /articles/labeling-issues-and-pull-requests
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
free-pro-team: '*'
|
||||
enterprise-server: '*'
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Managing labels
|
||||
intro: 'You can classify issues and pull requests by creating, editing, applying, and deleting labels.'
|
||||
redirect_from:
|
||||
- /articles/managing-Labels
|
||||
- /articles/labeling-issues-and-pull-requests
|
||||
- /github/managing-your-work-on-github/labeling-issues-and-pull-requests
|
||||
- /articles/about-labels
|
||||
- /github/managing-your-work-on-github/about-labels
|
||||
- /articles/creating-and-editing-labels-for-issues-and-pull-requests
|
||||
- /articles/creating-a-label
|
||||
- /github/managing-your-work-on-github/creating-a-label
|
||||
- /articles/customizing-issue-labels/
|
||||
- /articles/applying-labels-to-issues-and-pull-requests
|
||||
- /github/managing-your-work-on-github/applying-labels-to-issues-and-pull-requests
|
||||
- /articles/editing-a-label
|
||||
- /github/managing-your-work-on-github/editing-a-label
|
||||
- /articles/deleting-a-label
|
||||
- /github/managing-your-work-on-github/deleting-a-label
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
free-pro-team: '*'
|
||||
enterprise-server: '*'
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### About labels
|
||||
|
||||
You can manage your work on {% data variables.product.product_name %} by creating labels to categorize issues and pull requests. You can apply labels in the repository the label was created in. Once a label exists, you can use the label on any issue or pull request within that repository.
|
||||
|
||||
Anyone with read access to a repository can view and search the repository’s labels. To create, edit, apply, or delete a label, you must have write access to the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
### About default labels
|
||||
|
||||
{% data variables.product.product_name %} provides default labels in every new repository. You can use these default labels to help create a standard workflow in a repository.
|
||||
|
||||
Label | Description
|
||||
--- | ---
|
||||
`bug` | Indicates an unexpected problem or unintended behavior{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.17" %}
|
||||
`documentation` | Indicates a need for improvements or additions to documentation{% endif %}
|
||||
`duplicate` | Indicates similar issues or pull requests
|
||||
`enhancement` | Indicates new feature requests
|
||||
`good first issue` | Indicates a good issue for first-time contributors
|
||||
`help wanted` | Indicates that a maintainer wants help on an issue or pull request
|
||||
`invalid` | Indicates that an issue or pull request is no longer relevant
|
||||
`question` | Indicates that an issue or pull request needs more information
|
||||
`wontfix` | Indicates that work won't continue on an issue or pull request
|
||||
|
||||
Default labels are included in every new repository when the repository is created, but you can edit or delete the labels later.
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" %}
|
||||
Organization owners can customize the default labels for repositories in their organization. For more information, see "[Managing default labels for repositories in your organization](/articles/managing-default-labels-for-repositories-in-your-organization)."
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating a label
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.sidebar-issue-pr %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.labels %}
|
||||
4. To the right of the search field, click **New label**.
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.name-label %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.label-description %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.label-color-randomizer %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.create-label %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Applying labels to issues and pull requests
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.sidebar-issue-pr %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.select-items-in-issue-or-pr-list %}
|
||||
4. In the upper-right corner, click **Label**, then start typing the name of an existing label. Click the label's name to associate it with the selected items.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Editing a label
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.sidebar-issue-pr %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.labels %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.edit-label %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.name-label %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.label-description %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.label-color-randomizer %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.save-label %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Deleting a label
|
||||
Deleting a label will remove the label from issues and pull requests.
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.sidebar-issue-pr %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.labels %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.project-management.delete-label %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Further reading
|
||||
- "[About labels](/articles/about-labels)"
|
||||
- "[Filtering issues and pull requests by labels](/articles/filtering-issues-and-pull-requests-by-labels)"{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
- "[Managing default labels for repositories in your organization](/articles/managing-default-labels-for-repositories-in-your-organization)"{% endif %}{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
- "[Encouraging helpful contributions to your project with labels](/github/building-a-strong-community/encouraging-helpful-contributions-to-your-project-with-labels)"{% endif %}
|
||||
@@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Managing your work with issues
|
||||
title: Managing your work with issues and pull requests
|
||||
intro: 'You can manage your work on {% data variables.product.product_name %} by creating issues to track ideas, enhancements, tasks, or bugs.'
|
||||
mapTopic: true
|
||||
redirect_from:
|
||||
- /github/managing-your-work-on-github/managing-your-work-with-issues
|
||||
- /articles/managing-your-work-with-issues
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
free-pro-team: '*'
|
||||
@@ -59,6 +59,7 @@ In addition to managing organization-level settings, organization owners have ad
|
||||
| Edit wikis | **X** | **X** | **X** | **X** | **X** |{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
| [Report abusive or spammy content](/articles/reporting-abuse-or-spam) | **X** | **X** | **X** | **X** | **X** |{% endif %}
|
||||
| Apply labels | | **X** | **X** | **X** | **X** |
|
||||
| Create, edit, delete labels | | | **X** | **X** | **X** |
|
||||
| Close, reopen, and assign all issues and pull requests | | **X** | **X** | **X** | **X** |
|
||||
| Apply milestones | | **X** | **X** | **X** | **X** |
|
||||
| Mark [duplicate issues and pull requests](/articles/about-duplicate-issues-and-pull-requests)| | **X** | **X** | **X** | **X** |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -54,8 +54,6 @@ If you live in a supported region, you can follow these instructions to submit y
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.sponsors.double-check-stripe-info %}
|
||||
|
||||
If you live in an unsupported region and are accepted to the beta of {% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %}, you will receive an email with instructions to provide your bank information so that you can receive payments via ACH transfer or wire transfer.
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.sponsors.navigate-to-dev-sponsors-dashboard %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.sponsors.create-stripe-account %}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
[Markdown](http://daringfireball.net/projects/markdown/) is a human-friendly syntax for formatting plain text. Our documentation is written with [GitHub Flavored Markdown](https://docs.github.com/en/github/writing-on-github/about-writing-and-formatting-on-github), a custom version of Markdown used across GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
This site's Markdown rendering is powered by the [`@github-docs/render-content`](https://github.com/docs/render-content) and [`hubdown`](https://github.com/electron/hubdown) npm packages, which are in turn built on the [`remark`](https://remark.js.org/) Markdown processor.
|
||||
This site's Markdown rendering is powered by the [`/lib/render-content`](/lib/render-content) and [`hubdown`](https://github.com/electron/hubdown) npm packages, which are in turn built on the [`remark`](https://remark.js.org/) Markdown processor.
|
||||
|
||||
## Callout tags
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ queries:
|
||||
- uses: security-and-quality
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The following configuration file disables the default queries and specifies a set of custom queries to run instead. It also configures {% data variables.product.prodname_codeql %} to scan files in the _src_ directory (relative to the root), and to exclude the _node_modules_ directory (also relative to the root), as well as any file whose name ends in _.test.js_.
|
||||
The following configuration file disables the default queries and specifies a set of custom queries to run instead. It also configures {% data variables.product.prodname_codeql %} to scan files in the _src_ directory (relative to the root), except for the _src/node_modules_ directory, and except for files whose name ends in _.test.js_. Files in _src/node_modules_ and files with names ending _.test.js_ are therefore excluded from analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
``` yaml
|
||||
name: "My {% data variables.product.prodname_codeql %} config"
|
||||
@@ -24,9 +24,9 @@ queries:
|
||||
- name: Use a query suite file (run queries from a query suite in this repo)
|
||||
uses: ./codeql-qlpacks/complex-python-qlpack/rootAndBar.qls
|
||||
|
||||
paths-ignore:
|
||||
- node_modules
|
||||
- '**/*.test.js'
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- src
|
||||
paths-ignore:
|
||||
- src/node_modules
|
||||
- '**/*.test.js'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -15,11 +15,11 @@
|
||||
<h1 class="mb-3 font-mktg">{{ page.shortTitle }}</h1>
|
||||
<div class="lead-mktg text-gray">{{ page.intro }}</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="{{ page.introLinks.quickstart }}" class="btn-mktg btn-large f4 mt-3">
|
||||
<a href="{{ page.introLinks.quickstart }}" class="btn-mktg btn-large f4 mt-3 mr-3">
|
||||
{% data ui.product_landing.quick_start %}
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="{{ page.introLinks.reference }}" class="ml-3 btn-mktg btn-outline-mktg btn-large f4 mt-3">
|
||||
<a href="{{ page.introLinks.reference }}" class="btn-mktg btn-outline-mktg btn-large f4 mt-3">
|
||||
{% data ui.product_landing.reference_guides %}
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
53
lib/render-content/README.md
Normal file
53
lib/render-content/README.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
Markdown and Liquid rendering pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const renderContent = require('.')
|
||||
|
||||
const html = await renderContent(`
|
||||
# Beep
|
||||
{{ foo }}
|
||||
`, {
|
||||
foo: 'bar'
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Creates:
|
||||
|
||||
```html
|
||||
<h1 id="beep"><a href="#beep">Beep</a></h1>
|
||||
<p>bar</p>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## API
|
||||
|
||||
### renderContent(markdown, context = {}, options = {})
|
||||
|
||||
Render a string of `markdown` with optional `context`. Returns a `Promise`.
|
||||
|
||||
Liquid will be looking for includes in `${process.cwd()}/includes`.
|
||||
|
||||
Options:
|
||||
|
||||
- `encodeEntities`: Encode html entities. Default: `false`.
|
||||
- `fileName`: File name for debugging purposes.
|
||||
- `textOnly`: Output text instead of html using [cheerio](https://ghub.io/cheerio).
|
||||
|
||||
### .liquid
|
||||
|
||||
The [Liquid](https://ghub.io/liquid) instance used internally.
|
||||
|
||||
### Code block headers
|
||||
|
||||
You can add a header to code blocks by adding the `{:copy}` annotation after the code fences:
|
||||
|
||||
```js{:copy}
|
||||
const copyMe = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This renders:
|
||||
|
||||
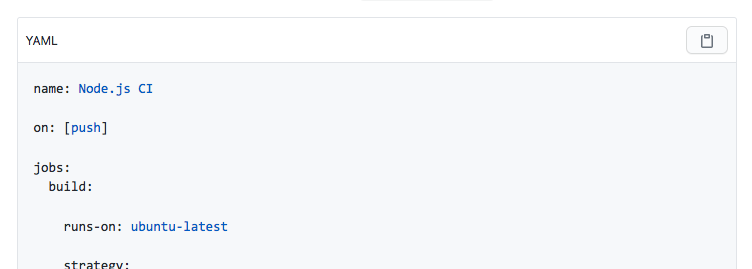
|
||||
|
||||
The un-highlighted text is available as `button.js-btn-copy`'s `data-clipboard-text` attribute.
|
||||
@@ -1,17 +1,17 @@
|
||||
const renderContent = require('@github-docs/render-content')
|
||||
const { ExtendedMarkdown, tags } = require('./liquid-tags/extended-markdown')
|
||||
const renderContent = require('./renderContent')
|
||||
const { ExtendedMarkdown, tags } = require('../liquid-tags/extended-markdown')
|
||||
|
||||
// Include custom tags like {% link_with_intro /article/foo %}
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('liquid_tag', require('./liquid-tags/liquid-tag'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('link', require('./liquid-tags/link'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('link_with_intro', require('./liquid-tags/link-with-intro'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('homepage_link_with_intro', require('./liquid-tags/homepage-link-with-intro'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('link_in_list', require('./liquid-tags/link-in-list'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('topic_link_in_list', require('./liquid-tags/topic-link-in-list'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('link_with_short_title', require('./liquid-tags/link-with-short-title'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('indented_data_reference', require('./liquid-tags/indented-data-reference'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('data', require('./liquid-tags/data'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('octicon', require('./liquid-tags/octicon'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('liquid_tag', require('../liquid-tags/liquid-tag'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('link', require('../liquid-tags/link'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('link_with_intro', require('../liquid-tags/link-with-intro'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('homepage_link_with_intro', require('../liquid-tags/homepage-link-with-intro'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('link_in_list', require('../liquid-tags/link-in-list'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('topic_link_in_list', require('../liquid-tags/topic-link-in-list'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('link_with_short_title', require('../liquid-tags/link-with-short-title'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('indented_data_reference', require('../liquid-tags/indented-data-reference'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('data', require('../liquid-tags/data'))
|
||||
renderContent.liquid.registerTag('octicon', require('../liquid-tags/octicon'))
|
||||
|
||||
for (const tag in tags) {
|
||||
// Register all the extended markdown tags, like {% note %} and {% warning %}
|
||||
61
lib/render-content/liquid.js
Normal file
61
lib/render-content/liquid.js
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
const Liquid = require('liquid')
|
||||
const semver = require('semver')
|
||||
const path = require('path')
|
||||
const engine = new Liquid.Engine()
|
||||
engine.registerFileSystem(
|
||||
new Liquid.LocalFileSystem(path.join(process.cwd(), 'includes'))
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// GHE versions are not valid SemVer, but can be coerced...
|
||||
// https://github.com/npm/node-semver#coercion
|
||||
|
||||
Liquid.Condition.operators.ver_gt = (cond, left, right) => {
|
||||
if (!matchesVersionString(left)) return false
|
||||
if (!matchesVersionString(right)) return false
|
||||
|
||||
const [leftPlan, leftRelease] = splitVersion(left)
|
||||
const [rightPlan, rightRelease] = splitVersion(right)
|
||||
|
||||
if (leftPlan !== rightPlan) return false
|
||||
|
||||
return semver.gt(semver.coerce(leftRelease), semver.coerce(rightRelease))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Liquid.Condition.operators.ver_lt = (cond, left, right) => {
|
||||
if (!matchesVersionString(left)) return false
|
||||
if (!matchesVersionString(right)) return false
|
||||
|
||||
const [leftPlan, leftRelease] = splitVersion(left)
|
||||
const [rightPlan, rightRelease] = splitVersion(right)
|
||||
|
||||
if (leftPlan !== rightPlan) return false
|
||||
|
||||
return semver.lt(semver.coerce(leftRelease), semver.coerce(rightRelease))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
module.exports = engine
|
||||
|
||||
function matchesVersionString (input) {
|
||||
return input && input.match(/^(?:[a-z](?:[a-z-]*[a-z])?@)?\d+(?:\.\d+)*/)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Support new version formats where version = plan@release
|
||||
// e.g., enterprise-server@2.21, where enterprise-server is the plan and 2.21 is the release
|
||||
// e.g., free-pro-team@latest, where free-pro-team is the plan and latest is the release
|
||||
// in addition to legacy formats where the version passed is simply 2.21
|
||||
function splitVersion (version) {
|
||||
// The default plan when working with versions is "enterprise-server".
|
||||
// Default to that value here to support backward compatibility from before
|
||||
// plans were explicitly included.
|
||||
let plan = 'enterprise-server'
|
||||
let release
|
||||
|
||||
const lastIndex = version.lastIndexOf('@')
|
||||
if (lastIndex === -1) {
|
||||
release = version
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
plan = version.slice(0, lastIndex)
|
||||
release = version.slice(lastIndex + 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return [plan, release]
|
||||
}
|
||||
138
lib/render-content/plugins/code-header.js
Normal file
138
lib/render-content/plugins/code-header.js
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,138 @@
|
||||
const h = require('hastscript')
|
||||
const octicons = require('@primer/octicons')
|
||||
const parse5 = require('parse5')
|
||||
const fromParse5 = require('hast-util-from-parse5')
|
||||
|
||||
const LANGUAGE_MAP = {
|
||||
asp: 'ASP',
|
||||
aspx: 'ASP',
|
||||
'aspx-vb': 'ASP',
|
||||
as3: 'ActionScript',
|
||||
apache: 'ApacheConf',
|
||||
nasm: 'Assembly',
|
||||
bat: 'Batchfile',
|
||||
'c#': 'C#',
|
||||
csharp: 'C#',
|
||||
c: 'C',
|
||||
'c++': 'C++',
|
||||
cpp: 'C++',
|
||||
chpl: 'Chapel',
|
||||
coffee: 'CoffeeScript',
|
||||
'coffee-script': 'CoffeeScript',
|
||||
cfm: 'ColdFusion',
|
||||
'common-lisp': 'Common Lisp',
|
||||
lisp: 'Common Lisp',
|
||||
dpatch: 'Darcs Patch',
|
||||
dart: 'Dart',
|
||||
elisp: 'Emacs Lisp',
|
||||
emacs: 'Emacs Lisp',
|
||||
'emacs-lisp': 'Emacs Lisp',
|
||||
pot: 'Gettext Catalog',
|
||||
html: 'HTML',
|
||||
xhtml: 'HTML',
|
||||
'html+erb': 'HTML+ERB',
|
||||
erb: 'HTML+ERB',
|
||||
irc: 'IRC log',
|
||||
json: 'JSON',
|
||||
jsp: 'Java Server Pages',
|
||||
java: 'Java',
|
||||
javascript: 'JavaScript',
|
||||
js: 'JavaScript',
|
||||
lhs: 'Literate Haskell',
|
||||
'literate-haskell': 'Literate Haskell',
|
||||
objc: 'Objective-C',
|
||||
openedge: 'OpenEdge ABL',
|
||||
progress: 'OpenEdge ABL',
|
||||
abl: 'OpenEdge ABL',
|
||||
pir: 'Parrot Internal Representation',
|
||||
posh: 'PowerShell',
|
||||
puppet: 'Puppet',
|
||||
'pure-data': 'Pure Data',
|
||||
raw: 'Raw token data',
|
||||
rb: 'Ruby',
|
||||
ruby: 'Ruby',
|
||||
r: 'R',
|
||||
scheme: 'Scheme',
|
||||
bash: 'Shell',
|
||||
sh: 'Shell',
|
||||
shell: 'Shell',
|
||||
zsh: 'Shell',
|
||||
supercollider: 'SuperCollider',
|
||||
tex: 'TeX',
|
||||
ts: 'TypeScript',
|
||||
vim: 'Vim script',
|
||||
viml: 'Vim script',
|
||||
rst: 'reStructuredText',
|
||||
xbm: 'X BitMap',
|
||||
xpm: 'X PixMap',
|
||||
yaml: 'YAML',
|
||||
yml: 'YAML',
|
||||
|
||||
// Unofficial languages
|
||||
shellsession: 'Shell',
|
||||
jsx: 'JSX'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const COPY_REGEX = /\{:copy\}$/
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Adds a bar above code blocks that shows the language and a copy button
|
||||
*/
|
||||
module.exports = function addCodeHeader (node) {
|
||||
// Check if the language matches `lang{:copy}`
|
||||
const hasCopy = node.lang && COPY_REGEX.test(node.lang)
|
||||
|
||||
if (hasCopy) {
|
||||
// js{:copy} => js
|
||||
node.lang = node.lang.replace(COPY_REGEX, '')
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// It doesn't have the copy annotation, so don't add the header
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Display the language using the above map of `{ [shortCode]: language }`
|
||||
const language = LANGUAGE_MAP[node.lang] || node.lang || 'Code'
|
||||
|
||||
const btnIconHtml = octicons.clippy.toSVG()
|
||||
const btnIconAst = parse5.parse(String(btnIconHtml))
|
||||
const btnIcon = fromParse5(btnIconAst, btnIconHtml)
|
||||
|
||||
// Need to create the header using Markdown AST utilities, to fit
|
||||
// into the Unified processor ecosystem.
|
||||
const header = h(
|
||||
'header',
|
||||
{
|
||||
class: [
|
||||
'd-flex',
|
||||
'flex-items-center',
|
||||
'flex-justify-between',
|
||||
'p-2',
|
||||
'text-small',
|
||||
'rounded-top-1',
|
||||
'border'
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
[
|
||||
h('span', language),
|
||||
h(
|
||||
'button',
|
||||
{
|
||||
class: [
|
||||
'js-btn-copy',
|
||||
'btn',
|
||||
'btn-sm',
|
||||
'tooltipped',
|
||||
'tooltipped-nw'
|
||||
],
|
||||
'data-clipboard-text': node.value,
|
||||
'aria-label': 'Copy code to clipboard'
|
||||
},
|
||||
btnIcon
|
||||
)
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
before: [header]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
106
lib/render-content/renderContent.js
Normal file
106
lib/render-content/renderContent.js
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
|
||||
const liquid = require('./liquid')
|
||||
const codeHeader = require('./plugins/code-header')
|
||||
const hubdown = require('hubdown')
|
||||
const remarkCodeExtra = require('remark-code-extra')
|
||||
const cheerio = require('cheerio')
|
||||
const Entities = require('html-entities').XmlEntities
|
||||
const entities = new Entities()
|
||||
const stripHtmlComments = require('strip-html-comments')
|
||||
|
||||
// used below to remove extra newlines in TOC lists
|
||||
const endLine = '</a>\r?\n'
|
||||
const blankLine = '\\s*?[\r\n]*'
|
||||
const startNextLine = '[^\\S\r\n]*?[-\\*] <a'
|
||||
const blankLineInList = new RegExp(
|
||||
`(${endLine})${blankLine}(${startNextLine})`,
|
||||
'mg'
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// used below to remove unwanted newlines from inline tags in tables
|
||||
const inlineTags = ['a', 'code', 'em']
|
||||
const inlineTagString = `(?:${inlineTags.join('|')})`
|
||||
const inlineTagRegex = new RegExp(`\n?(</?${inlineTagString}>?)\n?`, 'gm')
|
||||
|
||||
// parse multiple times because some templates contain more templates. :]
|
||||
module.exports = async function renderContent (
|
||||
template,
|
||||
context = {},
|
||||
options = {}
|
||||
) {
|
||||
try {
|
||||
// remove any newlines that precede html comments, then remove the comments
|
||||
if (template) {
|
||||
template = stripHtmlComments(template.replace(/\n<!--/g, '<!--'))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template = await liquid.parseAndRender(template, context)
|
||||
|
||||
// this workaround loses syntax highlighting but correctly handles tags like <em> and entities like <
|
||||
template = template.replace(
|
||||
/``` ?shell\r?\n\s*?(\S[\s\S]*?)\r?\n.*?```/gm,
|
||||
'<pre><code class="hljs language-shell">$1</code></pre>'
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// clean up empty lines in TOC lists left by unrendered list items (due to productVersions)
|
||||
// for example, remove the blank line here:
|
||||
// - <a>foo</a>
|
||||
//
|
||||
// - <a>bar</a>
|
||||
if (template.includes('</a>')) {
|
||||
template = template.replace(blankLineInList, '$1$2')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// this removes any extra newlines left by (now resolved) liquid
|
||||
// statements so that extra space doesn't mess with list numbering
|
||||
template = template.replace(/(\r?\n){3}/g, '\n\n')
|
||||
|
||||
let { content: html } = await hubdown(template, {
|
||||
// Disable automatic language guessing in syntax highlighting
|
||||
highlight: { subset: false },
|
||||
runBefore: [[
|
||||
remarkCodeExtra, { transform: codeHeader }
|
||||
]]
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
// Remove unwanted newlines (which appear as spaces) from inline tags inside tables
|
||||
if (html.includes('<table>')) html = removeNewlinesFromInlineTags(html)
|
||||
|
||||
if (options.textOnly) {
|
||||
html = cheerio
|
||||
.load(html)
|
||||
.text()
|
||||
.trim()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (options.encodeEntities) html = entities.encode(html)
|
||||
|
||||
return html.trim()
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
if (options.filename) {
|
||||
console.error(`renderContent failed on file: ${options.filename}`)
|
||||
}
|
||||
throw error
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function removeNewlinesFromInlineTags (html) {
|
||||
const $ = cheerio.load(html)
|
||||
|
||||
// see https://cheerio.js.org/#html-htmlstring-
|
||||
$(inlineTags.join(','))
|
||||
.parents('td')
|
||||
.get()
|
||||
.map(tag =>
|
||||
$(tag).html(
|
||||
$(tag)
|
||||
.html()
|
||||
.replace(inlineTagRegex, '$1')
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return $('body').html()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Object.assign(module.exports, {
|
||||
liquid
|
||||
})
|
||||
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
@@ -52599,7 +52599,7 @@
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"summary": "Search issues and pull requests",
|
||||
"description": "Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results [per page](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.18/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination).\n\nWhen searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue **title**, issue **body**, and issue **comment body** fields when you pass the `text-match` media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see [Text match metadata](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.18/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata).\n\nFor example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.\n\n`q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc`\n\nThis query searches for the keyword `windows`, within any open issue that is labeled as `bug`. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, whick means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.\n\n**Note:** For [user-to-server](https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests) GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the `is:issue` or `is:pull-request` qualifier will receive an HTTP `422 Unprocessable Entity` response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the `is` qualifier, see \"[Searching only issues or pull requests](https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests).\"",
|
||||
"description": "Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results [per page](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.18/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination).\n\nWhen searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue **title**, issue **body**, and issue **comment body** fields when you pass the `text-match` media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see [Text match metadata](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.18/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata).\n\nFor example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.\n\n`q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc`\n\nThis query searches for the keyword `windows`, within any open issue that is labeled as `bug`. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, which means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.\n\n**Note:** For [user-to-server](https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests) GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the `is:issue` or `is:pull-request` qualifier will receive an HTTP `422 Unprocessable Entity` response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the `is` qualifier, see \"[Searching only issues or pull requests](https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests).\"",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
"search"
|
||||
],
|
||||
@@ -52622,7 +52622,7 @@
|
||||
"<a href=\"{{ restGitHubAppsLink }}\">Works with GitHub Apps</a>"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"bodyParameters": [],
|
||||
"descriptionHTML": "<p>Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.18/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination\">per page</a>.</p>\n<p>When searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue <strong>title</strong>, issue <strong>body</strong>, and issue <strong>comment body</strong> fields when you pass the <code>text-match</code> media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.18/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata\">Text match metadata</a>.</p>\n<p>For example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.</p>\n<p><code>q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc</code></p>\n<p>This query searches for the keyword <code>windows</code>, within any open issue that is labeled as <code>bug</code>. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, whick means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.</p>\n<p><strong>Note:</strong> For <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests\">user-to-server</a> GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the <code>is:issue</code> or <code>is:pull-request</code> qualifier will receive an HTTP <code>422 Unprocessable Entity</code> response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the <code>is</code> qualifier, see \"<a href=\"https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests\">Searching only issues or pull requests</a>.\"</p>",
|
||||
"descriptionHTML": "<p>Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.18/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination\">per page</a>.</p>\n<p>When searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue <strong>title</strong>, issue <strong>body</strong>, and issue <strong>comment body</strong> fields when you pass the <code>text-match</code> media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.18/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata\">Text match metadata</a>.</p>\n<p>For example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.</p>\n<p><code>q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc</code></p>\n<p>This query searches for the keyword <code>windows</code>, within any open issue that is labeled as <code>bug</code>. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, which means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.</p>\n<p><strong>Note:</strong> For <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests\">user-to-server</a> GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the <code>is:issue</code> or <code>is:pull-request</code> qualifier will receive an HTTP <code>422 Unprocessable Entity</code> response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the <code>is</code> qualifier, see \"<a href=\"https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests\">Searching only issues or pull requests</a>.\"</p>",
|
||||
"responses": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"httpStatusCode": "200",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -53409,7 +53409,7 @@
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"summary": "Search issues and pull requests",
|
||||
"description": "Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results [per page](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.19/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination).\n\nWhen searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue **title**, issue **body**, and issue **comment body** fields when you pass the `text-match` media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see [Text match metadata](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.19/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata).\n\nFor example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.\n\n`q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc`\n\nThis query searches for the keyword `windows`, within any open issue that is labeled as `bug`. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, whick means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.\n\n**Note:** For [user-to-server](https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests) GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the `is:issue` or `is:pull-request` qualifier will receive an HTTP `422 Unprocessable Entity` response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the `is` qualifier, see \"[Searching only issues or pull requests](https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests).\"",
|
||||
"description": "Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results [per page](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.19/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination).\n\nWhen searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue **title**, issue **body**, and issue **comment body** fields when you pass the `text-match` media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see [Text match metadata](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.19/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata).\n\nFor example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.\n\n`q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc`\n\nThis query searches for the keyword `windows`, within any open issue that is labeled as `bug`. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, which means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.\n\n**Note:** For [user-to-server](https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests) GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the `is:issue` or `is:pull-request` qualifier will receive an HTTP `422 Unprocessable Entity` response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the `is` qualifier, see \"[Searching only issues or pull requests](https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests).\"",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
"search"
|
||||
],
|
||||
@@ -53432,7 +53432,7 @@
|
||||
"<a href=\"{{ restGitHubAppsLink }}\">Works with GitHub Apps</a>"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"bodyParameters": [],
|
||||
"descriptionHTML": "<p>Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.19/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination\">per page</a>.</p>\n<p>When searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue <strong>title</strong>, issue <strong>body</strong>, and issue <strong>comment body</strong> fields when you pass the <code>text-match</code> media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.19/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata\">Text match metadata</a>.</p>\n<p>For example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.</p>\n<p><code>q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc</code></p>\n<p>This query searches for the keyword <code>windows</code>, within any open issue that is labeled as <code>bug</code>. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, whick means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.</p>\n<p><strong>Note:</strong> For <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests\">user-to-server</a> GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the <code>is:issue</code> or <code>is:pull-request</code> qualifier will receive an HTTP <code>422 Unprocessable Entity</code> response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the <code>is</code> qualifier, see \"<a href=\"https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests\">Searching only issues or pull requests</a>.\"</p>",
|
||||
"descriptionHTML": "<p>Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.19/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination\">per page</a>.</p>\n<p>When searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue <strong>title</strong>, issue <strong>body</strong>, and issue <strong>comment body</strong> fields when you pass the <code>text-match</code> media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.19/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata\">Text match metadata</a>.</p>\n<p>For example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.</p>\n<p><code>q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc</code></p>\n<p>This query searches for the keyword <code>windows</code>, within any open issue that is labeled as <code>bug</code>. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, which means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.</p>\n<p><strong>Note:</strong> For <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests\">user-to-server</a> GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the <code>is:issue</code> or <code>is:pull-request</code> qualifier will receive an HTTP <code>422 Unprocessable Entity</code> response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the <code>is</code> qualifier, see \"<a href=\"https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests\">Searching only issues or pull requests</a>.\"</p>",
|
||||
"responses": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"httpStatusCode": "200",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -54061,7 +54061,7 @@
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"summary": "Search issues and pull requests",
|
||||
"description": "Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results [per page](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.20/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination).\n\nWhen searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue **title**, issue **body**, and issue **comment body** fields when you pass the `text-match` media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see [Text match metadata](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.20/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata).\n\nFor example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.\n\n`q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc`\n\nThis query searches for the keyword `windows`, within any open issue that is labeled as `bug`. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, whick means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.\n\n**Note:** For [user-to-server](https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests) GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the `is:issue` or `is:pull-request` qualifier will receive an HTTP `422 Unprocessable Entity` response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the `is` qualifier, see \"[Searching only issues or pull requests](https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests).\"",
|
||||
"description": "Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results [per page](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.20/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination).\n\nWhen searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue **title**, issue **body**, and issue **comment body** fields when you pass the `text-match` media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see [Text match metadata](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.20/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata).\n\nFor example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.\n\n`q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc`\n\nThis query searches for the keyword `windows`, within any open issue that is labeled as `bug`. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, which means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.\n\n**Note:** For [user-to-server](https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests) GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the `is:issue` or `is:pull-request` qualifier will receive an HTTP `422 Unprocessable Entity` response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the `is` qualifier, see \"[Searching only issues or pull requests](https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests).\"",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
"search"
|
||||
],
|
||||
@@ -54084,7 +54084,7 @@
|
||||
"<a href=\"{{ restGitHubAppsLink }}\">Works with GitHub Apps</a>"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"bodyParameters": [],
|
||||
"descriptionHTML": "<p>Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.20/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination\">per page</a>.</p>\n<p>When searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue <strong>title</strong>, issue <strong>body</strong>, and issue <strong>comment body</strong> fields when you pass the <code>text-match</code> media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.20/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata\">Text match metadata</a>.</p>\n<p>For example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.</p>\n<p><code>q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc</code></p>\n<p>This query searches for the keyword <code>windows</code>, within any open issue that is labeled as <code>bug</code>. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, whick means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.</p>\n<p><strong>Note:</strong> For <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests\">user-to-server</a> GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the <code>is:issue</code> or <code>is:pull-request</code> qualifier will receive an HTTP <code>422 Unprocessable Entity</code> response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the <code>is</code> qualifier, see \"<a href=\"https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests\">Searching only issues or pull requests</a>.\"</p>",
|
||||
"descriptionHTML": "<p>Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.20/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination\">per page</a>.</p>\n<p>When searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue <strong>title</strong>, issue <strong>body</strong>, and issue <strong>comment body</strong> fields when you pass the <code>text-match</code> media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.20/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata\">Text match metadata</a>.</p>\n<p>For example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.</p>\n<p><code>q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc</code></p>\n<p>This query searches for the keyword <code>windows</code>, within any open issue that is labeled as <code>bug</code>. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, which means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.</p>\n<p><strong>Note:</strong> For <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests\">user-to-server</a> GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the <code>is:issue</code> or <code>is:pull-request</code> qualifier will receive an HTTP <code>422 Unprocessable Entity</code> response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the <code>is</code> qualifier, see \"<a href=\"https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests\">Searching only issues or pull requests</a>.\"</p>",
|
||||
"responses": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"httpStatusCode": "200",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -58041,7 +58041,7 @@
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"summary": "Search issues and pull requests",
|
||||
"description": "Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results [per page](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.21/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination).\n\nWhen searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue **title**, issue **body**, and issue **comment body** fields when you pass the `text-match` media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see [Text match metadata](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.21/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata).\n\nFor example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.\n\n`q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc`\n\nThis query searches for the keyword `windows`, within any open issue that is labeled as `bug`. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, whick means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.\n\n**Note:** For [user-to-server](https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests) GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the `is:issue` or `is:pull-request` qualifier will receive an HTTP `422 Unprocessable Entity` response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the `is` qualifier, see \"[Searching only issues or pull requests](https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests).\"",
|
||||
"description": "Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results [per page](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.21/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination).\n\nWhen searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue **title**, issue **body**, and issue **comment body** fields when you pass the `text-match` media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see [Text match metadata](https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.21/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata).\n\nFor example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.\n\n`q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc`\n\nThis query searches for the keyword `windows`, within any open issue that is labeled as `bug`. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, which means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.\n\n**Note:** For [user-to-server](https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests) GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the `is:issue` or `is:pull-request` qualifier will receive an HTTP `422 Unprocessable Entity` response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the `is` qualifier, see \"[Searching only issues or pull requests](https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests).\"",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
"search"
|
||||
],
|
||||
@@ -58064,7 +58064,7 @@
|
||||
"<a href=\"{{ restGitHubAppsLink }}\">Works with GitHub Apps</a>"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"bodyParameters": [],
|
||||
"descriptionHTML": "<p>Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.21/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination\">per page</a>.</p>\n<p>When searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue <strong>title</strong>, issue <strong>body</strong>, and issue <strong>comment body</strong> fields when you pass the <code>text-match</code> media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.21/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata\">Text match metadata</a>.</p>\n<p>For example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.</p>\n<p><code>q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc</code></p>\n<p>This query searches for the keyword <code>windows</code>, within any open issue that is labeled as <code>bug</code>. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, whick means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.</p>\n<p><strong>Note:</strong> For <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests\">user-to-server</a> GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the <code>is:issue</code> or <code>is:pull-request</code> qualifier will receive an HTTP <code>422 Unprocessable Entity</code> response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the <code>is</code> qualifier, see \"<a href=\"https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests\">Searching only issues or pull requests</a>.\"</p>",
|
||||
"descriptionHTML": "<p>Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.21/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination\">per page</a>.</p>\n<p>When searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue <strong>title</strong>, issue <strong>body</strong>, and issue <strong>comment body</strong> fields when you pass the <code>text-match</code> media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/enterprise-server@2.21/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata\">Text match metadata</a>.</p>\n<p>For example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.</p>\n<p><code>q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc</code></p>\n<p>This query searches for the keyword <code>windows</code>, within any open issue that is labeled as <code>bug</code>. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, which means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.</p>\n<p><strong>Note:</strong> For <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests\">user-to-server</a> GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the <code>is:issue</code> or <code>is:pull-request</code> qualifier will receive an HTTP <code>422 Unprocessable Entity</code> response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the <code>is</code> qualifier, see \"<a href=\"https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests\">Searching only issues or pull requests</a>.\"</p>",
|
||||
"responses": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"httpStatusCode": "200",
|
||||
|
||||
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
@@ -55688,7 +55688,7 @@
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"summary": "Search issues and pull requests",
|
||||
"description": "Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results [per page](https://docs.github.com/github-ae@latest/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination).\n\nWhen searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue **title**, issue **body**, and issue **comment body** fields when you pass the `text-match` media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see [Text match metadata](https://docs.github.com/github-ae@latest/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata).\n\nFor example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.\n\n`q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc`\n\nThis query searches for the keyword `windows`, within any open issue that is labeled as `bug`. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, whick means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.\n\n**Note:** For [user-to-server](https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests) GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the `is:issue` or `is:pull-request` qualifier will receive an HTTP `422 Unprocessable Entity` response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the `is` qualifier, see \"[Searching only issues or pull requests](https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests).\"",
|
||||
"description": "Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results [per page](https://docs.github.com/github-ae@latest/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination).\n\nWhen searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue **title**, issue **body**, and issue **comment body** fields when you pass the `text-match` media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see [Text match metadata](https://docs.github.com/github-ae@latest/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata).\n\nFor example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.\n\n`q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc`\n\nThis query searches for the keyword `windows`, within any open issue that is labeled as `bug`. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, which means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.\n\n**Note:** For [user-to-server](https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests) GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the `is:issue` or `is:pull-request` qualifier will receive an HTTP `422 Unprocessable Entity` response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the `is` qualifier, see \"[Searching only issues or pull requests](https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests).\"",
|
||||
"tags": [
|
||||
"search"
|
||||
],
|
||||
@@ -55711,7 +55711,7 @@
|
||||
"<a href=\"{{ restGitHubAppsLink }}\">Works with GitHub Apps</a>"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"bodyParameters": [],
|
||||
"descriptionHTML": "<p>Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/github-ae@latest/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination\">per page</a>.</p>\n<p>When searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue <strong>title</strong>, issue <strong>body</strong>, and issue <strong>comment body</strong> fields when you pass the <code>text-match</code> media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/github-ae@latest/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata\">Text match metadata</a>.</p>\n<p>For example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.</p>\n<p><code>q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc</code></p>\n<p>This query searches for the keyword <code>windows</code>, within any open issue that is labeled as <code>bug</code>. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, whick means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.</p>\n<p><strong>Note:</strong> For <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests\">user-to-server</a> GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the <code>is:issue</code> or <code>is:pull-request</code> qualifier will receive an HTTP <code>422 Unprocessable Entity</code> response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the <code>is</code> qualifier, see \"<a href=\"https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests\">Searching only issues or pull requests</a>.\"</p>",
|
||||
"descriptionHTML": "<p>Find issues by state and keyword. This method returns up to 100 results <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/github-ae@latest/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#pagination\">per page</a>.</p>\n<p>When searching for issues, you can get text match metadata for the issue <strong>title</strong>, issue <strong>body</strong>, and issue <strong>comment body</strong> fields when you pass the <code>text-match</code> media type. For more details about how to receive highlighted\nsearch results, see <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/github-ae@latest/rest/reference/search#text-match-metadata\">Text match metadata</a>.</p>\n<p>For example, if you want to find the oldest unresolved Python bugs on Windows. Your query might look something like this.</p>\n<p><code>q=windows+label:bug+language:python+state:open&sort=created&order=asc</code></p>\n<p>This query searches for the keyword <code>windows</code>, within any open issue that is labeled as <code>bug</code>. The search runs across repositories whose primary language is Python. The results are sorted by creation date in ascending order, which means the oldest issues appear first in the search results.</p>\n<p><strong>Note:</strong> For <a href=\"https://docs.github.com/developers/apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests\">user-to-server</a> GitHub App requests, you can't retrieve a combination of issues and pull requests in a single query. Requests that don't include the <code>is:issue</code> or <code>is:pull-request</code> qualifier will receive an HTTP <code>422 Unprocessable Entity</code> response. To get results for both issues and pull requests, you must send separate queries for issues and pull requests. For more information about the <code>is</code> qualifier, see \"<a href=\"https://docs.github.com/github/searching-for-information-on-github/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-only-issues-or-pull-requests\">Searching only issues or pull requests</a>.\"</p>",
|
||||
"responses": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"httpStatusCode": "200",
|
||||
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ const nonEnterpriseDefaultVersion = require('../../lib/non-enterprise-default-ve
|
||||
const allVersions = require('../../lib/all-versions')
|
||||
|
||||
module.exports = async (req, res, next) => {
|
||||
if (!req.path.includes('webhooks')) return next()
|
||||
if (!req.path.includes('webhook')) return next()
|
||||
|
||||
// Get the name of the dir under lib/webhooks/static
|
||||
// For example, free-pro-team@latest corresponds to dotcom,
|
||||
|
||||
224
package-lock.json
generated
224
package-lock.json
generated
@@ -1144,12 +1144,6 @@
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/strip-json-comments/-/strip-json-comments-3.1.1.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-6fPc+R4ihwqP6N/aIv2f1gMH8lOVtWQHoqC4yK6oSDVVocumAsfCqjkXnqiYMhmMwS/mEHLp7Vehlt3ql6lEig==",
|
||||
"dev": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type-fest": {
|
||||
"version": "0.8.1",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/type-fest/-/type-fest-0.8.1.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-4dbzIzqvjtgiM5rw1k5rEHtBANKmdudhGyBEajN01fEyhaAIhsoKNy6y7+IN93IfpFtwY9iqi7kD+xwKhQsNJA==",
|
||||
"dev": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -1193,31 +1187,6 @@
|
||||
"revalidator": "^0.3.1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"@github-docs/render-content": {
|
||||
"version": "5.2.0",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/@github-docs/render-content/-/render-content-5.2.0.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-/rrDSvspp+xRn7xHD+0Wv7oobn8yw8qx1BN7rpoS2PpNIgmd9QBNW8m8aS8CI2Y41BF7wPSDvxxx8EYoKsXlDQ==",
|
||||
"requires": {
|
||||
"@primer/octicons": "^11.0.0",
|
||||
"cheerio": "^1.0.0-rc.3",
|
||||
"hast-util-from-parse5": "^6.0.0",
|
||||
"hastscript": "^6.0.0",
|
||||
"html-entities": "^1.2.1",
|
||||
"hubdown": "^2.6.0",
|
||||
"liquid": "^5.1.0",
|
||||
"parse5": "^6.0.1",
|
||||
"remark-code-extra": "^1.0.1",
|
||||
"semver": "^5.7.1",
|
||||
"strip-html-comments": "^1.0.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"parse5": {
|
||||
"version": "6.0.1",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/parse5/-/parse5-6.0.1.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-Ofn/CTFzRGTTxwpNEs9PP93gXShHcTq255nzRYSKe8AkVpZY7e1fpmTfOyoIvjP5HG7Z2ZM7VS9PPhQGW2pOpw=="
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"@hapi/address": {
|
||||
"version": "2.1.4",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/@hapi/address/-/address-2.1.4.tgz",
|
||||
@@ -3454,54 +3423,13 @@
|
||||
"integrity": "sha1-qJS3XUvE9s1nnvMkSp/Y9Gri1Cg="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"array.prototype.flat": {
|
||||
"version": "1.2.4",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/array.prototype.flat/-/array.prototype.flat-1.2.4.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-4470Xi3GAPAjZqFcljX2xzckv1qeKPizoNkiS0+O4IoPR2ZNpcjE0pkhdihlDouK+x6QOast26B4Q/O9DJnwSg==",
|
||||
"version": "1.2.3",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/array.prototype.flat/-/array.prototype.flat-1.2.3.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-gBlRZV0VSmfPIeWfuuy56XZMvbVfbEUnOXUvt3F/eUUUSyzlgLxhEX4YAEpxNAogRGehPSnfXyPtYyKAhkzQhQ==",
|
||||
"dev": true,
|
||||
"requires": {
|
||||
"call-bind": "^1.0.0",
|
||||
"define-properties": "^1.1.3",
|
||||
"es-abstract": "^1.18.0-next.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"es-abstract": {
|
||||
"version": "1.18.0-next.1",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/es-abstract/-/es-abstract-1.18.0-next.1.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-I4UGspA0wpZXWENrdA0uHbnhte683t3qT/1VFH9aX2dA5PPSf6QW5HHXf5HImaqPmjXaVeVk4RGWnaylmV7uAA==",
|
||||
"dev": true,
|
||||
"requires": {
|
||||
"es-to-primitive": "^1.2.1",
|
||||
"function-bind": "^1.1.1",
|
||||
"has": "^1.0.3",
|
||||
"has-symbols": "^1.0.1",
|
||||
"is-callable": "^1.2.2",
|
||||
"is-negative-zero": "^2.0.0",
|
||||
"is-regex": "^1.1.1",
|
||||
"object-inspect": "^1.8.0",
|
||||
"object-keys": "^1.1.1",
|
||||
"object.assign": "^4.1.1",
|
||||
"string.prototype.trimend": "^1.0.1",
|
||||
"string.prototype.trimstart": "^1.0.1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"object-inspect": {
|
||||
"version": "1.8.0",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/object-inspect/-/object-inspect-1.8.0.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-jLdtEOB112fORuypAyl/50VRVIBIdVQOSUUGQHzJ4xBSbit81zRarz7GThkEFZy1RceYrWYcPcBFPQwHyAc1gA==",
|
||||
"dev": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"object.assign": {
|
||||
"version": "4.1.2",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/object.assign/-/object.assign-4.1.2.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-ixT2L5THXsApyiUPYKmW+2EHpXXe5Ii3M+f4e+aJFAHao5amFRW6J0OO6c/LU8Be47utCx2GL89hxGB6XSmKuQ==",
|
||||
"dev": true,
|
||||
"requires": {
|
||||
"call-bind": "^1.0.0",
|
||||
"define-properties": "^1.1.3",
|
||||
"has-symbols": "^1.0.1",
|
||||
"object-keys": "^1.1.1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
"es-abstract": "^1.17.0-next.1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"arrify": {
|
||||
@@ -3706,11 +3634,12 @@
|
||||
"dev": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"resolve": {
|
||||
"version": "1.17.0",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/resolve/-/resolve-1.17.0.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-ic+7JYiV8Vi2yzQGFWOkiZD5Z9z7O2Zhm9XMaTxdJExKasieFCr+yXZ/WmXsckHiKl12ar0y6XiXDx3m4RHn1w==",
|
||||
"version": "1.19.0",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/resolve/-/resolve-1.19.0.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-rArEXAgsBG4UgRGcynxWIWKFvh/XZCcS8UJdHhwy91zwAvCZIbcs+vAbflgBnNjYMs/i/i+/Ux6IZhML1yPvxg==",
|
||||
"dev": true,
|
||||
"requires": {
|
||||
"is-core-module": "^2.1.0",
|
||||
"path-parse": "^1.0.6"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -4601,9 +4530,9 @@
|
||||
"dev": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"ccount": {
|
||||
"version": "1.0.5",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/ccount/-/ccount-1.0.5.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-MOli1W+nfbPLlKEhInaxhRdp7KVLFxLN5ykwzHgLsLI3H3gs5jjFAK4Eoj3OzzcxCtumDaI8onoVDeQyWaNTkw=="
|
||||
"version": "1.1.0",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/ccount/-/ccount-1.1.0.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-vlNK021QdI7PNeiUh/lKkC/mNHHfV0m/Ad5JoI0TYtlBnJAslM/JIkm/tGC88bkLIwO6OQ5uV6ztS6kVAtCDlg=="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"chalk": {
|
||||
"version": "4.1.0",
|
||||
@@ -4725,6 +4654,16 @@
|
||||
"htmlparser2": "^3.9.1",
|
||||
"lodash": "^4.15.0",
|
||||
"parse5": "^3.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"parse5": {
|
||||
"version": "3.0.3",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/parse5/-/parse5-3.0.3.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-rgO9Zg5LLLkfJF9E6CCmXlSE4UVceloys8JrFqCcHloC3usd/kJCyPDwH2SOlzix2j3xaP9sUX3e8+kvkuleAA==",
|
||||
"requires": {
|
||||
"@types/node": "*"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"chokidar": {
|
||||
@@ -6267,9 +6206,9 @@
|
||||
"integrity": "sha1-l4hXRCxEdJ5CBmE+N5RiBYJqvYA="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"detab": {
|
||||
"version": "2.0.3",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/detab/-/detab-2.0.3.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-Up8P0clUVwq0FnFjDclzZsy9PadzRn5FFxrr47tQQvMHqyiFYVbpH8oXDzWtF0Q7pYy3l+RPmtBl+BsFF6wH0A==",
|
||||
"version": "2.0.4",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/detab/-/detab-2.0.4.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-8zdsQA5bIkoRECvCrNKPla84lyoR7DSAyf7p0YgXzBO9PDJx8KntPUay7NS6yp+KdxdVtiE5SpHKtbp2ZQyA9g==",
|
||||
"requires": {
|
||||
"repeat-string": "^1.5.4"
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -7059,19 +6998,13 @@
|
||||
"requires": {
|
||||
"prelude-ls": "^1.2.1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type-fest": {
|
||||
"version": "0.8.1",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/type-fest/-/type-fest-0.8.1.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-4dbzIzqvjtgiM5rw1k5rEHtBANKmdudhGyBEajN01fEyhaAIhsoKNy6y7+IN93IfpFtwY9iqi7kD+xwKhQsNJA==",
|
||||
"dev": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"eslint-config-standard": {
|
||||
"version": "16.0.2",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/eslint-config-standard/-/eslint-config-standard-16.0.2.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-fx3f1rJDsl9bY7qzyX8SAtP8GBSk6MfXFaTfaGgk12aAYW4gJSyRm7dM790L6cbXv63fvjY4XeSzXnb4WM+SKw==",
|
||||
"version": "16.0.1",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/eslint-config-standard/-/eslint-config-standard-16.0.1.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-WBBiQQZdaPyL+4sPkGWhWrHCDtvJoU195B9j8yXE9uFQnX34gMXI5CeBRm95gx3PMEZPM5OpwET10hH4F4SxCA==",
|
||||
"dev": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"eslint-import-resolver-node": {
|
||||
@@ -9663,29 +9596,16 @@
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"hast-util-from-parse5": {
|
||||
"version": "6.0.0",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/hast-util-from-parse5/-/hast-util-from-parse5-6.0.0.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-3ZYnfKenbbkhhNdmOQqgH10vnvPivTdsOJCri+APn0Kty+nRkDHArnaX9Hiaf8H+Ig+vkNptL+SRY/6RwWJk1Q==",
|
||||
"version": "6.0.1",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/hast-util-from-parse5/-/hast-util-from-parse5-6.0.1.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-jeJUWiN5pSxW12Rh01smtVkZgZr33wBokLzKLwinYOUfSzm1Nl/c3GUGebDyOKjdsRgMvoVbV0VpAcpjF4NrJA==",
|
||||
"requires": {
|
||||
"@types/parse5": "^5.0.0",
|
||||
"ccount": "^1.0.0",
|
||||
"hastscript": "^5.0.0",
|
||||
"hastscript": "^6.0.0",
|
||||
"property-information": "^5.0.0",
|
||||
"vfile": "^4.0.0",
|
||||
"vfile-location": "^3.2.0",
|
||||
"web-namespaces": "^1.0.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"hastscript": {
|
||||
"version": "5.1.2",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/hastscript/-/hastscript-5.1.2.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-WlztFuK+Lrvi3EggsqOkQ52rKbxkXL3RwB6t5lwoa8QLMemoWfBuL43eDrwOamJyR7uKQKdmKYaBH1NZBiIRrQ==",
|
||||
"requires": {
|
||||
"comma-separated-tokens": "^1.0.0",
|
||||
"hast-util-parse-selector": "^2.0.0",
|
||||
"property-information": "^5.0.0",
|
||||
"space-separated-tokens": "^1.0.0"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"hast-util-has-property": {
|
||||
@@ -9699,9 +9619,9 @@
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-oUmNua0bFbdrD/ELDSSEadRVtWZOf3iF6Lbv81naqsIV99RnSCieTbWuWCY8BAeEfKJTKl0gRdokv+dELutHGQ=="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"hast-util-parse-selector": {
|
||||
"version": "2.2.4",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/hast-util-parse-selector/-/hast-util-parse-selector-2.2.4.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-gW3sxfynIvZApL4L07wryYF4+C9VvH3AUi7LAnVXV4MneGEgwOByXvFo18BgmTWnm7oHAe874jKbIB1YhHSIzA=="
|
||||
"version": "2.2.5",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/hast-util-parse-selector/-/hast-util-parse-selector-2.2.5.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-7j6mrk/qqkSehsM92wQjdIgWM2/BW61u/53G6xmC8i1OmEdKLHbk419QKQUjz6LglWsfqoiHmyMRkP1BGjecNQ=="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"hast-util-raw": {
|
||||
"version": "5.0.2",
|
||||
@@ -9885,9 +9805,9 @@
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-Io1zA2yOA1YJslkr+AJlWSf2yWFkKjvkcL9Ni1XSUqnGLr/qRQe2UI3Cn/J9MsJht7yEVCe0SscY1HgVMujbgg=="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"highlight.js": {
|
||||
"version": "10.3.1",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/highlight.js/-/highlight.js-10.3.1.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-jeW8rdPdhshYKObedYg5XGbpVgb1/DT4AHvDFXhkU7UnGSIjy9kkJ7zHG7qplhFHMitTSzh5/iClKQk3Kb2RFQ=="
|
||||
"version": "10.4.0",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/highlight.js/-/highlight.js-10.4.0.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-EfrUGcQ63oLJbj0J0RI9ebX6TAITbsDBLbsjr881L/X5fMO9+oadKzEF21C7R3ULKG6Gv3uoab2HiqVJa/4+oA=="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"highlightjs-graphql": {
|
||||
"version": "1.0.2",
|
||||
@@ -15017,12 +14937,12 @@
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-G2Lj61tXDnVFFOi8VZds+SoQjtQC3dgokKdDG2mTm1tx4m50NUHBOZSBwQQHyy0V12A0JTG4icfZQH+xPyh8VA=="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"lowlight": {
|
||||
"version": "1.16.0",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/lowlight/-/lowlight-1.16.0.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-ECLdzIJvBEjK4ef51sWiGZyz21yx4IEPaF/62DRxLehoOHkWqN3OsLB1GUMfc6Mcf87rR5eW7z6lI9cNEXZDsQ==",
|
||||
"version": "1.17.0",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/lowlight/-/lowlight-1.17.0.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-vmtBgYKD+QVNy7tIa7ulz5d//Il9R4MooOVh4nkOf9R9Cb/Dk5TXMSTieg/vDulkBkIWj59/BIlyFQxT9X1oAQ==",
|
||||
"requires": {
|
||||
"fault": "^1.0.0",
|
||||
"highlight.js": "~10.3.0"
|
||||
"highlight.js": "~10.4.0"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"macos-release": {
|
||||
@@ -15221,11 +15141,11 @@
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-GSmOT2EbHrINBf9SR7CDELwlJ8AENk3Qn7OikK4nFYAu3Ote2+JYNVvkpAEQm3/TLNEJFD/xZJjzyxg3KBWOzw=="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"resolve": {
|
||||
"version": "1.19.0",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/resolve/-/resolve-1.19.0.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-rArEXAgsBG4UgRGcynxWIWKFvh/XZCcS8UJdHhwy91zwAvCZIbcs+vAbflgBnNjYMs/i/i+/Ux6IZhML1yPvxg==",
|
||||
"version": "1.18.1",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/resolve/-/resolve-1.18.1.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-lDfCPaMKfOJXjy0dPayzPdF1phampNWr3qFCjAu+rw/qbQmr5jWH5xN2hwh9QKfw9E5v4hwV7A+jrCmL8yjjqA==",
|
||||
"requires": {
|
||||
"is-core-module": "^2.1.0",
|
||||
"is-core-module": "^2.0.0",
|
||||
"path-parse": "^1.0.6"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -15235,9 +15155,9 @@
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-OrOb32TeeambH6UrhtShmF7CRDqhL6/5XpPNp2DuRH6+9QLw/orhp72j87v8Qa1ScDkvrrBNpZcDejAirJmfXQ=="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type-fest": {
|
||||
"version": "0.18.1",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/type-fest/-/type-fest-0.18.1.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-OIAYXk8+ISY+qTOwkHtKqzAuxchoMiD9Udx+FSGQDuiRR+PJKJHc2NJAXlbhkGwTt/4/nKZxELY1w3ReWOL8mw=="
|
||||
"version": "0.18.0",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/type-fest/-/type-fest-0.18.0.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-fbDukFPnJBdn2eZ3RR+5mK2slHLFd6gYHY7jna1KWWy4Yr4XysHuCdXRzy+RiG/HwG4WJat00vdC2UHky5eKiQ=="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"yallist": {
|
||||
"version": "4.0.0",
|
||||
@@ -16697,12 +16617,9 @@
|
||||
"integrity": "sha1-bVuTSkVpk7I9N/QKOC1vFmao5cY="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"parse5": {
|
||||
"version": "3.0.3",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/parse5/-/parse5-3.0.3.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-rgO9Zg5LLLkfJF9E6CCmXlSE4UVceloys8JrFqCcHloC3usd/kJCyPDwH2SOlzix2j3xaP9sUX3e8+kvkuleAA==",
|
||||
"requires": {
|
||||
"@types/node": "*"
|
||||
}
|
||||
"version": "6.0.1",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/parse5/-/parse5-6.0.1.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-Ofn/CTFzRGTTxwpNEs9PP93gXShHcTq255nzRYSKe8AkVpZY7e1fpmTfOyoIvjP5HG7Z2ZM7VS9PPhQGW2pOpw=="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"parseurl": {
|
||||
"version": "1.3.3",
|
||||
@@ -17767,6 +17684,13 @@
|
||||
"unist-util-remove-position": "^1.0.0",
|
||||
"vfile-location": "^2.0.0",
|
||||
"xtend": "^4.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"vfile-location": {
|
||||
"version": "2.0.6",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/vfile-location/-/vfile-location-2.0.6.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-sSFdyCP3G6Ka0CEmN83A2YCMKIieHx0EDaj5IDP4g1pa5ZJ4FJDvpO0WODLxo4LUX4oe52gmSCK7Jw4SBghqxA=="
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"remark-rehype": {
|
||||
@@ -19895,9 +19819,9 @@
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-C4+gOpvmxaSMKuEf9Qc134F1ZuOHVXKRbtEflf4NTtuuJDEIJ9p5PXsalL8SkeRw+qit1Mo+yuvMPAKwWg/1hA=="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"trim-trailing-lines": {
|
||||
"version": "1.1.3",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/trim-trailing-lines/-/trim-trailing-lines-1.1.3.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-4ku0mmjXifQcTVfYDfR5lpgV7zVqPg6zV9rdZmwOPqq0+Zq19xDqEgagqVbc4pOOShbncuAOIs59R3+3gcF3ZA=="
|
||||
"version": "1.1.4",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/trim-trailing-lines/-/trim-trailing-lines-1.1.4.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-rjUWSqnfTNrjbB9NQWfPMH/xRK1deHeGsHoVfpxJ++XeYXE0d6B1En37AHfw3jtfTU7dzMzZL2jjpe8Qb5gLIQ=="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"trough": {
|
||||
"version": "1.0.5",
|
||||
@@ -19988,6 +19912,12 @@
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-0fr/mIH1dlO+x7TlcMy+bIDqKPsw/70tVyeHW787goQjhmqaZe10uwLujubK9q9Lg6Fiho1KUKDYz0Z7k7g5/g==",
|
||||
"dev": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type-fest": {
|
||||
"version": "0.8.1",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/type-fest/-/type-fest-0.8.1.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-4dbzIzqvjtgiM5rw1k5rEHtBANKmdudhGyBEajN01fEyhaAIhsoKNy6y7+IN93IfpFtwY9iqi7kD+xwKhQsNJA==",
|
||||
"dev": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type-is": {
|
||||
"version": "1.6.18",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/type-is/-/type-is-1.6.18.tgz",
|
||||
@@ -20155,9 +20085,9 @@
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"unist-util-generated": {
|
||||
"version": "1.1.5",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/unist-util-generated/-/unist-util-generated-1.1.5.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-1TC+NxQa4N9pNdayCYA1EGUOCAO0Le3fVp7Jzns6lnua/mYgwHo0tz5WUAfrdpNch1RZLHc61VZ1SDgrtNXLSw=="
|
||||
"version": "1.1.6",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/unist-util-generated/-/unist-util-generated-1.1.6.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-cln2Mm1/CZzN5ttGK7vkoGw+RZ8VcUH6BtGbq98DDtRGquAAOXig1mrBQYelOwMXYS8rK+vZDyyojSjp7JX+Lg=="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"unist-util-is": {
|
||||
"version": "3.0.0",
|
||||
@@ -20522,16 +20452,16 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"is-buffer": {
|
||||
"version": "2.0.4",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/is-buffer/-/is-buffer-2.0.4.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-Kq1rokWXOPXWuaMAqZiJW4XxsmD9zGx9q4aePabbn3qCRGedtH7Cm+zV8WETitMfu1wdh+Rvd6w5egwSngUX2A=="
|
||||
"version": "2.0.5",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/is-buffer/-/is-buffer-2.0.5.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-i2R6zNFDwgEHJyQUtJEk0XFi1i0dPFn/oqjK3/vPCcDeJvW5NQ83V8QbicfF1SupOaB0h8ntgBC2YiE7dfyctQ=="
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"vfile-location": {
|
||||
"version": "2.0.6",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/vfile-location/-/vfile-location-2.0.6.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-sSFdyCP3G6Ka0CEmN83A2YCMKIieHx0EDaj5IDP4g1pa5ZJ4FJDvpO0WODLxo4LUX4oe52gmSCK7Jw4SBghqxA=="
|
||||
"version": "3.2.0",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/vfile-location/-/vfile-location-3.2.0.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-aLEIZKv/oxuCDZ8lkJGhuhztf/BW4M+iHdCwglA/eWc+vtuRFJj8EtgceYFX4LRjOhCAAiNHsKGssC6onJ+jbA=="
|
||||
},
|
||||
"vfile-message": {
|
||||
"version": "2.0.4",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -15,7 +15,6 @@
|
||||
"@babel/runtime": "^7.11.2",
|
||||
"@github-docs/data-directory": "^1.2.0",
|
||||
"@github-docs/frontmatter": "^1.3.1",
|
||||
"@github-docs/render-content": "^5.2.0",
|
||||
"@octokit/rest": "^16.38.1",
|
||||
"@primer/css": "^15.1.0",
|
||||
"@primer/octicons": "^11.0.0",
|
||||
@@ -40,10 +39,13 @@
|
||||
"github-slugger": "^1.2.1",
|
||||
"got": "^9.6.0",
|
||||
"gray-matter": "^4.0.1",
|
||||
"hast-util-from-parse5": "^6.0.1",
|
||||
"hastscript": "^6.0.0",
|
||||
"helmet": "^3.21.2",
|
||||
"hot-shots": "^8.2.0",
|
||||
"html-entities": "^1.2.1",
|
||||
"html-truncate": "^1.2.2",
|
||||
"hubdown": "^2.6.0",
|
||||
"imurmurhash": "^0.1.4",
|
||||
"instantsearch.js": "^4.8.2",
|
||||
"is-url": "^1.2.4",
|
||||
@@ -57,11 +59,13 @@
|
||||
"mkdirp": "^1.0.3",
|
||||
"morgan": "^1.9.1",
|
||||
"node-fetch": "^2.6.1",
|
||||
"parse5": "^6.0.1",
|
||||
"platform-utils": "^1.2.0",
|
||||
"port-used": "^2.0.8",
|
||||
"querystring": "^0.2.0",
|
||||
"rate-limit-redis": "^2.0.0",
|
||||
"readline-sync": "^1.4.10",
|
||||
"remark-code-extra": "^1.0.1",
|
||||
"resolve-url-loader": "^3.1.2",
|
||||
"rimraf": "^3.0.0",
|
||||
"sass": "^1.26.3",
|
||||
@@ -69,6 +73,7 @@
|
||||
"search-with-your-keyboard": "1.1.0",
|
||||
"semver": "^5.7.1",
|
||||
"slash": "^3.0.0",
|
||||
"strip-html-comments": "^1.0.0",
|
||||
"style-loader": "^1.2.1",
|
||||
"uuid": "^8.3.0",
|
||||
"walk-sync": "^1.1.4",
|
||||
|
||||
270
tests/unit/render-content.js
Normal file
270
tests/unit/render-content.js
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,270 @@
|
||||
const cheerio = require('cheerio')
|
||||
const renderContent = require('../../lib/render-content/renderContent')
|
||||
const { EOL } = require('os')
|
||||
|
||||
// Use platform-specific line endings for realistic tests when templates have
|
||||
// been loaded from disk
|
||||
const nl = str => str.replace(/\n/g, EOL)
|
||||
|
||||
describe('renderContent', () => {
|
||||
test(
|
||||
'takes a template and a context and returns a string (async)',
|
||||
async () => {
|
||||
const template = 'my favorite color is {{ color }}.'
|
||||
const context = { color: 'orange' }
|
||||
const output = await renderContent(template, context)
|
||||
expect(output, '<p>my favorite color is orange.</p>')
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
test('preserves content within {% raw %} tags', async () => {
|
||||
const template = nl(
|
||||
'For example: {% raw %}{% include cool_header.html %}{% endraw %}.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
const expected = '<p>For example: {% include cool_header.html %}.</p>'
|
||||
const output = await renderContent(template)
|
||||
expect(output).toBe(expected)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
test(
|
||||
'removes extra newlines to prevent lists from breaking',
|
||||
async () => {
|
||||
const template = nl(`
|
||||
1. item one
|
||||
1. item two
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1. item three`)
|
||||
|
||||
const html = await renderContent(template)
|
||||
const $ = cheerio.load(html, { xmlMode: true })
|
||||
expect($('ol').length).toBe(1)
|
||||
expect($('ol > li').length).toBe(3)
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
test('removes extra newlines from lists of links', async () => {
|
||||
const template = nl(`- <a>item</a>
|
||||
|
||||
- <a>item</a>`)
|
||||
|
||||
const html = await renderContent(template)
|
||||
const $ = cheerio.load(html, { xmlMode: true })
|
||||
expect($('ul p').length, 0)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
test('renders text only', async () => {
|
||||
const template = 'my favorite color is {{ color }}.'
|
||||
const context = { color: 'orange' }
|
||||
const output = await renderContent(template, context, { textOnly: true })
|
||||
expect(output, 'my favorite color is orange.')
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
test('throws on rendering errors', async () => {
|
||||
const template = 1
|
||||
const context = {}
|
||||
|
||||
let err
|
||||
|
||||
try {
|
||||
await renderContent(template, context)
|
||||
} catch (_err) {
|
||||
err = _err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
expect(err).toBeTruthy()
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
test(
|
||||
'warns and throws on rendering errors when the file name is passed',
|
||||
async () => {
|
||||
const template = 1
|
||||
const context = {}
|
||||
|
||||
let err
|
||||
let warned = false
|
||||
|
||||
const error = console.error
|
||||
console.error = message => {
|
||||
expect(message, 'renderContent failed on file: name')
|
||||
console.error = error
|
||||
warned = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
try {
|
||||
await renderContent(template, context, { filename: 'name' })
|
||||
} catch (_err) {
|
||||
err = _err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
expect(err).toBeTruthy()
|
||||
expect(warned).toBeTruthy()
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
test('renders empty templates', async () => {
|
||||
const template = ''
|
||||
const context = {}
|
||||
const output = await renderContent(template, context)
|
||||
expect(output).toBe('')
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
test('encodes entities', async () => {
|
||||
const template = '<beep></beep>'
|
||||
const context = {}
|
||||
const output = await renderContent(template, context, {
|
||||
encodeEntities: true
|
||||
})
|
||||
expect(output).toBe('<p><beep></beep></p>')
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
test('does not render newlines around links in tables', async () => {
|
||||
const template = nl(`
|
||||
| Keyboard shortcut | Description
|
||||
|-----------|------------
|
||||
|<kbd>g</kbd> <kbd>c</kbd> | Go to the **Code** tab
|
||||
|<kbd>g</kbd> <kbd>i</kbd> | Go to the **Issues** tab. For more information, see "[About issues](/articles/about-issues)."
|
||||
`)
|
||||
const html = await renderContent(template)
|
||||
const $ = cheerio.load(html, { xmlMode: true })
|
||||
expect(
|
||||
$.html().includes(
|
||||
'"<a href="/articles/about-issues">About issues</a>."'
|
||||
)
|
||||
).toBeTruthy()
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
test(
|
||||
'does not render newlines around inline code in tables',
|
||||
async () => {
|
||||
const template = nl(`
|
||||
| Package manager | formats |
|
||||
| --- | --- |
|
||||
| Python | \`requirements.txt\`, \`pipfile.lock\`
|
||||
`)
|
||||
const html = await renderContent(template)
|
||||
const $ = cheerio.load(html, { xmlMode: true })
|
||||
expect(
|
||||
$.html().includes(
|
||||
'<code>requirements.txt</code>, <code>pipfile.lock</code>'
|
||||
)
|
||||
).toBeTruthy()
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
test('does not render newlines around emphasis in code', async () => {
|
||||
const template = nl(`
|
||||
| Qualifier | Example
|
||||
| ------------- | -------------
|
||||
| <code>user:<em>USERNAME</em></code> | [**user:defunkt ubuntu**](https://github.com/search?q=user%3Adefunkt+ubuntu&type=Issues) matches issues with the word "ubuntu" from repositories owned by @defunkt.
|
||||
`)
|
||||
const html = await renderContent(template)
|
||||
const $ = cheerio.load(html, { xmlMode: true })
|
||||
expect($.html().includes('<code>user:<em>USERNAME</em></code>')).toBeTruthy()
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
test('renders code blocks with # comments', async () => {
|
||||
const template = nl(`
|
||||
1. This is a list item with code containing a comment:
|
||||
\`\`\`shell
|
||||
$ foo the bar
|
||||
# some comment here
|
||||
\`\`\`
|
||||
1. This is another list item.
|
||||
`)
|
||||
const html = await renderContent(template)
|
||||
const $ = cheerio.load(html, { xmlMode: true })
|
||||
expect($('ol').length).toBe(1)
|
||||
expect($.html().includes('# some comment here')).toBeTruthy()
|
||||
expect($.html().includes('<h1 id="some-comment-here">')).toBeFalsy()
|
||||
expect($.html().includes('<a href="#some-comment-here">')).toBeFalsy()
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
test('renders headings at the right level', async () => {
|
||||
const template = nl(`
|
||||
# This is a level one
|
||||
|
||||
## This is a level two
|
||||
|
||||
### This is a level three
|
||||
|
||||
#### This is a level four
|
||||
|
||||
##### This is a level five
|
||||
`)
|
||||
const html = await renderContent(template)
|
||||
const $ = cheerio.load(html, { xmlMode: true })
|
||||
expect(
|
||||
$.html().includes(
|
||||
'<h1 id="this-is-a-level-one"><a href="#this-is-a-level-one">This is a level one</a></h1>'
|
||||
)
|
||||
).toBeTruthy()
|
||||
expect(
|
||||
$.html().includes(
|
||||
'<h2 id="this-is-a-level-two"><a href="#this-is-a-level-two">This is a level two</a></h2>'
|
||||
)
|
||||
).toBeTruthy()
|
||||
expect(
|
||||
$.html().includes(
|
||||
'<h3 id="this-is-a-level-three"><a href="#this-is-a-level-three">This is a level three</a></h3>'
|
||||
)
|
||||
).toBeTruthy()
|
||||
expect(
|
||||
$.html().includes(
|
||||
'<h4 id="this-is-a-level-four"><a href="#this-is-a-level-four">This is a level four</a></h4>'
|
||||
)
|
||||
).toBeTruthy()
|
||||
expect(
|
||||
$.html().includes(
|
||||
'<h5 id="this-is-a-level-five"><a href="#this-is-a-level-five">This is a level five</a></h5>'
|
||||
)
|
||||
).toBeTruthy()
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
test('does syntax highlighting', async () => {
|
||||
const template = nl(`
|
||||
\`\`\`js
|
||||
const example = true
|
||||
\`\`\`\`
|
||||
`)
|
||||
const html = await renderContent(template)
|
||||
const $ = cheerio.load(html, { xmlMode: true })
|
||||
expect($.html().includes('<pre><code class="hljs language-js">')).toBeTruthy()
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
test('does not autoguess code block language', async () => {
|
||||
const template = nl(`
|
||||
\`\`\`
|
||||
some code
|
||||
\`\`\`\
|
||||
`)
|
||||
const html = await renderContent(template)
|
||||
const $ = cheerio.load(html, { xmlMode: true })
|
||||
expect($.html().includes('<pre><code>some code\n</code></pre>')).toBeTruthy()
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
test('renders a line break in a table', async () => {
|
||||
const content = `| Webhook event payload | Activity types |
|
||||
| --------------------- | -------------- |
|
||||
| [\`issues\`](/webhooks/event-payloads/#issues) | - \`opened\`<br/>- \`edited\`<br/>- \`other\` |`
|
||||
const file = await renderContent(content)
|
||||
expect(file).toBe(
|
||||
'<table><thead><tr><th>Webhook event payload</th><th>Activity types</th></tr></thead><tbody><tr><td><a href="/webhooks/event-payloads/#issues"><code>issues</code></a></td><td>- <code>opened</code><br>- <code>edited</code><br>- <code>other</code></td></tr></tbody></table>'
|
||||
)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
test(
|
||||
'renders a copy button for code blocks with {:copy} annotation',
|
||||
async () => {
|
||||
const template = nl(`
|
||||
\`\`\`js{:copy}
|
||||
some code
|
||||
\`\`\`\
|
||||
`)
|
||||
const html = await renderContent(template)
|
||||
const $ = cheerio.load(html)
|
||||
const el = $('button.js-btn-copy')
|
||||
expect(el.data('clipboard-text')).toBe('some code')
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
})
|
||||
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ All organizations have a single default self-hosted runner group. Organizations
|
||||
|
||||
Self-hosted runners are automatically assigned to the default group when created, and can only be members of one group at a time. You can move a runner from the default group to any group you create.
|
||||
|
||||
When creating a group, you must choose a policy that defines which repositories have access to the runner group. You can configure a runner group to be accessible to a specific list of repositories, all private repositories, or all repositories in the organization.
|
||||
When creating a group, you must choose a policy that defines which repositories have access to the runner group.
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.organizations.navigate-to-org %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.organizations.org_settings %}
|
||||
@@ -41,9 +41,19 @@ When creating a group, you must choose a policy that defines which repositories
|
||||
1. In the **Self-hosted runners** section, click **Add new**, and then **New group**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
1. Enter a name for your runner group, and select an access policy from the **Repository access** dropdown list.
|
||||
1. Enter a name for your runner group, and assign a policy for repository access.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.22" %} You can configure a runner group to be accessible to a specific list of repositories, or to all repositories in the organization. By default, public repositories can't access runners in a runner group, but you can use the **Allow public repositories** option to override this.{% else if currentVersion == "enterprise-server@2.22"%}You can configure a runner group to be accessible to a specific list of repositories, all private repositories, or all repositories in the organization.{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% warning %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Warnung**
|
||||
{% indented_data_reference site.data.reusables.github-actions.self-hosted-runner-security spaces=3 %}
|
||||
Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Informationen zu selbst-gehosteten Runnern](/actions/hosting-your-own-runners/about-self-hosted-runners#self-hosted-runner-security-with-public-repositories)“.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endwarning %}
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
1. Click **Save group** to create the group and apply the policy.
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating a self-hosted runner group for an enterprise
|
||||
@@ -52,7 +62,7 @@ Enterprises can add their self-hosted runners to groups for access management. E
|
||||
|
||||
Self-hosted runners are automatically assigned to the default group when created, and can only be members of one group at a time. You can assign the runner to a specific group during the registration process, or you can later move the runner from the default group to a custom group.
|
||||
|
||||
When creating a group, you must choose a policy that grants access to all organizations in the enterprise or choose specific organizations.
|
||||
When creating a group, you must choose a policy that defines which organizations have access to the runner group.
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise-accounts.access-enterprise %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise-accounts.policies-tab %}
|
||||
@@ -61,7 +71,17 @@ When creating a group, you must choose a policy that grants access to all organi
|
||||
1. Click **Add new**, and then **New group**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
1. Enter a name for your runner group, and select an access policy from the **Organization access** dropdown list.
|
||||
1. Enter a name for your runner group, and assign a policy for organization access.
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.22" %} You can configure a runner group to be accessible to a specific list of organizations, or all organizations in the enterprise. By default, public repositories can't access runners in a runner group, but you can use the **Allow public repositories** option to override this.{% else if currentVersion == "enterprise-server@2.22"%}You can configure a runner group to be accessible to all organizations in the enterprise or choose specific organizations.{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% warning %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Warnung**
|
||||
{% indented_data_reference site.data.reusables.github-actions.self-hosted-runner-security spaces=3 %}
|
||||
Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Informationen zu selbst-gehosteten Runnern](/actions/hosting-your-own-runners/about-self-hosted-runners#self-hosted-runner-security-with-public-repositories)“.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endwarning %}
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
1. Click **Save group** to create the group and apply the policy.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -572,6 +572,8 @@ on:
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.developer-site.pull_request_forked_repos_link %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.22" %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### `pull_request_target`
|
||||
|
||||
This event is similar to `pull_request`, except that it runs in the context of the base repository of the pull request, rather than in the merge commit. This means that you can more safely make your secrets available to the workflows triggered by the pull request, because only workflows defined in the commit on the base repository are run. For example, this event allows you to create workflows that label and comment on pull requests, based on the contents of the event payload.
|
||||
@@ -589,6 +591,8 @@ on: pull_request_target
|
||||
types: [assigned, opened, synchronize, reopened]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### `Push`
|
||||
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
@@ -689,6 +693,8 @@ on:
|
||||
types: [started]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.22" %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### `workflow_run`
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.webhooks.workflow_run_desc %}
|
||||
@@ -711,6 +717,8 @@ on:
|
||||
- requested
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Neue Workflows mit einem persönlichen Zugangs-Token auslösen
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.github-actions.actions-do-not-trigger-workflows %} weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Authentifizierung mit dem GITHUB_TOKEN](/actions/configuring-and-managing-workflows/authenticating-with-the-github_token)“.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -876,9 +876,40 @@ strategy:
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
|
||||
##### Using environment variables in a matrix
|
||||
|
||||
You can add custom environment variables for each test combination by using `include` with `env`. You can then refer to the custom environment variables in a later step.
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, the matrix entries for `node-version` are each configured to use different values for the `site` and `datacenter` environment variables. The `Echo site details` step then uses {% raw %}`env: ${{ matrix.env }}`{% endraw %} to refer to the custom variables:
|
||||
|
||||
{% raw %}
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
name: Node.js CI
|
||||
on: [push]
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
build:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
include:
|
||||
- node-version: 10.x
|
||||
site: "prod"
|
||||
datacenter: "site-a"
|
||||
- node-version: 12.x
|
||||
site: "dev"
|
||||
datacenter: "site-b"
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Echo site details
|
||||
env:
|
||||
SITE: ${{ matrix.site }}
|
||||
DATACENTER: ${{ matrix.datacenter }}
|
||||
run: echo $SITE $DATACENTER
|
||||
```
|
||||
{% endraw %}
|
||||
|
||||
### **`jobs.<job_id>.strategy.fail-fast`**
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn diese Option auf `true` gesetzt ist, bricht {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} alle laufenden Aufträge ab, sobald ein `matrix`-Auftrag fehlschlägt. Standard: `true`
|
||||
Wenn diese Option auf `true` gesetzt ist, bricht {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} alle laufenden Jobs ab, sobald ein Job der `matrix` fehlschlägt. Standard: `true`
|
||||
|
||||
### **`jobs.<job_id>.strategy.max-parallel`**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -84,7 +84,7 @@ Dadurch können Sie den UUID Ihres Knotens in `cluster.conf` ermitteln.
|
||||
Allows you to exempt a list of users from API rate limits. For more information, see "[Rate Limiting](/enterprise/{{ page.version }}/v3/#rate-limiting)."
|
||||
|
||||
``` shell
|
||||
$ ghe-config app.github.rate_limiting_exempt_users "<em>hubot</em> <em>github-actions</em>"
|
||||
$ ghe-config app.github.rate-limiting-exempt-users "<em>hubot</em> <em>github-actions</em>"
|
||||
# Exempts the users hubot and github-actions from rate limits
|
||||
```
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -57,32 +57,36 @@ Before you define a secondary datacenter for your passive nodes, ensure that you
|
||||
mysql-master = <em>HOSTNAME</em>
|
||||
redis-master = <em>HOSTNAME</em>
|
||||
<strong>primary-datacenter = default</strong>
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Optionally, change the name of the primary datacenter to something more descriptive or accurate by editing the value of `primary-datacenter`.
|
||||
|
||||
4. {% data reusables.enterprise_clustering.configuration-file-heading %} Under each node's heading, add a new key-value pair to assign the node to a datacenter. Use the same value as `primary-datacenter` from step 3 above. For example, if you want to use the default name (`default`), add the following key-value pair to the section for each node.
|
||||
|
||||
datacenter = default
|
||||
```
|
||||
datacenter = default
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When you're done, the section for each node in the cluster configuration file should look like the following example. {% data reusables.enterprise_clustering.key-value-pair-order-irrelevant %}
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
[cluster "<em>HOSTNAME</em>"]
|
||||
<strong>datacenter = default</strong>
|
||||
hostname = <em>HOSTNAME</em>
|
||||
ipv4 = <em>IP ADDRESS</em>
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
[cluster "<em>HOSTNAME</em>"]
|
||||
<strong>datacenter = default</strong>
|
||||
hostname = <em>HOSTNAME</em>
|
||||
ipv4 = <em>IP ADDRESS</em>
|
||||
...
|
||||
...
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: If you changed the name of the primary datacenter in step 3, find the `consul-datacenter` key-value pair in the section for each node and change the value to the renamed primary datacenter. For example, if you named the primary datacenter `primary`, use the following key-value pair for each node.
|
||||
**Note**: If you changed the name of the primary datacenter in step 3, find the `consul-datacenter` key-value pair in the section for each node and change the value to the renamed primary datacenter. For example, if you named the primary datacenter `primary`, use the following key-value pair for each node.
|
||||
|
||||
consul-datacenter = primary
|
||||
```
|
||||
consul-datacenter = primary
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise_clustering.apply-configuration %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -103,31 +107,37 @@ For an example configuration, see "[Example configuration](#example-configuratio
|
||||
|
||||
1. For each node in your cluster, provision a matching virtual machine with identical specifications, running the same version of {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %}. Note the IPv4 address and hostname for each new cluster node. For more information, see "[Prerequisites](#prerequisites)."
|
||||
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: If you're reconfiguring high availability after a failover, you can use the old nodes from the primary datacenter instead.
|
||||
**Note**: If you're reconfiguring high availability after a failover, you can use the old nodes from the primary datacenter instead.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise_clustering.ssh-to-a-node %}
|
||||
|
||||
3. Back up your existing cluster configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
cp /data/user/common/cluster.conf ~/$(date +%Y-%m-%d)-cluster.conf.backup
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cp /data/user/common/cluster.conf ~/$(date +%Y-%m-%d)-cluster.conf.backup
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Create a copy of your existing cluster configuration file in a temporary location, like _/home/admin/cluster-passive.conf_. Delete unique key-value pairs for IP addresses (`ipv*`), UUIDs (`uuid`), and public keys for WireGuard (`wireguard-pubkey`).
|
||||
|
||||
grep -Ev "(?:|ipv|uuid|vpn|wireguard\-pubkey)" /data/user/common/cluster.conf > ~/cluster-passive.conf
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
grep -Ev "(?:|ipv|uuid|vpn|wireguard\-pubkey)" /data/user/common/cluster.conf > ~/cluster-passive.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Remove the `[cluster]` section from the temporary cluster configuration file that you copied in the previous step.
|
||||
|
||||
git config -f ~/cluster-passive.conf --remove-section cluster
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git config -f ~/cluster-passive.conf --remove-section cluster
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
6. Decide on a name for the secondary datacenter where you provisioned your passive nodes, then update the temporary cluster configuration file with the new datacenter name. Replace `SECONDARY` with the name you choose.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sed -i 's/datacenter = default/datacenter = <em>SECONDARY</em>/g' ~/cluster-passive.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
sed -i 's/datacenter = default/datacenter = <em>SECONDARY</em>/g' ~/cluster-passive.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
7. Decide on a pattern for the passive nodes' hostnames.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -140,7 +150,7 @@ For an example configuration, see "[Example configuration](#example-configuratio
|
||||
8. Open the temporary cluster configuration file from step 3 in a text editor. For example, you can use Vim.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo vim ~/cluster-passive.conf
|
||||
sudo vim ~/cluster-passive.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
9. In each section within the temporary cluster configuration file, update the node's configuration. {% data reusables.enterprise_clustering.configuration-file-heading %}
|
||||
@@ -150,37 +160,37 @@ For an example configuration, see "[Example configuration](#example-configuratio
|
||||
- Add a new key-value pair, `replica = enabled`.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
[cluster "<em>NEW PASSIVE NODE HOSTNAME</em>"]
|
||||
[cluster "<em>NEW PASSIVE NODE HOSTNAME</em>"]
|
||||
...
|
||||
hostname = <em>NEW PASSIVE NODE HOSTNAME</em>
|
||||
ipv4 = <em>NEW PASSIVE NODE IPV4 ADDRESS</em>
|
||||
<strong>replica = enabled</strong>
|
||||
...
|
||||
...
|
||||
hostname = <em>NEW PASSIVE NODE HOSTNAME</em>
|
||||
ipv4 = <em>NEW PASSIVE NODE IPV4 ADDRESS</em>
|
||||
<strong>replica = enabled</strong>
|
||||
...
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
10. Append the contents of the temporary cluster configuration file that you created in step 4 to the active configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
cat ~/cluster-passive.conf >> /data/user/common/cluster.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
cat ~/cluster-passive.conf >> /data/user/common/cluster.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
11. Designate the primary MySQL and Redis nodes in the secondary datacenter. Replace `REPLICA MYSQL PRIMARY HOSTNAME` and `REPLICA REDIS PRIMARY HOSTNAME` with the hostnames of the passives node that you provisioned to match your existing MySQL and Redis primaries.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git config -f /data/user/common/cluster.conf cluster.mysql-master-replica <em>REPLICA MYSQL PRIMARY HOSTNAME</em>
|
||||
git config -f /data/user/common/cluster.conf cluster.redis-master-replica <em>REPLICA REDIS PRIMARY HOSTNAME</em>
|
||||
```
|
||||
git config -f /data/user/common/cluster.conf cluster.mysql-master-replica <em>REPLICA MYSQL PRIMARY HOSTNAME</em>
|
||||
git config -f /data/user/common/cluster.conf cluster.redis-master-replica <em>REPLICA REDIS PRIMARY HOSTNAME</em>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
12. Enable MySQL to fail over automatically when you fail over to the passive replica nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git config -f /data/user/common/cluster.conf cluster.mysql-auto-failover true
|
||||
git config -f /data/user/common/cluster.conf cluster.mysql-auto-failover true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{% warning %}
|
||||
{% warning %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Warning**: Review your cluster configuration file before proceeding.
|
||||
**Warning**: Review your cluster configuration file before proceeding.
|
||||
|
||||
- In the top-level `[cluster]` section, ensure that the values for `mysql-master-replica` and `redis-master-replica` are the correct hostnames for the passive nodes in the secondary datacenter that will serve as the MySQL and Redis primaries after a failover.
|
||||
- In each section for an active node named `[cluster "<em>ACTIVE NODE HOSTNAME</em>"]`, double-check the following key-value pairs.
|
||||
@@ -194,9 +204,9 @@ For an example configuration, see "[Example configuration](#example-configuratio
|
||||
- `replica` should be configured as `enabled`.
|
||||
- Take the opportunity to remove sections for offline nodes that are no longer in use.
|
||||
|
||||
To review an example configuration, see "[Example configuration](#example-configuration)."
|
||||
To review an example configuration, see "[Example configuration](#example-configuration)."
|
||||
|
||||
{% endwarning %}
|
||||
{% endwarning %}
|
||||
|
||||
13. Initialize the new cluster configuration. {% data reusables.enterprise.use-a-multiplexer %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -207,7 +217,7 @@ For an example configuration, see "[Example configuration](#example-configuratio
|
||||
14. After the initialization finishes, {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %} displays the following message.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
Finished cluster initialization
|
||||
Finished cluster initialization
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise_clustering.apply-configuration %}
|
||||
@@ -293,20 +303,28 @@ Initial replication between the active and passive nodes in your cluster takes t
|
||||
You can monitor the progress on any node in the cluster, using command-line tools available via the {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %} administrative shell. For more information about the administrative shell, see "[Accessing the administrative shell (SSH)](/enterprise/admin/configuration/accessing-the-administrative-shell-ssh)."
|
||||
|
||||
- Monitor replication of databases:
|
||||
|
||||
/usr/local/share/enterprise/ghe-cluster-status-mysql
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/usr/local/share/enterprise/ghe-cluster-status-mysql
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Monitor replication of repository and Gist data:
|
||||
|
||||
ghe-spokes status
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ghe-spokes status
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Monitor replication of attachment and LFS data:
|
||||
|
||||
ghe-storage replication-status
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ghe-storage replication-status
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Monitor replication of Pages data:
|
||||
|
||||
ghe-dpages replication-status
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ghe-dpages replication-status
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can use `ghe-cluster-status` to review the overall health of your cluster. For more information, see "[Command-line utilities](/enterprise/admin/configuration/command-line-utilities#ghe-cluster-status)."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,6 +20,8 @@ Wenn sich mehr Benutzer {% data variables.product.product_location %} anschließ
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Minimum requirements
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise_installation.hardware-rec-table %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Größe der Datenpartition erhöhen
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,14 +26,14 @@ Bevor Sie {% data variables.product.product_location %} auf Google Cloud Platfor
|
||||
|
||||
{% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %} wird auf den folgenden Google Compute Engine-Maschinentypen (GCE) unterstützt. Weitere Informationen finden Sie im Google Cloud Platform-Artikel zu den „[Maschinentypen](https://cloud.google.com/compute/docs/machine-types)“.
|
||||
|
||||
| | Oberer Speicher |
|
||||
| | --------------- |
|
||||
| | n1-highmem-4 |
|
||||
| | n1-highmem-8 |
|
||||
| | n1-highmem-16 |
|
||||
| | n1-highmem-32 |
|
||||
| | n1-highmem-64 |
|
||||
| | n1-highmem-96 |
|
||||
| Oberer Speicher |
|
||||
| --------------- |
|
||||
| n1-highmem-4 |
|
||||
| n1-highmem-8 |
|
||||
| n1-highmem-16 |
|
||||
| n1-highmem-32 |
|
||||
| n1-highmem-64 |
|
||||
| n1-highmem-96 |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Empfohlene Maschinentypen
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ Basierend auf der Anzahl Deiner Benutzerlizenzen empfehlen wir die folgenden Mas
|
||||
1. Listen Sie mithilfe des Befehlszeilentools [gcloud compute](https://cloud.google.com/compute/docs/gcloud-compute/) die öffentlichen {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %}-Images auf:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ gcloud compute images list --project github-enterprise-public --no-standard-images
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Notieren Sie sich den Image-Namen für das neueste GCE-Image von {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %}.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -63,18 +63,18 @@ Basierend auf der Anzahl Deiner Benutzerlizenzen empfehlen wir die folgenden Mas
|
||||
GCE-VMs werden als Mitglied eines Netzwerks erstellt, das eine Firewall besitzt. Für das der {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %}-VM zugeordnete Netzwerk müssen Sie die Firewall so konfigurieren, dass die in der folgenden Tabelle aufgelisteten erforderlichen Ports zugelassen werden. Weitere Informationen zu den Firewallregeln auf Google Cloud Platform finden Sie im Leitfaden „[Übersicht über Firewallregeln](https://cloud.google.com/vpc/docs/firewalls)“.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Erstellen Sie mithilfe des Befehlszeilentools „gcloud compute“ das Netzwerk. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[gcloud compute networks create](https://cloud.google.com/sdk/gcloud/reference/compute/networks/create)“ in der Google-Dokumentation.
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ gcloud compute networks create <em>NETWORK-NAME</em> --subnet-mode auto
|
||||
```
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ gcloud compute networks create <em>NETWORK-NAME</em> --subnet-mode auto
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. Erstellen Sie eine Firewallregel für jeden der Ports in der folgenden Tabelle. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[gcloud compute firewall-rules](https://cloud.google.com/sdk/gcloud/reference/compute/firewall-rules/)“ in der Google-Dokumentation.
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ gcloud compute firewall-rules create <em>RULE-NAME</em> \
|
||||
--network <em>NETWORK-NAME</em> \
|
||||
--allow tcp:22,tcp:25,tcp:80,tcp:122,udp:161,tcp:443,udp:1194,tcp:8080,tcp:8443,tcp:9418,icmp
|
||||
```
|
||||
Diese Tabelle zeigt die erforderlichen Ports und wofür sie verwendet werden.
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ gcloud compute firewall-rules create <em>RULE-NAME</em> \
|
||||
--network <em>NETWORK-NAME</em> \
|
||||
--allow tcp:22,tcp:25,tcp:80,tcp:122,udp:161,tcp:443,udp:1194,tcp:8080,tcp:8443,tcp:9418,icmp
|
||||
```
|
||||
Diese Tabelle zeigt die erforderlichen Ports und wofür sie verwendet werden.
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise_installation.necessary_ports %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise_installation.necessary_ports %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Statische IP zuordnen und mit der VM verknüpfen
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -87,21 +87,21 @@ In Hochverfügbarkeitskonfigurationen in der Produktion sollten primären und Re
|
||||
Zum Erstellen der {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %}-Instanz müssen Sie eine GCE-Instanz mit Ihrem {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %}-Image erstellen und ein zusätzliches Storage-Volume für Ihre Instanzdaten anhängen. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Grundlegendes zur Hardware](#hardware-considerations)“.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Erstelle mit Hilfe des Befehlszeilen-Werkzeugs gcloud einen Datenträger, der als angehängtes Speicher-Volume für Deine Instanzdaten dient, und konfiguriere die Größe entsprechend der Anzahl Deiner Benutzerlizenzen. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[gcloud compute disks create](https://cloud.google.com/sdk/gcloud/reference/compute/disks/create)“ in der Google-Dokumentation.
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ gcloud compute disks create <em>DATA-DISK-NAME</em> --size <em>DATA-DISK-SIZE</em> --type <em>DATA-DISK-TYPE</em> --zone <em>ZONE</em>
|
||||
```
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ gcloud compute disks create <em>DATA-DISK-NAME</em> --size <em>DATA-DISK-SIZE</em> --type <em>DATA-DISK-TYPE</em> --zone <em>ZONE</em>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Erstellen Sie anschließend eine Instanz mit dem Namen des von Ihnen ausgewählten {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %}-Images, und hängen Sie die Daten-Disk an. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[gcloud compute instances create](https://cloud.google.com/sdk/gcloud/reference/compute/instances/create)“ in der Google-Dokumentation.
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ gcloud compute instances create <em>INSTANCE-NAME</em> \
|
||||
--machine-type n1-standard-8 \
|
||||
--image <em>GITHUB-ENTERPRISE-IMAGE-NAME</em> \
|
||||
--disk name=<em>DATA-DISK-NAME</em> \
|
||||
--metadata serial-port-enable=1 \
|
||||
--zone <em>ZONE</em> \
|
||||
--network <em>NETWORK-NAME</em> \
|
||||
--image-project github-enterprise-public
|
||||
```
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ gcloud compute instances create <em>INSTANCE-NAME</em> \
|
||||
--machine-type n1-standard-8 \
|
||||
--image <em>GITHUB-ENTERPRISE-IMAGE-NAME</em> \
|
||||
--disk name=<em>DATA-DISK-NAME</em> \
|
||||
--metadata serial-port-enable=1 \
|
||||
--zone <em>ZONE</em> \
|
||||
--network <em>NETWORK-NAME</em> \
|
||||
--image-project github-enterprise-public
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Instanz konfigurieren
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,26 +1,31 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Informationen zu „Enterprise“ (Unternehmens)-Konten
|
||||
intro: 'Mit {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %} kannst Du ein Unternehmenskonto erstellen, um Administratoren einen einzigen Sichtbarkeits- und Verwaltungspunkt für ihre Abrechnungs- und Lizenznutzung zu geben.'
|
||||
intro: 'With {% data variables.product.product_name %}, you can use an enterprise account to give administrators a single point of visibility and management{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %} for billing and license usage{% endif %}.'
|
||||
redirect_from:
|
||||
- /enterprise/admin/installation/about-enterprise-accounts
|
||||
- /enterprise/admin/overview/about-enterprise-accounts
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
enterprise-server: '*'
|
||||
enterprise-server: '>=2.20'
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Informationen zu Unternehmenskonten auf {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %}
|
||||
### Informationen zu Unternehmenskonten auf {% data variables.product.product_name %}
|
||||
|
||||
Mit einem Unternehmens-Konto kannst Du mehrere {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}-Organisationen und {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %}-Instanzen verwalten. Ihr Enterprise-Konto benötigt einen Handle, beispielsweise eine Organisation oder ein persönliches Konto auf {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}. Enterprise-Administratoren können Einstellungen und Voreinstellungen verwalten, darunter folgende:
|
||||
An enterprise account allows you to manage multiple organizations{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %} and {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %} instances{% else %} on {% data variables.product.product_name %}{% endif %}. Ihr Enterprise-Konto benötigt einen Handle, beispielsweise eine Organisation oder ein persönliches Konto auf {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}. Enterprise-Administratoren können Einstellungen und Voreinstellungen verwalten, darunter folgende:
|
||||
|
||||
- Mitgliederzugang und -verwaltung (Organisationsmitglieder, externe Mitarbeiter)
|
||||
- Abrechnung und Nutzung ({% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %}-Instanzen, Benutzerlizenzen, {% data variables.large_files.product_name_short %}-Pakete)
|
||||
- Sicherheit (Single-Sign-On, Zwei-Faktor-Authentifizierung)
|
||||
- Anfragen und Unterstützen von Bundle-Sharing mit {% data variables.contact.enterprise_support %}
|
||||
- Member access and management (organization members, outside collaborators){% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
- Billing and usage ({% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %} instances, user licenses, {% data variables.large_files.product_name_short %} packs){% endif %}
|
||||
- Security{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}(single sign-on, two factor authentication)
|
||||
- Requests {% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}and support bundle sharing {% endif %}with {% data variables.contact.enterprise_support %}{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise-accounts.enterprise-accounts-billing %}
|
||||
{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}{% data reusables.enterprise-accounts.enterprise-accounts-billing %} For more information about managing your {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_cloud %} subscription, see "[Viewing the subscription and usage for your enterprise account](/articles/viewing-the-subscription-and-usage-for-your-enterprise-account)." {% endif %}For more information about managing your {% data variables.product.product_name %} billing settings, see "[Managing billing for your enterprise](/admin/overview/managing-billing-for-your-enterprise)."
|
||||
|
||||
{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Informationen über die Unterschiede zwischen {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_cloud %} und {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %} findest Du auf „[Produkte von {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}](/articles/githubs-products)." Um auf {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %} zu hochzustufen oder um mit einem Unternehmenskonto einzusteigen, kontaktiere bitte {% data variables.contact.contact_enterprise_sales %}.
|
||||
|
||||
### {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %}-Lizenzen verwalten, die mit Deinem Unternehmens-Konto verknüpft sind
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise-accounts.admin-managing-licenses %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ versions:
|
||||
|
||||
{% data variables.product.prodname_registry %} on {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %} uses external blob storage to store your packages. The amount of storage required depends on your usage of {% data variables.product.prodname_registry %}.
|
||||
|
||||
At this time, {% data variables.product.prodname_registry %} supports blob storage with Amazon Web Services (AWS) S3. MinIO is also supported, but configuration is not currently implemented in the {% data variables.product.product_name %} interface. You can use MinIO for storage by following the instructions for AWS S3, entering the analogous information for your MinIO configuration.
|
||||
At this time, {% data variables.product.prodname_registry %} supports blob storage with Amazon Web Services (AWS) S3. MinIO is also supported, but configuration is not currently implemented in the {% data variables.product.product_name %} interface. You can use MinIO for storage by following the instructions for AWS S3, entering the analogous information for your MinIO configuration. Before configuring third-party storage for {% data variables.product.prodname_registry %} on {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}, you must set up a bucket with your third-party storage provider. For more information on installing and running a MinIO bucket to use with {% data variables.product.prodname_registry %}, see the "[Quickstart for configuring MinIO storage](/admin/packages/quickstart-for-configuring-minio-storage)."
|
||||
|
||||
For the best experience, we recommend using a dedicated bucket for {% data variables.product.prodname_registry %}, separate from the bucket you use for {% data variables.product.prodname_actions %} storage.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,5 +10,6 @@ versions:
|
||||
{% data reusables.package_registry.packages-ghes-release-stage %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% link_with_intro /enabling-github-packages-for-your-enterprise %}
|
||||
{% link_with_intro /quickstart-for-configuring-minio-storage %}
|
||||
{% link_with_intro /configuring-packages-support-for-your-enterprise %}
|
||||
{% link_with_intro /configuring-third-party-storage-for-packages %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Quickstart for configuring MinIO storage
|
||||
intro: 'Set up MinIO as a storage provider for using {% data variables.product.prodname_registry %} on your enterprise.'
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
enterprise-server: '>=2.22'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.package_registry.packages-ghes-release-stage %}
|
||||
|
||||
Before you can enable and configure {% data variables.product.prodname_registry %} on {% data variables.product.product_location_enterprise %}, you need to prepare your third-party storage solution.
|
||||
|
||||
MinIO offers object storage with support for the S3 API and {% data variables.product.prodname_registry %} on your enterprise.
|
||||
|
||||
This quickstart shows you how to set up MinIO using Docker for use with {% data variables.product.prodname_registry %} but you have other options for managing MinIO besides Docker. For more information about MinIO, see the official [MinIO docs](https://docs.min.io/).
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Choose a MinIO mode for your needs
|
||||
|
||||
| MinIO mode | Optimized for | Storage infrastructure required |
|
||||
| ----------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------ | ------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| Standalone MinIO (on a single host) | Fast setup | N/A |
|
||||
| MinIO as a NAS gateway | NAS (Network-attached storage) | NAS devices |
|
||||
| Clustered MinIO (also called Distributed MinIO) | Data security | Storage servers running in a cluster |
|
||||
|
||||
For more information about your options, see the official [MinIO docs](https://docs.min.io/).
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Install, run, and sign in to MinIO
|
||||
|
||||
1. Set up your preferred environment variables for MinIO.
|
||||
|
||||
These examples use `MINIO_DIR`:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ export MINIO_DIR=$(pwd)/minio
|
||||
$ mkdir -p $MINIO_DIR
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Install MinIO.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ docker pull minio/minio
|
||||
```
|
||||
For more information, see the official "[MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide)."
|
||||
|
||||
3. Sign in to MinIO using your MinIO access key and secret.
|
||||
|
||||
{% linux %}
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ export MINIO_ACCESS_KEY=$(cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc 'a-zA-Z0-9' | fold -w 32 | head -n 1)
|
||||
# this one is actually a secret, so careful
|
||||
$ export MINIO_SECRET_KEY=$(cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc 'a-zA-Z0-9' | fold -w 32 | head -n 1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
{% endlinux %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% mac %}
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ export MINIO_ACCESS_KEY=$(cat /dev/urandom | LC_CTYPE=C tr -dc 'a-zA-Z0-9' | fold -w 32 | head -n 1)
|
||||
# this one is actually a secret, so careful
|
||||
$ export MINIO_SECRET_KEY=$(cat /dev/urandom | LC_CTYPE=C tr -dc 'a-zA-Z0-9' | fold -w 32 | head -n 1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
{% endmac %}
|
||||
|
||||
You can access your MinIO keys using the environment variables:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ echo $MINIO_ACCESS_KEY
|
||||
$ echo $MINIO_SECRET_KEY
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Run MinIO in your chosen mode.
|
||||
|
||||
* Run MinIO using Docker on a single host:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ docker run -p 9000:9000 \
|
||||
-v $MINIO_DIR:/data \
|
||||
-e "MINIO_ACCESS_KEY=$MINIO_ACCESS_KEY" \
|
||||
-e "MINIO_SECRET_KEY=$MINIO_SECRET_KEY" \
|
||||
minio/minio server /data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more information, see "[MinIO Docker Quickstart guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-docker-quickstart-guide.html)."
|
||||
|
||||
* Run MinIO using Docker as a NAS gateway:
|
||||
|
||||
This setup is useful for deployments where there is already a NAS you want to use as the backup storage for {% data variables.product.prodname_registry %}.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ docker run -p 9000:9000 \
|
||||
-v $MINIO_DIR:/data \
|
||||
-e "MINIO_ACCESS_KEY=$MINIO_ACCESS_KEY" \
|
||||
-e "MINIO_SECRET_KEY=$MINIO_SECRET_KEY" \
|
||||
minio/minio gateway nas /data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more information, see "[MinIO Gateway for NAS](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-gateway-for-nas.html)."
|
||||
|
||||
* Run MinIO using Docker as a cluster. This MinIO deployment uses several hosts and MinIO's erasure coding for the strongest data protection. To run MinIO in a cluster mode, see the "[Distributed MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/distributed-minio-quickstart-guide.html).
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Create your MinIO bucket for {% data variables.product.prodname_registry %}
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install the MinIO client.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ docker pull minio/mc
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Create a bucket with a host URL that {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %} can access.
|
||||
|
||||
* Local deployments example:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ export MC_HOST_minio="http://${MINIO_ACCESS_KEY}:${MINIO_SECRET_KEY} @localhost:9000"
|
||||
$ docker run minio/mc <em>BUCKET-NAME</em>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This example can be used for MinIO standalone or MinIO as a NAS gateway.
|
||||
|
||||
* Clustered deployments example:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ export MC_HOST_minio="http://${MINIO_ACCESS_KEY}:${MINIO_SECRET_KEY} @minioclustername.example.com:9000"
|
||||
$ docker run minio/mc mb packages
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Nächste Schritte:
|
||||
|
||||
To finish configuring storage for {% data variables.product.prodname_registry %}, you'll need to copy the MinIO storage URL:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
echo "http://${MINIO_ACCESS_KEY}:${MINIO_SECRET_KEY}@minioclustername.example.com:9000"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the next steps, see "[Configuring third-party storage for packages](/admin/packages/configuring-third-party-storage-for-packages)."
|
||||
@@ -26,10 +26,10 @@ Sie können ein Linux-Containerverwaltungstool zum Erstellen einer Pre-Receive-H
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
FROM gliderlabs/alpine:3.3
|
||||
RUN apk add --no-cache git bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
FROM gliderlabs/alpine:3.3
|
||||
RUN apk add --no-cache git bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
3. Erstellen Sie im Verzeichnis, in dem die `Dockerfile.alpine-3.3` enthalten ist, ein Image:
|
||||
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ Sie können ein Linux-Containerverwaltungstool zum Erstellen einer Pre-Receive-H
|
||||
> ---> Using cache
|
||||
> ---> 0250ab3be9c5
|
||||
> Successfully built 0250ab3be9c5
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
4. Erstellen Sie einen Container:
|
||||
@@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ Sie können ein Linux-Containerverwaltungstool zum Erstellen einer Pre-Receive-H
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ docker create --name pre-receive.alpine-3.3 pre-receive.alpine-3.3 /bin/true
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
5. Exportieren Sie den Docker-Container in eine `gzip`-komprimierte `TAR`-Datei:
|
||||
@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ Sie können ein Linux-Containerverwaltungstool zum Erstellen einer Pre-Receive-H
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ docker export pre-receive.alpine-3.3 | gzip > alpine-3.3.tar.gz
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Diese Datei `alpine-3.3.tar.gz` kann auf die Appliance {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %} hochgeladen werden.
|
||||
@@ -76,9 +76,9 @@ Diese Datei `alpine-3.3.tar.gz` kann auf die Appliance {% data variables.product
|
||||
2. Erstellen Sie eine `gzip`-komprimierte `TAR`-Datei des Verzeichnisses `chroot`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ cd /path/to/chroot
|
||||
$ tar -czf /path/to/pre-receive-environment.tar.gz .
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ cd /path/to/chroot
|
||||
$ tar -czf /path/to/pre-receive-environment.tar.gz .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -86,10 +86,11 @@ Diese Datei `alpine-3.3.tar.gz` kann auf die Appliance {% data variables.product
|
||||
|
||||
**Hinweise:**
|
||||
|
||||
- Schließe keine führenden Verzeichnispfade von Dateien innerhalb des tar-Archivs ein, wie beispielsweise `/path/to/chroot`.
|
||||
- `/bin/sh` muss existieren und als Einstiegspunkt in die chroot-Umgebung ausführbar sein.
|
||||
- Im Gegensatz zu herkömmlichen Chroots ist das Verzeichnis `dev` für Vorempfang-Hooks nicht erforderlich.
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
- Schließe keine führenden Verzeichnispfade von Dateien innerhalb des tar-Archivs ein, wie beispielsweise `/path/to/chroot`.
|
||||
- `/bin/sh` muss existieren und als Einstiegspunkt in die chroot-Umgebung ausführbar sein.
|
||||
- Im Gegensatz zu herkömmlichen Chroots ist das Verzeichnis `dev` für Vorempfang-Hooks nicht erforderlich.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Informationen zum Erstellen einer chroot-Umgebung finden Sie unter „[Chroot](https://wiki.debian.org/chroot)“ aus dem *Debian-Wiki*, „[BasicChroot](https://help.ubuntu.com/community/BasicChroot)“ aus dem *Hilfe-Wiki der Ubuntu-Community* oder „[Installing Alpine Linux in a chroot (Alpine Linux in einem chroot installieren](http://wiki.alpinelinux.org/wiki/Installing_Alpine_Linux_in_a_chroot)“ aus dem *Alpine Linux-Wiki*.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -129,4 +130,4 @@ Weitere Informationen zum Erstellen einer chroot-Umgebung finden Sie unter „[C
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
admin@ghe-host:~$ ghe-hook-env-create AlpineTestEnv /home/admin/alpine-3.3.tar.gz
|
||||
> Pre-receive hook environment 'AlpineTestEnv' (2) has been created.
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -70,19 +70,19 @@ Es wird empfohlen, Hooks in einem einzelnen Repository zu konsolidieren. Wenn da
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ sudo chmod +x <em>SCRIPT_FILE.sh</em>
|
||||
```
|
||||
Stellen Sie für Windows-Benutzer sicher, dass die Skripts über Ausführungsberechtigungen verfügen:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Stellen Sie für Windows-Benutzer sicher, dass die Skripts über Ausführungsberechtigungen verfügen:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git update-index --chmod=+x <em>SCRIPT_FILE.sh</em>
|
||||
```
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git update-index --chmod=+x <em>SCRIPT_FILE.sh</em>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Committen und übertragen Sie Ihr vorgesehenes Pre-Receive-Hook-Repository auf der {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %}-Instanz per Push-Vorgang.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ git commit -m "<em>YOUR COMMIT MESSAGE</em>"
|
||||
$ git push
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. [Erstellen Sie den Pre-Receive-Hook](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/admin/guides/developer-workflow/managing-pre-receive-hooks-on-the-github-enterprise-server-appliance/#creating-pre-receive-hooks) auf der {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %}-Instanz.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -93,40 +93,40 @@ Sie können ein Pre-Receive-Hook-Skript lokal testen, bevor Sie es auf Ihrer {%
|
||||
|
||||
2. Erstellen Sie eine Datei namens `Dockerfile.dev`, die Folgendes enthält:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
FROM gliderlabs/alpine:3.3
|
||||
RUN \
|
||||
apk add --no-cache git openssh bash && \
|
||||
ssh-keygen -A && \
|
||||
sed -i "s/#AuthorizedKeysFile/AuthorizedKeysFile/g" /etc/ssh/sshd_config && \
|
||||
adduser git -D -G root -h /home/git -s /bin/bash && \
|
||||
passwd -d git && \
|
||||
su git -c "mkdir /home/git/.ssh && \
|
||||
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -f /home/git/.ssh/id_ed25519 -P '' && \
|
||||
mv /home/git/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub /home/git/.ssh/authorized_keys && \
|
||||
mkdir /home/git/test.git && \
|
||||
git --bare init /home/git/test.git"
|
||||
```
|
||||
FROM gliderlabs/alpine:3.3
|
||||
RUN \
|
||||
apk add --no-cache git openssh bash && \
|
||||
ssh-keygen -A && \
|
||||
sed -i "s/#AuthorizedKeysFile/AuthorizedKeysFile/g" /etc/ssh/sshd_config && \
|
||||
adduser git -D -G root -h /home/git -s /bin/bash && \
|
||||
passwd -d git && \
|
||||
su git -c "mkdir /home/git/.ssh && \
|
||||
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -f /home/git/.ssh/id_ed25519 -P '' && \
|
||||
mv /home/git/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub /home/git/.ssh/authorized_keys && \
|
||||
mkdir /home/git/test.git && \
|
||||
git --bare init /home/git/test.git"
|
||||
|
||||
VOLUME ["/home/git/.ssh", "/home/git/test.git/hooks"]
|
||||
WORKDIR /home/git
|
||||
VOLUME ["/home/git/.ssh", "/home/git/test.git/hooks"]
|
||||
WORKDIR /home/git
|
||||
|
||||
CMD ["/usr/sbin/sshd", "-D"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
CMD ["/usr/sbin/sshd", "-D"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Erstellen Sie ein Pre-Receive-Testskript namens `always_reject.sh`. Dieses Beispielskript lehnt alle Push-Vorgänge ab, was zum Sperren eines Repositorys nützlich ist:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env bash
|
||||
|
||||
echo "error: rejecting all pushes"
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
echo "error: rejecting all pushes"
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Stellen Sie sicher, dass das Skript `always_reject.sh` über Ausführungsberechtigungen verfügt:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ chmod +x always_reject.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Erstellen Sie im Verzeichnis, in dem die `Dockerfile.dev` enthalten ist, ein Image:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -149,32 +149,32 @@ Sie können ein Pre-Receive-Hook-Skript lokal testen, bevor Sie es auf Ihrer {%
|
||||
....truncated output....
|
||||
> Initialized empty Git repository in /home/git/test.git/
|
||||
> Successfully built dd8610c24f82
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
6. Führen Sie einen Datencontainer aus, der einen generierten SSH-Schlüssel enthält:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ docker run --name data pre-receive.dev /bin/true
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
7. Kopieren Sie den Pre-Receive-Hook `always_reject.sh` in den Datencontainer:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ docker cp always_reject.sh data:/home/git/test.git/hooks/pre-receive
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
8. Führen Sie einen Anwendungscontainer aus, der `sshd` und den Hook ausführt. Beachten Sie die zurückgegebene Container-ID.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ docker run -d -p 52311:22 --volumes-from data pre-receive.dev
|
||||
> 7f888bc700b8d23405dbcaf039e6c71d486793cad7d8ae4dd184f4a47000bc58
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
9. Kopieren Sie den generierten SSH-Schlüssel aus dem Datencontainer auf den lokalen Computer:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ docker cp data:/home/git/.ssh/id_ed25519 .
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
10. Ändern Sie die Remote-Instanz eines Test-Repositorys, und übertragen Sie das Repository `test.git` per Push-Vorgang innerhalb des Docker-Containers. In diesem Beispiel wird `git@github.com:octocat/Hello-World.git` verwendet. Sie können jedoch auch andere Repositorys verwenden. In diesem Beispiel wird davon ausgegangen, dass Ihr lokaler Computer (127.0.0.1) den Port 52311 bindet. Sie können jedoch eine andere IP-Adresse verwenden, wenn Docker auf einem Remote-Computer ausgeführt wird.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -193,9 +193,9 @@ Sie können ein Pre-Receive-Hook-Skript lokal testen, bevor Sie es auf Ihrer {%
|
||||
> To git@192.168.99.100:test.git
|
||||
> ! [remote rejected] main -> main (pre-receive hook declined)
|
||||
> error: failed to push some refs to 'git@192.168.99.100:test.git'
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Beachten Sie, dass der Push abgelehnt wurde, nachdem Sie den Pre-Receive-Hook ausgeführt und die Ausgabe des Skripts wiedergegeben haben.
|
||||
Beachten Sie, dass der Push abgelehnt wurde, nachdem Sie den Pre-Receive-Hook ausgeführt und die Ausgabe des Skripts wiedergegeben haben.
|
||||
|
||||
### Weiterführende Informationen
|
||||
- „[Git anpassen – eine Git-erzwungene Beispielrichtlinie](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Customizing-Git-An-Example-Git-Enforced-Policy)“ von der *Pro Git-Website*
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ versions:
|
||||
|
||||
Each time someone creates a new repository on your enterprise, that person must choose a visibility for the repository. When you configure a default visibility setting for the enterprise, you choose which visibility is selected by default. Weitere Informationen zu Repository-Sichtbarkeiten findest Du unter „[Informationen zur Sichtbarkeit eines Repositorys](/github/creating-cloning-and-archiving-repositories/about-repository-visibility)“.
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn ein Site-Administrator Mitgliedern das Erstellen bestimmter Arten Repositorys verwehrt, werden Mitglieder nicht in der Lage sein, ein Repository dieser Art zu erstellen, selbst wenn die Einstellung zur Sichtbarkeit diesen Typ als Standard vorgibt. For more information, see "[Setting a policy for repository creation](#setting-a-policy-for-repository-creation)."
|
||||
If an enterprise owner disallows members from creating certain types of repositories, members will not be able to create that type of repository even if the visibility setting defaults to that type. For more information, see "[Setting a policy for repository creation](#setting-a-policy-for-repository-creation)."
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise-accounts.access-enterprise %}
|
||||
{% if currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.21" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
@@ -49,9 +49,9 @@ Wenn ein Site-Administrator Mitgliedern das Erstellen bestimmter Arten Repositor
|
||||
|
||||
### Setting a policy for changing a repository's visibility
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie Mitglieder daran hindern, die Sichtbarkeit des Repositorys zu ändern, können nur Websiteadministratoren öffentliche Repositorys als privat oder private Repositorys als öffentlich festlegen.
|
||||
When you prevent members from changing repository visibility, only enterprise owners can change the visibility of a repository.
|
||||
|
||||
Falls ein Websiteadministrator die Möglichkeit der Repository-Erstellung auf Organisationsinhaber beschränkt hat, können Mitglieder die Sichtbarkeit eines Repositorys nicht ändern. Hat ein Websiteadministrator dagegen die Möglichkeit von Mitgliedern auf die Erstellung privater Repositorys beschränkt, können Mitglieder die Sichtbarkeit eines Repositorys von öffentlich auf privat festlegen. For more information, see "[Setting a policy for repository creation](#setting-a-policy-for-repository-creation)."
|
||||
If an enterprise owner has restricted repository creation to organization owners only, then members will not be able to change repository visibility. If an enterprise owner has restricted member repository creation to private repositories only, then members will only be able to change the visibility of a repository to private. For more information, see "[Setting a policy for repository creation](#setting-a-policy-for-repository-creation)."
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise-accounts.access-enterprise %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise-accounts.policies-tab %}
|
||||
@@ -75,6 +75,15 @@ Falls ein Websiteadministrator die Möglichkeit der Repository-Erstellung auf Or
|
||||
6. Wählen Sie im Dropdownmenü unter „Repository creation“ (Repository-Erstellung) eine Richtlinie aus. 
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Eine Richtlinie zum Forken privater oder interner Repositorys erzwingen
|
||||
|
||||
Across all organizations owned by your enterprise, you can allow people with access to a private or internal repository to fork the repository, never allow forking of private or internal repositories, or allow owners to administer the setting on the organization level.
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise-accounts.access-enterprise %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise-accounts.policies-tab %}
|
||||
3. Lies auf der Registerkarte **Repository policies** (Repository-Richtlinien) unter „Repository forking“ (Repository-Forking) die Informationen zum Ändern der Einstellung. {% data reusables.enterprise-accounts.view-current-policy-config-orgs %}
|
||||
4. Wähle im Dropdownmenü unter „Repository forking“ (Repository-Forking) eine Richtlinie aus. 
|
||||
|
||||
### Setting a policy for repository deletion and transfer
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise-accounts.access-enterprise %}
|
||||
@@ -166,6 +175,8 @@ Sie können die standardmäßig übernommenen Einstellungen überschreiben, inde
|
||||
- **Block to the default branch** (Übertragung an den Standardbranch blockieren), damit die an den Standardbranch übertragenen erzwungenen Push-Vorgänge blockiert werden. 
|
||||
6. Wählen Sie optional **Enforce on all repositories** (Auf allen Repositorys erzwingen) aus, um Repository-spezifische Einstellungen zu überschreiben. Note that this will **not** override an enterprise-wide policy. 
|
||||
|
||||
{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuring anonymous Git read access
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise_user_management.disclaimer-for-git-read-access %}
|
||||
@@ -192,7 +203,6 @@ If necessary, you can prevent repository administrators from changing anonymous
|
||||
4. Klicken Sie unter „Anonymous Git read access“ (Anonymer Git-Lesezugriff) auf das Dropdownmenü, und klicken Sie auf **Enabled** (Aktiviert). 
|
||||
3. Optionally, to prevent repository admins from changing anonymous Git read access settings in all repositories on your enterprise, select **Prevent repository admins from changing anonymous Git read access**. 
|
||||
|
||||
{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
#### Setting anonymous Git read access for a specific repository
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.enterprise_site_admin_settings.access-settings %}
|
||||
@@ -203,6 +213,7 @@ If necessary, you can prevent repository administrators from changing anonymous
|
||||
6. Klicken Sie unter „Danger Zone“ (Gefahrenzone) neben „Enable Anonymous Git read access“ (Anonymen Git-Lesezugriff aktivieren) auf **Enable** (Aktivieren). 
|
||||
7. Überprüfen Sie die Änderungen. Klicken Sie zur Bestätigung auf **Yes, enable anonymous Git read access** (Ja, anonymen Git-Lesezugriff aktivieren). 
|
||||
8. Aktivieren Sie optional **Prevent repository admins from changing anonymous Git read access** (Repository-Administratoren daran hindern, den anonymen Git-Lesezugriff zu ändern), um Repository-Administratoren daran zu hindern, diese Einstellung für dieses Repository zu ändern. 
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.22" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
|
||||
8
translations/de-DE/content/admin/release-notes.md
Normal file
8
translations/de-DE/content/admin/release-notes.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Release notes
|
||||
intro: The release notes for {{ allVersions[currentVersion].versionTitle }}.
|
||||
layout: release-notes
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
enterprise-server: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -36,12 +36,12 @@ versions:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Enterprise configuration settings
|
||||
|
||||
| Name | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| -------------------------------------------------------:| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `business.update_member_repository_creation_permission` | A site admin restricts repository creation in organizations in the enterprise. For more information, see "[Enforcing repository management policies in your enterprise](/admin/policies/enforcing-repository-management-policies-in-your-enterprise#setting-a-policy-for-repository-creation)." |
|
||||
| `business.clear_members_can_create_repos` | A site admin clears a restriction on repository creation in organizations in the enterprise. For more information, see "[Enforcing repository management policies in your enterprise](/admin/policies/enforcing-repository-management-policies-in-your-enterprise#setting-a-policy-for-repository-creation)." |
|
||||
| `enterprise.config.lock_anonymous_git_access` | A site admin locks anonymous Git read access to prevent repository admins from changing existing anonymous Git read access settings for repositories in the enterprise. For more information, see "[Enforcing repository management policies in your enterprise](/admin/policies/enforcing-repository-management-policies-in-your-enterprise#configuring-anonymous-git-read-access)." |
|
||||
| `enterprise.config.unlock_anonymous_git_access` | A site admin unlocks anonymous Git read access to allow repository admins to change existing anonymous Git read access settings for repositories in the enterprise. For more information, see "[Enforcing repository management policies in your enterprise](/admin/policies/enforcing-repository-management-policies-in-your-enterprise#configuring-anonymous-git-read-access)." |
|
||||
| Name | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| -------------------------------------------------------:| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `business.update_member_repository_creation_permission` | A site admin restricts repository creation in organizations in the enterprise. For more information, see "[Enforcing repository management policies in your enterprise](/admin/policies/enforcing-repository-management-policies-in-your-enterprise#setting-a-policy-for-repository-creation)." |
|
||||
| `business.clear_members_can_create_repos` | A site admin clears a restriction on repository creation in organizations in the enterprise. For more information, see "[Enforcing repository management policies in your enterprise](/admin/policies/enforcing-repository-management-policies-in-your-enterprise#setting-a-policy-for-repository-creation)."{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
| `enterprise.config.lock_anonymous_git_access` | A site admin locks anonymous Git read access to prevent repository admins from changing existing anonymous Git read access settings for repositories in the enterprise. For more information, see "[Enforcing repository management policies in your enterprise](/admin/policies/enforcing-repository-management-policies-in-your-enterprise#configuring-anonymous-git-read-access)." |
|
||||
| `enterprise.config.unlock_anonymous_git_access` | A site admin unlocks anonymous Git read access to allow repository admins to change existing anonymous Git read access settings for repositories in the enterprise. For more information, see "[Enforcing repository management policies in your enterprise](/admin/policies/enforcing-repository-management-policies-in-your-enterprise#configuring-anonymous-git-read-access)."{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Issues und Pull Requests
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ versions:
|
||||
|
||||
| Name | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------------:| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `repo.access` | Ein privates Repository wurde als öffentlich festgelegt, oder ein öffentliches Repository wurde als privat festgelegt. |
|
||||
| `repo.access` | The visibility of a repository changed to private{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}, public,{% endif %} or internal. |
|
||||
| `repo.archive` | Ein Repository wurde archiviert. For more information, see "[Archiving a {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} repository](/github/creating-cloning-and-archiving-repositories/archiving-a-github-repository)." |
|
||||
| `repo.add_member` | Einem Repository wurde ein Mitarbeiter hinzugefügt. |
|
||||
| `repo.config` | Ein Websiteadministrator hat erzwungene Push-Vorgänge blockiert. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Erzwungene Push-Vorgänge an ein Repository blockieren](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/admin/guides/developer-workflow/blocking-force-pushes-to-a-repository/)“. |
|
||||
@@ -89,11 +89,11 @@ versions:
|
||||
| `repo.rename` | Ein Repository wurde umbenannt. |
|
||||
| `repo.transfer` | Ein Benutzer hat eine Anfrage akzeptiert, ein übertragenes Repository zu empfangen. |
|
||||
| `repo.transfer_start` | Ein Benutzer hat eine Anfrage gesendet, ein Repository an einen anderen Benutzer oder an eine andere Organisation zu übertragen. |
|
||||
| `repo.unarchive` | Die Archivierung eines Repositorys wurde aufgehoben. For more information, see "[Archiving a {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} repository](/github/creating-cloning-and-archiving-repositories/archiving-a-github-repository)." |
|
||||
| `repo.config.disable_anonymous_git_access` | Der anonyme Git-Lesezugriff ist für ein öffentliches Repository deaktiviert. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Anonymen Git-Lesezugriff für ein Repository aktivieren](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/user/articles/enabling-anonymous-git-read-access-for-a-repository)“. |
|
||||
| `repo.config.enable_anonymous_git_access` | Der anonyme Git-Lesezugriff ist für ein öffentliches Repository aktiviert. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Anonymen Git-Lesezugriff für ein Repository aktivieren](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/user/articles/enabling-anonymous-git-read-access-for-a-repository)“. |
|
||||
| `repo.unarchive` | Die Archivierung eines Repositorys wurde aufgehoben. For more information, see "[Archiving a {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} repository](/github/creating-cloning-and-archiving-repositories/archiving-a-github-repository)."{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
| `repo.config.disable_anonymous_git_access` | Anonymous Git read access is disabled for a repository. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Anonymen Git-Lesezugriff für ein Repository aktivieren](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/user/articles/enabling-anonymous-git-read-access-for-a-repository)“. |
|
||||
| `repo.config.enable_anonymous_git_access` | Anonymous Git read access is enabled for a repository. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Anonymen Git-Lesezugriff für ein Repository aktivieren](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/user/articles/enabling-anonymous-git-read-access-for-a-repository)“. |
|
||||
| `repo.config.lock_anonymous_git_access` | Die Einstellung für den anonymen Git-Lesezugriff eines Repositorys ist gesperrt, wodurch Repository-Administratoren daran gehindert werden, diese Einstellung zu ändern (zu aktivieren oder zu deaktivieren). Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Änderung des anonymen Git-Lesezugriffs durch Benutzer verhindern](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/admin/guides/user-management/preventing-users-from-changing-anonymous-git-read-access)“. |
|
||||
| `repo.config.unlock_anonymous_git_access` | Die Einstellung für den anonymen Git-Lesezugriff ist entsperrt, wodurch Repository-Administratoren diese Einstellung ändern (aktivieren oder deaktivieren) können. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Änderung des anonymen Git-Lesezugriffs durch Benutzer verhindern](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/admin/guides/user-management/preventing-users-from-changing-anonymous-git-read-access)“. |
|
||||
| `repo.config.unlock_anonymous_git_access` | Die Einstellung für den anonymen Git-Lesezugriff ist entsperrt, wodurch Repository-Administratoren diese Einstellung ändern (aktivieren oder deaktivieren) können. For more information, see "[Preventing users from changing anonymous Git read access](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/admin/guides/user-management/preventing-users-from-changing-anonymous-git-read-access)."{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Websiteadministratortools
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ redirect_from:
|
||||
- /enterprise/admin/categories/admin-bootcamp/
|
||||
- /enterprise/admin/user-management/organizations-and-teams
|
||||
- /enterprise/admin/user-management/managing-organizations-in-your-enterprise
|
||||
intro: 'Organisationen eignen sich ideal zum Erstellen von getrennten Benutzergruppen in Ihrem Unternehmen, beispielsweise Abteilungen oder Gruppen, die an ähnlichen Projekten arbeiten. Benutzer in anderen Organisationen können auf öffentliche Repositorys zugreifen, die zu einer Organisation gehören. Demgegenüber können auf private Repositorys nur Mitglieder der Organisation zugreifen.'
|
||||
intro: 'Organisationen eignen sich ideal zum Erstellen von getrennten Benutzergruppen in Ihrem Unternehmen, beispielsweise Abteilungen oder Gruppen, die an ähnlichen Projekten arbeiten. {% if currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}Internal{% else %}Public and internal{% endif %} repositories that belong to an organization are accessible to users in other organizations, while private repositories are inaccessible to anyone but members of the organization that are granted access.'
|
||||
mapTopic: true
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
enterprise-server: '*'
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -114,11 +114,13 @@ curl -H "Authorization: token OAUTH-TOKEN" {% data variables.product.api_url_pre
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.21" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
### Device flow
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion ver_lt "enterprise-server@3.1" %}
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** The device flow is in public beta and subject to change.{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %} To enable this beta feature, see "[Activating beta features for apps](/developers/apps/activating-beta-features-for-apps)."{% endif %}
|
||||
**Note:** The device flow is in public beta and subject to change.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
The device flow allows you to authorize users for a headless app, such as a CLI tool or Git credential manager.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -123,11 +123,13 @@ curl -H "Authorization: token OAUTH-TOKEN" {% data variables.product.api_url_pre
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.21" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
### Device flow
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion ver_lt "enterprise-server@3.1" %}
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** The device flow is in public beta and subject to change.{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %} To enable this beta feature, see "[Activating beta features for apps](/developers/apps/activating-beta-features-for-apps)."{% endif %}
|
||||
**Note:** The device flow is in public beta and subject to change.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
The device flow allows you to authorize users for a headless app, such as a CLI tool or Git credential manager.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1288,7 +1288,7 @@ The event’s actor is the [user](/v3/users/) who starred a repository, and the
|
||||
|
||||
{{ webhookPayloadsForCurrentVersion.watch.started }}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.21" %}
|
||||
### workflow_dispatch
|
||||
|
||||
This event occurs when someone triggers a workflow run on GitHub or sends a `POST` request to the "[Create a workflow dispatch event](/rest/reference/actions/#create-a-workflow-dispatch-event)" endpoint. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter "[Ereignisse, die Workflows auslösen](/actions/reference/events-that-trigger-workflows#workflow_dispatch)."
|
||||
@@ -1302,9 +1302,10 @@ This event occurs when someone triggers a workflow run on GitHub or sends a `POS
|
||||
{{ webhookPayloadsForCurrentVersion.workflow_dispatch }}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.22" %}
|
||||
### workflow_run
|
||||
|
||||
When a {% data variables.product.prodname_actions %} workflow run is requested or completed. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter "[Ereignisse, die Workflows auslösen](/actions/reference/events-that-trigger-workflows#workflow_run)."
|
||||
When a {% data variables.product.prodname_actions %} workflow run is requested or completed. For more information, see "[Events that trigger workflows](/actions/reference/events-that-trigger-workflows#workflow_run)."
|
||||
|
||||
#### Availability
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1322,3 +1323,4 @@ When a {% data variables.product.prodname_actions %} workflow run is requested o
|
||||
#### Webhook payload example
|
||||
|
||||
{{ webhookPayloadsForCurrentVersion.workflow_run }}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -18,6 +18,8 @@ Dienstleister können mit {% data variables.product.company_short %} zusammenarb
|
||||
|
||||
### Informationen über {% data variables.product.prodname_secret_scanning %} für öffentliche Repositorys
|
||||
|
||||
{% data variables.product.prodname_secret_scanning_caps %} is automatically enabled on public repositories, where it scans code for secrets, to check for known secret formats. When a match of your secret format is found in a public repository, {% data variables.product.company_short %} doesn't publicly disclose the information as an alert, but instead sends a payload to an HTTP endpoint of your choice. For an overview of how secret scanning works on public repositories, see "[Secret scanning](/developers/overview/secret-scanning)."
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Du in ein öffentliches Repository überträgst, wird {% data variables.product.product_name %} den Inhalt des Commit auf Geheimnisse durchsuchen. Wenn Du ein privates Repository auf öffentlich umstellst, wird {% data variables.product.product_name %} das gesamte Repository nach Geheimnissen durchsuchen.
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn {% data variables.product.prodname_secret_scanning %} einen Satz von Anmeldeinformationen erkennt, benachrichtigen wir den Dienstanbieter, der das Geheimnis ausgegeben hat. Der Dienstanbieter prüft die Anmeldeinformationen und entscheidet dann, ob er das Geheimnis widerrufen, ein neues Geheimnis ausstellen oder sich direkt an Dich wenden soll, was von den damit verbundenen Risiken für Dich oder den Dienstleister abhängt.
|
||||
@@ -65,6 +67,8 @@ Wenn {% data variables.product.prodname_secret_scanning %} einen Satz von Anmeld
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.secret-scanning.beta %}
|
||||
|
||||
If you're a repository administrator or an organization owner, you can enable {% data variables.product.prodname_secret_scanning %} for private repositories that are owned by organizations. You can enable {% data variables.product.prodname_secret_scanning %} for all your repositories, or for all new repositories within your organization. {% data variables.product.prodname_secret_scanning_caps %} is not available for user account-owned private repositories. For more information, see "[Managing security and analysis settings for your repository](/github/administering-a-repository/managing-security-and-analysis-settings-for-your-repository)" and "[Managing security and analysis settings for your organization](/github/setting-up-and-managing-organizations-and-teams/managing-security-and-analysis-settings-for-your-organization)."
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Du Commits in ein privates Repository überträgst, das {% data variables.product.prodname_secret_scanning %} aktiviert hat, wird {% data variables.product.product_name %} den Inhalt des Commits nach Geheimnissen durchsuchen.
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn {% data variables.product.prodname_secret_scanning %} ein Geheimnis in einem privaten Repository entdeckt, wird {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} Warnungen senden.
|
||||
@@ -73,6 +77,8 @@ Wenn {% data variables.product.prodname_secret_scanning %} ein Geheimnis in eine
|
||||
|
||||
- {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} zeigt eine Warnung im Repository an. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Warnungen von {% data variables.product.prodname_secret_scanning %} verwalten](/github/administering-a-repository/managing-alerts-from-secret-scanning)."
|
||||
|
||||
Repository administrators and organization owners can grant users and team access to {% data variables.product.prodname_secret_scanning %} alerts. For more information, see "[Managing security and analysis settings for your repository](/github/administering-a-repository/managing-security-and-analysis-settings-for-your-repository#granting-access-to-security-alerts)."
|
||||
|
||||
{% data variables.product.product_name %} durchsucht derzeit private Repositorys nach Geheimnissen, die von den folgenden Dienstanbietern veröffentlicht wurden.
|
||||
|
||||
- Adafruit
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ Rufe https://github.com/topics/ auf, um die am häufigsten verwendeten Themen zu
|
||||
|
||||
Repository-Administratoren können beliebige Themen zu einem Repository hinzufügen. Helpful topics to classify a repository include the repository's intended purpose, subject area, community, or language.{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %} Additionally, {% data variables.product.product_name %} analyzes public repository content and generates suggested topics that repository admins can accept or reject. Die Inhalte privater Repositorys werden nicht analysiert, und es gibt keine Themenvorschläge für private Repositorys.{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
Öffentliche und private Repositorys können Themen haben, aber in den Resultaten der Themensuche wirst Du nur die privaten Repositorys sehen, auf die Du Zugriff hast.
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}Internal {% else %}Public, internal, {% endif %}and private repositories can have topics, although you will only see private repositories that you have access to in topic search results.
|
||||
|
||||
Du kannst nach Repositorys suchen, die mit einem bestimmten Thema verknüpft sind. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Nach Repositorys suchen](/articles/searching-for-repositories/#search-by-topic)“. Sie können auch nach einer Liste von Themen auf {% data variables.product.product_name %} suchen. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Themen suchen](/articles/searching-topics).“
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ versions:
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Du noch kein Bild hinzugefügt hast, werden sich Repository-Links erweitern, um grundlegende Informationen zum Repository sowie den Avatar des Inhabers anzeigen. Durch das Hinzufügen eines Bildes zu Deinem Repository vereinfachst Du die Identifizierung Deines Projekts auf den verschiedenen Social-Media-Kanälen.
|
||||
|
||||
Du kannst ein Bild in ein privates Repository hochladen, aber Dein Bild kann nur von einem öffentlichen Repository her geteilt werden.
|
||||
{% if currentVersion != "github-ae@latest" %}You can upload an image to a private repository, but your image can only be shared from a public repository.{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% tip %}
|
||||
Tipp: Dein Bild sollte eine PNG-, JPG- oder GIF-Datei mit weniger als 1 MB sein. Für eine optimale Darstellung empfehlen wir eine Bildgröße von 640 x 320 Pixeln.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -13,17 +13,16 @@ versions:
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.organizations.owners-and-admins-can %} ein Organisations-Repository löschen. Wenn **Allow members to delete or transfer repositories for this organization** (Mitgliedern das Löschen oder Übertragen von Repositorys für diese Organisation erlauben) deaktiviert wurde, können nur Organisationsinhaber Repositorys der Organisation löschen. {% data reusables.organizations.new-repo-permissions-more-info %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
{% if currentVersion != "github-ae@latest" %}Deleting a public repository will not delete any forks of the repository.{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% warning %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Warnung**: Wenn Du ein Repository löschst, werden die Releaseanhänge und Teamberechtigungen **dauerhaft** gelöscht. Diese Aktion **kann nicht** rückgängig gemacht werden.
|
||||
**Warnings**:
|
||||
|
||||
- Deleting a repository will **permanently** delete release attachments and team permissions. Diese Aktion **kann nicht** rückgängig gemacht werden.
|
||||
- Deleting a private {% if currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" or currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}or internal {% endif %}repository will delete all forks of the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endwarning %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
Beachte auch Folgendes:
|
||||
- Beim Löschen eines privaten Repositorys werden all seine Forks ebenfalls gelöscht.
|
||||
- Beim Löschen eines öffentlichen Repositorys werden seine Forks nicht gelöscht.
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
Bestimmte gelöschte Repositorys können innerhalb von 90 Tagen wiederhergestellt werden. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Ein gelöschtes Repository wiederherstellen](/articles/restoring-a-deleted-repository).“
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,7 +5,6 @@ redirect_from:
|
||||
- /articles/enabling-anonymous-git-read-access-for-a-repository
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
enterprise-server: '*'
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Repository-Administratoren können die Einstellung für den anonymen Git-Lesezugriff für ein bestimmtes Repository ändern, wenn folgende Voraussetzungen erfüllt sind:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Repository-Einstellungen verwalten
|
||||
intro: 'Repository-Administratoren und Organisationsinhaber können mehrere Einstellungen ändern, beispielsweise die Namen und die Inhaberschaft eines Repositorys und die Sichtbarkeit (privat oder öffentlich) eines Repositorys. Sie können ein Repository auch löschen.'
|
||||
intro: 'Repository administrators and organization owners can change settings for a repository, like the name, ownership, and visibility, or delete the repository.'
|
||||
mapTopic: true
|
||||
redirect_from:
|
||||
- /articles/managing-repository-settings
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,28 +22,28 @@ versions:
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-security-and-analysis %}
|
||||
4. Under "Configure security and analysis features", to the right of the feature, click **Disable** or **Enable**. 
|
||||
|
||||
### Granting access to {% data variables.product.prodname_dependabot_alerts %}
|
||||
### Zugriff auf Sicherheitsmeldungen gewähren
|
||||
|
||||
After you enable {% data variables.product.prodname_dependabot_alerts %} for a repository in an organization, organization owners and repository administrators can view the alerts by default. You can give additional teams and people access to the alerts for a repository.
|
||||
After you enable {% data variables.product.prodname_dependabot %} or {% data variables.product.prodname_secret_scanning %} alerts for a repository in an organization, organization owners and repository administrators can view the alerts by default. You can give additional teams and people access to the alerts for a repository.
|
||||
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
|
||||
Organization owners and repository administrators can only grant access to view {% data variables.product.prodname_dependabot_alerts %} to people or teams who have write access to the repo.
|
||||
Organization owners and repository administrators can only grant access to view security alerts, such as {% data variables.product.prodname_dependabot %} and {% data variables.product.prodname_secret_scanning %} alerts, to people or teams who have write access to the repo.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.sidebar-settings %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-security-and-analysis %}
|
||||
4. Under "Dependabot alerts", in the search field, start typing the name of the person or team you'd like to find, then click a name in the list of matches. 
|
||||
5. Klicke auf **Save changes** (Änderungen speichern). 
|
||||
4. Under "Access to alerts", in the search field, start typing the name of the person or team you'd like to find, then click a name in the list of matches. 
|
||||
5. Klicke auf **Save changes** (Änderungen speichern). 
|
||||
|
||||
### Removing access to {% data variables.product.prodname_dependabot_alerts %}
|
||||
### Zugriff auf Sicherheitsmeldungen entfernen
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.sidebar-settings %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-security-and-analysis %}
|
||||
4. Under "Dependabot alerts", to the right of the person or team whose access you'd like to remove, click {% octicon "x" aria-label="X symbol" %}. 
|
||||
4. Under "Access to alerts", to the right of the person or team whose access you'd like to remove, click {% octicon "x" aria-label="X symbol" %}. 
|
||||
|
||||
### Weiterführende Informationen
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -19,17 +19,36 @@ Organisationsinhaber können die Möglichkeit, die Sichtbarkeit des Repositorys
|
||||
We recommend reviewing the following caveats before you change the visibility of a repository.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Repository als privat festlegen
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
* {% data variables.product.product_name %} will detach public forks of the public repository and put them into a new network. Public forks are not made private.{% endif %}
|
||||
* If you change a repository's visibility from internal to private, {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} will remove forks that belong to any user without access to the newly private repository. {% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}The visibility of any forks will also change to private.{% elsif currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}If the internal repository has any forks, the visibility of the forks is already private.{% endif %} For more information, see "[What happens to forks when a repository is deleted or changes visibility?](/articles/what-happens-to-forks-when-a-repository-is-deleted-or-changes-visibility)"{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
* If you're using {% data variables.product.prodname_free_user %} for user accounts or organizations, some features won't be available in the repository after you change the visibility to private. {% data reusables.gated-features.more-info %}{% endif %}
|
||||
* Any published {% data variables.product.prodname_pages %} site will be automatically unpublished.{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %} If you added a custom domain to the {% data variables.product.prodname_pages %} site, you should remove or update your DNS records before making the repository private, to avoid the risk of a domain takeover. For more information, see "[Managing a custom domain for your {% data variables.product.prodname_pages %} site](/articles/managing-a-custom-domain-for-your-github-pages-site)."{% endif %}{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
* {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} will no longer included the repository in the {% data variables.product.prodname_archive %}. For more information, see "[About archiving content and data on {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}](/github/creating-cloning-and-archiving-repositories/about-archiving-content-and-data-on-github#about-the-github-archive-program)."{% endif %}{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
* Anonymous Git read access is no longer available. For more information, see "[Enabling anonymous Git read access for a repository](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/user/articles/enabling-anonymous-git-read-access-for-a-repository)."{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
* {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} will detach public forks of the public repository and put them into a new network. Öffentliche Forks werden nicht in private Forks umgewandelt. {% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" %}If you change a repository's visibility from internal to private, {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} will remove forks that belong to any user without access to the newly private repository.{% endif %} For more information, see "[What happens to forks when a repository is deleted or changes visibility?](/articles/what-happens-to-forks-when-a-repository-is-deleted-or-changes-visibility#changing-a-public-repository-to-a-private-repository)"
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}* If you're using {% data variables.product.prodname_free_user %} for user accounts or organizations, some features won't be available in the repository after you change the visibility to private. {% data reusables.gated-features.more-info %}
|
||||
* Jede veröffentlichte {% data variables.product.prodname_pages %}-Website wird automatisch zurückgezogen. Wenn Sie Ihrer {% data variables.product.prodname_pages %}-Website eine benutzerdefinierte Domain hinzugefügt hatten, sollten Sie Ihre DNS-Einträge vor der Umschaltung des Repositorys in ein privates Repository entfernen oder aktualisieren, um das Risiko eines Domain-Takeovers auszuschließen. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Eine benutzerdefinierte Domäne für Deine {% data variables.product.prodname_pages %}-Website verwalten](/articles/managing-a-custom-domain-for-your-github-pages-site).“
|
||||
* {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} will no longer included the repository in the {% data variables.product.prodname_archive %}. For more information, see "[About archiving content and data on {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}](/github/creating-cloning-and-archiving-repositories/about-archiving-content-and-data-on-github#about-the-github-archive-program)."{% endif %}
|
||||
{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}* Anonymous Git read access is no longer available. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Anonymen Git-Lesezugriff für ein Repository aktivieren](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/user/articles/enabling-anonymous-git-read-access-for-a-repository)“.{% endif %}
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Repository als intern festlegen
|
||||
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** {% data reusables.gated-features.internal-repos %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
|
||||
* Any forks of the repository will remain in the repository network, and {% data variables.product.product_name %} maintains the relationship between the root repository and the fork. For more information, see "[What happens to forks when a repository is deleted or changes visibility?](/articles/what-happens-to-forks-when-a-repository-is-deleted-or-changes-visibility)"
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Repository als öffentlich festlegen
|
||||
|
||||
* {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} will detach private forks and turn them into a standalone private repository. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Was geschieht mit Forks, wenn ein Repository gelöscht wird oder sich dessen Sichtbarkeit ändert?](/articles/what-happens-to-forks-when-a-repository-is-deleted-or-changes-visibility#changing-a-private-repository-to-a-public-repository).“
|
||||
* If you're converting your private repository to a public repository as part of a move toward creating an open source project, see the [Open Source Guides](http://opensource.guide) for helpful tips and guidelines.{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %} You can also take a free course on managing an open source project with [{% data variables.product.prodname_learning %}]({% data variables.product.prodname_learning_link %}). Sobald Dein Repository der Öffentlichkeit zugänglich ist, kannst Du im Community-Profil des Repositorys überprüfen, ob Dein Projekt die Best Practices zur Unterstützung von Mitarbeitern erfüllt. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Community-Profil anzeigen](/articles/viewing-your-community-profile)“.{% endif %}
|
||||
* {% data variables.product.product_name %} will detach private forks and turn them into a standalone private repository. For more information, see "[What happens to forks when a repository is deleted or changes visibility?](/articles/what-happens-to-forks-when-a-repository-is-deleted-or-changes-visibility#changing-a-private-repository-to-a-public-repository)"{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
* If you're converting your private repository to a public repository as part of a move toward creating an open source project, see the [Open Source Guides](http://opensource.guide) for helpful tips and guidelines. You can also take a free course on managing an open source project with [{% data variables.product.prodname_learning %}]({% data variables.product.prodname_learning_link %}). Sobald Dein Repository der Öffentlichkeit zugänglich ist, kannst Du im Community-Profil des Repositorys überprüfen, ob Dein Projekt die Best Practices zur Unterstützung von Mitarbeitern erfüllt. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Community-Profil anzeigen](/articles/viewing-your-community-profile)“.{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.21" %}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ versions:
|
||||
free-pro-team: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Zum Hosten Ihrer Bilder verwendet {% data variables.product.product_name %} den [Open-Source-Projekt-Camo](https://github.com/atmos/camo). Camo erzeugt für jedes Bild, das mit `https://camo.githubusercontent.com/` beginnt, einen anonymen URL-Proxy und verbirgt Deine Browserdaten und ähnliche Informationen vor anderen Benutzern.
|
||||
Zum Hosten Ihrer Bilder verwendet {% data variables.product.product_name %} den [Open-Source-Projekt-Camo](https://github.com/atmos/camo). Camo generates an anonymous URL proxy for each image which hides your browser details and related information from other users. The URL starts `https://<subdomain>.githubusercontent.com/`, with different subdomains depending on how you uploaded the image.
|
||||
|
||||
Jeder, der Deine anonymisierte Bild-URL direkt oder indirekt erhält, kann Dein Bild anzeigen. Beschränke vertrauliche Bilder zu deren Schutz auf ein privates Netzwerk oder einen Server, der eine Authentifizierung erfordert, anstatt Camo zu verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -24,8 +24,8 @@ Nachdem Sie einen neuen SSH-Schlüssel zu Ihrem {% data variables.product.produc
|
||||
Wenn Deine SSH-Schlüsseldatei einen anderen Namen hat als die Datei im Beispielcode, passe den Dateinamen entsprechend an. Achte beim Kopieren des Schlüssels darauf, keine neuen Zeilen oder Leerzeichen hinzuzufügen.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ pbcopy < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
|
||||
# Kopiert den Inhalt der Datei id_rsa.pub in die Zwischenablage
|
||||
$ pbcopy < ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
|
||||
# Copies the contents of the id_ed25519.pub file to your clipboard
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{% tip %}
|
||||
@@ -51,8 +51,8 @@ Nachdem Sie einen neuen SSH-Schlüssel zu Ihrem {% data variables.product.produc
|
||||
Wenn Deine SSH-Schlüsseldatei einen anderen Namen hat als die Datei im Beispielcode, passe den Dateinamen entsprechend an. Achte beim Kopieren des Schlüssels darauf, keine neuen Zeilen oder Leerzeichen hinzuzufügen.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ clip < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
|
||||
# Kopiert den Inhalt der Datei id_rsa.pub in die Zwischenablage
|
||||
$ clip < ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
|
||||
# Copies the contents of the id_ed25519.pub file to your clipboard
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{% tip %}
|
||||
@@ -81,8 +81,8 @@ Nachdem Sie einen neuen SSH-Schlüssel zu Ihrem {% data variables.product.produc
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install xclip
|
||||
# Herunterladen und installieren von xclip. If you don't have `apt-get`, you might need to use another installer (like `yum`)
|
||||
|
||||
$ xclip -selection clipboard < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
|
||||
# Copies the contents of the id_rsa.pub file to your clipboard
|
||||
$ xclip -selection clipboard < ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
|
||||
# Copies the contents of the id_ed25519.pub file to your clipboard
|
||||
```
|
||||
{% tip %}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -98,13 +98,19 @@ Bevor Du einen neuen SSH-Schlüssel zum SSH-Agenten für die Verwaltung Deiner S
|
||||
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_ed25519
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** If you chose not to add a passphrase to your key, you should omit the `UseKeychain` line.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
|
||||
3. Fügen Sie Ihren privaten SSH-Schlüssel zu ssh-agent hinzu, und speichern Sie Ihre Passphrase in der Keychain. {% data reusables.ssh.add-ssh-key-to-ssh-agent %}
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ ssh-add -K ~/.ssh/id_ed25519
|
||||
```
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Hinweis:** Die Option `-K` ist die Standardversion von `ssh-add` von Apple, bei der die Passphrase für das Hinzufügen eines SSH-Schlüssels zum SSH-Agenten in Deiner Keychain gespeichert wird.
|
||||
**Hinweis:** Die Option `-K` ist die Standardversion von `ssh-add` von Apple, bei der die Passphrase für das Hinzufügen eines SSH-Schlüssels zum SSH-Agenten in Deiner Keychain gespeichert wird. If you chose not to add a passphrase to your key, run the command without the `-K` option.
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie die Standardversion von Apple nicht installiert haben, tritt möglicherweise ein Fehler auf. Weitere Informationen zum Beheben dieses Fehlers finden Sie unter [Fehler: „ssh-add: illegal option -- K“](/articles/error-ssh-add-illegal-option-k)“.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Dein Sicherheitsprotokoll überprüfen
|
||||
intro: Du kannst das Sicherheitsprotokoll für Dein Benutzerkonto überprüfen, um Dich betreffende Aktionen besser zu verstehen, die von Dir oder anderen Benutzern durchgeführt wurden.
|
||||
miniTocMaxHeadingLevel: 4
|
||||
redirect_from:
|
||||
- /articles/reviewing-your-security-log
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
@@ -30,210 +31,26 @@ The security log lists all actions performed within the last 90 days{% if curren
|
||||
#### Suche nach der Art der durchgeführten Aktion
|
||||
{% else %}
|
||||
### Ereignisse im Sicherheitsprotokoll verstehen
|
||||
|
||||
Die Aktionen in Deinem Sicherheitsprotokoll sind nach folgenden Kategorien gruppiert:{% endif %}
|
||||
| Kategoriename | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| --------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
| `account_recovery_token` | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit dem [Hinzufügen eines Wiederherstellungstokens](/articles/configuring-two-factor-authentication-recovery-methods). |
|
||||
| `Abrechnung` | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit Deinen Abrechnungsinformationen. |
|
||||
| `marketplace_agreement_signature (Unterzeichnung Marketplace-Vereinbarung)` | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit der Signierung der {% data variables.product.prodname_marketplace %}-Entwicklervereinbarung. |
|
||||
| `marketplace_listing (Eintrag auf Marketplace)` | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit dem Eintragen von Apps auf {% data variables.product.prodname_marketplace %}.{% endif %}
|
||||
| `oauth_access` | Contains all activities related to [{% data variables.product.prodname_oauth_app %}s](/articles/authorizing-oauth-apps) you've connected with.{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
| `payment_method` | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit der Bezahlung Deines {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}-Abonnements.{% endif %}
|
||||
| `profile_picture` | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit Deinem Profilbild. |
|
||||
| `project (Projekt)` | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit Projektboards. |
|
||||
| `public_key` | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit [Deinen öffentlichen SSH-Schlüsseln](/articles/adding-a-new-ssh-key-to-your-github-account). |
|
||||
| `repo` | Contains all activities related to the repositories you own.{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
| `sponsors` | Contains all events related to {% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} and sponsor buttons (see "[About {% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %}](/articles/about-github-sponsors)" and "[Displaying a sponsor button in your repository](/articles/displaying-a-sponsor-button-in-your-repository)"){% endif %}{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
| `Team` | Contains all activities related to teams you are a part of.{% endif %}{% if currentVersion != "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
| `two_factor_authentication` | Contains all activities related to [two-factor authentication](/articles/securing-your-account-with-two-factor-authentication-2fa).{% endif %}
|
||||
| `Benutzer` | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit Deinem Konto. |
|
||||
|
||||
Eine Beschreibung der Ereignisse dieser Kategorien findest Du nachfolgend.
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Kategorie `account_recovery_token`
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| confirm | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du [ein neues Token erfolgreich bei einem Wiederherstellungsanbieter speicherst](/articles/configuring-two-factor-authentication-recovery-methods). |
|
||||
| recover | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du [ein Kontowiederherstellungstoken erfolgreich einlöst](/articles/recovering-your-account-if-you-lose-your-2fa-credentials). |
|
||||
| recover_error | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Token verwendet wird, {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} dieses aber nicht validieren kann. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Kategorie `billing` (Abrechnung)
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| --------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| change_billing_type | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie Ihre [Zahlungsmethode](/articles/adding-or-editing-a-payment-method) für {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} ändern. |
|
||||
| change_email | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du [Deine E-Mail-Adresse änderst](/articles/changing-your-primary-email-address). |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Kategorie `marketplace_agreement_signature`
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| create | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du die {% data variables.product.prodname_marketplace %}-Entwicklervereinbarung signierst. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Kategorie `marketplace_listing` (Eintrag auf Marketplace)
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ---------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| genehmigen | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Dein Eintrag für die Aufnahme in {% data variables.product.prodname_marketplace %} genehmigt wird. |
|
||||
| create | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du einen Eintrag für Deine App in {% data variables.product.prodname_marketplace %} erstellst. |
|
||||
| delist | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Ihr Listing von {% data variables.product.prodname_marketplace %} entfernt wird. |
|
||||
| redraft | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Dein Eintrag in den Entwurfsstatus zurückversetzt wird. |
|
||||
| reject | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Dein Eintrag für die Aufnahme in {% data variables.product.prodname_marketplace %} nicht genehmigt wird. |
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Kategorie `oauth_access`
|
||||
The events listed in your security log are triggered by your actions. Actions are grouped into the following categories:
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| create | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie einer [{% data variables.product.prodname_oauth_app %} Zugriff erteilen](/articles/authorizing-oauth-apps). |
|
||||
| destroy | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie einer [{% data variables.product.prodname_oauth_app %} den Zugriff auf Ihr Konto entziehen](/articles/reviewing-your-authorized-integrations). |
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Kategorie `payment_method`
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| clear | Wird ausgelöst, wenn eine [registrierte Zahlungsmethode](/articles/removing-a-payment-method) entfernt wird. |
|
||||
| create | Wird ausgelöst, wenn eine Zahlungsmethode, beispielsweise eine Kreditkarte oder ein PayPal-Konto, hinzugefügt wird. |
|
||||
| aktualisieren | Wird ausgelöst, wenn eine vorhandene Zahlungsmethode geändert wird. |
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Kategorie `profile_picture`
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| aktualisieren | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du [Dein Profilbild festlegst oder änderst](/articles/setting-your-profile-picture/). |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Kategorie `project`
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ------------------------ | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `create` | Wird bei der Erstellung eines Projektboards ausgelöst. |
|
||||
| `rename` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Projektboard umbenannt wird. |
|
||||
| `aktualisieren` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Projektboard geändert wird. |
|
||||
| `delete` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Projektboard gelöscht wird. |
|
||||
| `link` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Repository mit einem Projektboard verknüpft wird. |
|
||||
| `unlink` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn die Verknüpfung eines Repositorys mit einem Projektboard aufgehoben wird. |
|
||||
| `project.access` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn die Sichtbarkeit eines Projektboards geändert wird. |
|
||||
| `update_user_permission` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein externer Mitarbeiter einem Projektboard hinzugefügt oder entfernt wird oder wenn sich seine Berechtigungsebene verändert. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Kategorie `public_key`
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| create | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie [Ihrem {% data variables.product.product_name %}-Konto einen neuen öffentlichen SSH-Schlüssel hinzufügen](/articles/adding-a-new-ssh-key-to-your-github-account). |
|
||||
| delete | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie [einen öffentlichen SSH-Schlüssel aus Ihrem {% data variables.product.product_name %}-Konto entfernen](/articles/reviewing-your-ssh-keys). |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Kategorie `repo`
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| access | Wird ausgelöst, wenn die Sichtbarkeit eines Repositorys, dessen Inhaber Du bist, [von „privat“ auf „öffentlich“ gesetzt wird](/articles/making-a-private-repository-public) (oder umgekehrt). |
|
||||
| add_member | Triggered when a {% data variables.product.product_name %} user is {% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}[invited to have collaboration access](/articles/inviting-collaborators-to-a-personal-repository){% else %}[given collaboration access](/articles/inviting-collaborators-to-a-personal-repository){% endif %} to a repository. |
|
||||
| add_topic | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Repository-Inhaber einem Repository [ein Thema hinzufügt](/articles/classifying-your-repository-with-topics). |
|
||||
| archived | Triggered when a repository owner [archives a repository](/articles/about-archiving-repositories).{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
| config.disable_anonymous_git_access | Wird ausgelöst, wenn für ein öffentliches Repository der [anonyme Git-Lesezugriff deaktiviert](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/user/articles/enabling-anonymous-git-read-access-for-a-repository) wird. |
|
||||
| config.enable_anonymous_git_access | Wird ausgelöst, wenn für ein öffentliches Repository der [anonyme Git-Lesezugriff aktiviert](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/user/articles/enabling-anonymous-git-read-access-for-a-repository) wird. |
|
||||
| config.lock_anonymous_git_access | Wird ausgelöst, wenn für ein Repository die [Einstellung für den anonymen Git-Lesezugriff gesperrt](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/admin/guides/user-management/preventing-users-from-changing-anonymous-git-read-access) wird. |
|
||||
| config.unlock_anonymous_git_access | Wird ausgelöst, wenn für ein Repository die [Einstellungssperre für den anonymen Git-Lesezugriff aufgehoben](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/admin/guides/user-management/preventing-users-from-changing-anonymous-git-read-access) wird.{% endif %}
|
||||
| create | Wird ausgelöst, wenn [ein neues Repository erstellt](/articles/creating-a-new-repository) wird. |
|
||||
| destroy | Triggered when [a repository is deleted](/articles/deleting-a-repository).{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
| deaktivieren | Triggered when a repository is disabled (e.g., for [insufficient funds](/articles/unlocking-a-locked-account)).{% endif %}{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
| aktivieren | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Repository wieder aktiviert wird.{% endif %}
|
||||
| remove_member | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein {% data variables.product.product_name %}-Benutzer [als Mitarbeiter aus einem Repository entfernt wird](/articles/removing-a-collaborator-from-a-personal-repository). |
|
||||
| remove_topic | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Repository-Inhaber ein Thema aus einem Repository entfernt. |
|
||||
| rename | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein [Repository umbenannt](/articles/renaming-a-repository) wird. |
|
||||
| übertragen | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein [Repository übertragen](/articles/how-to-transfer-a-repository) wird. |
|
||||
| transfer_start | Wird ausgelöst, wenn die Übertragung eines Repositorys initiiert wurde. |
|
||||
| unarchived | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Repository-Inhaber die Archivierung eines Repositorys aufhebt. |
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
#### Kategorie `sponsors`
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ----------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| repo_funding_link_button_toggle | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du eine Sponsorenschaltfläche in Deinem Repository aktivierst oder deaktivierst (siehe „[Sponsorenschaltfläche in Deinem Repository anzeigen](/articles/displaying-a-sponsor-button-in-your-repository)“) |
|
||||
| repo_funding_links_file_action | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du die FUNDING-Datei in Deinem Repository änderst (siehe „[Sponsorenschaltfläche in Deinem Repository anzeigen](/articles/displaying-a-sponsor-button-in-your-repository)“) |
|
||||
| sponsor_sponsorship_cancel | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du ein Sponsoring beendest (siehe „[Sponsoring herabstufen](/articles/downgrading-a-sponsorship)“) |
|
||||
| sponsor_sponsorship_create | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du einen Entwickler unterstützt (siehe „[Unterstützen eines Open-Source-Mitarbeiters](/github/supporting-the-open-source-community-with-github-sponsors/sponsoring-an-open-source-contributor#sponsoring-a-developer)") |
|
||||
| sponsor_sponsorship_preference_change | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du Deine Einstellung zum Empfangen von E-Mail-Updates von einem unterstützten Entwickler änderst (siehe „[Dein Sponsoring verwalten](/articles/managing-your-sponsorship)“) |
|
||||
| sponsor_sponsorship_tier_change | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du Dein Sponsoring herauf- oder herabstufst (siehe „[Sponsoring heraufstufen](/articles/upgrading-a-sponsorship)“ und „[Sponsoring herabstufen](/articles/downgrading-a-sponsorship)“) |
|
||||
| sponsored_developer_approve | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Dein {% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %}-Konto genehmigt ist (siehe „[{% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} für Dein Benutzerkonto aufsetzen](/github/supporting-the-open-source-community-with-github-sponsors/setting-up-github-sponsors-for-your-user-account)") |
|
||||
| sponsored_developer_create | Wird aufgelöst, wenn Dein {% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %}-Konto erstellt wird (siehe „[{% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} für Dein Benutzerkonto aufsetzen](/github/supporting-the-open-source-community-with-github-sponsors/setting-up-github-sponsors-for-your-user-account)") |
|
||||
| sponsored_developer_profile_update | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du Dein „unterstützter Benutzer"-Profil veränderst (siehe „[Deine Profildetails für {% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} verändern](/github/supporting-the-open-source-community-with-github-sponsors/editing-your-profile-details-for-github-sponsors)") |
|
||||
| sponsored_developer_request_approval | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du Deine Bewerbung für {% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} für die Bewilligung einreichst (siehe „[{% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} für Dein Benutzerkonto aufsetzen](/github/supporting-the-open-source-community-with-github-sponsors/setting-up-github-sponsors-for-your-user-account)") |
|
||||
| sponsored_developer_tier_description_update | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du die Beschreibung einer Sponsoring-Stufe änderst (siehe „[Sponsoring-Stufen ändern](/articles/changing-your-sponsorship-tiers)“) |
|
||||
| sponsored_developer_update_newsletter_send | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du Deinen Sponsoren einen E-Mail-Update sendest (siehe „[Sponsoren kontaktieren](/articles/contacting-your-sponsors)“) |
|
||||
| waitlist_invite_sponsored_developer | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du eingeladen wirst, {% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} von der Warteliste her beizutreten (siehe „[{% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} für Dein Benutzerkonto aufsetzen](/github/supporting-the-open-source-community-with-github-sponsors/setting-up-github-sponsors-for-your-user-account)") |
|
||||
| waitlist_join | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du der Warteliste beitrittst, um ein „unterstützter Entwickler" zu werden (siehe [{% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} für Dein Benutzerkonto aufsetzen](/github/supporting-the-open-source-community-with-github-sponsors/setting-up-github-sponsors-for-your-user-account)") |
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
#### Kategorie `successor_invitation`
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| accept | Wird ausgelöst, wenn du eine Erneuerungseinladung annimmst (siehe „[Inhaber-Kontinuität Deiner Benutzerkonto-Repositorys aufrechterhalten](/github/setting-up-and-managing-your-github-user-account/maintaining-ownership-continuity-of-your-user-accounts-repositories)") |
|
||||
| cancel | Wird ausgelöst, wenn du eine Erneuerungseinladung kündigst (siehe „[Inhaber-Kontinuität Deiner Benutzerkonto-Repositorys aufrechterhalten](/github/setting-up-and-managing-your-github-user-account/maintaining-ownership-continuity-of-your-user-accounts-repositories)") |
|
||||
| create | Wird ausgelöst, wenn du eine Erneuerungseinladung erstellst (siehe „[Inhaber-Kontinuität Deiner Benutzerkonto-Repositorys aufrechterhalten](/github/setting-up-and-managing-your-github-user-account/maintaining-ownership-continuity-of-your-user-accounts-repositories)") |
|
||||
| decline | Wird ausgelöst, wenn du eine Erneuerungseinladung ablehnst (siehe „[Inhaber-Kontinuität Deiner Benutzerkonto-Repositorys aufrechterhalten](/github/setting-up-and-managing-your-github-user-account/maintaining-ownership-continuity-of-your-user-accounts-repositories)") |
|
||||
| revoke | Wird ausgelöst, wenn du eine Erneuerungseinladung zurückziehst (siehe „[Inhaber-Kontinuität Deiner Benutzerkonto-Repositorys aufrechterhalten](/github/setting-up-and-managing-your-github-user-account/maintaining-ownership-continuity-of-your-user-accounts-repositories)") |
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Kategorie `team`
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| add_member | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Mitglied einer Organisation, zu der Du gehörst, [Dich zu einem Team hinzufügt](/articles/adding-organization-members-to-a-team). |
|
||||
| add_repository | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Team, dessen Mitglied Du bist, die Kontrolle über ein Repository erhält. |
|
||||
| create | Wird ausgelöst, wenn in einer Organisation, zu der Du gehörst, ein neues Team erstellt wird. |
|
||||
| destroy | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Team, dessen Mitglied Du bist, aus einer Organisation gelöscht wird. |
|
||||
| remove_member | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Mitglied einer Organisation [aus einem Team entfernt wird](/articles/removing-organization-members-from-a-team), dessen Mitglied Du bist. |
|
||||
| remove_repository | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Repository nicht mehr unter der Kontrolle eines Teams steht. |
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion != "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
#### Kategorie `two_factor_authentication`
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| -------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| enabled | Wird bei der Aktivierung der [Zwei-Faktor-Authentifizierung](/articles/securing-your-account-with-two-factor-authentication-2fa) ausgelöst. |
|
||||
| disabled | Wird bei der Deaktivierung der Zwei-Faktor-Authentifizierung ausgelöst. |
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Kategorie `user`
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ---------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| add_email | Triggered when you {% if currentVersion != "github-ae@latest" %}[add a new email address](/articles/changing-your-primary-email-address){% else %}add a new email address{% endif %}. |
|
||||
| create | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie ein neues Benutzerkonto erstellen. |
|
||||
| remove_email | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie eine E-Mail-Adresse entfernen. |
|
||||
| rename | Triggered when you rename your account.{% if currentVersion != "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
| change_password | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie Ihr Passwort ändern. |
|
||||
| forgot_password | Triggered when you ask for [a password reset](/articles/how-can-i-reset-my-password).{% endif %}
|
||||
| login | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du Dich bei {% data variables.product.product_location %} anmeldest. |
|
||||
| failed_login | Triggered when you failed to log in successfully.{% if currentVersion != "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
| two_factor_requested | Triggered when {% data variables.product.product_name %} asks you for [your two-factor authentication code](/articles/accessing-github-using-two-factor-authentication).{% endif %}
|
||||
| show_private_contributions_count | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie [private Beiträge in Ihrem Profil veröffentlichen](/articles/publicizing-or-hiding-your-private-contributions-on-your-profile). |
|
||||
| hide_private_contributions_count | Triggered when you [hide private contributions on your profile](/articles/publicizing-or-hiding-your-private-contributions-on-your-profile).{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
| report_content | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie [ein Issue oder einen Pull Request bzw. einen Kommentar zu einem Issue, einem Pull Request oder einem Commit melden](/articles/reporting-abuse-or-spam).{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Kategorie `user_status`
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| aktualisieren | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie den Status Ihres Profils festlegen oder ändern. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Status festlegen](/articles/personalizing-your-profile/#setting-a-status).“ |
|
||||
| destroy | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie den Status Ihres Profils löschen. |
|
||||
| Kategoriename | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
| [`account_recovery_token`](#account_recovery_token-category-actions) | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit dem [Hinzufügen eines Wiederherstellungstokens](/articles/configuring-two-factor-authentication-recovery-methods). |
|
||||
| [`Abrechnung`](#billing-category-actions) | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit Ihren Abrechnungsinformationen. |
|
||||
| [`marketplace_agreement_signature (Unterzeichnung Marketplace-Vereinbarung)`](#marketplace_agreement_signature-category-actions) | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit der Signierung der {% data variables.product.prodname_marketplace %}-Entwicklervereinbarung. |
|
||||
| [`marketplace_listing (Eintrag auf Marketplace)`](#marketplace_listing-category-actions) | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit dem Eintragen von Apps auf {% data variables.product.prodname_marketplace %}.{% endif %}
|
||||
| [`oauth_access`](#oauth_access-category-actions) | Contains all activities related to [{% data variables.product.prodname_oauth_app %}s](/articles/authorizing-oauth-apps) you've connected with.{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
| [`payment_method`](#payment_method-category-actions) | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit der Bezahlung Ihres {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}-Abonnements.{% endif %}
|
||||
| [`profile_picture`](#profile_picture-category-actions) | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit Ihrem Profilbild. |
|
||||
| [`project (Projekt)`](#project-category-actions) | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit Projektboards. |
|
||||
| [`public_key`](#public_key-category-actions) | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit [Ihren öffentlichen SSH-Schlüsseln](/articles/adding-a-new-ssh-key-to-your-github-account). |
|
||||
| [`repo`](#repo-category-actions) | Contains all activities related to the repositories you own.{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
| [`sponsors`](#sponsors-category-actions) | Contains all events related to {% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} and sponsor buttons (see "[About {% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %}](/articles/about-github-sponsors)" and "[Displaying a sponsor button in your repository](/articles/displaying-a-sponsor-button-in-your-repository)"){% endif %}{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
| [`Team`](#team-category-actions) | Contains all activities related to teams you are a part of.{% endif %}{% if currentVersion != "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
| [`two_factor_authentication`](#two_factor_authentication-category-actions) | Contains all activities related to [two-factor authentication](/articles/securing-your-account-with-two-factor-authentication-2fa).{% endif %}
|
||||
| [`Benutzer`](#user-category-actions) | Umfasst alle Aktivitäten in Verbindung mit Deinem Konto. |
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -243,3 +60,193 @@ Eine Beschreibung der Ereignisse dieser Kategorien findest Du nachfolgend.
|
||||
{% data reusables.audit_log.exported-log-keys-and-values %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Security log actions
|
||||
|
||||
An overview of some of the most common actions that are recorded as events in the security log.
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### `account_recovery_token` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| `confirm` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du [ein neues Token erfolgreich bei einem Wiederherstellungsanbieter speicherst](/articles/configuring-two-factor-authentication-recovery-methods). |
|
||||
| `recover` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du [ein Kontowiederherstellungstoken erfolgreich einlöst](/articles/recovering-your-account-if-you-lose-your-2fa-credentials). |
|
||||
| `recover_error` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Token verwendet wird, {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} dieses aber nicht validieren kann. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### `billing` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| --------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| `change_billing_type` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie Ihre [Zahlungsmethode](/articles/adding-or-editing-a-payment-method) für {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} ändern. |
|
||||
| `change_email` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du [Deine E-Mail-Adresse änderst](/articles/changing-your-primary-email-address). |
|
||||
|
||||
#### `marketplace_agreement_signature` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| -------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `create` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du die {% data variables.product.prodname_marketplace %}-Entwicklervereinbarung signierst. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### `marketplace_listing` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ------------ | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `genehmigen` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Dein Eintrag für die Aufnahme in {% data variables.product.prodname_marketplace %} genehmigt wird. |
|
||||
| `create` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du einen Eintrag für Deine App in {% data variables.product.prodname_marketplace %} erstellst. |
|
||||
| `delist` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Ihr Listing von {% data variables.product.prodname_marketplace %} entfernt wird. |
|
||||
| `redraft` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Dein Eintrag in den Entwurfsstatus zurückversetzt wird. |
|
||||
| `reject` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Dein Eintrag für die Aufnahme in {% data variables.product.prodname_marketplace %} nicht genehmigt wird. |
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### `oauth_access` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| --------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `create` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie einer [{% data variables.product.prodname_oauth_app %} Zugriff erteilen](/articles/authorizing-oauth-apps). |
|
||||
| `destroy` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie einer [{% data variables.product.prodname_oauth_app %} den Zugriff auf Ihr Konto entziehen](/articles/reviewing-your-authorized-integrations). |
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### `payment_method` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `clear` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn eine [registrierte Zahlungsmethode](/articles/removing-a-payment-method) entfernt wird. |
|
||||
| `create` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn eine Zahlungsmethode, beispielsweise eine Kreditkarte oder ein PayPal-Konto, hinzugefügt wird. |
|
||||
| `aktualisieren` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn eine vorhandene Zahlungsmethode geändert wird. |
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### `profile_picture` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| --------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `aktualisieren` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du [Dein Profilbild festlegst oder änderst](/articles/setting-your-profile-picture/). |
|
||||
|
||||
#### `project` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ------------------------ | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `access` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn die Sichtbarkeit eines Projektboards geändert wird. |
|
||||
| `create` | Wird bei der Erstellung eines Projektboards ausgelöst. |
|
||||
| `rename` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Projektboard umbenannt wird. |
|
||||
| `aktualisieren` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Projektboard geändert wird. |
|
||||
| `delete` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Projektboard gelöscht wird. |
|
||||
| `link` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Repository mit einem Projektboard verknüpft wird. |
|
||||
| `unlink` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn die Verknüpfung eines Repositorys mit einem Projektboard aufgehoben wird. |
|
||||
| `update_user_permission` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein externer Mitarbeiter einem Projektboard hinzugefügt oder entfernt wird oder wenn sich seine Berechtigungsebene verändert. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### `public_key` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| -------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| `create` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie [Ihrem {% data variables.product.product_name %}-Konto einen neuen öffentlichen SSH-Schlüssel hinzufügen](/articles/adding-a-new-ssh-key-to-your-github-account). |
|
||||
| `delete` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie [einen öffentlichen SSH-Schlüssel aus Ihrem {% data variables.product.product_name %}-Konto entfernen](/articles/reviewing-your-ssh-keys). |
|
||||
|
||||
#### `repo` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `access` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn die Sichtbarkeit eines Repositorys, dessen Inhaber Du bist, [von „privat“ auf „öffentlich“ gesetzt wird](/articles/making-a-private-repository-public) (oder umgekehrt). |
|
||||
| `add_member` | Triggered when a {% data variables.product.product_name %} user is {% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}[invited to have collaboration access](/articles/inviting-collaborators-to-a-personal-repository){% else %}[given collaboration access](/articles/inviting-collaborators-to-a-personal-repository){% endif %} to a repository. |
|
||||
| `add_topic` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Repository-Inhaber einem Repository [ein Thema hinzufügt](/articles/classifying-your-repository-with-topics). |
|
||||
| `archived` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Repository-Inhaber ein [Repository archiviert](/articles/about-archiving-repositories).{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
| `config.disable_anonymous_git_access` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn für ein öffentliches Repository der [anonyme Git-Lesezugriff deaktiviert](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/user/articles/enabling-anonymous-git-read-access-for-a-repository) wird. |
|
||||
| `config.enable_anonymous_git_access` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn für ein öffentliches Repository der [anonyme Git-Lesezugriff aktiviert](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/user/articles/enabling-anonymous-git-read-access-for-a-repository) wird. |
|
||||
| `config.lock_anonymous_git_access` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn für ein Repository die [Einstellung für den anonymen Git-Lesezugriff gesperrt](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/admin/guides/user-management/preventing-users-from-changing-anonymous-git-read-access) wird. |
|
||||
| `config.unlock_anonymous_git_access` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn für ein Repository die [Einstellungssperre für den anonymen Git-Lesezugriff aufgehoben](/enterprise/{{ currentVersion }}/admin/guides/user-management/preventing-users-from-changing-anonymous-git-read-access) wird.{% endif %}
|
||||
| `create` | Wird bei der [Erstellung eines neuen Repositorys](/articles/creating-a-new-repository) ausgelöst. |
|
||||
| `destroy` | Triggered when [a repository is deleted](/articles/deleting-a-repository).{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
| `deaktivieren` | Triggered when a repository is disabled (e.g., for [insufficient funds](/articles/unlocking-a-locked-account)).{% endif %}{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
| `aktivieren` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Repository wieder aktiviert wird.{% endif %}
|
||||
| `remove_member` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein {% data variables.product.product_name %}-Benutzer [als Mitarbeiter aus einem Repository entfernt wird](/articles/removing-a-collaborator-from-a-personal-repository). |
|
||||
| `remove_topic` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Repository-Inhaber ein Thema aus einem Repository entfernt. |
|
||||
| `rename` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein [Repository umbenannt](/articles/renaming-a-repository) wird. |
|
||||
| `übertragen` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein [Repository übertragen](/articles/how-to-transfer-a-repository) wird. |
|
||||
| `transfer_start` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn die Übertragung eines Repositorys initiiert wurde. |
|
||||
| `unarchived` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Repository-Inhaber die Archivierung eines Repositorys aufhebt. |
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
#### `sponsors` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| --------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `repo_funding_link_button_toggle` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du eine Sponsorenschaltfläche in Deinem Repository aktivierst oder deaktivierst (siehe „[Sponsorenschaltfläche in Deinem Repository anzeigen](/articles/displaying-a-sponsor-button-in-your-repository)“) |
|
||||
| `repo_funding_links_file_action` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du die FUNDING-Datei in Deinem Repository änderst (siehe „[Sponsorenschaltfläche in Deinem Repository anzeigen](/articles/displaying-a-sponsor-button-in-your-repository)“) |
|
||||
| `sponsor_sponsorship_cancel` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie ein Sponsoring beenden (siehe „[Sponsoring herabstufen](/articles/downgrading-a-sponsorship)“). |
|
||||
| `sponsor_sponsorship_create` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du einen Entwickler unterstützt (siehe „[Unterstützen eines Open-Source-Mitarbeiters](/github/supporting-the-open-source-community-with-github-sponsors/sponsoring-an-open-source-contributor#sponsoring-a-developer)") |
|
||||
| `sponsor_sponsorship_preference_change` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie Ihre Einstellung zum Empfangen von E-Mail-Aktualisierungen von einem gesponserten Entwickler ändern (siehe „[Sponsoring verwalten](/articles/managing-your-sponsorship)“). |
|
||||
| `sponsor_sponsorship_tier_change` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie Ihr Sponsoring upgraden oder herabstufen (siehe „[Sponsoring upgraden](/articles/upgrading-a-sponsorship)“ und „[Sponsoring herabstufen](/articles/downgrading-a-sponsorship)“). |
|
||||
| `sponsored_developer_approve` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Dein {% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %}-Konto genehmigt ist (siehe „[{% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} für Dein Benutzerkonto aufsetzen](/github/supporting-the-open-source-community-with-github-sponsors/setting-up-github-sponsors-for-your-user-account)") |
|
||||
| `sponsored_developer_create` | Wird aufgelöst, wenn Dein {% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %}-Konto erstellt wird (siehe „[{% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} für Dein Benutzerkonto aufsetzen](/github/supporting-the-open-source-community-with-github-sponsors/setting-up-github-sponsors-for-your-user-account)") |
|
||||
| `sponsored_developer_profile_update` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du Dein „unterstützter Benutzer"-Profil veränderst (siehe „[Deine Profildetails für {% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} verändern](/github/supporting-the-open-source-community-with-github-sponsors/editing-your-profile-details-for-github-sponsors)") |
|
||||
| `sponsored_developer_request_approval` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du Deine Bewerbung für {% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} für die Bewilligung einreichst (siehe „[{% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} für Dein Benutzerkonto aufsetzen](/github/supporting-the-open-source-community-with-github-sponsors/setting-up-github-sponsors-for-your-user-account)") |
|
||||
| `sponsored_developer_tier_description_update` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie die Beschreibung einer Sponsoring-Stufe ändern (siehe „[Sponsoring-Stufen ändern](/articles/changing-your-sponsorship-tiers)“). |
|
||||
| `sponsored_developer_update_newsletter_send` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie Ihren Sponsoren eine E-Mail-Aktualisierung senden (siehe „[Sponsoren kontaktieren](/articles/contacting-your-sponsors)“). |
|
||||
| `waitlist_invite_sponsored_developer` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du eingeladen wirst, {% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} von der Warteliste her beizutreten (siehe „[{% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} für Dein Benutzerkonto aufsetzen](/github/supporting-the-open-source-community-with-github-sponsors/setting-up-github-sponsors-for-your-user-account)") |
|
||||
| `waitlist_join` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du der Warteliste beitrittst, um ein „unterstützter Entwickler" zu werden (siehe [{% data variables.product.prodname_sponsors %} für Dein Benutzerkonto aufsetzen](/github/supporting-the-open-source-community-with-github-sponsors/setting-up-github-sponsors-for-your-user-account)") |
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
#### `successor_invitation` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| --------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| `accept` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn du eine Erneuerungseinladung annimmst (siehe „[Inhaber-Kontinuität Deiner Benutzerkonto-Repositorys aufrechterhalten](/github/setting-up-and-managing-your-github-user-account/maintaining-ownership-continuity-of-your-user-accounts-repositories)") |
|
||||
| `cancel` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn du eine Erneuerungseinladung kündigst (siehe „[Inhaber-Kontinuität Deiner Benutzerkonto-Repositorys aufrechterhalten](/github/setting-up-and-managing-your-github-user-account/maintaining-ownership-continuity-of-your-user-accounts-repositories)") |
|
||||
| `create` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn du eine Erneuerungseinladung erstellst (siehe „[Inhaber-Kontinuität Deiner Benutzerkonto-Repositorys aufrechterhalten](/github/setting-up-and-managing-your-github-user-account/maintaining-ownership-continuity-of-your-user-accounts-repositories)") |
|
||||
| `decline` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn du eine Erneuerungseinladung ablehnst (siehe „[Inhaber-Kontinuität Deiner Benutzerkonto-Repositorys aufrechterhalten](/github/setting-up-and-managing-your-github-user-account/maintaining-ownership-continuity-of-your-user-accounts-repositories)") |
|
||||
| `revoke` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn du eine Erneuerungseinladung zurückziehst (siehe „[Inhaber-Kontinuität Deiner Benutzerkonto-Repositorys aufrechterhalten](/github/setting-up-and-managing-your-github-user-account/maintaining-ownership-continuity-of-your-user-accounts-repositories)") |
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### `team` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `add_member` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Mitglied einer Organisation, zu der Sie gehören, [Sie zu einem Team hinzufügt](/articles/adding-organization-members-to-a-team). |
|
||||
| `add_repository` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Team, dessen Mitglied Sie sind, die Kontrolle über ein Repository erhält. |
|
||||
| `create` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn in einer Organisation, zu der Sie gehören, ein neues Team erstellt wird. |
|
||||
| `destroy` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Team, dessen Mitglied Sie sind, aus einer Organisation gelöscht wird. |
|
||||
| `remove_member` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Mitglied einer Organisation aus einem [Team entfernt wird](/articles/removing-organization-members-from-a-team), dessen Mitglied Sie sind. |
|
||||
| `remove_repository` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn ein Repository nicht mehr unter der Kontrolle eines Teams steht. |
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion != "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
#### `two_factor_authentication` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ---------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `enabled` | Wird bei der Aktivierung der [Zwei-Faktor-Authentifizierung](/articles/securing-your-account-with-two-factor-authentication-2fa) ausgelöst. |
|
||||
| `disabled` | Wird bei der Deaktivierung der Zwei-Faktor-Authentifizierung ausgelöst. |
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### `user` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| ---------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `add_email` | Triggered when you {% if currentVersion != "github-ae@latest" %}[add a new email address](/articles/changing-your-primary-email-address){% else %}add a new email address{% endif %}. |
|
||||
| `create` | Triggered when you create a new user account.{% if currentVersion != "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
| `change_password` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie Ihr Passwort ändern. |
|
||||
| `forgot_password` | Triggered when you ask for [a password reset](/articles/how-can-i-reset-my-password).{% endif %}
|
||||
| `hide_private_contributions_count` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie [private Beiträge in Ihrem Profil verbergen](/articles/publicizing-or-hiding-your-private-contributions-on-your-profile). |
|
||||
| `login` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du Dich bei {% data variables.product.product_location %} anmeldest. |
|
||||
| `failed_login` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Ihre Anmeldung fehlschlägt. |
|
||||
| `remove_email` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie eine E-Mail-Adresse entfernen. |
|
||||
| `rename` | Triggered when you rename your account.{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
| `report_content` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Sie [ein Issue oder einen Pull Request bzw. einen Kommentar zu einem Issue, einem Pull Request oder einem Commit melden](/articles/reporting-abuse-or-spam).{% endif %}
|
||||
| `show_private_contributions_count` | Triggered when you [publicize private contributions on your profile](/articles/publicizing-or-hiding-your-private-contributions-on-your-profile).{% if currentVersion != "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
| `two_factor_requested` | Triggered when {% data variables.product.product_name %} asks you for [your two-factor authentication code](/articles/accessing-github-using-two-factor-authentication).{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### `user_status` category actions
|
||||
|
||||
| Aktion | Beschreibung |
|
||||
| --------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `aktualisieren` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du den Status Deines Profils festlegst oder änderst. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Status festlegen](/articles/personalizing-your-profile/#setting-a-status).“ |
|
||||
| `destroy` | Wird ausgelöst, wenn Du den Status Deines Profils löschst. |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +11,11 @@ versions:
|
||||
|
||||
Nachdem Du in Deinem Repository Vorlagen für Issues und Pull Requests erstellt hast, können Mitarbeiter die Vorlagen verwenden, um Issues zu öffnen oder vorgeschlagene Änderungen in ihren Pull Requests gemäß den Beitragsrichtlinien des Repositorys zu beschreiben. Weitere Informationen zum Hinzufügen von Beitragsrichtlinien zu einem Repository findest Du unter „[Richtlinien für Repository-Mitarbeiter festlegen](/articles/setting-guidelines-for-repository-contributors).“
|
||||
|
||||
You can create default issue and pull request templates for your organization{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" %} or user account{% endif %}. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Eine Standard Community-Unterstützungsdatei erstellen](/github/building-a-strong-community/creating-a-default-community-health-file)."
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
|
||||
You can create default issue and pull request templates for your organization or user account. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Eine Standard Community-Unterstützungsdatei erstellen](/github/building-a-strong-community/creating-a-default-community-health-file)."
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Vorlagen für Issues
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -25,9 +29,9 @@ Mit dem Vorlagengenerator kannst Du für jede Vorlage einen Titel und eine Besch
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.issue-template-config %} Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Issuevorlagen für Dein Repository konfigurieren](/github/building-a-strong-community/configuring-issue-templates-for-your-repository#configuring-the-template-chooser)."
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
Issuevorlagen werden auf dem Standardbranch des Repositorys in einem verborgenen `.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE`-Verzeichnis gespeichert. Wenn Du eine Vorlage in einem anderen Branch erstellst, steht sie Mitarbeitern nicht zur Verfügung. Bei den Dateinamen von Issuevorlagen wird nicht zwischen Groß- und Kleinschreibung unterschieden, und es wird eine *.md*-Erweiterung benötigt. {% data reusables.repositories.valid-community-issues %}
|
||||
Issue-Vorlagen werden auf dem Standardbranch des Repositorys in einem verborgenen `.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE`-Verzeichnis gespeichert. Wenn Sie eine Vorlage in einem anderen Branch erstellen, steht sie Mitarbeitern nicht zur Verfügung. Bei den Dateinamen von Issuevorlagen wird nicht zwischen Groß- und Kleinschreibung unterschieden, und es wird eine *.md*-Erweiterung benötigt. {% data reusables.repositories.valid-community-issues %}
|
||||
|
||||
Es ist möglich, manuell eine einzelne Issuevorlage in Markdown mit dem Workflow für ältere Issuevorlagen zu erstellen, und Projektmitarbeiter werden automatisch den Inhalt der Vorlage im Issue-Text sehen. Wir empfehlen jedoch, den aktualisierten Mehrfach-Issue-Vorlagengenerator zu verwenden, um Issuevorlagen zu erstellen. Weitere Informationen zum veralteten Workflow findest Du unter „[Eine einzelne Issue-Vorlage für Dein Repository manuell erstellen](/articles/manually-creating-a-single-issue-template-for-your-repository).“
|
||||
Es ist möglich, manuell eine einzelne Issue-Vorlage in Markdown mit dem Workflow für ältere Issue-Vorlagen zu erstellen, wobei die Projektmitarbeiter automatisch den Inhalt der Vorlage im Issue-Text sehen. Wir empfehlen jedoch, den aktualisierten Vorlagengenerator zum Erstellen mehrerer Issues zu verwenden, um Issue-Vorlagen zu erstellen. Weitere Informationen zum veralteten Workflow finden Sie unter „[Eine einzelne Issue-Vorlage für Ihr Repository manuell erstellen](/articles/manually-creating-a-single-issue-template-for-your-repository)“.
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.security-guidelines %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -37,6 +41,6 @@ Wenn Sie eine Pull-Request-Vorlage zu Ihrem Repository hinzufügen, sehen Projek
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Du musst Vorlagen auf dem Standardbranch des Repositorys erstellen. Vorlagen, die in anderen Branches erstellt wurden, stehen Mitarbeitern nicht zur Verfügung. Du kannst Deine Vorlage für Pull Requests im sichtbaren Stammverzeichnis des Repositorys, im Ordner `docs` oder im verborgenen Verzeichnis `.github` speichern. Bei den Dateinamen von Pull-Request-Vorlagen wird nicht zwischen Groß- und Kleinschreibung unterschieden, und es kann eine *.md*- oder *.txt*-Erweiterung angefügt werden.
|
||||
Vorlagen müssen Sie auf dem Standardbranch des Repositorys erstellen. Vorlagen, die in anderen Branches erstellt wurden, stehen Mitarbeitern nicht zur Verfügung. Sie können Ihre Vorlage für Pull Requests im sichtbaren Stammverzeichnis des Repositorys, im Ordner `docs` oder im verborgenen Verzeichnis `.github` speichern. Bei den Dateinamen von Pull-Request-Vorlagen wird nicht zwischen Groß- und Kleinschreibung unterschieden, und es kann eine *.md*- oder *.txt*-Erweiterung angefügt werden.
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Eine Pull-Request-Vorlage für Dein Repository erstellen](/articles/creating-a-pull-request-template-for-your-repository).“
|
||||
Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Eine Pull-Request-Vorlage für Ihr Repository erstellen](/articles/creating-a-pull-request-template-for-your-repository)“.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -15,9 +15,9 @@ Jedes {% data variables.product.product_name %}-Repository enthält einen Abschn
|
||||
|
||||
Mit Wikis können Sie Inhalte wie überall sonst auf {% data variables.product.product_name %} verfassen. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Erste Schritte zum Schreiben und Formatieren auf {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}](/articles/getting-started-with-writing-and-formatting-on-github)“. Wir verwenden [unsere Open-Source Markup-Bibliothek](https://github.com/github/markup), um verschiedene Formate in HTML zu konvertieren, sodass Du entscheiden kannst, in Markdown oder jedem anderen unterstützten Format zu schreiben.
|
||||
|
||||
Wikis sind in öffentlichen Repositorys für die Öffentlichkeit zugänglich und in privaten Repositorys auf Personen mit Zugriff auf das Repository beschränkt. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Sichtbarkeit eines Repositorys festlegen](/articles/setting-repository-visibility).“
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}If you create a wiki in a public repository, the wiki is available to {% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}anyone with access to {% data variables.product.product_location %}{% else %}the public{% endif %}. {% endif %}If you create a wiki in an internal or private repository, {% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}people{% elsif currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}enterprise members{% endif %} with access to the repository can also access the wiki. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Sichtbarkeit eines Repositorys festlegen](/articles/setting-repository-visibility).“
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können Wikis direkt auf {% data variables.product.product_name %} bearbeiten, oder Sie können Wiki-Dateien lokal bearbeiten. Standardmäßig können nur Personen mit Schreibzugriff auf Ihr Repository Änderungen an Wikis vornehmen, jedoch können Sie jedem auf {% data variables.product.product_name %} erlauben, an einem Wiki in einem öffentlichen Repository mitzuwirken. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Zugriffsberechtigungen für Wikis ändern](/articles/changing-access-permissions-for-wikis)“.
|
||||
Sie können Wikis direkt auf {% data variables.product.product_name %} bearbeiten, oder Sie können Wiki-Dateien lokal bearbeiten. By default, only people with write access to your repository can make changes to wikis, although you can allow everyone on {% data variables.product.product_location %} to contribute to a wiki in {% if currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}an internal{% else %}a public{% endif %} repository. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Zugriffsberechtigungen für Wikis ändern](/articles/changing-access-permissions-for-wikis)“.
|
||||
|
||||
### Weiterführende Informationen
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,6 @@ redirect_from:
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
free-pro-team: '*'
|
||||
enterprise-server: '*'
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Du eine nachweisbare Lizenz in Dein Repository einfügst, wird sie den Benutzern, die Dein Repository besuchen, oben auf der Repository-Seite angezeigt. Um die gesamte Lizenzdatei zu lesen, klicke auf den Namen der Lizenz.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -13,7 +13,11 @@ Um Personen auf bestimmte Support-Ressourcen zu verweisen, kannst Du eine SUPPOR
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can create default support resources for your organization{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" %} or user account{% endif %}. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Eine Standard Community-Unterstützungsdatei erstellen](/github/building-a-strong-community/creating-a-default-community-health-file)."
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
|
||||
You can create default support resources for your organization or user account. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Eine Standard Community-Unterstützungsdatei erstellen](/github/building-a-strong-community/creating-a-default-community-health-file)."
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% tip %}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,10 +10,16 @@ versions:
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.default-issue-templates %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Issuevorlagen erstellen
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,6 @@ redirect_from:
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
free-pro-team: '*'
|
||||
enterprise-server: '*'
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Informationen zu Standard-Community-Unterstützungsdateien
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -13,7 +13,11 @@ Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Informationen zu Vorlagen für Issues
|
||||
|
||||
Du kannst in einem der unterstützten Ordner ein Unterverzeichnis *PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE* erstellen, um mehrere Pull-Request-Vorlagen zu speichern. Mit dem Abfrageparameter `template` kannst Du die Vorlage wählen, mit der der Pull-Request-Text ausgefüllt werden soll. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Informationen zur Automatisierung für Issues und Pull Requests mit Abfrageparametern](/articles/about-automation-for-issues-and-pull-requests-with-query-parameters).“
|
||||
|
||||
You can create default pull request templates for your organization{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" %} or user account{% endif %}. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Eine Standard Community-Unterstützungsdatei erstellen](/github/building-a-strong-community/creating-a-default-community-health-file)."
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
|
||||
You can create default pull request templates for your organization{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" %} or user account{% endif %}. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Eine Standard Community-Unterstützungsdatei erstellen](/github/building-a-strong-community/creating-a-default-community-health-file)."
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Eine Pull-Request-Vorlage hinzufügen
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ Das Sperren einer Unterhaltung erstellt ein Zeitleistenereignis, das für alle B
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Solange eine Unterhaltung gesperrt ist, können nur [Personen mit Schreibzugriff](/articles/repository-permission-levels-for-an-organization/) und [Repository-Inhaber und -Mitarbeiter](/articles/permission-levels-for-a-user-account-repository/#collaborator-access-on-a-repository-owned-by-a-user-account) Kommentare hinzufügen, ausblenden und löschen.
|
||||
Solange eine Unterhaltung gesperrt ist, können nur [Personen mit Schreibzugriff](/articles/repository-permission-levels-for-an-organization/) und [Repository-Inhaber und -Mitarbeiter](/articles/permission-levels-for-a-user-account-repository/#collaborator-access-for-a-repository-owned-by-a-user-account) Kommentare hinzufügen, ausblenden und löschen.
|
||||
|
||||
Um nach gesperrten Unterhaltungen in einem nicht archivierten Repository zu suchen, kannst Du die Qualifizierer `is:locked` und `archived:false` verwenden. In archivierten Repositorys sind Unterhaltungen automatisch gesperrt. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Issues und Pull Requests durchsuchen](/articles/searching-issues-and-pull-requests#search-based-on-whether-a-conversation-is-locked).“
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -39,8 +39,12 @@ assignees: octocat
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.default-issue-templates %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Eine Issuevorlage hinzufügen
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +20,11 @@ Mitarbeitern helfen die Richtlinien, korrekt formulierte Pull Requests einzureic
|
||||
|
||||
Sowohl Inhaber als auch Mitarbeiter sparen dank Beitragsrichtlinien Zeit und Mühen, die durch fehlerhaft formulierte Pull Requests oder Issues entstehen, die abgelehnt und erneut eingereicht werden müssen.
|
||||
|
||||
You can create default contribution guidelines for your organization{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" %} or user account{% endif %}. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Eine Standard Community-Unterstützungsdatei erstellen](/github/building-a-strong-community/creating-a-default-community-health-file)."
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
|
||||
You can create default contribution guidelines for your organization{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" %} or user account{% endif %}. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Eine Standard Community-Unterstützungsdatei erstellen](/github/building-a-strong-community/creating-a-default-community-health-file)."
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% tip %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -45,7 +49,7 @@ You can create default contribution guidelines for your organization{% if curren
|
||||
|
||||
### Beispiele für Beitragsrichtlinien
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Du nun nicht sicher bist, was Du hier festlegen sollst, findest Du nachfolgend einige gute Beispiele für Beitragsrichtlinien:
|
||||
Wenn Sie nun nicht wissen, was Sie hier festlegen sollen, finden Sie nachfolgend einige gute Beispiele für Beitragsrichtlinien:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Beitragsrichtlinien](https://github.com/atom/atom/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md) für den Editor Atom
|
||||
- [Beitragsrichtlinien](https://github.com/rails/rails/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md) für Ruby on Rails
|
||||
@@ -53,5 +57,5 @@ Wenn Du nun nicht sicher bist, was Du hier festlegen sollst, findest Du nachfolg
|
||||
|
||||
### Weiterführende Informationen
|
||||
- The Open Source Guides' section "[Starting an Open Source Project](https://opensource.guide/starting-a-project/)"{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
- [{% data variables.product.prodname_learning %}]({% data variables.product.prodname_learning_link %}){% endif %}
|
||||
- „[Eine Lizenz zu einem Repository hinzufügen](/articles/adding-a-license-to-a-repository)“
|
||||
- [{% data variables.product.prodname_learning %}]({% data variables.product.prodname_learning_link %}){% endif %}{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
- "[Adding a license to a repository](/articles/adding-a-license-to-a-repository)"{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ Du benötigst Schreibzugriff auf ein Repository, um einen Branch zu erstellen, e
|
||||
|
||||
### About the default branch
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.branches.new-repo-default-branch %} The default branch is the branch that {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} displays when anyone visits your repository. The default branch is also the initial branch that Git checks out locally out when someone clones the repository. {% data reusables.branches.default-branch-automatically-base-branch %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.branches.new-repo-default-branch %} The default branch is the branch that {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} displays when anyone visits your repository. The default branch is also the initial branch that Git checks out locally when someone clones the repository. {% data reusables.branches.default-branch-automatically-base-branch %}
|
||||
|
||||
By default, {% data variables.product.product_name %} names the default branch {% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.22" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}`main`{% else %}`master`{% endif %} in any new repository.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ Wenn ein Branch geschützt ist, trifft Folgendes zu:
|
||||
- Wenn erforderliche Pull-Request-Reviews auf dem Branch aktiviert sind, kannst Du Änderungen erst dann in den Branch zusammenführen, wenn alle Anforderungen der Richtlinie für Pull-Request-Reviews erfüllt sind. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Einen Pull Request zusammenführen](/articles/merging-a-pull-request).“
|
||||
- Wenn der erforderliche Review von einem Codeinhaber auf einem Branch aktiviert ist und der Code mit einem Inhaber durch einen Pull Request geändert wird, muss ein Codeinhaber den Pull Request genehmigen, bevor er zusammengeführt werden kann. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Informationen zu Codeinhabern](/articles/about-code-owners).“
|
||||
- Wenn die obligatorische Commit-Signatur auf einem Branch aktiviert ist, kannst Du keine Commits an den Branch übertragen, die nicht signiert und verifiziert sind. For more information, see "[About commit signature verification](/articles/about-commit-signature-verification)" and "[About required commit signing](/articles/about-required-commit-signing)."{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.21" %}
|
||||
- Wenn du den Konflikt-Editor von {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} benutzt, um Konflikte für eine Pull Request zu beheben, die Du aus einem geschützten Branch erstellt hast, wird Dir {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} helfen, einen alternativen Branch für den Pull-Request zu erstellen, so dass Deine Auflösung der Konflikte zusammengeführt werden kann. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Einen Mergekonflikt auf {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} beheben](/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/resolving-a-merge-conflict-on-github).“{% endif %}
|
||||
- If you use {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}'s conflict editor to fix conflicts for a pull request that you created from a protected branch, {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} helps you to create an alternative branch for the pull request, so that your resolution of the conflicts can be merged. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Einen Mergekonflikt auf {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %} beheben](/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/resolving-a-merge-conflict-on-github).“{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Weiterführende Informationen
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,14 +16,20 @@ versions:
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Du ein privates Repository löschst, werden alle zugehörigen privaten Forks ebenfalls gelöscht.
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Öffentliches Repository löschen
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Du ein öffentliches Repository löschst, wird einer der vorhandenen öffentlichen Forks als das neue übergeordnete Repository ausgewählt. Alle anderen Repositorys werden von diesem neuen übergeordneten Element abgezweigt, und nachfolgende Pull Requests werden an dieses neue übergeordnete Element gesendet.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Private Forks und Berechtigungen
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.private_forks_inherit_permissions %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Öffentliches Repository in ein privates Repository ändern
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn ein öffentliches Repository auf privat festgelegt wird, werden die zugehörigen öffentlichen Forks in ein neues Netzwerk abgespalten. Wie beim Löschen eines öffentlichen Repositorys wird einer der vorhandenen öffentliches Forks als das neue übergeordnete Repository ausgewählt, und alle anderen Repositorys werden von diesem neuen übergeordneten Element abgezweigt. Nachfolgende Pull Requests werden an dieses neue übergeordnete Element gesendet.
|
||||
@@ -40,15 +46,36 @@ Wenn ein öffentliches Repository auf privat festgelegt und anschließend gelös
|
||||
|
||||
#### Privates Repository in ein öffentliches Repository ändern
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn ein privates Repository auf öffentlich festgelegt wird, werden alle privaten Forks in eigenständige private Repositorys umgewandelt und werden zum übergeordneten Element ihres eigenen neuen Repository-Netzwerks. Private Forks werden niemals automatisch auf öffentlich festgelegt, da sie sensible Commits enthalten können, die nicht veröffentlicht werden sollten.
|
||||
Wenn ein privates Repository auf öffentlich festgelegt wird, werden alle privaten Forks in ein eigenständiges privates Repository umgewandelt und avancieren zum übergeordneten Element des eigenen neuen Repository-Netzwerks. Private Forks werden niemals automatisch auf öffentlich festgelegt, da sie sensible Commits enthalten können, die nicht veröffentlicht werden sollten.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Öffentliches Repository löschen
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn ein privates Repository auf öffentlich festgelegt und anschließend gelöscht wird, bleiben die zugehörigen privaten Forks in separaten Netzwerken als eigenständige private Repositorys erhalten.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.19" %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Changing the visibility of an internal repository
|
||||
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** {% data reusables.gated-features.internal-repos %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
|
||||
If the policy for your enterprise permits forking, any fork of an internal repository will be private. If you change the visibility of an internal repository, any fork owned by an organization or user account will remain private.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Deleting the internal repository
|
||||
|
||||
If you change the visibility of an internal repository and then delete the repository, the forks will continue to exist in a separate network.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Weiterführende Informationen
|
||||
|
||||
- „[Sichtbarkeit eines Repositorys festlegen](/articles/setting-repository-visibility)“
|
||||
- „[Informationen zu Forks](/articles/about-forks)“
|
||||
- „[Die Forking-Richtlinie für Dein Repository verwalten](/github/administering-a-repository/managing-the-forking-policy-for-your-repository)"
|
||||
- „[Die Forking-Richtlinie für Deine Organisation verwalten](/github/setting-up-and-managing-organizations-and-teams/managing-the-forking-policy-for-your-organization)"
|
||||
- "{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}[Enforcing repository management policies in your enterprise account](/github/setting-up-and-managing-your-enterprise/enforcing-repository-management-policies-in-your-enterprise-account#enforcing-a-policy-on-forking-private-or-internal-repositories){% else %}[Enforcing repository management policies in your enterprise](/admin/policies/enforcing-repository-management-policies-in-your-enterprise#enforcing-a-policy-on-forking-private-or-internal-repositories){% endif %}"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +11,11 @@ versions:
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
A README file, along with {% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}a [repository license](/articles/licensing-a-repository), [contribution guidelines](/articles/setting-guidelines-for-repository-contributors), and a [code of conduct](/articles/adding-a-code-of-conduct-to-your-project){% else %}a [repository license](/articles/licensing-a-repository) and [contribution guidelines](/articles/setting-guidelines-for-repository-contributors){% endif %}, helps you communicate expectations for and manage contributions to your project.
|
||||
### Informationen zu README-Dateien
|
||||
|
||||
You can add a README file to a repository to communicate important information about your project. A README, along with a repository license{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}, contribution guidelines, and a code of conduct{% elsif enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %} and contribution guidelines{% endif %}, communicates expectations for your project and helps you manage contributions.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information about providing guidelines for your project, see {% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}"[Adding a code of conduct to your project](/github/building-a-strong-community/adding-a-code-of-conduct-to-your-project)" and {% endif %}"[Setting up your project for healthy contributions](/github/building-a-strong-community/setting-up-your-project-for-healthy-contributions)."
|
||||
|
||||
Die README-Datei ist oft das erste Element, das ein Benutzer beim Besuch Deines Repositorys sieht. README-Dateien enthalten in der Regel folgende Informationen:
|
||||
- Was ist die Aufgabe des Projekts?
|
||||
@@ -26,8 +30,12 @@ Wenn Sie Ihre README-Datei im Stammverzeichnis, im Ordner `docs` oder im verborg
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.21" %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.21"%}
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.profile.profile-readme %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,6 @@ redirect_from:
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
free-pro-team: '*'
|
||||
enterprise-server: '*'
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Die richtige Lizenz auswählen
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +17,7 @@ Du bist nicht dazu verpflichtet, eine Lizenz auszuwählen. Bedenke jedoch, dass
|
||||
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** If you publish your source code in a public repository on GitHub, {% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}according to the [Terms of Service](/articles/github-terms-of-service), {% endif %}other GitHub users have the right to view and fork your repository within the GitHub site. Wenn Du bereits ein öffentliches Repository erstellt hast und nicht mehr möchtest, dass andere Benutzer darauf zugreifen, kannst Du festlegen, dass Dein Repository privat ist. Wenn Du ein öffentliches Repository in ein privates umwandelst, bleiben vorhandene Forks oder lokale Kopien bestehen, die andere Benutzer erstellt haben. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Ein öffentliches Repository in ein privates umwandeln](/articles/making-a-public-repository-private).“
|
||||
**Note:** If you publish your source code in a public repository on {% data variables.product.product_name %}, {% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}according to the [Terms of Service](/articles/github-terms-of-service), {% endif %}other users of {% data variables.product.product_location %} have the right to view and fork your repository. If you have already created a repository and no longer want users to have access to the repository, you can make the repository private. When you change the visibility of a repository to private, existing forks or local copies created by other users will still exist. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Sichtbarkeit eines Repositorys festlegen](/github/administering-a-repository/setting-repository-visibility).“
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -46,8 +46,12 @@ Connecting to {% data variables.product.prodname_github_codespaces %} with the
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuring a codespace for {% data variables.product.prodname_vs %}
|
||||
|
||||
The default codespace environment created by {% data variables.product.prodname_vs %} includes popular frameworks and tools such as .NET Core, Microsoft SQL Server, Python, and the Windows SDK. {% data variables.product.prodname_github_codespaces %} created with {% data variables.product.prodname_vs %} can be customized through a subset of `devcontainers.json` properties and a new tool called devinit, included with {% data variables.product.prodname_vs %}.
|
||||
A codespace, created with {% data variables.product.prodname_vs %}, can be customized through a new tool called devinit, a command line tool included with {% data variables.product.prodname_vs %}.
|
||||
|
||||
#### devinit
|
||||
|
||||
The [devinit](https://docs.microsoft.com/visualstudio/devinit/getting-started-with-devinit) command-line tool lets you install additional frameworks and tools into your Windows development codespaces, as well as run PowerShell scripts or modify environment variables. devinit supports a configuration file called [devinit.json](https://docs.microsoft.com/visualstudio/devinit/devinit-json), which can be added to your project for creating customized and repeatable development environments. For more information about Windows codespace configuration and devinit, see [Customize a codespace](https://docs.microsoft.com/visualstudio/ide/codespaces/customize-codespaces) in the {% data variables.product.prodname_vs %} documentation.
|
||||
[devinit](https://docs.microsoft.com/visualstudio/devinit/getting-started-with-devinit) lets you install additional frameworks and tools into your Windows development codespaces, modify environment variables, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
devinit supports a configuration file called [devinit.json](https://docs.microsoft.com/visualstudio/devinit/devinit-json). You can add this file to your project if you want to create a customized and repeatable development environment. When you use devinit with a [devcontainer.json](https://docs.microsoft.com/visualstudio/ide/codespaces/customize-codespaces#running-devinit-when-creating-a-codespace) file, your codespaces will be automatically configured on creation.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information about Windows codespace configuration and devinit, see [Customize a codespace](https://docs.microsoft.com/visualstudio/ide/codespaces/customize-codespaces) in the {% data variables.product.prodname_vs %} documentation. For more information about devinit, see [Getting started with devinit](https://docs.microsoft.com/visualstudio/devinit/getting-started-with-devinit).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,14 +10,26 @@ versions:
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können die unterschiedlichsten Projekte in {% data variables.product.product_name %}-Repositorys speichern, darunter auch Open-Source-Projekte. Mit [Open-Source-Projekten](http://opensource.org/about) kannst Du Code leichter für andere zugänglich machen, um eine bessere, zuverlässigere Software zu entwickeln.
|
||||
|
||||
{% elsif enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion or currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
|
||||
You can store a variety of projects in {% data variables.product.product_name %} repositories, including innersource projects. With innersource, you can share code to make better, more reliable software. Weitere Informationen zu InnerSource finden Sie im Whitepaper „[An introduction to innersource](https://resources.github.com/whitepapers/introduction-to-innersource/)“ (Einführung in InnerSource) von {% data variables.product.company_short %}.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Hinweis:** Du kannst öffentliche Repositorys für ein Open-Source-Projekt erstellen. Wenn Du ein öffentliches Repository erstellst, musst du unbedingt eine [Lizenzdatei](http://choosealicense.com/) hinzufügen, die bestimmt, wie Dein Projekt für andere Personen freigegeben wird. {% data reusables.open-source.open-source-guide-repositories %} {% data reusables.open-source.open-source-learning-lab %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.create_new %}
|
||||
2. Gib einen kurzen, leicht merkbaren Namen für Dein Repository ein. Beispiel: „hello world“. 
|
||||
3. Optional kannst Du auch eine Beschreibung des Repositorys hinzufügen. For example, "My first repository on
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -25,10 +25,16 @@ Du kannst Forks beispielsweise benutzen, um Änderungen im Zusammenhang mit der
|
||||
|
||||
Open-Source-Software basiert auf der Idee, dass wir durch gemeinsamen Code bessere, zuverlässigere Software erstellen können. Weitere Informationen findest Du in „[Über die Open-Source-Initiative](http://opensource.org/about)“ auf der Open-Source-Initiative-Website.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information about applying open source principles to your organization's development work on {% data variables.product.product_location %}, see {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}'s whitepaper "[An introduction to innersource](https://resources.github.com/whitepapers/introduction-to-innersource/)."
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Du ein öffentliches Repository von einem Fork eines Projekts eines anderen Benutzers erstellst, musst Du unbedingt eine Lizenzdatei hinzufügen, die bestimmt, wie Dein Projekt für andere Personen freigegeben wird. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Wähle eine Open-Source-Lizenz](http://choosealicense.com/)“ auf der choosealicense-Website.
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.open-source.open-source-guide-repositories %} {% data reusables.open-source.open-source-learning-lab %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% note %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Hinweis**: {% data reusables.repositories.desktop-fork %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ Um Deine Testversion optimal zu nutzen, folge diesen Schritten:
|
||||
- Webcast „[Kurzanleitung zu {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}](https://resources.github.com/webcasts/Quick-start-guide-to-GitHub/)“
|
||||
- „[Verstehen des {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}-Ablaufs](https://guides.github.com/introduction/flow/)“ unter „{% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}-Anleitungen“
|
||||
- „[Hello World](https://guides.github.com/activities/hello-world/)“ unter „{% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}-Anleitungen“
|
||||
3. To configure your instance to meet your organization's needs, see "[Configuring your enterprise](/admin/configuration/configuring-your-enterprise)."
|
||||
3. To configure your instance to meet your organization's needs, see "[Configuring your enterprise](/enterprise/admin/configuration/configuring-your-enterprise)."
|
||||
4. Integrieren Sie {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %} mit Ihrem Identity Provider. Details finden Sie unter „[SAML verwenden](/enterprise/admin/user-management/using-saml)“ und „[LDAP verwenden](/enterprise/admin/authentication/using-ldap)“.
|
||||
5. Lade beliebig viele Personen zum Test ein.
|
||||
- Füge die Benutzer zu Deiner {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_server %}-Instanz hinzu, entweder mit der integrierten Authentifizierung oder Deinem konfigurierten Identitätsanbieter. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Integrierte Authentifizierung verwenden](/enterprise/admin/user-management/using-built-in-authentication).“
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ You can see all of the alerts that affect a particular project{% if currentVersi
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.21" %}
|
||||
By default, we notify people with admin permissions in the affected repositories about new
|
||||
{% data variables.product.prodname_dependabot_alerts %}.{% endif %} {% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}{% data variables.product.product_name %} never publicly discloses identified vulnerabilities for any repository. You can also make {% data variables.product.prodname_dependabot_alerts %} visible to additional people or teams working repositories that you own or have admin permissions for. For more information, see "[Managing security and analysis settings for your repository](/github/administering-a-repository/managing-security-and-analysis-settings-for-your-repository#granting-access-to-dependabot-alerts)."
|
||||
{% data variables.product.prodname_dependabot_alerts %}.{% endif %} {% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}{% data variables.product.product_name %} never publicly discloses identified vulnerabilities for any repository. You can also make {% data variables.product.prodname_dependabot_alerts %} visible to additional people or teams working repositories that you own or have admin permissions for. For more information, see "[Managing security and analysis settings for your repository](/github/administering-a-repository/managing-security-and-analysis-settings-for-your-repository#granting-access-to-security-alerts)."
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion and currentVersion ver_lt "enterprise-server@2.22" %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -21,7 +21,12 @@ Du kannst Benachrichtigungen abonnieren für:
|
||||
- Eine Unterhaltung in einem spezifischen Issue, Pull Request oder Gist.
|
||||
- Alle Aktivitäten in einem Repository oder in einer Team-Diskussion.
|
||||
- CI-Aktivität wie beispielsweise der Status von Workflows in Repositorys, die mit {% data variables.product.prodname_actions %} aufgesetzt wurden.
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
- Issues, pulls requests, releases and discussions (if enabled) in a repository.
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.20" %}
|
||||
- Releases in einem Repository.
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
Du kannst auch automatisch alle Repositorys überwachen, auf die Du Push-Zugriff hast, mit Ausnahme von Forks. Du kannst jedes andere Repository, auf das Du Zugriff hast, manuell verfolgen durch klicken auf **Watch** (Beobachten).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -21,16 +21,17 @@ versions:
|
||||
|
||||
### Zustellungsoptionen für Benachrichtigungen
|
||||
|
||||
Du hast drei grundlegende Optionen für die Zustellung von Benachrichtigungen:
|
||||
- the notifications inbox on {% data variables.product.product_name %}{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
- the notifications inbox on {% data variables.product.prodname_mobile %}, which syncs with the inbox on {% data variables.product.product_name %}{% endif %}
|
||||
- an email client that uses a verified email address, which can also sync with the notifications inbox on {% data variables.product.product_name %}{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %} and {% data variables.product.prodname_mobile %}{% endif %}
|
||||
You can receive notifications for activity on {% data variables.product.product_name %} in the following locations.
|
||||
|
||||
- The notifications inbox in the {% data variables.product.product_name %} web interface{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
- The notifications inbox on {% data variables.product.prodname_mobile %}, which syncs with the inbox on {% data variables.product.product_name %}{% endif %}
|
||||
- An email client that uses a verified email address, which can also sync with the notifications inbox on {% data variables.product.product_name %}{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %} and {% data variables.product.prodname_mobile %}{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.notifications-v2.notifications-inbox-required-setting %} Weitere Informationen findest Du auf „[Deine Benachrichtigungseinstellungen wählen](#choosing-your-notification-settings)."
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.notifications-v2.tip-for-syncing-email-and-your-inbox-on-github %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.notifications.shared_state %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Benefits of the notifications inbox
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -59,8 +60,21 @@ E-Mail-Benachrichtigungen ermöglichen auch Flexibilität bei der Art von Benach
|
||||
|
||||
### Über die Teilnahme und das Beobachten von Benachrichtigungen
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Du ein Repository beobachtest, abonnierst Du Aktualisierungen für Aktivitäten in diesem Repository. Ebenfalls, wenn Du die Diskussionen eines bestimmten Teams verfolgst, abonnierst Du alle Aktualisierungen der Unterhaltung auf der Seite dieses Teams. Um Repositorys zu sehen, die Du beobachtest, siehe [https://github.com/watching](https://github.com/watching). Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Abonnements und Benachrichtigungen auf GitHub verwalten](/github/managing-subscriptions-and-notifications-on-github/managing-subscriptions-for-activity-on-github)."
|
||||
Wenn Du ein Repository beobachtest, abonnierst Du Aktualisierungen für Aktivitäten in diesem Repository. Ebenfalls, wenn Du die Diskussionen eines bestimmten Teams verfolgst, abonnierst Du alle Aktualisierungen der Unterhaltung auf der Seite dieses Teams. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Informationen zu Teamdiskussionen](/github/building-a-strong-community/about-team-discussions)“.
|
||||
|
||||
To see repositories that you're watching, go to your [watching page](https://github.com/watching). Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Abonnements und Benachrichtigungen auf GitHub verwalten](/github/managing-subscriptions-and-notifications-on-github/managing-subscriptions-for-activity-on-github)."
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.20" %}
|
||||
#### Benachrichtigungen konfigurieren
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
You can configure notifications for a repository on the repository page, or on your watching page.
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.20" %} You can choose to only receive notifications for releases in a repository, or ignore all notifications for a repository.{% endif %}{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
|
||||
#### About custom notifications
|
||||
{% data reusables.notifications-v2.custom-notifications-beta %}
|
||||
You can customize notifications for a repository, for example, you can choose to only be notified when updates to one or more types of events (issues, pull request, releases, discussions) happen within a repository, or ignore all notifications for a repository.
|
||||
{% endif %} For more information, see "[Viewing your subscriptions](/github/managing-subscriptions-and-notifications-on-github/viewing-your-subscriptions#configuring-your-watch-settings-for-an-individual-repository)."
|
||||
|
||||
#### Participating in conversations
|
||||
Jedes Mal, wenn Du in einer Unterhaltung kommentierst oder wenn jemand Deinen Benutzernamen @erwähnt, bist Du _Teilnehmer_ in einer Unterhaltung. Standardmäßig abonnierst Du automatisch eine Unterhaltung, wenn Du daran teilnimmst. Du kannst Dich manuell von einer Unterhaltung abmelden, an der Du teilgenommen hast, indem Du auf dem Issue oder Pull Request auf **Unsubscribe** (Abmelden) klickst oder durch die Option **Unsubscribe** (Abmelden) im Posteingang für Benachrichtigungen.
|
||||
|
||||
For conversations you're watching or participating in, you can choose whether you want to receive notifications by email or through the notifications inbox on {% data variables.product.product_name %}{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %} and {% data variables.product.prodname_mobile %}{% endif %}.
|
||||
@@ -95,7 +109,9 @@ Wähle eine Standard-E-Mail-Adresse, an die Du Aktualisierungen für Unterhaltun
|
||||
- Pull-Request-Pushes.
|
||||
- Deine eigenen Aktualisierungen, wie wenn Du beispielsweise einen Issue oder Pull Request öffnest, kommentierst oder schließt.
|
||||
|
||||
Abhängig von der Organisation, die das Repository besitzt, kannst Du auch Benachrichtigungen für bestimmte Repositories an verschiedene E-Mail-Adressen senden. Beispielsweise kannst Du Benachrichtigungen für ein bestimmtes öffentliches Repository an eine verifizierte persönliche E-Mail-Adresse senden. Deine Organisation verlangt möglicherweise, dass E-Mail-Adressen für bestimmte Domänen verifiziert sein müssen. Weitere Informationen findest Du auf „[Auswählen, wohin die E-Mail-Benachrichtigungen Deiner Organisation gesendet werden](/github/managing-subscriptions-and-notifications-on-github/configuring-notifications#choosing-where-your-organizations-email-notifications-are-sent)."
|
||||
Depending on the organization that owns the repository, you can also send notifications to different email addresses. Deine Organisation verlangt möglicherweise, dass E-Mail-Adressen für bestimmte Domänen verifiziert sein müssen. For more information, see "[Choosing where your organization’s email notifications are sent](/github/managing-subscriptions-and-notifications-on-github/configuring-notifications#choosing-where-your-organizations-email-notifications-are-sent)."
|
||||
|
||||
You can also send notifications for a specific repository to an email address. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter "[Informationen zu E-Mail-Benachrichtigungen für Pushes in Dein Repository](/github/administering-a-repository/about-email-notifications-for-pushes-to-your-repository)."
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.notifications-v2.email-notification-caveats %}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -55,6 +55,13 @@ Wenn Du ein Repository nicht mehr beobachtest, meldest Du Dich von zukünftigen
|
||||
{% data reusables.notifications.access_notifications %}
|
||||
1. Verwende in der linken Seitenleiste, unterhalb der Liste der Repositorys, das Dropdownmenü „Manage Notifications" (Benachrichtigungen verwalten) und klicke auf **Watched repositories** (beobachtete Repositorys). 
|
||||
2. Nimm auf der Seite der beobachteten Repositorys eine Bewertung dieser Repositorys vor und wähle dann aus:
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.20" %}
|
||||
- ein Repository nicht mehr beobachten
|
||||
- nur Releases für ein Repository beobachten
|
||||
- ignoriere alle Benachrichtigungen für ein Repository
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
- ein Repository nicht mehr beobachten
|
||||
- ignoriere alle Benachrichtigungen für ein Repository
|
||||
- customize the types of event you receive notifications for (issues, pull requests, releases or discussions, if enabled)
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,16 @@ Wenn Dein Posteingang zu viele Benachrichtigungen zum Verwalten hat, überlege D
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Benachrichtigungen konfigurieren](/github/managing-subscriptions-and-notifications-on-github/configuring-notifications#automatic-watching)."
|
||||
|
||||
Eine Übersicht Deiner Repository-Abonnements findest Du unter „[Repositorys überprüfen, die Du beobachtest](#reviewing-repositories-that-youre-watching). Viele Personen vergessen Repositorys, die sie in der Vergangenheit beobachtet haben. Über die Seite „Watched repositories" (beobachtete Repositorys) kannst Du die Beobachtung von Repositorys schnell deaktivieren. Weitere Informationen über Deine Abmeldeoptionen findest Du unter „[Abonnements verwalten](/github/managing-subscriptions-and-notifications-on-github/managing-your-subscriptions)."
|
||||
Eine Übersicht Deiner Repository-Abonnements findest Du unter „[Repositorys überprüfen, die Du beobachtest](#reviewing-repositories-that-youre-watching).
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
{% tip %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** You can select the types of event to be notified of by using the **Custom** option of the **Watch/Unwatch** dropdown list in your [watching page](https://github.com/watching) or on any repository page on {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom_the_website %}. For more information, see "[Configuring your watch settings for an individual repository](#configuring-your-watch-settings-for-an-individual-repository)" below.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endtip %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
Viele Personen vergessen Repositorys, die sie in der Vergangenheit beobachtet haben. Über die Seite „Watched repositories" (beobachtete Repositorys) kannst Du die Beobachtung von Repositorys schnell deaktivieren. For more information on ways to unsubscribe, see "[Unwatch recommendations](https://github.blog/changelog/2020-11-10-unwatch-recommendations/)" on {% data variables.product.prodname_blog %} and "[Managing your subscriptions](/github/managing-subscriptions-and-notifications-on-github/managing-your-subscriptions)." You can also create a triage worflow to help with the notifications you receive. For guidance on triage workflows, see "[Customizing a workflow for triaging your notifications](/github/managing-subscriptions-and-notifications-on-github/customizing-a-workflow-for-triaging-your-notifications)."
|
||||
|
||||
### Alle Deine Abonnements überprüfen
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -55,20 +64,38 @@ Eine Übersicht Deiner Repository-Abonnements findest Du unter „[Repositorys
|
||||
### Repositorys überprüfen, die Du beobachtest
|
||||
|
||||
1. Verwende in der linken Seitenleiste, unterhalb der Liste der Repositorys, das Dropdownmenü „Manage Notifications" (Benachrichtigungen verwalten) und klicke auf **Watched repositories** (beobachtete Repositorys). 
|
||||
|
||||
3. Evaluiere die von Dir beobachteten Repositorys und entscheide, ob deren Aktualisierungen für Dich immer noch relevant und hilfreich sind. Wenn Du ein Repository beobachtest, wirst Du über alle Unterhaltungen für dieses Repository benachrichtigt.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Evaluiere die von Dir beobachteten Repositorys und entscheide, ob deren Aktualisierungen für Dich immer noch relevant und hilfreich sind. Wenn Du ein Repository beobachtest, wirst Du über alle Unterhaltungen für dieses Repository benachrichtigt.
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.20" %}
|
||||

|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||

|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% tip %}
|
||||
|
||||
**Tipp:** Anstatt ein Repository zu beobachten, erwäge allenfalls nur Releases für ein Repository ansehen oder ein Repository gar nicht mehr zu beobachten. Wenn Du ein Repository nicht mehr beobachtest, kannst du immer noch benachrichtigt werden, wenn Du @erwähnt wirst oder in einem Thread teilnimmst. Wenn Du nur Releases für ein Repository beobachtest, wirst Du nur benachrichtigt, wenn es einen neuen Release gibt, wenn Du an einem Thread teilnimmst oder wenn Du oder ein Team, dem Du angehörst, @erwähnt wirst.
|
||||
**Tip:** Instead of watching a repository, consider only receiving notifications {% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}when there are updates to issues, pull requests, releases or discussions (if enabled for the repository), or any combination of these options,{% else %}for releases in a repository,{% endif %} or completely unwatching a repository.
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Du ein Repository nicht mehr beobachtest, kannst du immer noch benachrichtigt werden, wenn Du @erwähnt wirst oder in einem Thread teilnimmst. When you configure to receive notifications for certain event types, you're only notified when there are updates to these event types in the repository, you're participating in a thread, or you or a team you're on is @mentioned.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endtip %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Konfiguration der Beobachtungseinstellungen für ein einzelnes Repository
|
||||
|
||||
Du kannst wählen, ob Du ein einzelnes Repository ansehen möchtest oder nicht mehr. Du kannst auch wählen, dass Du nur bei neuen Releases benachrichtigt wirst oder Du kannst ein einzelnes Repository komplett ignorieren.
|
||||
Du kannst wählen, ob Du ein einzelnes Repository ansehen möchtest oder nicht mehr. You can also choose to only be notified of {% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}certain event types such as issues, pull requests, discussions (if enabled for the repository) and {% endif %}new releases, or completely ignore an individual repository.
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %}
|
||||
2. Klicke in der oberen rechten Ecke auf das Dropdownmenü „Watch" (Beobachten), um eine der Beobachtungsoptionen zu wählen. 
|
||||
2. Klicke in der oberen rechten Ecke auf das Dropdownmenü „Watch" (Beobachten), um eine der Beobachtungsoptionen zu wählen.
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "github-ae@latest" or currentVersion ver_gt "enterprise-server@2.20" %}
|
||||

|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||

|
||||
{% data reusables.notifications-v2.custom-notifications-beta %}
|
||||
The **Custom** option allows you to further customize notifications so that you're only notified when specific events happen in the repository, in addition to participating and @mentions.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you select "Issues", you will be notified about, and subscribed to, updates on every issue (including those that existed prior to you selecting this option) in the repository. If you're @mentioned in a pull request in this repository, you'll receive notifications for that too, and you'll be subscribed to updates on that specific pull request, in addition to being notified about issues.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Einen Issue erstellen
|
||||
intro: 'Mit Issues kannst Du Fehler, Verbesserungen oder andere Anforderungen nachverfolgen.'
|
||||
permissions: 'People with read permissions can create an issue in a repository where issues are enabled.'
|
||||
redirect_from:
|
||||
- /articles/creating-an-issue
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
@@ -9,8 +10,6 @@ versions:
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.create-issue-in-public-repository %}
|
||||
|
||||
Du kannst einen neuen Issue basierend auf dem Code eines vorhandenen Pull Requests erstellen. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Einen Issue im Code öffnen](/github/managing-your-work-on-github/opening-an-issue-from-code).“
|
||||
|
||||
Du kannst einen neuen Issue direkt aus einem Kommentar in einem Issue- oder Pull-Request-Review öffnen. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Öffnen eines Issue aus einem Kommentar](/github/managing-your-work-on-github/opening-an-issue-from-a-comment)."
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Einen Issue aus einem Kommentar öffnen
|
||||
intro: Du kannst einen neuen Issue aus einem spezifischen Kommentar in einem Issue oder Pull Request öffnen.
|
||||
permissions: 'People with read permissions can create an issue in a repository where issues are enabled.'
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
free-pro-team: '*'
|
||||
enterprise-server: '*'
|
||||
@@ -9,6 +10,8 @@ versions:
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Du einen Issue aus einem Kommentar öffnest, wird der Issue ein Ausschnitt enthalten, der zeigt, wo der Kommentar ursprünglich eingestellt wurde.
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.administrators-can-disable-issues %}
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigiere zum Kommentar, aus dem Du einen Issue öffnen möchtest.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Klicke in diesem Kommentar auf {% octicon "kebab-horizontal" aria-label="The horizontal kebab icon" %}. 
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Einen Issue im Code öffnen
|
||||
intro: Du kannst neue Issues von einer bestimmten Codezeile oder über mehreren Codezeilen in einer Datei oder einem Pull Request öffnen.
|
||||
permissions: 'People with read permissions can create an issue in a repository where issues are enabled.'
|
||||
redirect_from:
|
||||
- /articles/opening-an-issue-from-code
|
||||
versions:
|
||||
@@ -13,7 +14,7 @@ Wenn Du einen Issue im Code öffnest, enthält der Issue einen Ausschnitt mit de
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.create-issue-in-public-repository %}
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.administrators-can-disable-issues %}
|
||||
|
||||
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %}
|
||||
2. Suche den Code, auf den Du in einem Issue verweisen möchtest:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ versions:
|
||||
|
||||
Für die Übertragung eines offenen Issues in ein anderes Repository benötigst Du Schreibberechtigung sowohl für das Repository, aus dem der Issue stammt, wie auch für das Repository, in das der Issue übertragen wird. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter„[Berechtigungsebenen für die Repositorys einer Organisation](/articles/repository-permission-levels-for-an-organization)“.
|
||||
|
||||
Du kannst Issues nur zwischen Repositorys übertragen, die demselben Benutzer- oder Organisationskonto angehören. Du kannst einen Issue nicht aus einem privaten Repository in ein öffentliches Repository übertragen.
|
||||
You can only transfer issues between repositories owned by the same user or organization account.{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}You can't transfer an issue from a private repository to a public repository.{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Du einen Issue überträgst, bleiben seine Kommentare und Bearbeiter erhalten. The issue's labels and milestones are not retained. This issue will stay on any user-owned or organization-wide project boards and be removed from any repository project boards. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Informationen zu Projektboards](/articles/about-project-boards).“
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ versions:
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Du kannst global über {% data variables.product.product_name %} hinweg suchen oder Deine Suche auf ein bestimmtes Repositorys oder eine bestimmte Organisation beschränken.
|
||||
{% data reusables.search.you-can-search-globally %}
|
||||
|
||||
- Um global über {% data variables.product.product_name %} hinweg zu suchen, gib Deine Suchanfrage in das Suchfeld oben auf jeder Seite ein, und wähle im im Dropdownmenü der Suche „All {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}“ (Ganzes Produkt).
|
||||
- Um in einem bestimmten Repository oder einer bestimmten Organisation zu suchen, navigiere zur Repository- oder Organisationsseite, gib Deine Suchanfrage in das Suchfeld oben auf der Seite ein, und drücke die **Eingabetaste**.
|
||||
@@ -23,20 +23,21 @@ Du kannst global über {% data variables.product.product_name %} hinweg suchen o
|
||||
|
||||
**Hinweise:**
|
||||
|
||||
- {% data reusables.search.required_login %}
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
- {% data reusables.search.required_login %}{% endif %}
|
||||
- {% data variables.product.prodname_pages %}-Websites können auf {% data variables.product.product_name %} nicht durchsucht werden. Du kannst aber den Quellinhalt mithilfe der Codesuche durchsuchen, wenn er im Standardbranch eines Repositorys vorhanden ist. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Code durchsuchen](/articles/searching-code)“. Weitere Informationen über {% data variables.product.prodname_pages %} findest Du unter „[Was ist GitHub Pages?](/articles/what-is-github-pages/)“
|
||||
- Currently our search doesn't support exact matching.
|
||||
- Whenever you are searching in code files, only the first two results in each file will be returned.
|
||||
|
||||
{% endnote %}
|
||||
|
||||
Nach einer Suche auf {% data variables.product.product_name %} kannst Du die Ergebnisse sortieren oder durch Anklicken einer der Sprachen in der Seitenleiste weiter eingrenzen. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Suchergebnisse sortieren](/articles/sorting-search-results).“
|
||||
Nach einer Suche auf {% data variables.product.product_name %} können Sie die Ergebnisse sortieren oder durch Anklicken einer der Sprachen in der Seitenleiste weiter eingrenzen. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Suchergebnisse sortieren](/articles/sorting-search-results)“.
|
||||
|
||||
Bei der {% data variables.product.product_name %}-Suche wird ein ElasticSearch-Cluster verwendet, um Projekte jedes Mal zu indizieren, wenn eine Änderung an {% data variables.product.product_name %} übertragen wird. Issues und Pull Requests werden beim Anlegen oder Ändern indiziert.
|
||||
Bei der {% data variables.product.product_name %}-Suche wird ein ElasticSearch-Cluster verwendet, um Projekte jedes Mal zu indizieren, wenn eine Änderung an {% data variables.product.product_name %} gepusht wird. Issues und Pull Requests werden beim Anlegen oder Ändern indiziert.
|
||||
|
||||
### Arten von Suchen auf {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}
|
||||
|
||||
Du kannst die folgenden Arten von Informationen in allen öffentlichen {% data variables.product.product_name %}-Repositorys und in allen privaten {% data variables.product.product_name %}-Repositorys durchsuchen, auf die Du Zugriff hast:
|
||||
You can search for the following information across all repositories you can access on {% data variables.product.product_location %}.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Repositorys](/articles/searching-for-repositories)
|
||||
- [Themen](/articles/searching-topics)
|
||||
@@ -49,20 +50,20 @@ Du kannst die folgenden Arten von Informationen in allen öffentlichen {% data v
|
||||
|
||||
### Über eine visuelle Oberfläche suchen
|
||||
|
||||
Alternativ kannst Du {% data variables.product.product_name %} mit der {% data variables.search.search_page_url %} oder {% data variables.search.advanced_url %} durchsuchen.
|
||||
Alternativ können Sie {% data variables.product.product_name %} mit der {% data variables.search.search_page_url %} oder {% data variables.search.advanced_url %} durchsuchen.
|
||||
|
||||
Die {% data variables.search.advanced_url %} bietet eine visuelle Oberfläche zum Erstellen von Suchanfragen. Du kannst Deine Suchanfragen nach einer Vielzahl von Faktoren filtern, beispielsweise nach der Anzahl der Sterne oder der Anzahl der Forks eines Repositorys. Während Du die erweiterten Suchfelder ausfüllst, wird Deine Anfrage automatisch in der oberen Suchleiste erstellt.
|
||||
Die {% data variables.search.advanced_url %} bietet eine visuelle Oberfläche zum Erstellen von Suchanfragen. Sie können Ihre Suchanfragen nach einer Vielzahl von Faktoren filtern, beispielsweise nach der Anzahl der Sterne oder der Anzahl der Forks eines Repositorys. Wenn Sie die erweiterten Suchfelder ausfüllen, wird Ihre Anfrage automatisch in der oberen Suchleiste erstellt.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
{% if currentVersion != "github-ae@latest" %}
|
||||
### {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %} und {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom_the_website %} gleichzeitig durchsuchen
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %} verwenden und Sie Mitglied einer {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom_the_website %}-Organisation sind, die {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_cloud %} verwendet, kann Ihr {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %}-Websiteadministrator {% data variables.product.prodname_github_connect %} aktivieren, damit Sie beide Umgebungen gleichzeitig durchsuchen können. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[{% data variables.product.prodname_unified_search %} zwischen {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %} und {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom_the_website %} aktivieren](/enterprise/admin/guides/developer-workflow/enabling-unified-search-between-github-enterprise-server-and-github-com)“.
|
||||
Wenn Du {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %} verwendest und Mitglied einer {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom_the_website %}-Organisation bist, die {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_cloud %} verwendet, kann Dein {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %}-Websiteadministrator {% data variables.product.prodname_github_connect %} aktivieren, damit Du beide Umgebungen gleichzeitig durchsuchen kannst. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[{% data variables.product.prodname_unified_search %} zwischen {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %} und {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom_the_website %} aktivieren](/enterprise/admin/guides/developer-workflow/enabling-unified-search-between-github-enterprise-server-and-github-com).“
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können beide Umgebungen nur von {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %} aus durchsuchen. Um Ihre Suche nach Umgebung einzugrenzen, können Sie eine Filteroption in der {% data variables.search.advanced_url %} oder das Suchpräfix `environment:` verwenden. Um nur nach Inhalten auf {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %} zu suchen, verwenden Sie die Suchsyntax `environment:local`. Um nur nach Inhalten auf {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom_the_website %} zu suchen, verwenden Sie die Suchsyntax `environment:github`.
|
||||
Du kannst beide Umgebungen nur von {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %} aus durchsuchen. Um Deine Suche nach Umgebung einzugrenzen, kannst Du eine Filteroption in der {% data variables.search.advanced_url %} oder das Suchpräfix `environment:` verwenden. Um nur nach Inhalten auf {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %} zu suchen, verwende die Suchsyntax `environment:local`. Um nur nach Inhalten auf {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom_the_website %} zu suchen, verwende die Suchsyntax `environment:github`.
|
||||
|
||||
Ihr {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %}-Websiteadministrator kann {% data variables.product.prodname_unified_search %} für alle öffentlichen Repositorys, alle privaten Repositorys oder nur bestimmte private Repositorys in der verbundenen {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_cloud %}-Organisation aktivieren.
|
||||
Dein {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %}-Websiteadministrator kann {% data variables.product.prodname_unified_search %} für alle öffentlichen Repositorys, alle privaten Repositorys oder nur bestimmte private Repositorys in der verbundenen {% data variables.product.prodname_ghe_cloud %}-Organisation aktivieren.
|
||||
If your site administrator enables
|
||||
|
||||
{% data variables.product.prodname_unified_search %} in private repositories, you can only search in the private repositories that the administrator enabled {% data variables.product.prodname_unified_search %} for and that you have access to in the connected {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom_the_website %} organization. Deine {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %}-Administratoren und Organisationsinhaber auf {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom_the_website %} können keine privaten Repositorys durchsuchen, die Deinem Konto gehören. Um die entsprechenden privaten Repositorys zu durchsuchen, musst Du die Suche auf privaten Repositorys auf Deinen persönlichen Konten auf {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom_the_website %} und {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %} aktivieren. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Die Suche auf privaten {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom_the_website %}-Repositorys in Deinem {% data variables.product.prodname_enterprise %}-Konto aktivieren](/articles/enabling-private-github-com-repository-search-in-your-github-enterprise-server-account).“
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ versions:
|
||||
github-ae: '*'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können Code global auf {% data variables.product.product_name %} oder in bestimmten Repositorys oder Organisationen durchsuchen. Um den Code aller öffentlichen Repositorys zu durchsuchen, musst Du bei einem {% data variables.product.product_name %}-Konto angemeldet sein. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Informationen zur Suche auf GitHub](/articles/about-searching-on-github).“
|
||||
{% data reusables.search.you-can-search-globally %} For more information, see "[About searching on GitHub](/articles/about-searching-on-github)."
|
||||
|
||||
Du kannst Code nur mit den diesen Qualifizierern der Codesuche durchsuchen. Spezifische Qualifizierer für Repositorys, Benutzer oder Commits funktionieren bei der Durchsuchung von Code nicht.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -21,16 +21,16 @@ Du kannst Code nur mit den diesen Qualifizierern der Codesuche durchsuchen. Spez
|
||||
|
||||
Aufgrund der Komplexität der Codesuche gelten bei der Durchführung der Suche Einschränkungen:
|
||||
|
||||
- {% data reusables.search.required_login %}
|
||||
{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %}
|
||||
- {% data reusables.search.required_login %}{% endif %}
|
||||
- Code in [Forks](/articles/about-forks) ist nur durchsuchbar, wenn für den Fork mehr Sterne vergeben wurden als für das übergeordnete Repository. Forks mit weniger Sternen als das übergeordnete Repository sind **nicht** für die Codesuche indiziert. Um Forks mit mehr Sternen als das übergeordnete Repository in die Suchergebnisse einzuschließen, musst Du Deiner Abfrage `fork:true` oder `fork:only` hinzufügen. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter „[Forks durchsuchen](/articles/searching-in-forks)“.
|
||||
- Only the _default branch_ is indexed for code search.{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" %}
|
||||
- Nur Dateien kleiner 384 KB sind durchsuchbar.{% else %}* Nur Dateien kleiner 5 MB sind durchsuchbar.
|
||||
- Nur die ersten 500 KB jeder Datei sind durchsuchbar.{% endif %}
|
||||
- Nur Repositorys mit weniger als 500.000 Dateien sind durchsuchbar.
|
||||
- Angemeldete Benutzer können alle öffentlichen Repositorys durchsuchen.
|
||||
- Deine Quellcode-Suche muss mindestens einen Suchbegriff enthalten, ausgenommen bei [`filename`-Suchen](#search-by-filename). Beispielsweise ist eine Suche nach [`language:javascript`](https://github.com/search?utf8=%E2%9C%93&q=language%3Ajavascript&type=Code&ref=searchresults) ungültig, [`amazing language:javascript`](https://github.com/search?utf8=%E2%9C%93&q=amazing+language%3Ajavascript&type=Code&ref=searchresults) ist dagegen gültig.
|
||||
- Ihre Suchabfrage nach Code muss mindestens einen Suchbegriff enthalten. Ausgenommen hiervon sind Suchen nach [`filename`](#search-by-filename). Beispielsweise ist eine Suche nach [`language:javascript`](https://github.com/search?utf8=%E2%9C%93&q=language%3Ajavascript&type=Code&ref=searchresults) ungültig, [`amazing language:javascript`](https://github.com/search?utf8=%E2%9C%93&q=amazing+language%3Ajavascript&type=Code&ref=searchresults) ist dagegen gültig.
|
||||
- Die Suchergebnisse können maximal zwei gefundene Fragmente der gleichen Datei anzeigen, selbst wenn die Datei mehr Treffer enthält.
|
||||
- Folgende Platzhalterzeichen können in Suchabfragen nicht verwendet werden: <code>. , : ; / \ ` ' " = * ! ? # $ & + ^ | ~ < > ( ) { } [ ]</code>. Diese Zeichen werden bei der Suche schlicht ignoriert.
|
||||
- Folgende Platzhalterzeichen können in Suchabfragen nicht verwendet werden: <code>. , : ; / \ ` ' " = * ! ? # $ & + ^ | ~ < > ( ) { } [ ]</code>. Diese Zeichen werden bei der Suche ignoriert.
|
||||
|
||||
### Suche nach Dateiinhalten oder Dateipfad
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -96,14 +96,11 @@ Wenn Du Commits in allen Repositorys suchst, die einem bestimmten Benutzer oder
|
||||
| <code>org:<em>ORGNAME</em></code> | [**test org:github**](https://github.com/search?utf8=%E2%9C%93&q=test+org%3Agithub&type=Commits) sucht in Repositorys der Organisation @github nach Commits, deren Mitteilungen das Wort „test“ enthalten. |
|
||||
| <code>repo:<em>USERNAME/REPO</em></code> | [**language repo:defunkt/gibberish**](https://github.com/search?utf8=%E2%9C%93&q=language+repo%3Adefunkt%2Fgibberish&type=Commits) sucht im Repository „gibberish“ des Benutzers @defunkt nach Commits, deren Mitteilungen das Wort „language“ enthalten. |
|
||||
|
||||
### Öffentliche oder private Repositorys filtern
|
||||
### Filter by repository visibility
|
||||
|
||||
Der Qualifizierer `is` gleicht öffentliche oder private Commits ab.
|
||||
The `is` qualifier matches commits from repositories with the specified visibility. Weitere Informationen findest Du unter „[Über Sichtbarkeit von Repositorys](/github/creating-cloning-and-archiving-repositories/about-repository-visibility).
|
||||
|
||||
| Qualifizierer | Beispiel |
|
||||
| ------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `is:public` | [**is:public**](https://github.com/search?q=is%3Apublic&type=Commits) gleicht öffentliche Commits ab. |
|
||||
| `is:private` | [**is:public**](https://github.com/search?q=is%3Apublic&type=Commits) gleicht private Commits ab. |
|
||||
| Qualifier | Example | ------------- | ------------- |{% if currentVersion == "free-pro-team@latest" or enterpriseServerVersions contains currentVersion %} | `is:public` | [**is:public**](https://github.com/search?q=is%3Apublic&type=Commits) matches commits to public repositories.{% endif %} | `is:internal` | [**is:internal**](https://github.com/search?q=is%3Ainternal&type=Commits) matches commits to internal repositories. | `is:private` | [**is:private**](https://github.com/search?q=is%3Aprivate&type=Commits) matches commits to private repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
### Weiterführende Informationen
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user